Gearing up for the PRAXIS Art Test
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
random facts i need to learn about art
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
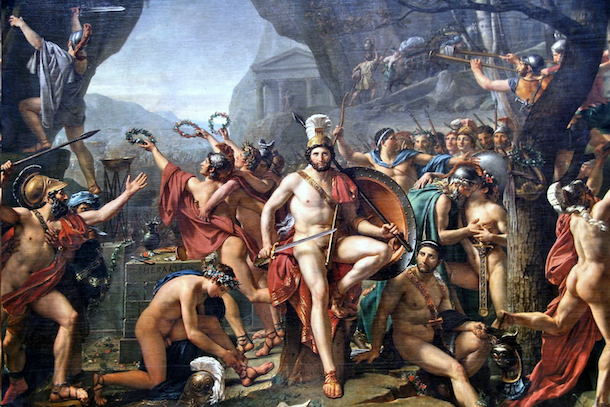
Pouncing
a method for transferring a preparatory drawing (often called a "cartoon") to a final surface, like canvas or plaster, allowing artists to accurately reproduce their designs
What are the Elements of Art and Design?
line, shape, space, value, form, texture, and color
What Are the Elements of Form?
the point, the line, the plane and the volume
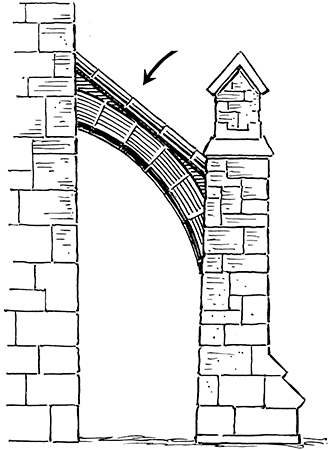
flying buttress
An arch that extends out from a tall stone wall
transept
(in a cross-shaped church) either of the two parts forming the arms of the cross shape, projecting at right angles from the nave

Parapet
a low protective barrier or wall that extends upwards from the edge of a roof, balcony, terrace, or other structure, designed to prevent falls and, historically, to offer shelter from attack

pediment
the triangular upper part of the front of a building in classical style, typically surmounting a portico of columns.

Classical Architecture
originating in ancient Greece and Rome, is characterized by symmetry, proportion, and the use of columns, pediments, and other architectural elements, with styles like Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian being prominent 10 AD
Art Nouveau Architecture
a movement prominent from the late 19th to early 20th centuries, is characterized by its organic, flowing lines, natural motifs, and a rejection of traditional architectural forms, often featuring floral and vegetal designs, asymmetry, and the use of materials like iron and glass
Gothic Architecture
a prominent European style from the late 12th to the 16th century, is characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, flying buttresses, and large stained-glass windows, emphasizing verticality and light
Baroque Architecture
is an extravagant architectural style that emerged in the late 16th century in Italy, characterized by dramatic use of light and shadow, bold ornamentation, and a sense of movement in design. It often features grand staircases, domes, and elaborate decorations.
Classicism
the following of ancient Greek or Roman principles and style in art and literature, generally associated with harmony, restraint, and adherence to recognized standards of form and craftsmanship, especially from the Renaissance to the 18th century.

Cubism
an early 20th-century style and movement in art, especially painting, in which perspective with a single viewpoint was abandoned and use was made of simple geometric shapes, interlocking planes, and, later, collage.

Dadaism
an anti-establishment art and literary movement that emerged in the early 20th century, reacting to the horrors of World War I by embracing chaos, nonsense, and irrationality, while challenging traditional artistic values and societal norm

Deconstructivism
a style characterized by a radical freedom of form, the open manifestation of complexity, and a rejection of traditional architectural norms and symmetry, often featuring asymmetrical shapes and unconventional materials that blur the boundaries between art and architecture.
Expressionism
a style of painting, music, or drama in which the artist or writer seeks to express emotional experience rather than impressions of the external world. Started 1885-1900s It often emphasizes subjective emotions and responses to events, using vivid colors and exaggerated forms.

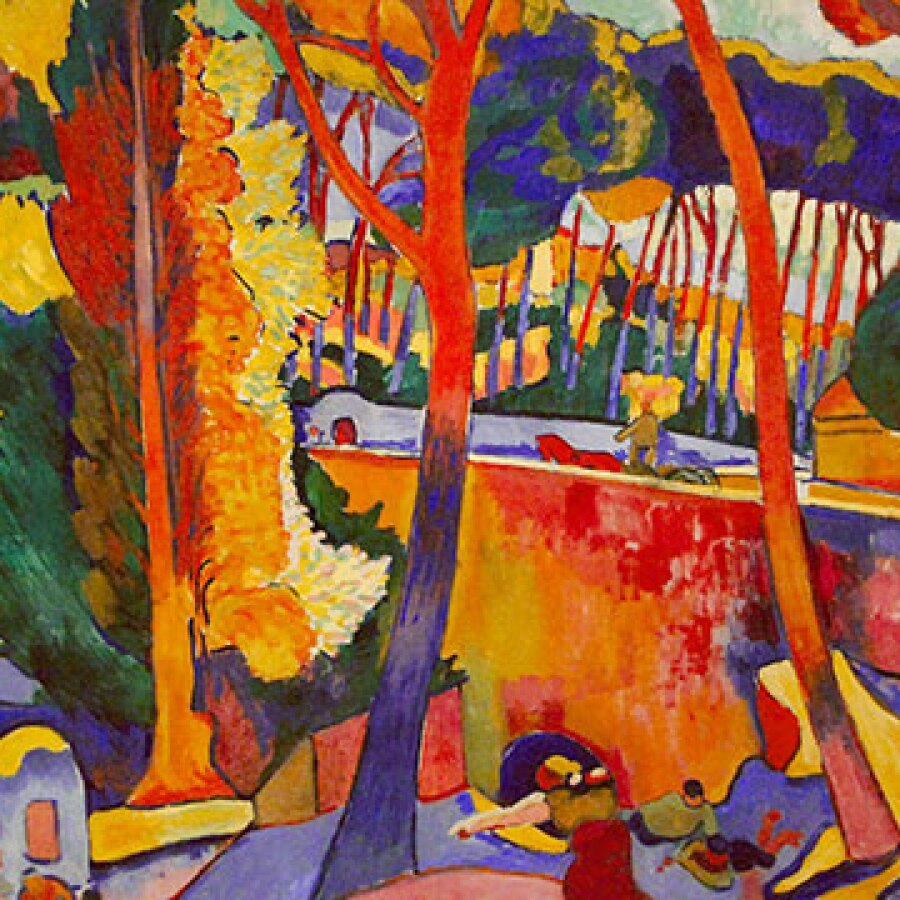
Fauvism
a style of painting with vivid expressionistic and nonnaturalistic use of color that flourished in Paris from 1905 and, although short-lived, had an important influence on subsequent artists, especially the German expressionists. Matisse was regarded as the movement's leading figure.

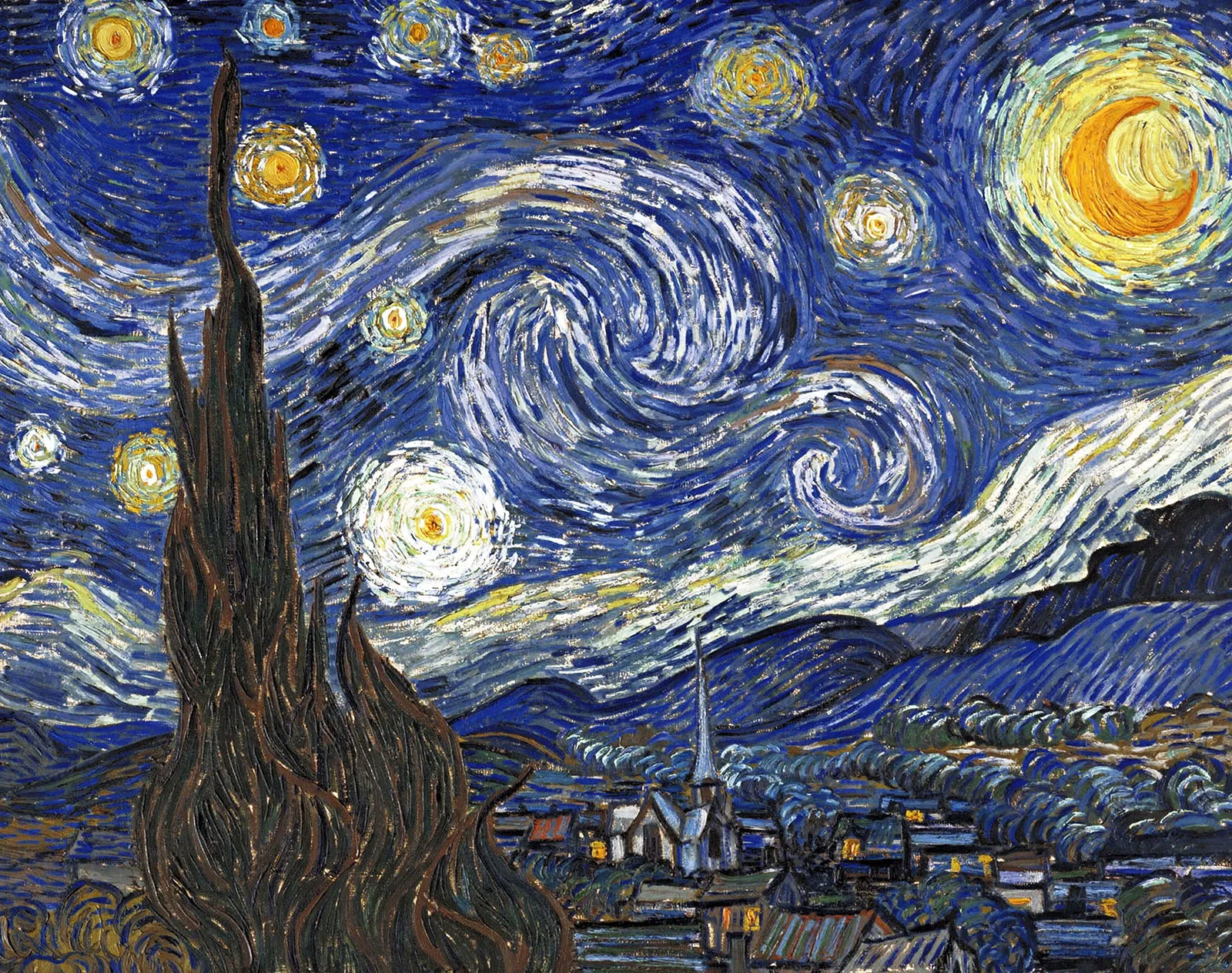
Impressionism
a style or movement in painting originating in France in the 1860s, characterized by a concern with depicting the visual impression of the moment, especially in terms of the shifting effect of light and color.
a literary or artistic style that seeks to capture a feeling or experience rather than to achieve accurate depiction.
Music
a style of composition (associated especially with Debussy) in which clarity of structure and theme is subordinate to harmonic effects, characteristically using the whole-tone scale

Mannerism
a style of 16th-century Italian art preceding the Baroque, characterized by unusual effects of scale, lighting, and perspective, and the use of bright, often lurid colors. It is particularly associated with the work of Pontormo, Vasari,and the later Michelangelo.

Medival
characterized by a blend of Roman, Christian, and Byzantine influences, often emphasizing religious themes and spiritual messages rather than realistic representationthat dominated European art from the 5th to the 15th century.

Minimalist
a movement that emerged in the 1960s, focuses on stripping away non-essential elements to expose the core essence of the artwork and the materials used, emphasizing simplicity, geometric forms, and a direct, unmediated experience for the viewer

Neoclassical
a movement primarily from the late 18th and early 19th centuries, is characterized by a revival of classical styles and themes, emphasizing simplicity, order, and a return to the ideals of ancient Greece and Rome.
