Nervous System Study Guide
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
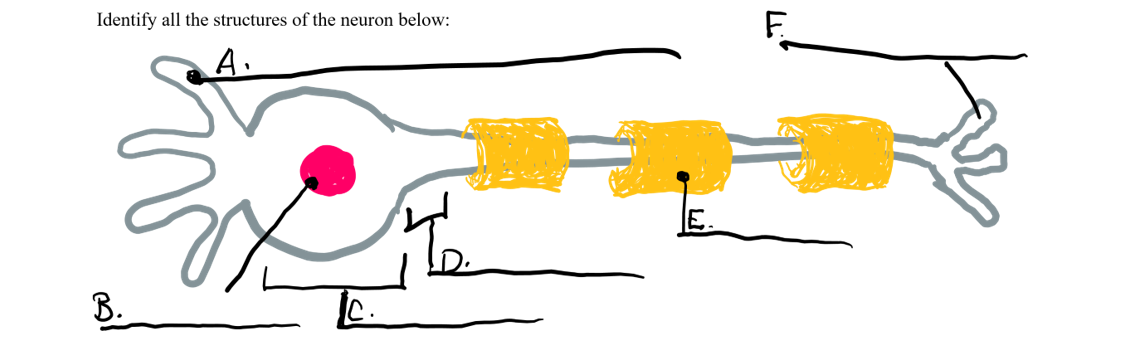
what is a
dendrite
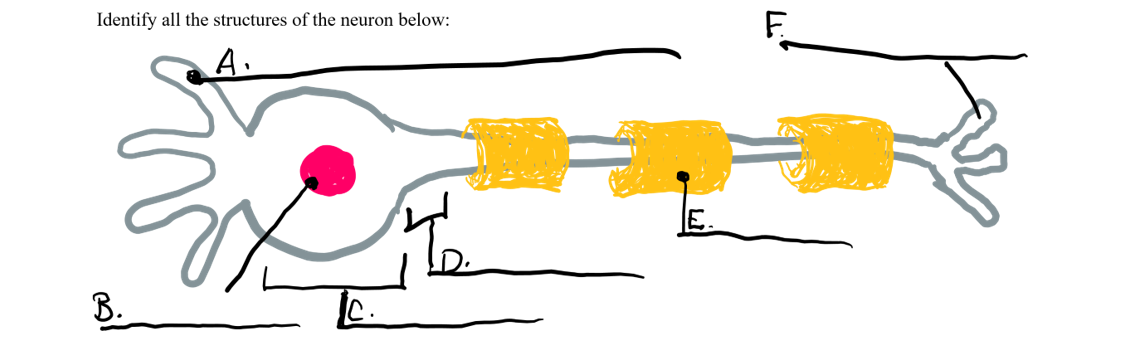
what is b
nucleus
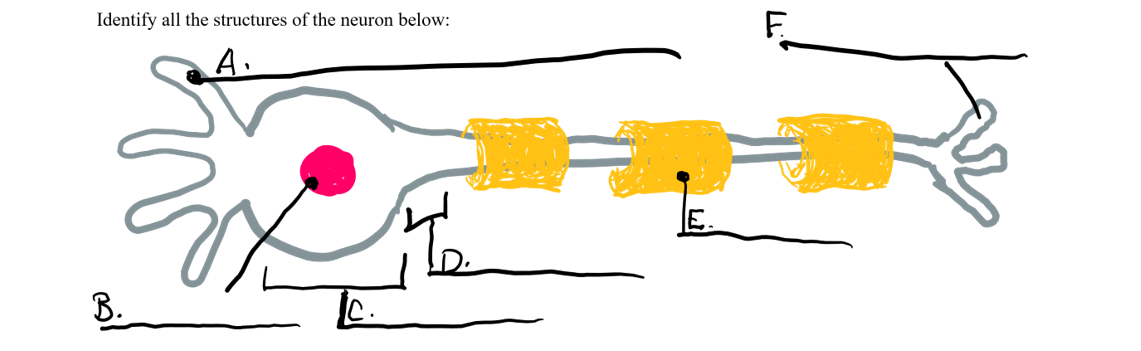
what is c
cell body
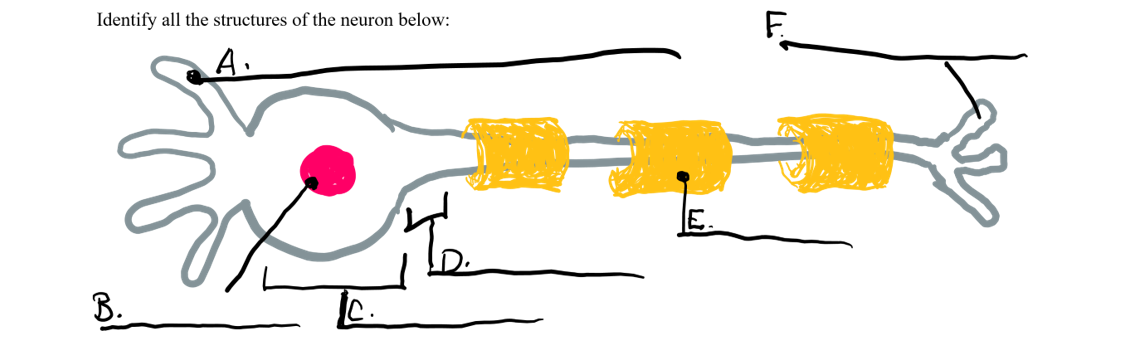
what is d
axon
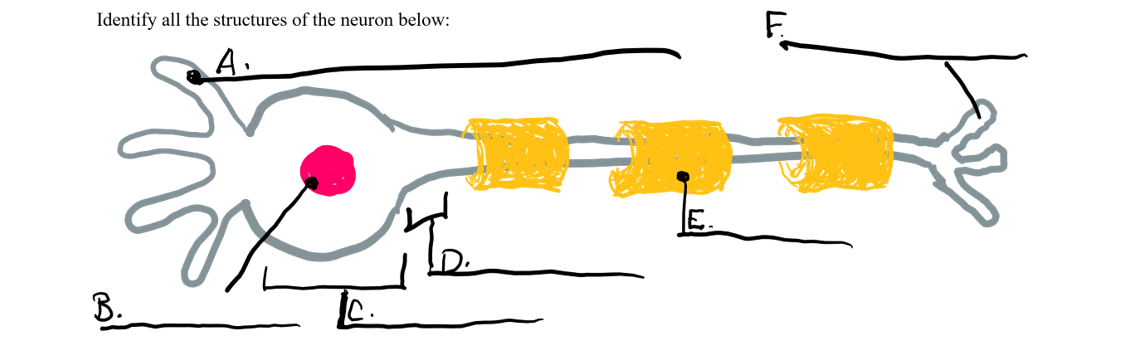
what is e
myelin sheath
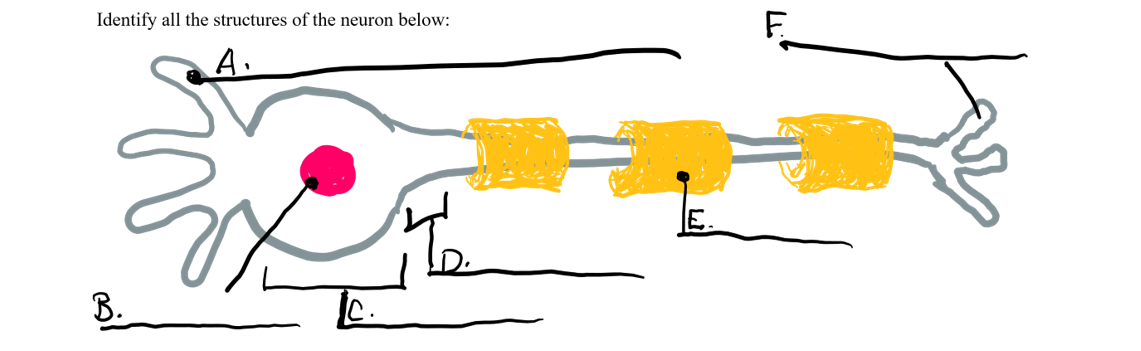
what is f
axon terminal
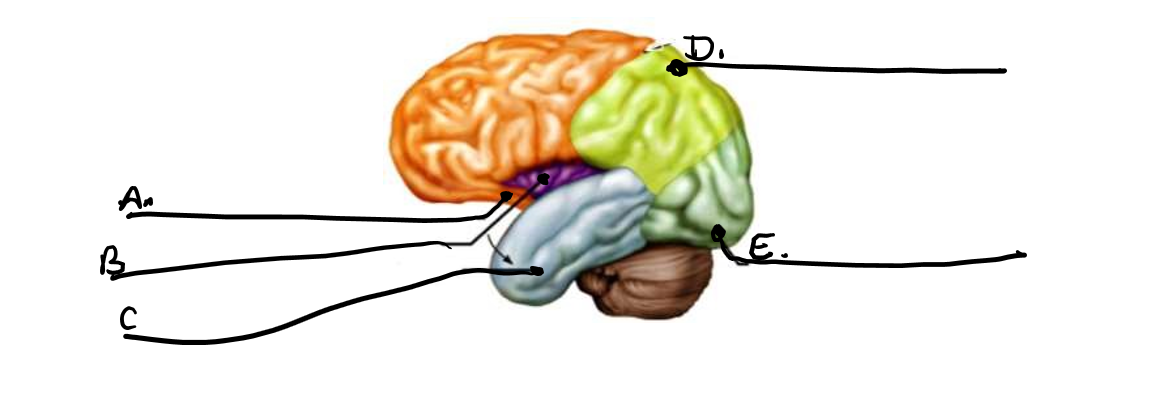
what is a
frontal lobe
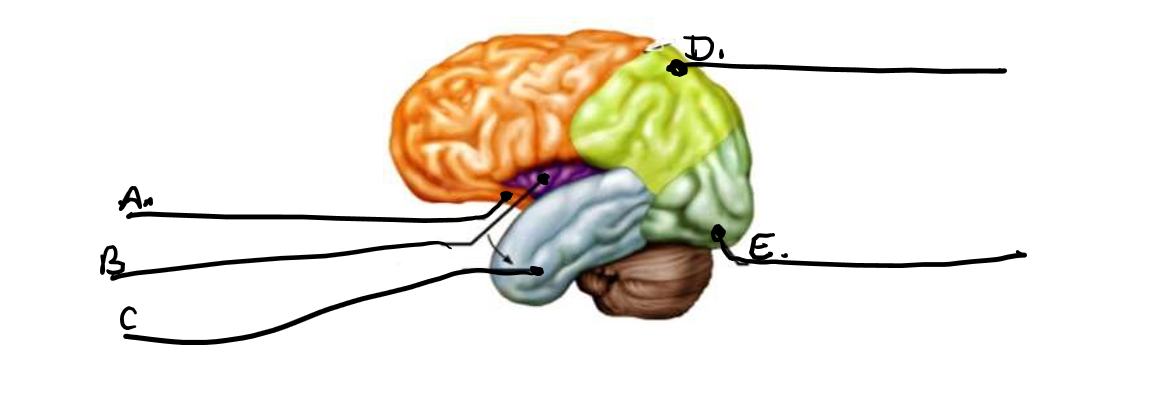
what is b
insula
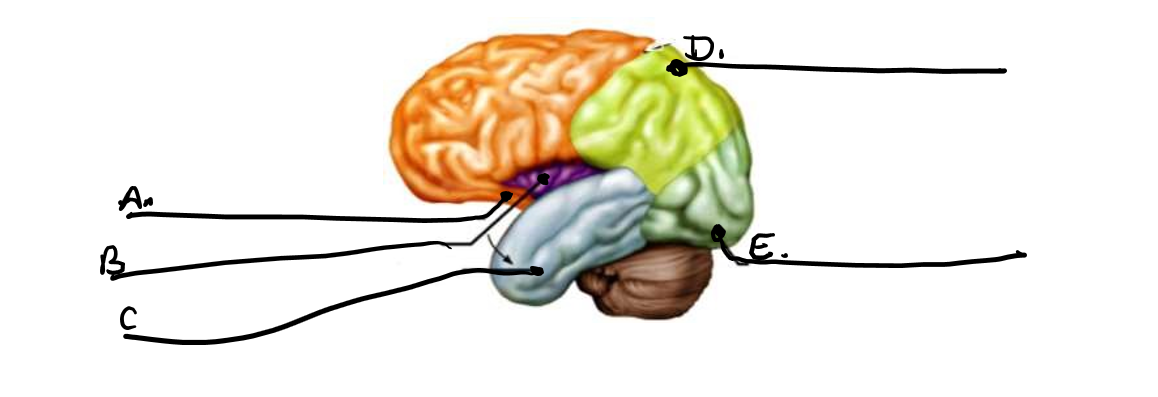
what is c
temporal lobe
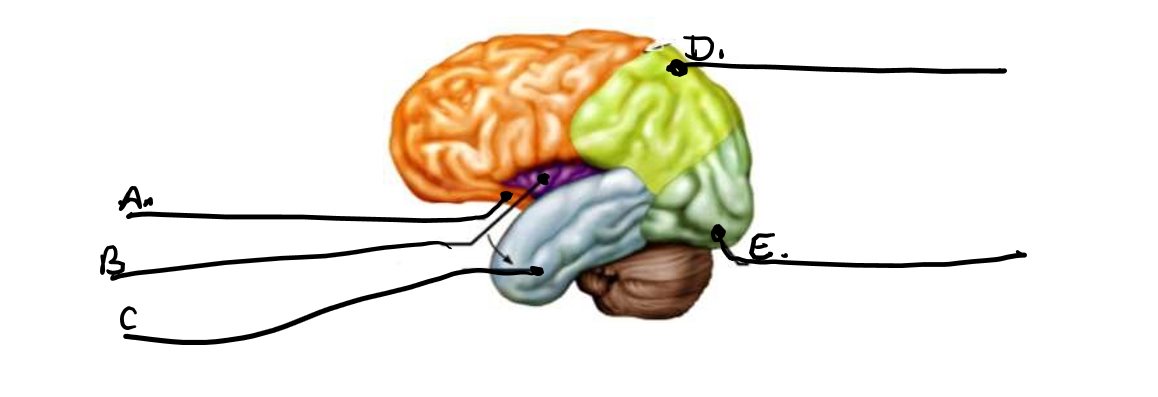
what is d
parietal lobe
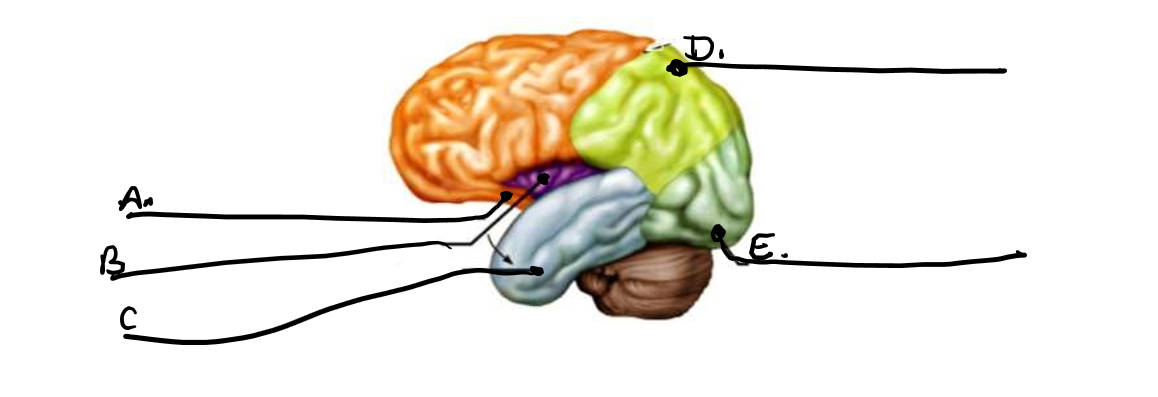
what is e
occipital lobe
where is the cutaneous sensory area
parietal lobe
where is the visual sensory area
occipital lobe
where is the auditrory sensory area
temporal lobe
where is the taste sensory area
base of center sulcus
where is the sensory area for smell
medial aspect of temporal lobe
frontal lobe association areas
concentration
planning
problem solving
Parietal lobe association areas
understanding speech
Choosing words for expression
Temporal lobe association areas
complex sensory information
Music
Memories
Complex patterns
Occipital lobe association areas
analyze and combine visual images with sensory experiences
What is controlled by the left hemisphere
reading/writing
Verbal skills
Analytical/computational skills
What is controlled by the right hemisphere
nonverbal motor tasks
Understanding music/visual patterns
Emotional/intuitive thought processes
How are short term memories converted into long term memories
Memory consolidation
working memory
Closed neuronal circuit
Circuit is stimulated over and over
When impulse flow ceases, so does memory
Short term memory
changes structure/function of neurons
Enhances synaptic function
Long term memory
frontal lobe
Controls voluntary muscles
Primary motor areas
Controls muscles needed for speech
Broca’s area
Received all sensory impulses; gateway for sensory impulses to cerebral cortex
Thalamus
Maintains homeostasis through visceral activities; links nervous and endocrine system
Hypothalamus
Controls emotions, produces feelings, interrupts sensory information
Limbic system
Parts of the brain stem
midbrain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
between diencephalon and pons
Contains bundles of fibers that join brain stem and spinal cord with higher parts of the brain
Centers for visual and auditory reflexes
Midbrain
between midbrain and medulla oblongata
Rounded bulge
Regulates rate and depth of breathing
Relays info from the medulla oblongata to the cerebellum
Pons
enlarged continuation of the spinal cord
Relays info between the brain and spinal cord
Has cardiac, vasomotor, and respiratory control centers
Various non vital reflex control centers
Medulla oblongata
interprets sensory information and depth perception
Help maintain posture
Coordination of skeletal muscle
Cerebellum
has unmyelinated axons
Gray matter
The potential difference (-70 mv) across the membrane of a resting neuron
no gates are open
No movement of ions
No action potential
Resting membrane potential
has myelinated axons
White matter
sodium-potassium pump running, inside of cell becomes less negative, -70mv → 30mv
depolarization
cell wants to regain negativity and go back to resting membrane potential, 30mv → -70 mv
repolarization
gates stay open too long, allows an overshoot of negativity, -80mv
hyperpolarization
helps with repolarization/regaining negativity
restores original ionic conditions
sodium-potassium pump
prevents the neuron from generating an action potential
ensures every action potential is seperate
enforce one way transmission of nerve impulses
absolute refractory period
interval following absolute refractory period
Na+ gates are closed
K+ gates are open
repolarization is occuring
relative refractory period
major motor chemical
ACH
neurotransmitter for sensory/motor neuron connections
amino acids
enzyme that breaks down ACH
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
cell in nervous tissues that sends electrical impulses
neuron
cell in nervous tissue that supports the neuron
glial/neuroglial
brings in/receives info from 5 senses to deliver to CNS
sensory/afferent division
contains somatic and autonomic nervous system
motor/efferent division
prodcues myelin on peripheral nerves
aid in repairing damaged myelin
promotes increased speed with neurotransmission
schwann cells
found in CNS
produces/repairs myelin
same function as schwann cell
oligodendrocyte
channels that are always open
passive/leakage channels
open when a specific neurotransmitter arrives/binds
chemically gated channels
open/close in response to an action impulse/change in charge across the membrane because of ions
voltage-gated channels
the larger the axon diameter, the _______
faster the impulse
fluid filled space seperating the presynaptic/postsynaptic neurons, maintains the impulse when traveling
synaptic cleft
dura mater: outermost
arachnoid: medial
pia mater: deepest layer
protect the central nervous system
meninges
cerebrospinalfluid filled cavities
ventricles
connects hemispheres of brain
corpus collosum
pairing different thoughts with feelings/emotions
memory consolidation
make up the diencephelon
thalamus and hypothalamus
what pairs with the basal nuclei
gray matter