lecture 11- Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Ligand
Molecule that binds to protein reversibly
PL
Protein ligand complex
Bonding site
Location on the protein molecules that interacts w/ ligand
Cooperativity
Binding of one ligand on one subunit affects binding on other subunits
Negative cooperativity
Binding of one ligand negatively affects /hinders the binding of another protein
How does ligand binding affect a protein with multiple subunits
When a ligand binds it often induces a conformational change that can change the binding site of the other subunits. By either making it so that ligand can”t bind or that it can.
What is Kd
Dissociation constant Kd=[P][L]/[PL] The concentration of ligand when 50% of protein would be in PL complex while the other 50% would be a free protien. Smaller value means higher affinity. (more PL than free ligands and proteins)
Myoglobin
Oxygen storage protein (binds to O2)
found in mammalian muscle tissue
Diagnostic of muscle injury
first protien sturtcure ever determined
Hemoglobin
Oxygen transport protein found in red blood cells
Binds to O2 in lungs and releases it in tissues
Job is to transport O2 from our lungs to tissue
Composed of four subunits, allowing cooperative binding
Plays a role in carbon dioxide transport and H+ transport
Quaternary structure
How does Hemoglobin and Myglobin bind to O2 ?
Hemoglobin and Myoglobin use a prosthetic group called Heme that is very good at binding to O2 since amino groups are not good at it
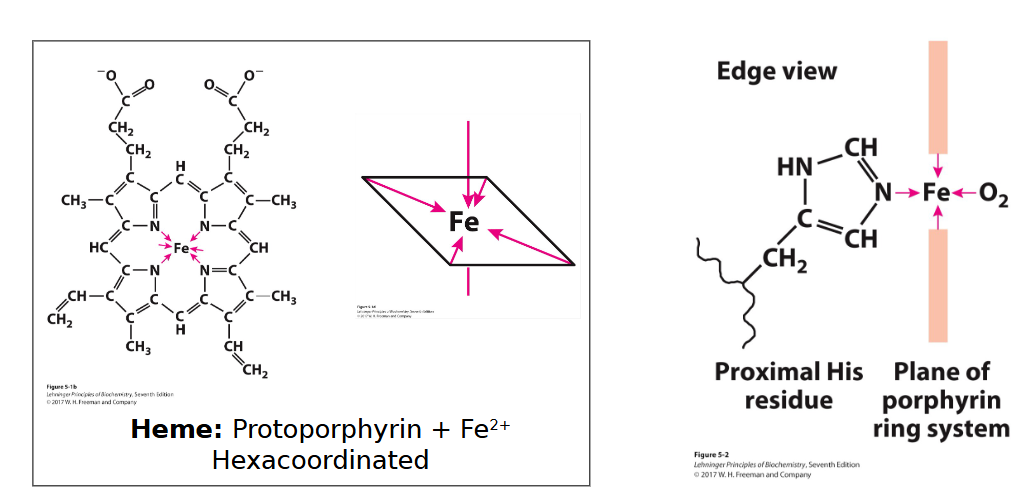
Heme, What is it, what is it composed of, what can it do, and how is it affected by binding to myoglobin
A prosthetic group that helps hemoglobin and myoglobin bind to oxygen
2 parts of heme:
Protoporphyrin ring
Fe2+
Really good at binding diatomic molecules like O₂
They are even better at CO₂, since it binds straight up, while oxygen binds at an angle
Myoglobin structure affects the specificity of ligand binding (heme).
Heme by itself has a much higher affinity for CO₂ than oxygen
But because distal His forms an interaction with O₂ that it doesn’t with CO₂, it only binds to O₂.
Structure of Heme
Planar ring called protoporphyrin with Fe2+ In the center connected to 4 nitrogens
Fe2+ can connect to 6 binding sites, but the nitrogens that are part of the protoporphyrin ring only connect to 4 (in the plane of heme), leaving 2 open.
A proximal histidine is occupying one of the 2 open binding sites
Leaving one open for O2
Myoglobin structure
Monomeric
small—153 153 amino acids
8 alpha helix
Has a single oxygen-binding site
tertiary structure
Nomenclature of Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
1st α-helix (N-terminus) is A, all the way to the (8th a-helix) C-terminus in alphabetical order
letter tells you what helix it is in
number tells you its position within the a-helix
Example His F8
Hemoglobin structure
Tetramic
Quartenary
2 alpha subunites
2 Beta subunits
4 heme groups( one heme for each subunit)
Hemoglobin interfaces
Hemoglobin has a large number of intersubunit contact between different subunits (so huge interface between the alpha 1 subunit and the beta 2 subunit )
so if a subunit of hemoglobin binds to oxygen, it will cause a conformational shift within the other subunits.
Oxygen binding induces a structural transition in hemoglobin (what are the two states )
When there is a lack of oxygen, the hemoglobin is in T-state (tense/deoxyhemoglobin) because the tense state has a low affinity(releases it more) for O₂ and predominates when O₂ is not bound
When oxygen concentration is added, it begins to shift the structure of the hemoglobin into the R-state. (relaxed state/oxyhemoglobin) with high concentrations of O2, hemoglobin now has a high affinity (holds it tighter) for oxygen and predominates when O2 is not bound.
T and R state are reversible
What stabilizes T-state?
T state is stabilized by a number of ionic interactionsThe interaction
“The chain of interactions inside hemoglobin connects the oxygen-binding site to the places where the subunits meet, allowing oxygen binding to change the overall shape of the protein.”(cooperative binding)
These ionic chains between interfaces protect T-state from binding to O2
What are the rearrangements of the heme that drive the T-to-R transition?
Heme is a planar ring-shaped molecule that holds Fe2+ in the center
However, in the T state (puckered heme, no O₂ bound), the iron does not sit perfectly flat on the ring
When it binds to O₂ and turns into the R state (planar heme), the O₂ pulls the iron into the plane of the ring. (downwards)
The heme becomes planar (unpuckered).
This small flattening movement tugs on the attached proximal histidine F8 and helix (to maintain coordination), which helps trigger the T → R conformational change in hemoglobin.
True or false in hemoglobin all 4 subunits can either be T or R You CANNOT have a mix. Since a change in one subunit causes a change in the rest.
True
How does cooperative ligand binding work for hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is positive cooperativity in its ligand binding
As O2 binds at the lungs, in order to pick up as much oxygen as possible, subunits transition from the T state to the R state (the entire tetramer converts). to the high affinity state
As O2 is released at the tissues in order to release as much oxygen as possible, subunits transition from R state to the T state (low affinity), and the entire tetramer converts
Why does the conformational change in Heme trigger T to R state transition
In the T state there are ionic bonds that resist the binding ofbinding of oxygen
When O₂ binds to the Fe2+ ino it moves down the plan of the protoporphyrin ring that pulls te F8 His residue wihc initiaes breaking of ionic bonds that were in T state which causes the conformational change.