Biology Module 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
Taxonomy
Def. The branch of biology that identifies, names, and classifies species based on natural features.
Based on 3 main groups of evidence:
* Anatomical (structure of an organism)
* Physiological (Functions of an organism)
* DNA
Based on 3 main groups of evidence:
* Anatomical (structure of an organism)
* Physiological (Functions of an organism)
* DNA
2
New cards
Levels of classification
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species (Do Kings Play Chess On Fine Green Sand)
3
New cards
Domains
Def. Largest classification category
There are 3 \____________:
1. Bacteria
2. Archaea
3. Eukarya
There are 3 \____________:
1. Bacteria
2. Archaea
3. Eukarya
4
New cards
Kingdoms: Bacteria & Archae
Cell type: Prokaryote
\# of cells: Unicellular
Reproduction: Asexual
\# of cells: Unicellular
Reproduction: Asexual
5
New cards
Kingdoms: Plantae & Animalia
Cell type: Eukaryote
\#of cells: Multicellular
Reproduction: Sexual
\#of cells: Multicellular
Reproduction: Sexual
6
New cards
Kingdoms: Protista
Cell type: Eukaryote
\#of cells: Unicellular & Multicellular
Reproduction: Asexual & Sexual
\#of cells: Unicellular & Multicellular
Reproduction: Asexual & Sexual
7
New cards
Kingdoms: Fungi
Cell type: Eukaryote
\#of cells: Mostly Multicellular
Reproduction: Sexual
\#of cells: Mostly Multicellular
Reproduction: Sexual
8
New cards
Species
Def. A group of organisms that look alike and can be interbreed under natural conditions to produce fertile offspring
9
New cards
Binomial Nomenclature
Def. A method of naming organisms by using two names
* The first part of the name is Genus and the second is species
* The first part of the name is Genus and the second is species
10
New cards
Phylogeny
Def. The history of the evolution of a species or group of organisms
11
New cards
Eukaryotes
Def. organisms containing nuclei and other types of membrane-bound organelles
12
New cards
Prokaryotes
Def. Organisms with cells lacking a true nucleus and most other organelles
13
New cards
Prokaryotes v. Eukaryotes
________________
* Smaller in size
* Cell division is NOT by mitosis and meiosis
* Example: E. Coli (Bacteria)
\
___________________
* Larger in size
* Cell division BY mitosis and meiosis
* Example: Cat (Animals)
* Smaller in size
* Cell division is NOT by mitosis and meiosis
* Example: E. Coli (Bacteria)
\
___________________
* Larger in size
* Cell division BY mitosis and meiosis
* Example: Cat (Animals)
14
New cards
Binary Fission
Def. A form of asexual reproduction in which one cell splits into two
Steps:
1. DNA duplicates
2. Cell elongates
3. Septum begins to form
4. Septum completes, distinct walls form
5. Cells divide
Steps:
1. DNA duplicates
2. Cell elongates
3. Septum begins to form
4. Septum completes, distinct walls form
5. Cells divide
15
New cards
Bacteria
- Many \___________ have one or more plasmids in their cytoplasm
- Plasmid: a small loop of DNA that usually carries a small loop of DNA
- Ribosomes: used for protein synthesis
- Flagella: used for movement, some bacteria attach to other cells or surfaces
- Plasmid: a small loop of DNA that usually carries a small loop of DNA
- Ribosomes: used for protein synthesis
- Flagella: used for movement, some bacteria attach to other cells or surfaces
16
New cards
Bacteria - Shapes and Prefixes
- Bacteria have three common \_____________
1. Coccus - Round
2. Bacillus - Rod Shaped
3. Spirillum - Spiral
- The \_________ are:
1. Diplo - Pair
2. Staphylo - Clumps
3. Strepto - Strings
1. Coccus - Round
2. Bacillus - Rod Shaped
3. Spirillum - Spiral
- The \_________ are:
1. Diplo - Pair
2. Staphylo - Clumps
3. Strepto - Strings
17
New cards
Bacteria - Reproduction
Bacteria \______________ by:
1. Binary Fission (20 mins)
2. Conjugation
- One bacteria passes a copy of a plasmid to a nearby cell through a hollow pilus
3. Endospores
- Endospores are dormant structure that forms inside certain bacteria in response to stress (poor conditions)
4. Transportation
- Bacteria picks up a loose fragment of DNA from its surroundings
1. Binary Fission (20 mins)
2. Conjugation
- One bacteria passes a copy of a plasmid to a nearby cell through a hollow pilus
3. Endospores
- Endospores are dormant structure that forms inside certain bacteria in response to stress (poor conditions)
4. Transportation
- Bacteria picks up a loose fragment of DNA from its surroundings
18
New cards
Classifying Bacteria
- The main way to classify \____________ is by gram stain
- This technique divides \_____________ into two groups
1. Gram-Positive - have a thick protein layer on their cell wall and stain purple
2. Gram-Negative - have a thin protein layer in their cell wall and stain pink
- This technique divides \_____________ into two groups
1. Gram-Positive - have a thick protein layer on their cell wall and stain purple
2. Gram-Negative - have a thin protein layer in their cell wall and stain pink
19
New cards
Positive Uses of Bacteria
* Exposure to our initial ________ through the birth canal prepares our immune system to respond to pathogens
* _________ is essential in the production of foods such as cheese, soya sauce, and chocolate
* Biotechnology - ________ have restriction enzymes that cut virus DNA as it enters them
* _________ is essential in the production of foods such as cheese, soya sauce, and chocolate
* Biotechnology - ________ have restriction enzymes that cut virus DNA as it enters them
20
New cards
Viruses
* Don’t fit into the 6 kingdoms
* They differ from eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
1. Outside a cell, they are non-living (dormant)
2. They are not cellular
3. Smaller than bacteria which are smaller than human cells
* They differ from eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
1. Outside a cell, they are non-living (dormant)
2. They are not cellular
3. Smaller than bacteria which are smaller than human cells
21
New cards
Virus classification
* Classified by size and shape of capsid
* Poly hedral - a many-sided virus
* Spherical
* Helical - a virus with a spiral cylinder shape
* Complex
* Poly hedral - a many-sided virus
* Spherical
* Helical - a virus with a spiral cylinder shape
* Complex
22
New cards
\
\
23
New cards
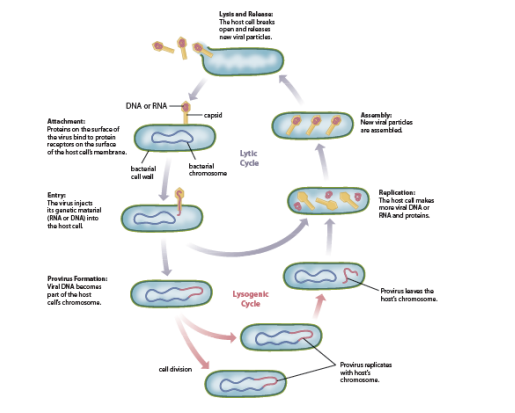
Lytic code & Lysogenic cycle (2.#)
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
1. Attachment - Proteins on the surface of the virus bind to protein receptors on the surface of the host’s cell membrane
2. Entry - The virus injects its genetic material (RNA or DNA) into the host cell
2\.1. Provirus formation - The viral DNA becomes a part of the host’s cell membrane
2\.2. Cell division - Provirus replicates with hosts chromosome
2\.3. Provirus leaves the host’s chromosome
3. Replication - The host cell makes more viral RNA or DNA and proteins
4. Assembly - New virus particles are assembled
5. Lysis & Release - The host cell breaks open and releases new viral particle
24
New cards
Vaccines
* Vaccines are weakened parts of a virus
* When altered viruses are injected, they trigger an immune system response that created a memory to fight it when you come into contact with the real thing
* When altered viruses are injected, they trigger an immune system response that created a memory to fight it when you come into contact with the real thing
25
New cards
Positive Uses of Viruses
* One solution to bacteria becoming immune to antibiotics is bacteria phages which infect bacteria
* they are very specific so only certain bacteria phages kill certain bacteria, all it takes is to inject the correct phage to kill the correct bacteria
* Gene therapy is also an option
* gene therapy is when biologists use viruses to inject the correct (non-faulty) DNA into a cell to give it the correct instructions
* they are very specific so only certain bacteria phages kill certain bacteria, all it takes is to inject the correct phage to kill the correct bacteria
* Gene therapy is also an option
* gene therapy is when biologists use viruses to inject the correct (non-faulty) DNA into a cell to give it the correct instructions