Successes and Challenges of the League of Nations in the 1920s
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
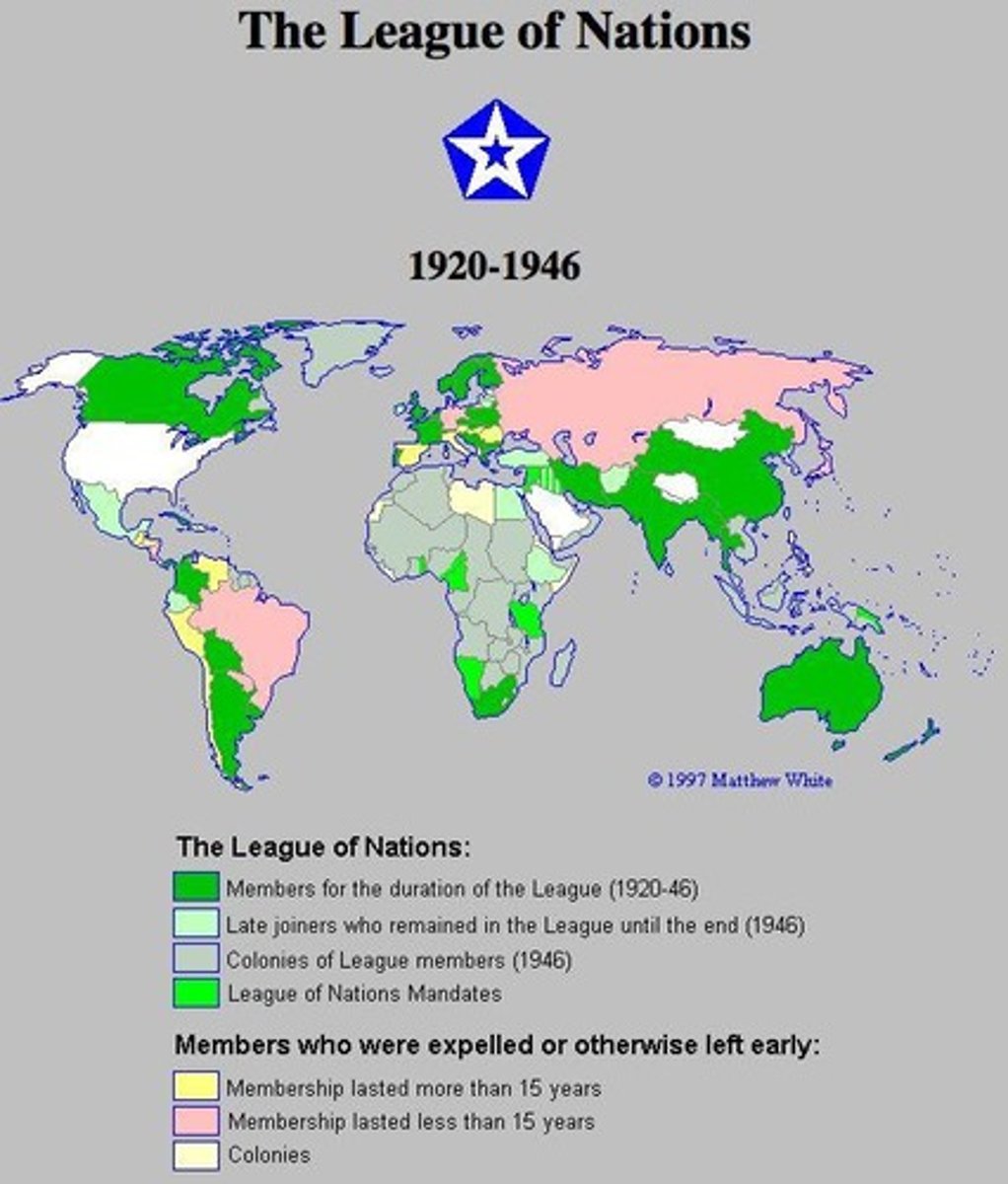
League of Nations
International organization aimed at preventing wars.
Woodrow Wilson
U.S. President who proposed the League.
Nobel Peace Prize
Award received by Wilson for peace efforts.
Disarmament
Limiting weapons to ensure national safety.
Secret Diplomacy
Unregistered treaties that contributed to WW1.
Arbitration
Settling disputes between nations fairly.
Collective Security
Nations cooperate to deter aggression.
Economic Sanctions
Trade refusal to punish aggressive states.
Plebiscites
Local votes to determine territorial ownership.
Saar Valley
Region that voted to return to Germany.
Mandates
Territories managed until they gain independence.
International Labor Organization (ILO)
Agency improving labor conditions globally.
Repatriation
Restoring prisoners of war to their countries.
Education Development
Encouraging education in member states.
Public Health Promotion
Initiatives to control and prevent diseases.
General Assembly
Main body of the League with one vote per state.
Council
Smaller body handling urgent League matters.
Secretariat
Administrative arm managing League operations.
Permanent Court of International Justice
Judicial body resolving legal disputes between states.

Commissions and Committees
Agencies addressing specific social issues.
Teschen (1920)
Successful dispute resolution by the League.
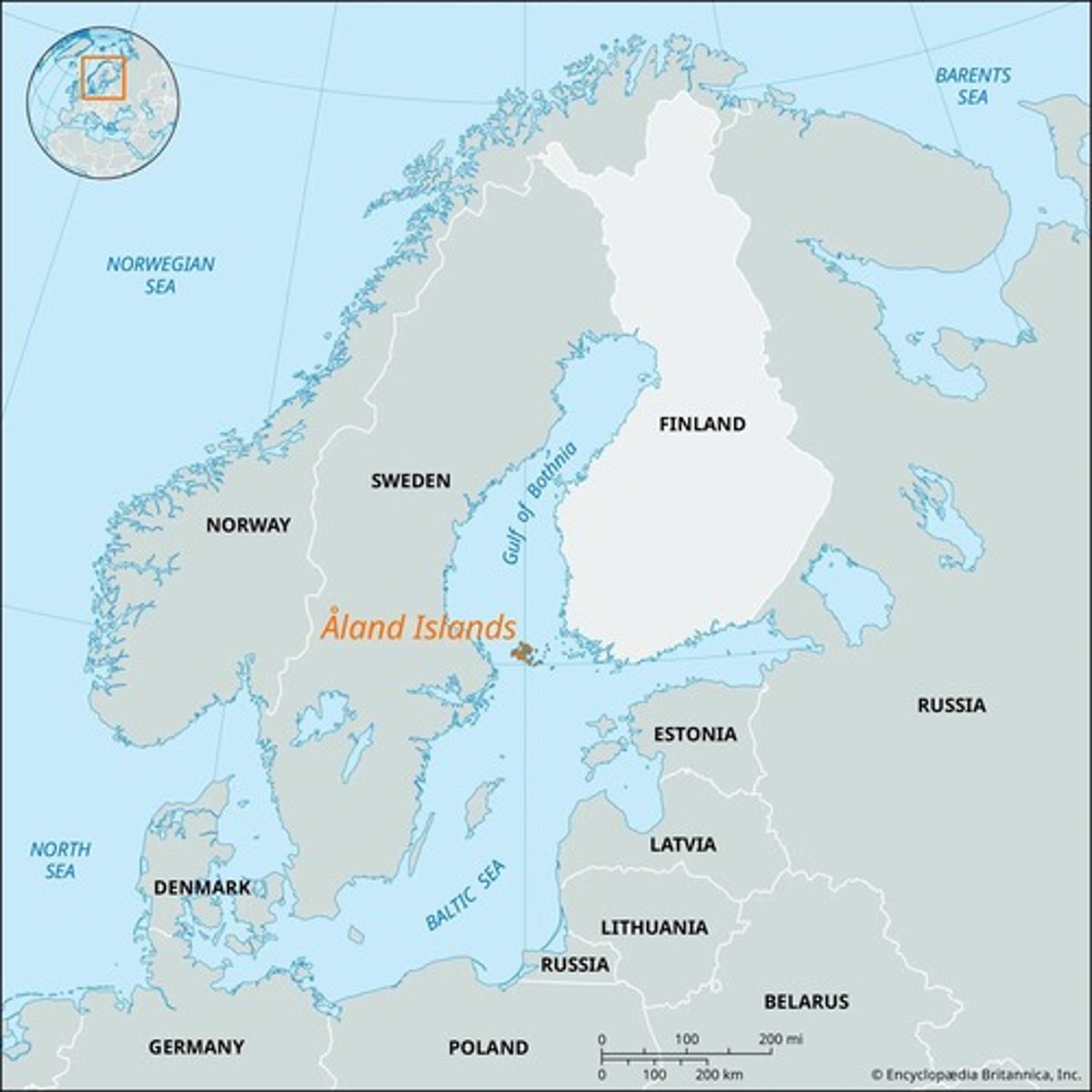
Aland Islands (1921)
Peaceful resolution of territorial conflict.
Upper Silesia (1921)
League's intervention in regional disputes.
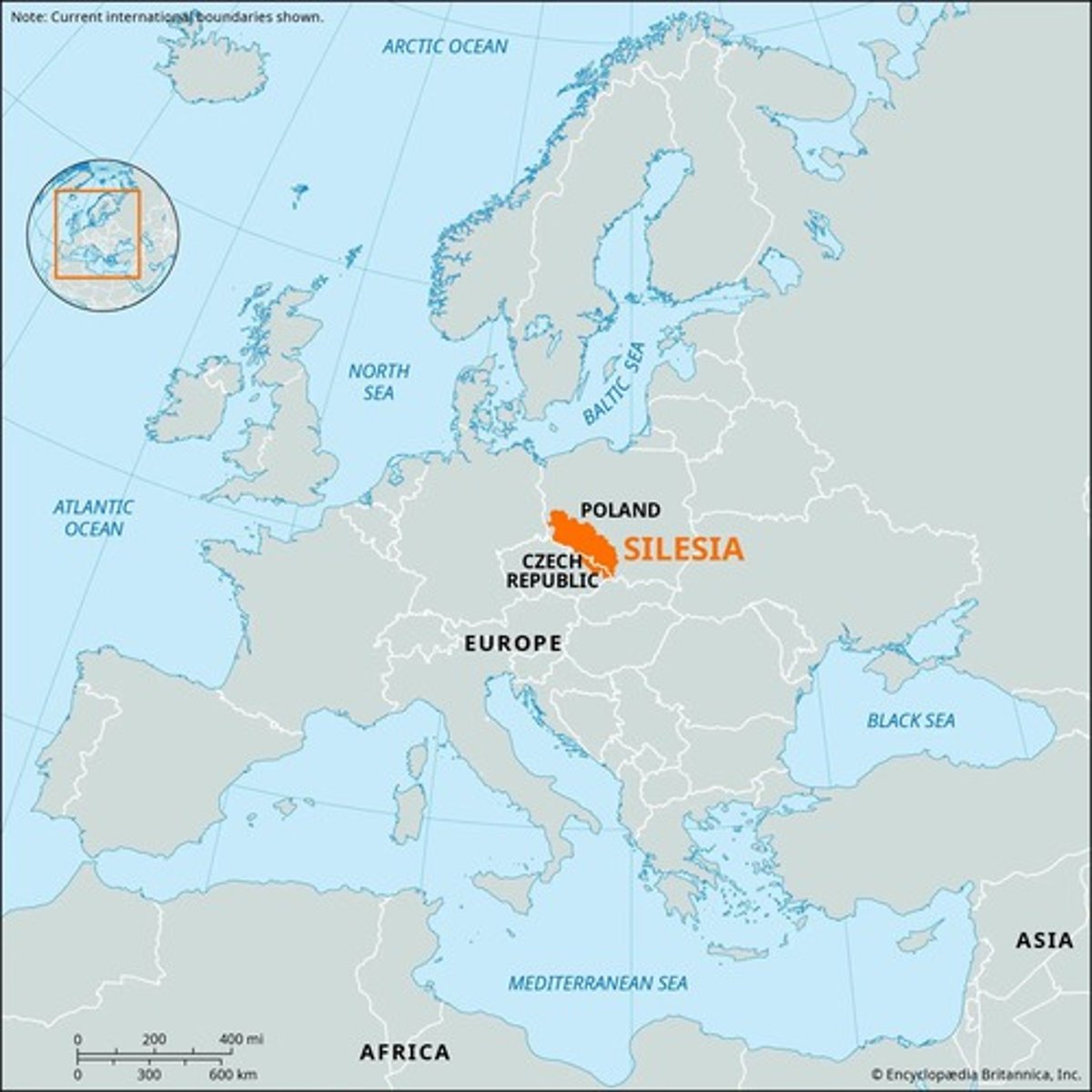
Upper Silesia
Contested territory between Germany and Poland.
Yugoslavia-Albania Border Dispute
Border conflicts mediated by the League in 1921.
Memel
Port city awarded to Lithuania by the League.
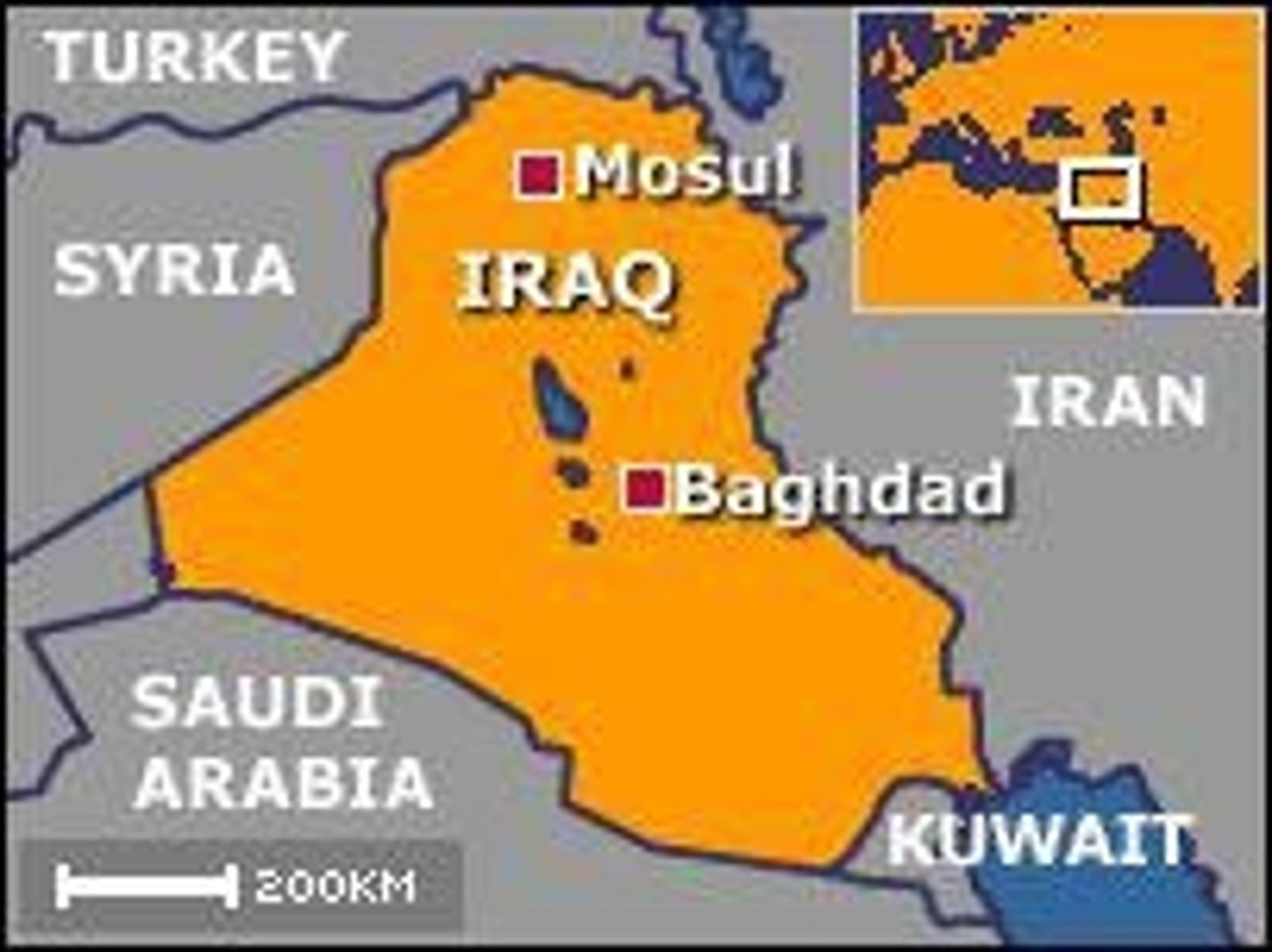
Mosul
Region awarded to Iraq after League investigation.
Greece-Bulgaria Border Dispute
League condemned Greece's invasion of Bulgaria.
Teschen
Plebiscite organized by League between Poland and Czechoslovakia.
Aland Islands
Dispute resolved in favor of Finland by League.
Vilna
Polish occupation of Lithuanian capital post-WWI.
Treaty of Riga
Poland expanded territory into Belarus in 1921.
Invasion of Ruhr
French and Belgian invasion due to German reparations.
Corfu Incident
League's failure to resolve Greek-Italian conflict.
Plebiscite
Popular vote to determine territorial claims.
Collective Security
League's principle of mutual defense among nations.
Criticism of League
Lack of intervention in major power disputes.
Dawes Plan
1924 plan to resettle Ruhr dispute, bypassing League.
International Port
Memel's port designated for international control.
Self-interest
Nations prioritized national interests over League cooperation.
Arbitration Success
League successfully mediated disputes among smaller nations.
Tensions Persisted
Disputes often left unresolved tensions between nations.
Major Powers
League's limitations due to absence of major powers.
League's Authority
Limited power to enforce decisions among member states.
Corfu Incident
1923 event where Italy invaded Greece.
Mussolini
Italian leader blaming Greece for Corfu deaths.
Council of Ambassadors
Intergovernmental agency monitoring peace post-WWI.
League of Nations (LON)
International organization aimed at maintaining peace.
Unanimity Requirement
All LON decisions needed unanimous agreement.
Collective Security
LON's principle requiring member state cooperation.
International Labor Organization (ILO)
Agency improving global labor conditions and rights.
Nansen Passport
ID for stateless refugees created in 1922.
Health Organization
Agency focused on disease prevention and research.
Mandates Commission
Oversaw territories transitioning to self-governance.
U.S. Refusal to Join
U.S. isolationism led to non-participation in LON.
Weaknesses of LON
Factors limiting LON's effectiveness in global peace.
Paris Peace Settlements
Unpopular agreements leading to LON's formation.
Isolationist Policies
Nations prioritizing self-interest over collective action.
Saar Region Plebiscite
Vote to determine region's return to Germany.
Financial Assistance
Support provided by LON for various needs.
Exploitation Issues
LON addressed trafficking and exploitation of vulnerable.
Cholera and Typhoid
Diseases targeted by health initiatives of LON.
Fridtjof Nansen
Led International Commission of Refugees, won Nobel Prize.
Old Age Pensions
Benefit established by ILO for worker security.
Minimum Wage Agreement
77 nations agreed to establish minimum wage.
Forced Labor Investigations
LON actions against labor abuses in Liberia.
Legacy of LON Agencies
Many LON agencies continued in the UN.