Science unit three cells and organisms Science unit three cells and organisms
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Endoplasmic reticulum
Transports proteins throughout the cells
Golgi apparatus
Finishes sorts, labels, and ships proteins
Lysosome
Digest foods and cleans up and recycles worn out organelles
Vacuoles
Used to store, food, water, or waste
Mitochondria
Breaks down sugar molecules to make energy
Cell wall
Give shape protection, and gives supports to cell
Chloroplast
Uses energy from the sun to make food for the plant does the process of photosynthesis
Organelle
Specialized structures in cells which perform cellular functions and are only found in eukaryotic cells
cell membrane
Surrounds the cell only let certain materials in and out of the cell
Cytoplasm
All organelles are suspended in this and all life functions take place here
Nucleus
It controls all the cell functions, especially reproduction
Ribosome
It’s the site of protein synthesis proteins are made here using the DNA code from the nucleus
Plant cells have
Chloroplast
Cell wall
Large vacuum
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Cell membrane
Golgi apparatus
Cytoplasm
Animal cells have
Lysosomes
Small vacuoles
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Ribosome
Cell membrane
Golgi apparatus
Cytoplasm
What two parts do plant cells have that animal cells do not
They do not have a cell wall and chloroplast
Cell
Unit of structure and functions for all life
Tissue
Composed of groups of similar cells
Organs,
composed of groups of tissues functioning together
Organ systems
Compose groups of organs functioning together
Types of cells
Prokaryotes
Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes
They do not have organelles. Examples are bacterial cells.
Eukaryotes
They have organelles and examples are plant or animal cells
Cell theory
All living things are made of cells
Cells are basic unit of structure and function
New cells come from pre-existing cells
Exception to cell theory
Viruses are not living
Where did the first cell come from?
Mitochondria and chloroplast have their own genetics and can reproduce on their own yet they are organelles not cells
Metabolism
All chemical reactions that occur in an organism to make and use energy
Homeostasis
Maintaining a constant internal, condition, regardless of the external environment
Examples are shivering and sweating
Cellular respiration
Produces energy occurs in the mitochondria
Aerobic
Needs oxygen
Anaerobic
Does not need oxygen
Regulation
Control and coordination of life processes it allows the body to maintain homeostasis
Reproduction
Production of offspring
Asexual
One parent
Sexual
Two parents the charger
Growth and repair
To increase in size change over individuals lifetime gets bigger and matures
Excretion
Removal of metabolism, waste CO2 sweat water
Nutrition
All organisms get nutrients through food
Autotrophic
Make their own food through photosynthesis
Heterotrophic
Get nutrients from the environment
Transport
Organism circulate and absorb materials through the cells
Synthesis
To build or make something from small to large
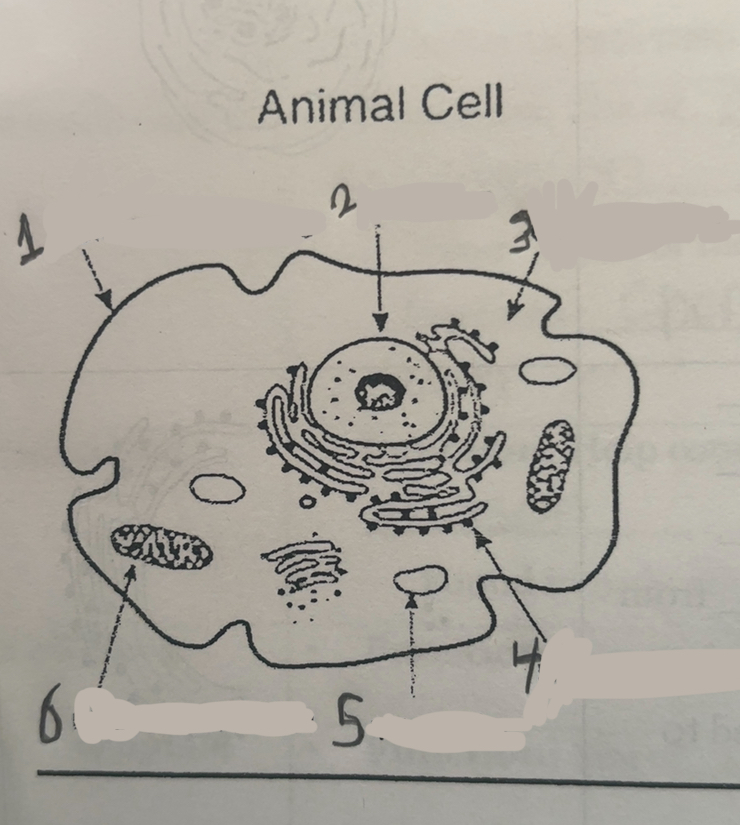
What is number one
Cell membrane
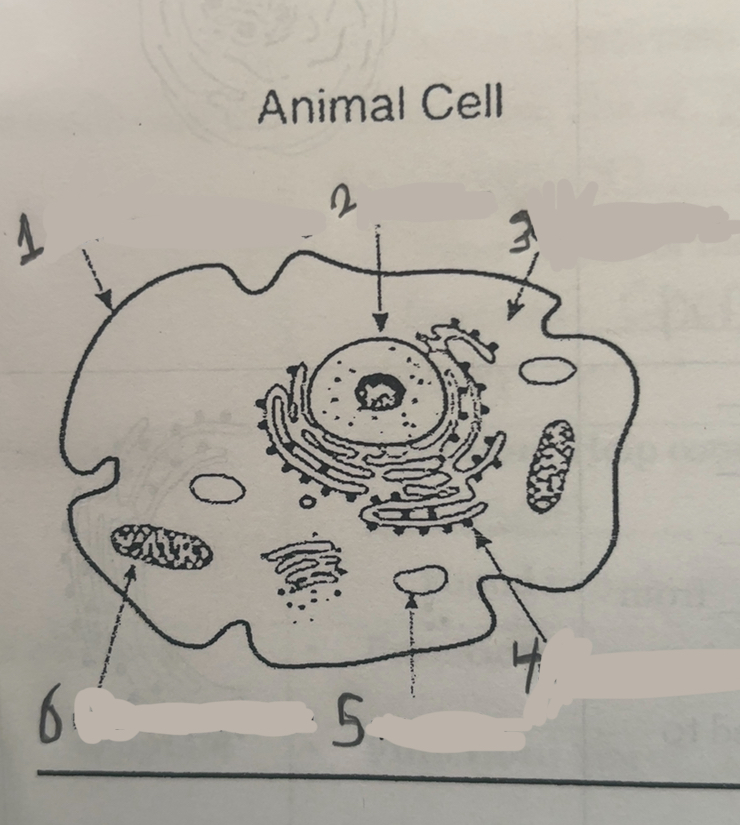
What is number two
Nucleus
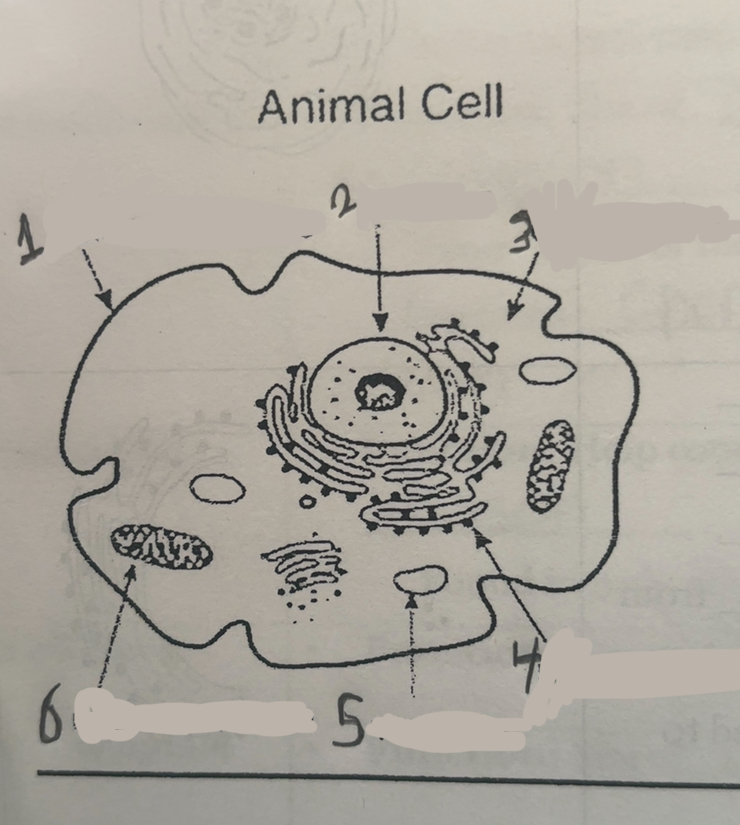
What is number three
Cytoplasm
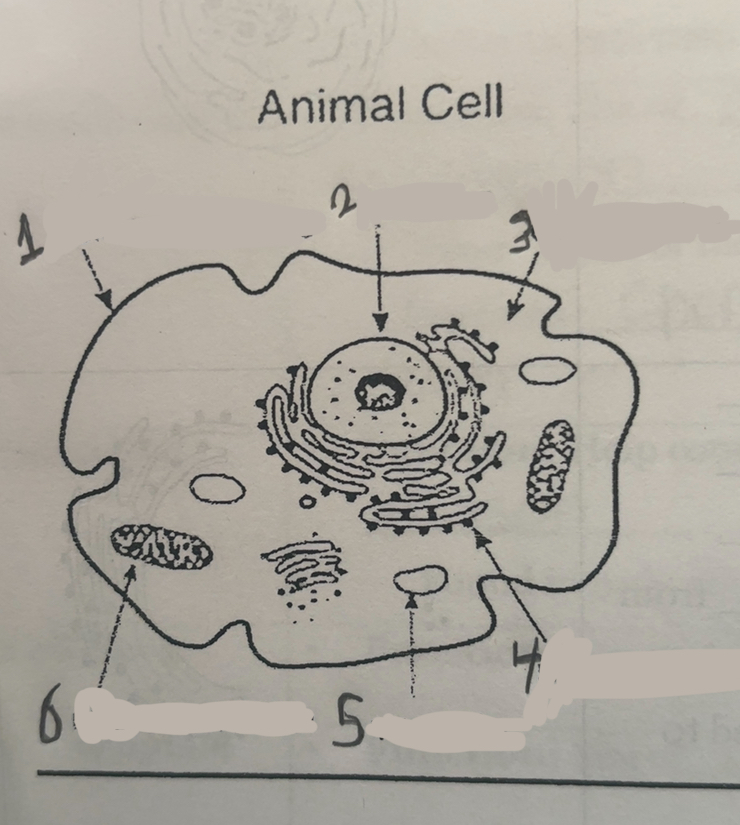
What is number four
Ribosomes
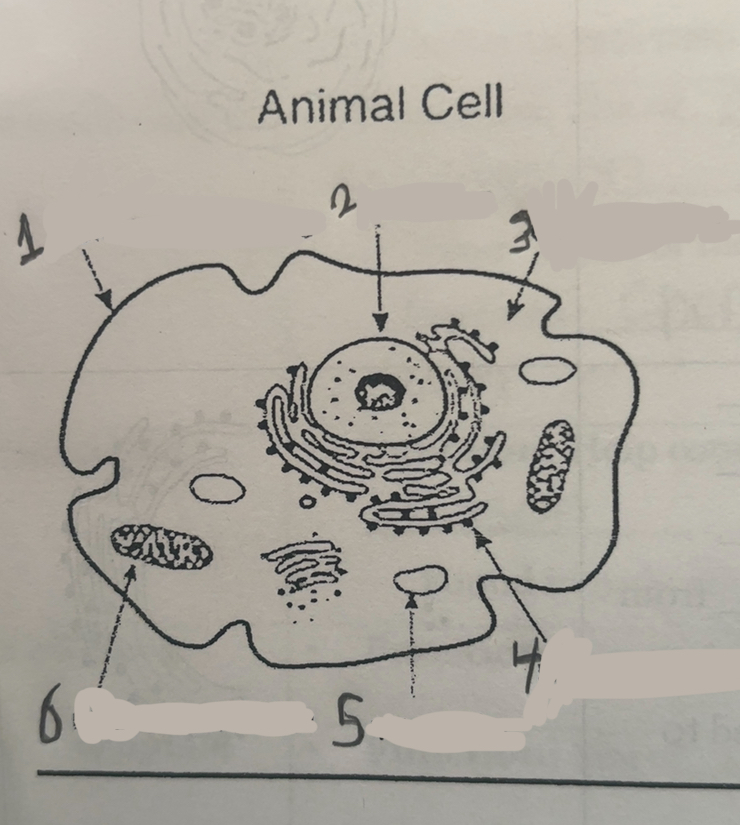
What is number five
Vacuums
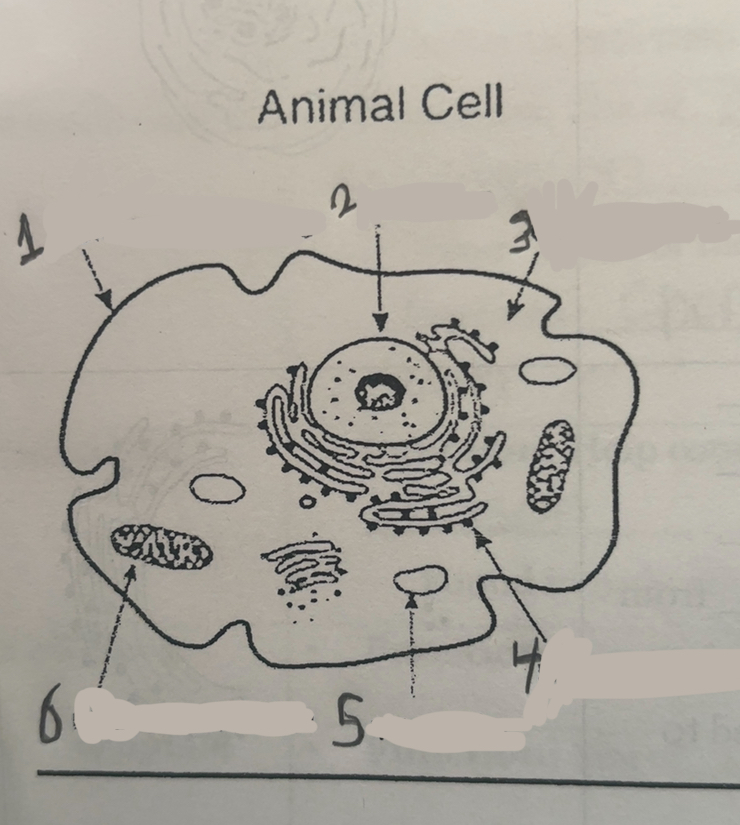
What is number six
Mitochondria
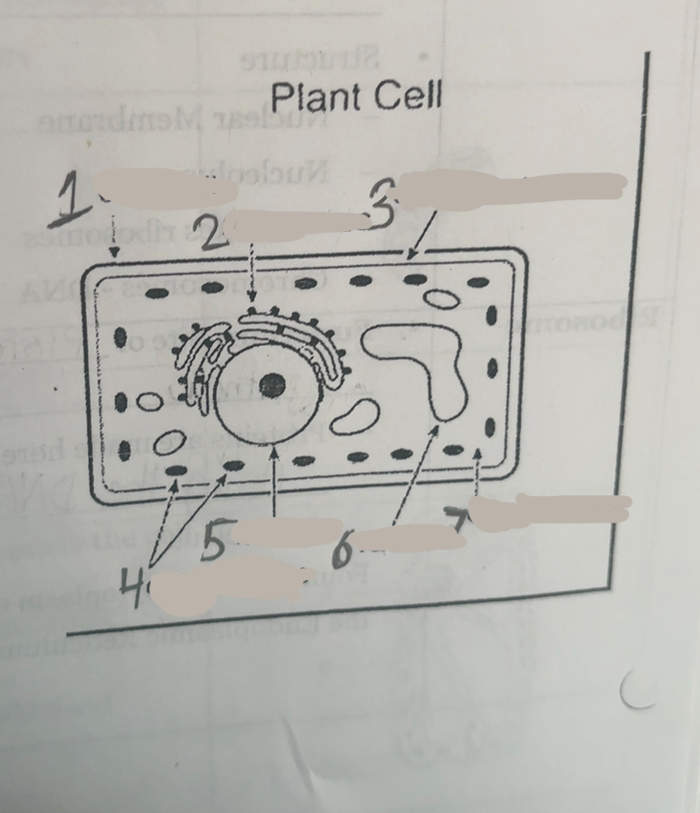
What is number one
Cell wall
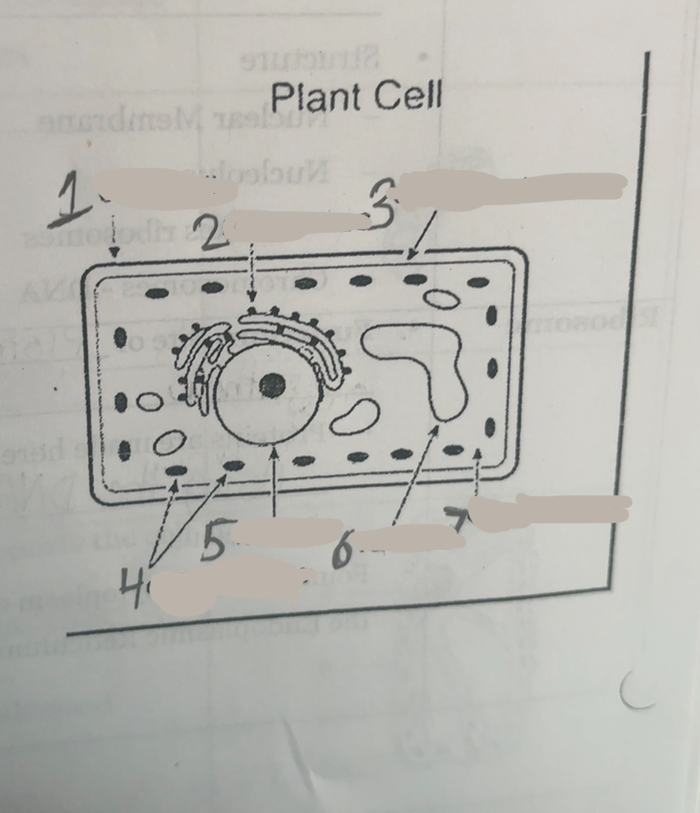
What is number two
Ribosomes
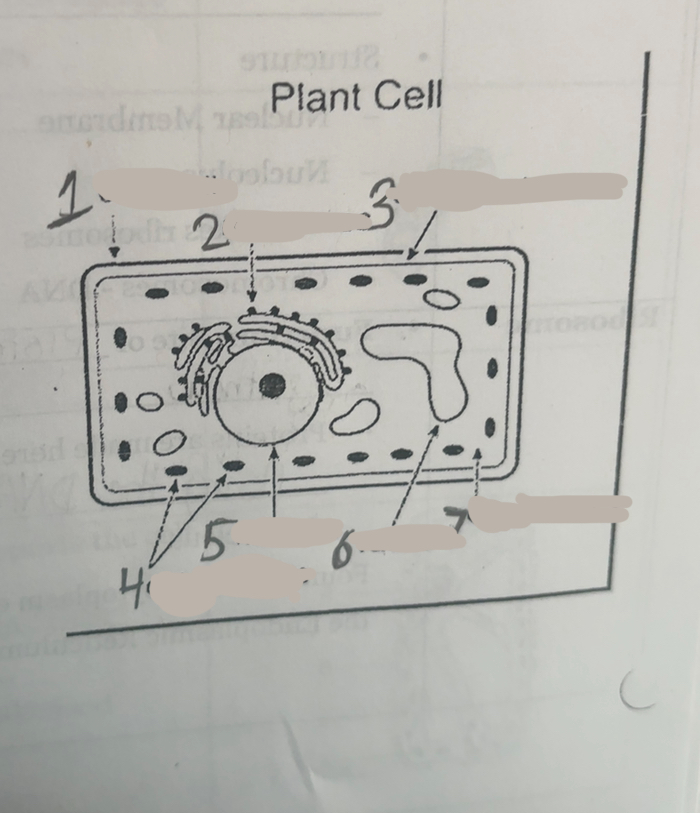
What is number three
Cell membrane
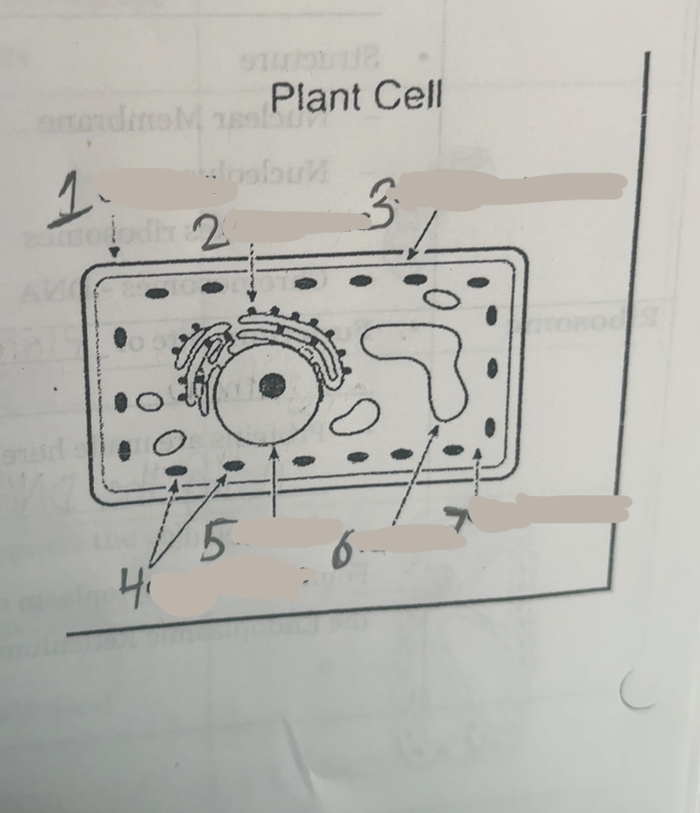
What is number four
Chloroplasts
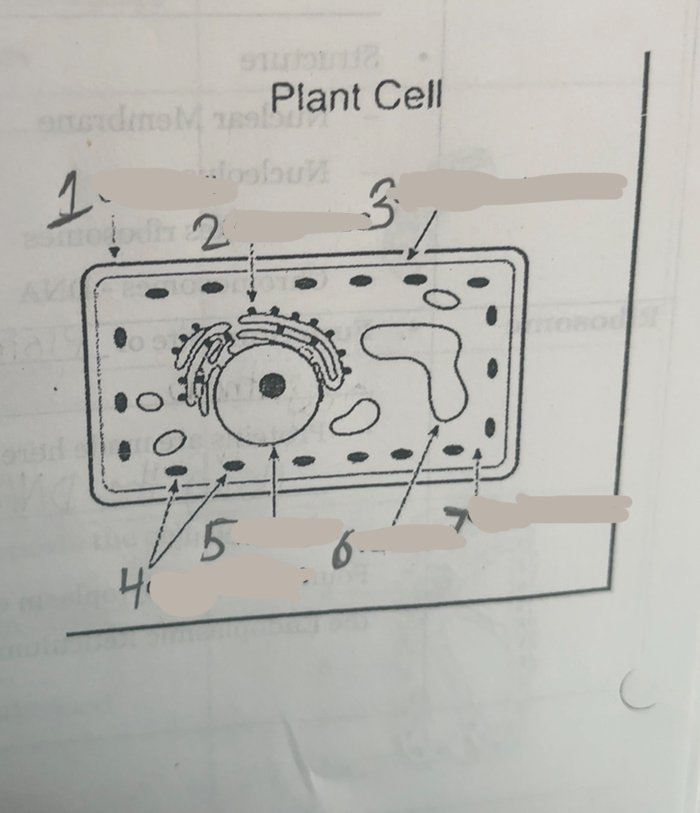
What is number five
Nucleus
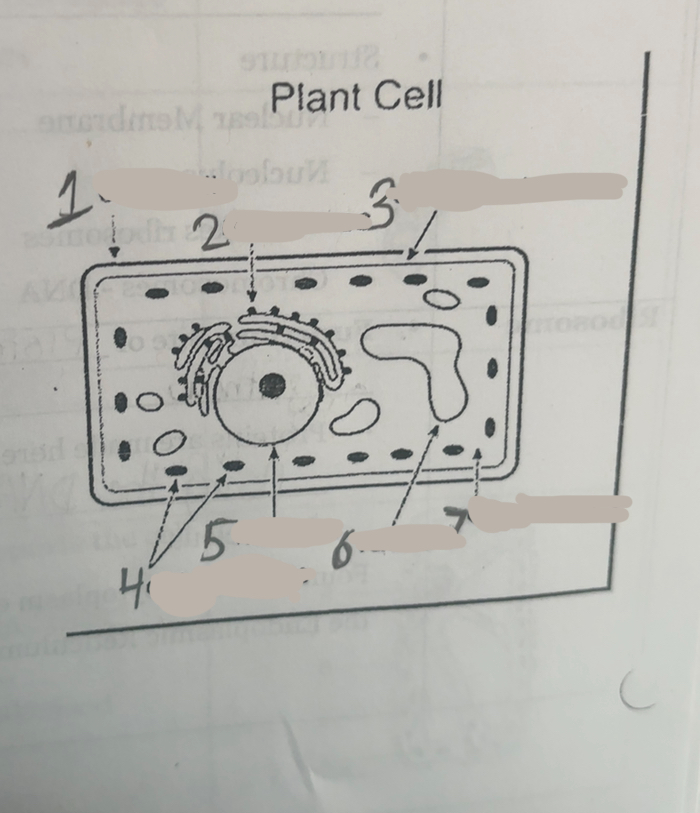
What is number six
Vacuoles
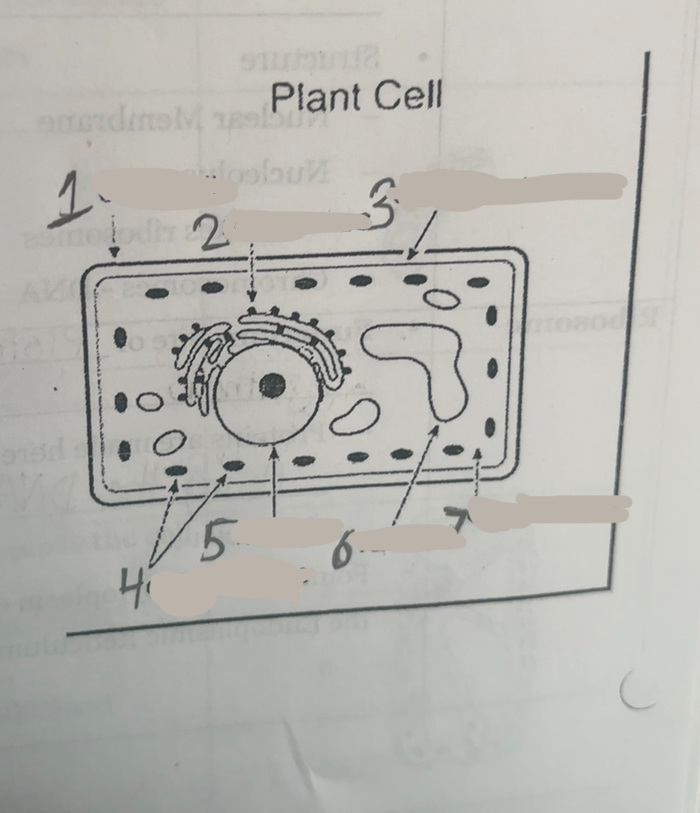
what is number seven
cytoplasm