iron, rust and redox
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is oxidation in terms of hydrogen and oxygen?
gain of oxygen and loss of hydrogen
what is reduction in terms of hydrogen and oxygen?
loss of oxygen and gain of hydrogen
what is oxidation in terms of electrons?
loss of electrons
what is reduction in terms of electrons?
gain of electrons
how can you remember oxidation and reduction in terms of electrons?
OILRIG
oxidation is loss
reduction is gain
what is the manufacturing of ammonia (NH3) known as?
the Haber process
nitrogen + hydrogen <->
ammonia
nitrogen + hydrogen <-> ammonia
N2 + 3H2 --> 2NH3
what is a redox reaction?
reactions in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously
the reaction of hydrogen with copper (||) oxide
the gas is hydrogen
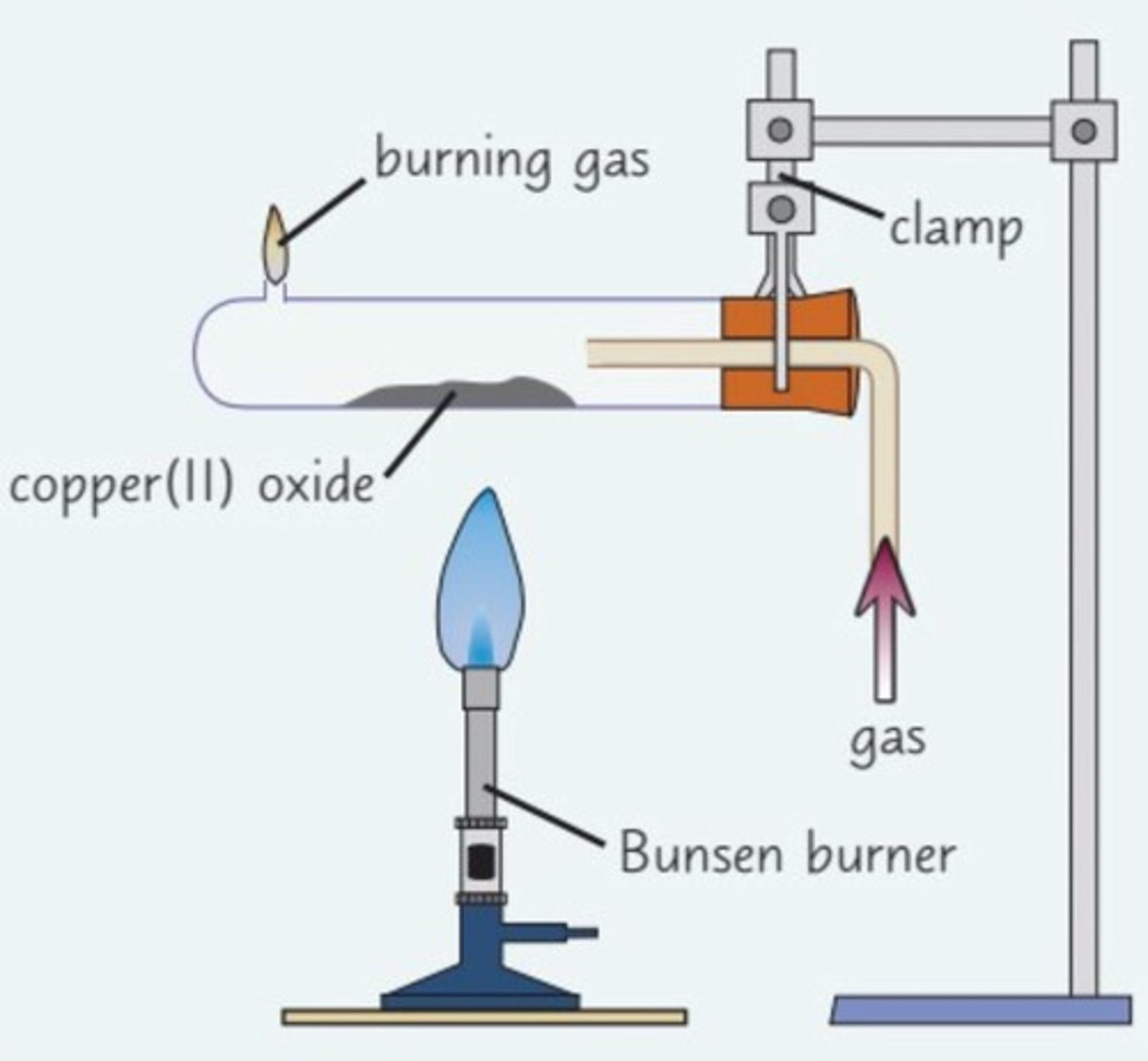
the reaction of hydrogen with copper (||) oxide. observations?
red-brown solid produced. steam will form around glass tube
the reaction of hydrogen with copper (||) oxide. what happened to the copper oxide? (include balanced symbol equation)
CuO + H2 -> Cu + H2O (g)
The CuO has been reduced as oxygen is removed.
The hydrogen is the reducing agent
Equation for combustion of hydrogen
2H2 + O2 -> 2H2O
chemical name for rust
Hydrated iron (III) oxide
chemical formula for rust
Fe2O3.XH2O
what is reacted with iron to form rust?
oxygen and water
what metals rust?
only iron, the other metals corrode
name a drying agent
anhydrous calcium chloride
Is rusting an oxidation or reduction reaction?
oxidation as iron gain oxygen
uses of iron and steel
1. buildings, bridges
2. ships, cars
3. nails
problems with rusting
1. dangerous
2. unsightly
what are most methods for rust prevention?
barrier methods
how does painting the steel prevent rusting?
puts a layer on the iron, providing a protection layer so that oxygen and water cannot come into contact with the iron.
used on bridges/large objects
how does galvanising the steel prevent rusting?
Zinc (usually used in galvanising steel) is more reactive than iron so by putting a coat of zinc on the iron, it will react with the oxygen and water first, protecting the iron.
when is the barrier method oil/grease used?
moving parts (e.g bicycle chains)
when is the barrier method plastic coating/rubber coating used?
when a soft surface is needed (e.g. handle bars and garden furniture)
sacrificial protection
magnesium bars put onto iron oilrigs. Mg is more reactive than Fe, so it will react first - protecting the Fe.
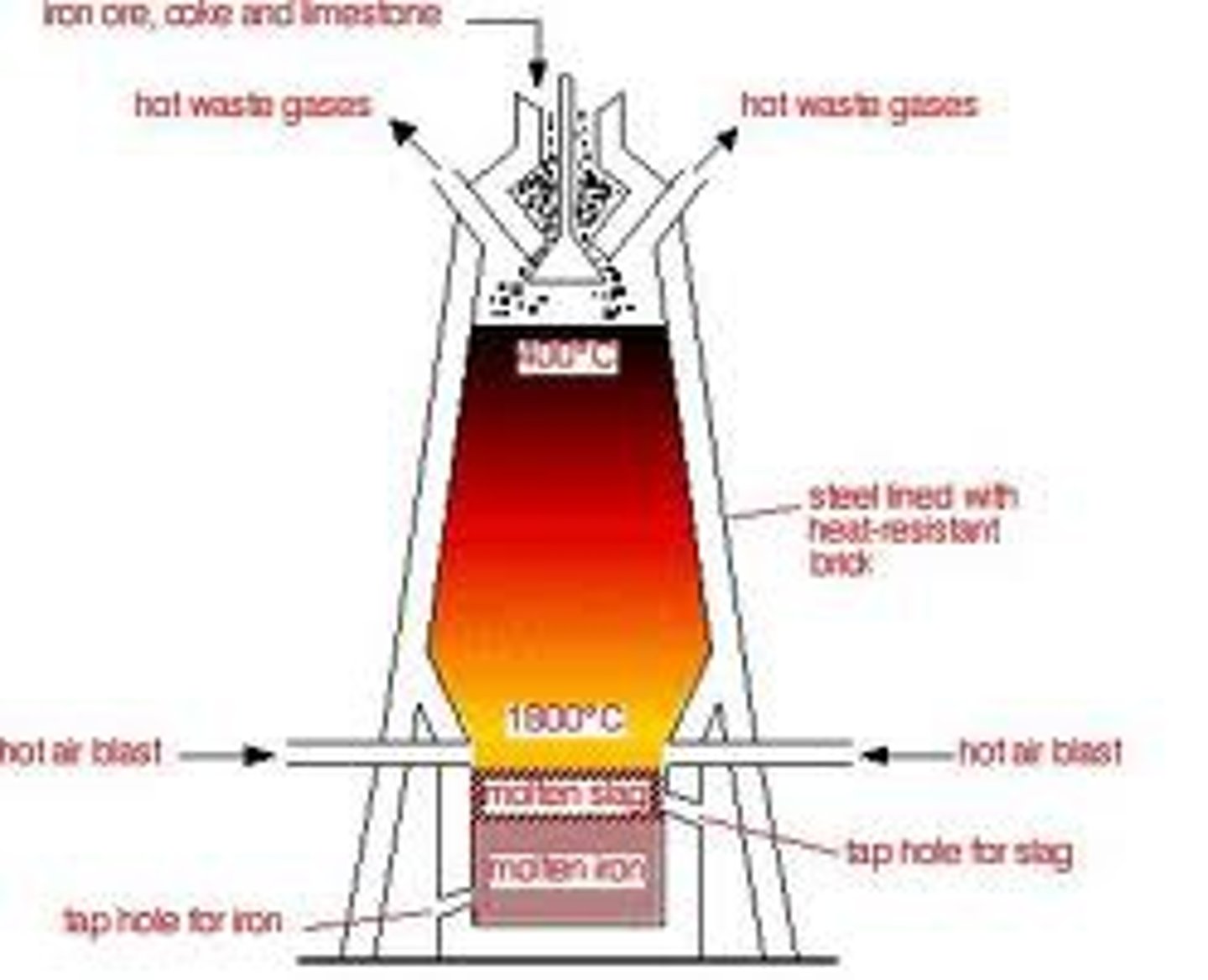
Blast Furnace
extraction of iron using carbon
iron ore
haematite
limestone (calcium carbonate)
CaCO3
haematite (iron ore)
iron (|||) oxide
Fe2O3
coke
carbon
C
Blast Furnace: Stage one
PRODUCTION OF REDUCING AGENT (CO)
1. C + O2 -> CO2 (oxidation)
Coke reacts with hot air to form carbon dioxide. This is exothermic -ΔH. The carbon is burned (combustion)
2. CO2 + C -> 2CO
The carbon dioxide reacts with more coke to form carbon monoxide - the reducing agent
Blast Furnace: Stage two
REDUCING IRON (|||) OXIDE
3. Fe2O3 + 3CO -> 2Fe + 3CO2 (redox)
Once carbon monoxide is formed, it reacts with Fe2O3, reduces it and forms Iron.
Blast Furnace: Stage three
REMOVING ACIDIC IMPURITIES
Haematite is not pure Fe2O3 - it contains acidic impurities such as silicon dioxide, to remove this we need a base.
4. CaCo3 -> CaO + CO2 (thermal decomposition)
The limestone breaks down once it enters the blast furnace. CaO - a base is formed
5. CaO +SiO2 -> CaSiO3
The base CaO reacts with the acidic SiO2 to form calcium silicate (slag), which is removed at the bottom of the blast furnace.