NHA CCMA 2025 SmarterMA Flashcards
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Schedule I Class Drugs
No Acceptable Medical Use, High Potential Abuse. EX: Heroin, LSD, Marijuana
Schedule II Class Drugs
Yes Acceptable Medical Use, High Potential Abuse. EX: Fentanyl, Oxycodone, Morphine, Meth
Schedule III Class Drugs
Yes Acceptable Medical Use, Low Potential Abuse: Codeine
Schedule IV Class Drugs
Yes Acceptable Medical Use, Lower Potential Abuse. x: Xanax, valium and ambien
Schedule V Class Drugs
Yes Acceptable Medical Use, Lowest Potential Abuse. Cough medicine with Codeine
Intradermal (ID) angle, needle gauge and length
5-15 degrees
25-27 gauge
1.25-1.5 in
ex: TB and allergy testing and flu vaccine
Intravenous (IV) angle, needle gauge and length
15-30 degrees
21-23 gauge
1-1.5in
ex: iv fluids
Subcutaneous (subQ)
45 degrees
23-25 gauge
5/8 in
ex: insulin
Intramuscular (IM)
90 degrees
22-25 gauge
1-1.5in
ex: epipen
Hemoglobin ranges for male and females
male: 13.5-17.5 g/dL and female: 10.5-13.5 g/dL
Steps for a venipuncture
1. Requisition and ordered tests
2. Verify patients identity and introduce yourself
3. Explain the process to the patient and consent
4. Gather Equipment
5. Wash hands and globe
6. Tie the tourniquet 3-4in above site and ask pt to make a fist
7. Clean area with back and forth strokes, 2.5in diameter
8. Prepare needle and tube holder while alcohol dries. Inspect needle for defects
9. Anchor vein with the thumb below site
10. Insert needle at 15-30 degrees angle, bevel up
11. Push the collection tube into the holder to puncture the tube stopper with the needle
12. Release tourniquet once blood flows, it should be on only for 1min less to avoid hemoconcentration
13. Fill tubes in order
14. Place gauze over site, withdraw needle and apply pressure to stop bleeding
15. Discard needle into biohazard sharp container
16. Label specimen with patients name, ID, time, date of collection and initials
17. Place tubes in biohazard transport bag
18. Check site before leaving. Apply pressure in increments, if bleeding is not stopping after 8 mins, seek help
19. Apply bandaid/tape gauze, and tell patient to remove after 1 hour
20. Clean up and dispose waste
21. remove gloves, wash hands, say bye to patient and inform that the provider will let them know of the results
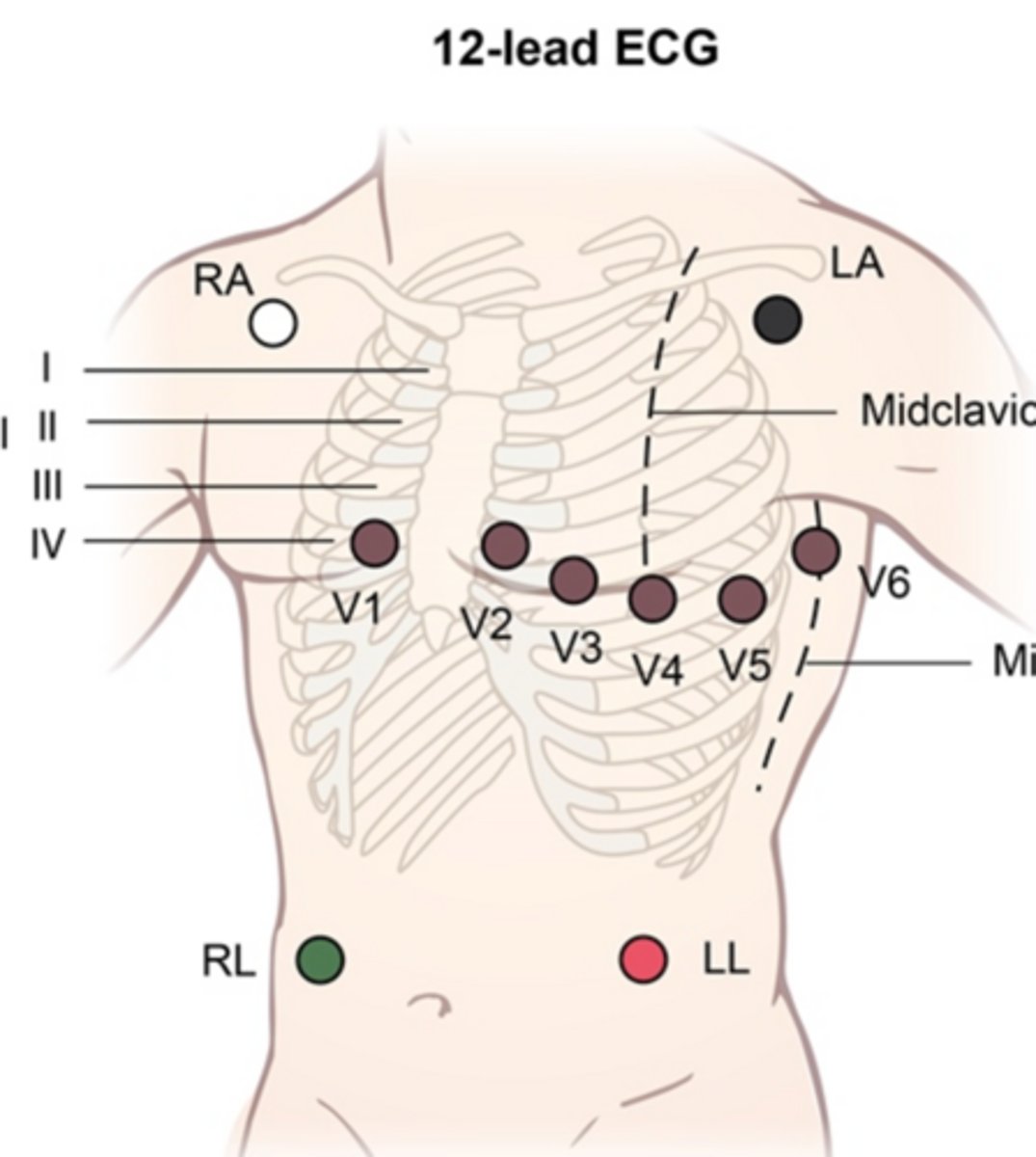
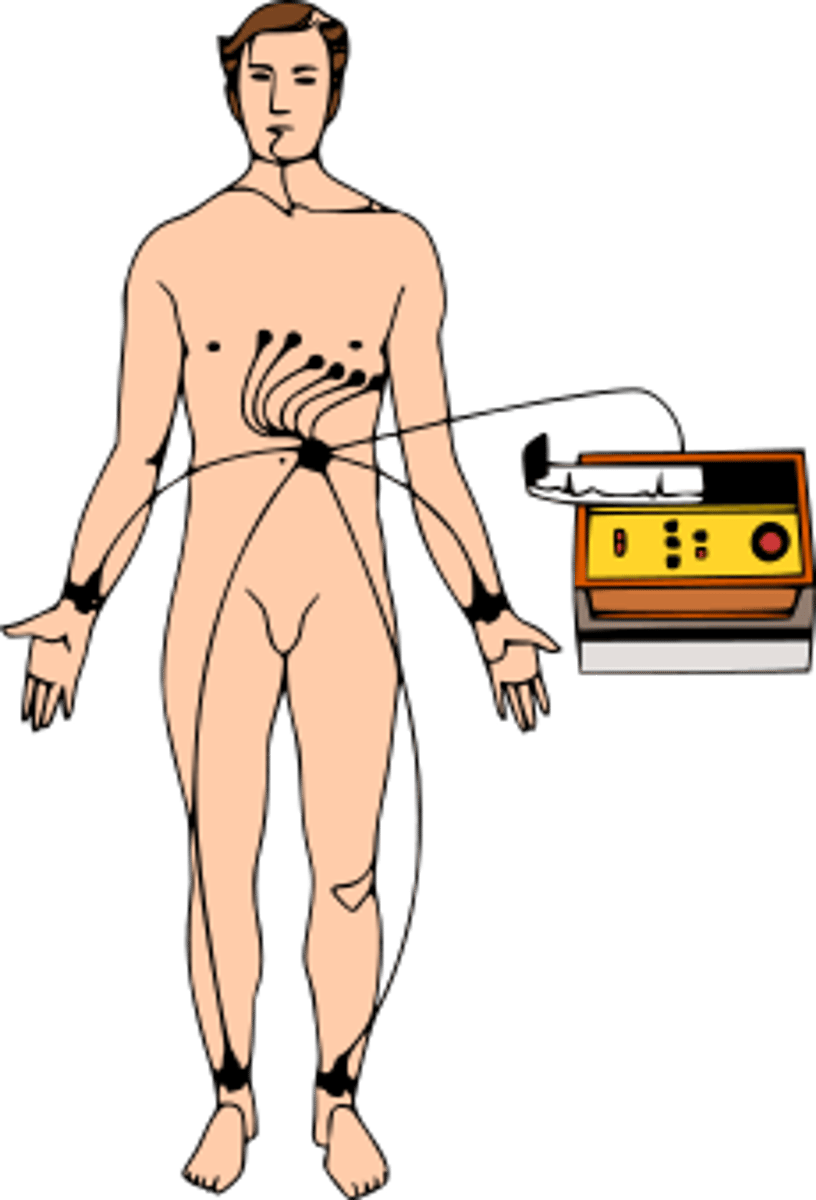
EKG lead placement
R/L arm/L leg
clouds over grass
coal over fire
V1: 4th ICS RSB
V2: 4th ICS LSB
V4: 5th ICS MCL
V3: BTWN V2 and V4
V6: 5th ICS Mid-axillary line
V5: 5th ICS Anterior axillary line
EKG Artifacts: AC interference
Electrical interference (cell phone or AC power lines) or no proper grounding on right electrode
EKG Artifacts: Somatic tremor
Patient muscle movement voluntarily or involuntarily
EKG Artifacts: Wandering Baseline
Poorly attached electrodes
EKG Artifacts: Interrupted Baseline
Electrode Disconnection due to poor contact between the electrodes and the skin
Scratch Test
Steps:
Prick the skin to introduce the allergen
drop the allergen
distance between each allergen is 1.5-2in apart
Hematocrit ranges
Adult men: 41%-53%
Adult women: 36%-46%
Hemoglobin ranges
Male: 13.5-17.5 g/dL
Female: 12-16 g/dL
Potassium Range
3.5-5.1 mEq/L
Blood Glucose range
70-110 mg/dL
EKG paper grid measuring
Each small square: 1 mm or 0.04 seconds
Each big square: 5mm, or 0.2 seconds
Weber vs Rinne Test
Weber: tuning fork on midline and ask what ear hearing in
Rinne: put tuning for on mastoid (behind ear canal) and ask when no longer hearing it then move near canal
Preanalytical, analytical and postanalytical phases in clinical lab testing process
Preanalytical: procedures from time a lab test is order to specimen collection and prep (lab req, drawing blood, labeling, identifying pt)
Analytical: testing phase where the specimen is analyzed in lab (processing the blood)
Postanalytical: interpreting results, reporting and archiving data (relaying results to pt)
Bipolar vs Unipolar leads
Bipolar leads: measure voltage between 2 points, have both positive and negative electrode, direct view of hearts electrical activity
I, II, III (limb leads)
Unipolar: measure voltage between single pt of reference, have only + electrode, give indirect view, comparing electrical activity to common reference
AVR, AVL, AVF limb leads
V1-6 precordial leads
12 lead ECG consists of 3 bipolar leads and 9 unipolar leads
Yellow test tube
Additive: sodium polyanetholsulfonate (SPS)
Specimen type: whole blood
Tests: blood culture (paternity/DNA)
Inversions: 8
Special instructions: sterile (aseptic technique)-clean site with iodine rather than 70% alcohol swab
Young (young lady bell rarely getsto greet lucy gray)
Yellow pee goes Spssss
Light Blue Tube
Contains Sodium Citrate. Used in Coagulation testing. Tests for PT, PTT, Fibrinogen, clotting factors, D dimer
Lucy Bell
Light blue SauCer
Red tube
Contains Silica (glass) or Plastic (clot activator) which activates clotting.
Plastic: chemistry panels
Glass: routine blood donor screening, diagnostic for infectious diseases, CMP, drug test
Rarely
Red glass or plastic cup
Gold or tiger top (red-grey)
Additive:
Serum separator tube (SST)
Clot Activator
Thixotropic gel
Test: serum determinations, may be used for routine blood donor screening and diagnostic testing for serum for infectious diseases
GetTo
Gold Tiger Clot SST
Orange Tube
Contains: Thrombin, RST
Effects on Specimen: Quickly clots blood
Uses: STAT serum chemistries
Green tube
Contains Sodium or Lithium Heparin.
Plasma Used in Chemistry: STAT routine chem test, ammonia, troponin, electrolytes, ABG
Sodium heparin: chromosome analysis
GReets
Green Audrey Heparin
Lavender tube
EDTA, whole blood hematology (CBC, RBC, WBC, platelet, HBA1c, Hct, SED Rate,
immunohematology testing, blood donor screening4
EDTA: preserves shape, size of cells
Lucy
Lavender EDTA
Pink tube
EDTA, blood bank
Gray tube
potassium oxalate and sodium fluoride
Blood Glucose testing (GTT, FBS), blood alcohol concentration test, drug test, lactic acid/lactate test
Gray
Gray OXlate
Light Yellow tube
Contain acid citrate dextrose (ACD) and are used for blood bank studies and DNA paternity testing
Dark Blue tube
Contains different additives, free of element contamination
Toxicology or nutritional chem determinations
Serum Separate Tube Inversion Times
"Yellow, Lavender, Green, and gray, flip them 8-10 today!"
"Serum tubes, flip them 5, this makes sure your serum survive"
Red, Gold, Tiger, SST
"For light blue, its 3 to 4, then you don't flip anymore"
Appearance of EKG artifacts
Somatic tremor artifact: jagged peaks with irregular height and spacing
Interrupted baseline: sudden disruption of tracing
AC interference: consistent thick and fuzzy tracing
Wanderline baseline: tracing that wanders away from the center of the paper
ABG procedure
1) prepare and position, use a pre-heparinized syringe
2) Choose an artery, near the radial wrist
3) Insert 30-45 degree angle
4) collect blood
5) Store and level, place in ice
Screening tests and age range
Colonoscopy: 45-75 years old, every 3 years
Mammogram: Female 45-54 old annually, females above 55 years old+ annually or every other year
PSA: males 55-69, annually or every other year
PAP: Females 21-29 y/o, every 3 years, females 30-65 years old every 3 years, but every 5 years if having HPV
Bone density test: females 65 y/o+, every 2 years
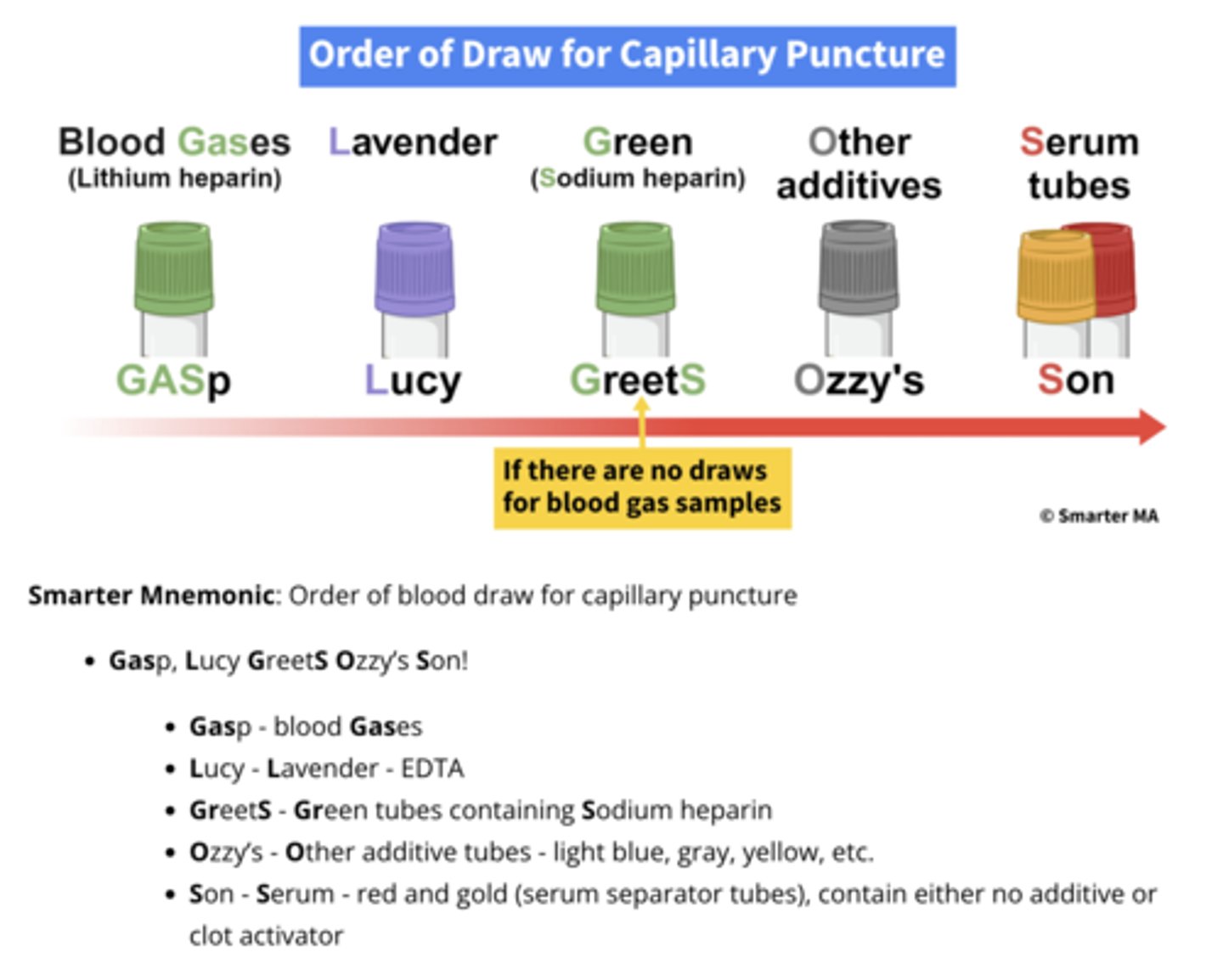
Order of draw for capillary puncture
Gasp Lucy GreetS Ozzy's Son
Blood Gases (lithium heparin), Lavender, Green (sodium heparin), Other additives, Serum tubes
Capillary blood tests cannot be used for:
ESR (erythrocyte sediment rate)
Blood cultures
Coagulation studies
ABG (needs artery)
HCPCS vs Level I vs Level II codes
HCPCS codes: alphanumeric billing codes used to identify medical services and procedures
Level I: CPT codes, maintained by the AMA, cover physician services and procedures
Level II: National codes, used for non physician services like DME, ambulance services and lab tests
HCPCS codes
A codes: ambulance and transportation
B codes: enteral and parenteral therapy
C does: outpatient prospective payments
D: dental
E: DME
G: PQRI physician quality reporting
H: Alc and drug abuse treatment
J: Drug adminstered other than oral
L: orthotics and prosthetics
M: Other medical services
P: Pathology and lab
Q: temporary and miscellaneous codes
R: Diagnostic radiology
S: Temporary National codes (not covered by medicare )
T: medicaid codes
V: Vision, hearing and speech pathology services, for ear, eye, and speech treatment
CLIA Waived Tests
Pregnancy tests
Nasal swab for flu A and B
H. Pylori
HbA1c
Hemoglobin
Spun Hct
Rapid Step test
Blood glucose
Cholesterol testing
Dipstick, tablet or multi stick urinanalysis
Fecal occult
Drug testing
Medicare part A, B, C, D, and Plan G or K
A: hospital insurance: inpatient and healthcare facilities
B:Medical insurance: services from healthcare providers, outpatient care, and DME
C: Medicare advantage: alt way to get A and B thru private insurance palns
D: Drug coverage
Plan G or K: Medicare supplemental insurance (Medigap), thru private insurance
Types of scheduling
*Wave booking: 5 patients booked at the beggining of the hour
*Modified-wave booking: 3 patients booked in the beginning of the hour and 2 patients are booked at 30 mins later, each hour
*Double-booking: 2 patients scheduled at 9:15
*Stream time-specific scheduling: patient A at 9:30, patient B booked at 10, patient C booked at 10:30
*Open booking: no patient appt, see pt in order which they arrive
*Cluster, categorization booking: all vaccines booked on Wednesday