Neural and Psychological Foundations of Attention: ID/ED Shifts, Executive Functions, and Cross-Species Evidence
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
What is attention according to William James?
Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of several simultaneously possible objects or trains of thought.
How does Colman define sustained attention?
Sustained attention is the ability to concentrate on a specific stimulus for a long period, enabling effective information processing.
What is selective attention?
Selective attention is the ability to focus on a stimulus in the presence of distractors.
What learning theory emphasizes the role of selective attention in reinforcement?
Mackintosh's theory (1975) suggests that attention to stimuli that predict reinforcement is learned.
What is the blocking effect in learning theory?
The blocking effect refers to the phenomenon where a previously learned stimulus (A+) prevents the learning of a new stimulus (X+) when presented together.
What is latent inhibition?
Latent inhibition is a learning phenomenon where prior exposure to a stimulus (X-) inhibits the learning of that stimulus when it is later paired with reinforcement (X+).
What are intradimensional shifts (IDS)?
Intradimensional shifts occur when subjects learn to attend to one dimension of a stimulus, such as color, while ignoring another dimension, such as orientation.
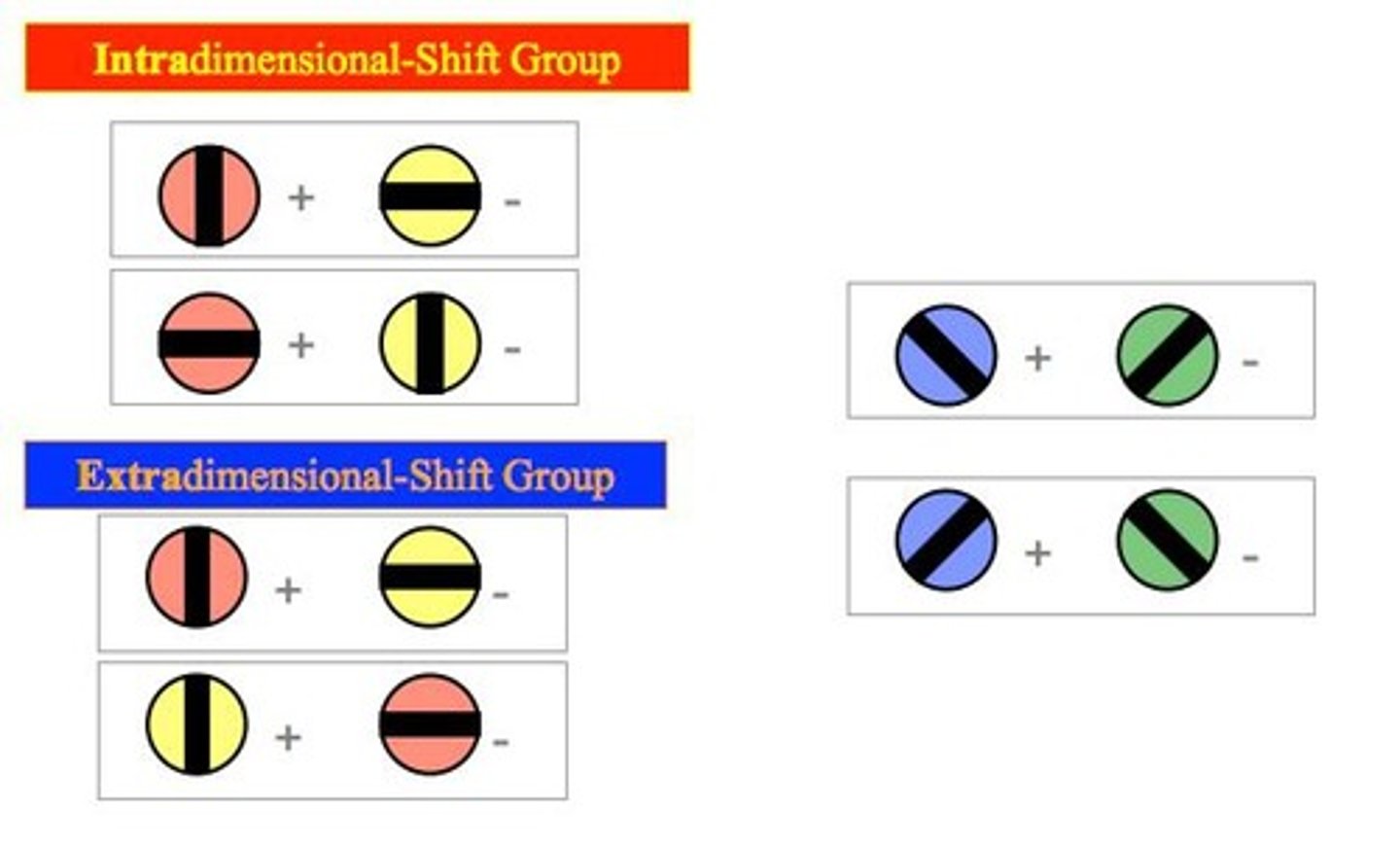
What are extradimensional shifts (EDS)?
Extradimensional shifts occur when subjects learn to attend to a different dimension of a stimulus, such as orientation, while ignoring color.
What is the significance of Stage 2 Discrimination in attentional learning?
In Stage 2 Discrimination, subjects must discriminate based on relevant features, demonstrating that attentional mechanisms are at play.
What does the Rescorla-Wagner model explain in the context of attentional learning?
The Rescorla-Wagner model explains performance in learning tasks but cannot account for findings that imply attentional mechanisms have occurred.
What is the main focus of the lecture on attention?
The lecture focuses on the mechanisms of attention, its importance in psychology, and its neural basis.
What are some examples of attention discussed in the lecture?
Examples include sustained attention and selective attention.
What is the optional-shift design in attention studies?
The optional-shift design refers to a method used to measure selective attention and transfer in experimental settings.
What is the role of distractors in selective attention?
Distractors can interfere with the ability to focus on the intended stimulus, impacting selective attention.
How do learning theories explain selective attention?
Learning theories suggest that selective attention can be learned through reinforcement and prediction of outcomes.
What is the importance of measuring selective attention?
Measuring selective attention helps in understanding how attention operates and its implications for learning and behavior.
What are some criticisms of attentional mechanisms in learning?
Critics argue that non-attentional theories can also explain phenomena related to selective attention, making it unclear if attentional mechanisms are the sole explanation.
What is the significance of the studies by Mackintosh and Little (1969)?
Their studies on intradimensional and extradimensional shifts provide insight into how attention is allocated in learning tasks.
What is the relationship between sustained attention and information processing?
Sustained attention allows for effective use of limited information-processing systems to handle vast amounts of sensory information.
What does the term 'focalization' refer to in the context of attention?
Focalization refers to the concentration of consciousness on a specific object or thought while withdrawing from others.
What is the implication of learning to ignore irrelevant dimensions in attentional shifts?
Learning to ignore irrelevant dimensions indicates that attention can be strategically allocated based on task demands.
How does attention relate to psychopathology in psychology?
Understanding attention mechanisms can provide insights into various psychological disorders and their treatment.
What are the two types of attention discussed in psychology?
Sustained attention and selective attention.
What is latent inhibition in the context of attention?
A phenomenon where prior exposure to a stimulus inhibits the ability to learn about that stimulus later.
What is cue competition?
When multiple cues compete for attention, affecting learning and memory.
What are intra-dimensional (ID) and extra-dimensional (ED) shifts?
ID shifts involve changes within the same dimension, while ED shifts involve changes across different dimensions.
What is the purpose of measuring selective attention?
To understand how attention can be directed and the effects of various stimuli on learning.
What are the benefits of multi-stage ID/ED designs?
They allow researchers to parse out different cognitive processes involved in attention.
What are some drawbacks of traditional designs in studying attention?
They may not effectively isolate cognitive processes or may rely on familiar stimuli.
What is the optional-shift design in attentional studies?
A method that assesses attentional processes by allowing subjects to choose between different stimuli.
What is the significance of the study by Mackintosh & Little (1969)?
It demonstrated intradimensional and extradimensional shift learning in pigeons using a between-subjects design.
What is reversal learning in the context of attention?
A process where subjects learn to switch their response to a previously rewarded stimulus after a change in reinforcement.
What does the computerized CANTAB measure in attentional studies?
It assesses cognitive functions including attention and set-shifting in humans and animals.
What is the role of the medial frontal cortex in attentional set shifting?
It mediates perceptual attentional set shifting, as shown in studies with rats.
What are total change designs in attentional research?
Experimental designs that allow the measurement of different psychological processes within the same participants.
What is the optional-shift design's Phase 1 focused on?
It assesses attentional processes in discrimination learning with different groups of rats.
What are the visual and auditory stimuli used in the optional-shift design?
Four visual stimuli (V1, V2, V3, V4) and four auditory stimuli (A1, A2, A3, A4).
What is the focus of Duffaud et al. (2007) in their study on optional-shift behavior?
They explored attentional processes in discrimination learning using an optional-shift design.
What is the significance of using within-subjects comparisons in total change designs?
It allows for a more controlled comparison of cognitive processes across different conditions.
What is the challenge of using simple discrimination at the start of training in ID/ED comparisons?
It may lead to one dimension being more familiar, affecting the results.
What does the term 'compound discrimination' refer to in attentional studies?
It involves learning to discriminate between multiple stimuli presented together.
What is the relevance of studying attentional processes across different species?
It helps to understand the evolutionary aspects of attention and cognitive processes.
What are some criticisms of the studies on attentional processes?
Critiques often focus on the limitations of designs and the generalizability of findings.
What is the optional-shift design in rodents?
A design that overcomes limitations of the total change design and requires a small set of stimuli for each dimension (visual or auditory), using a within-subjects approach.
What are ID/ED shifts?
ID/ED shifts refer to intra-dimensional and extra-dimensional shifts that can be learned by humans, monkeys, pigeons, and rodents, with a finding that ID shifts are superior to ED shifts, indicating attentional mechanisms.
What is the significance of the superiority of ID over ED shifts?
It suggests that various species exhibit attentional mechanisms, which challenges standard non-attentional theories of learning.
What are some examples of attentional processes discussed in the lecture?
Sustained attention and selective attention.
What are latent inhibition and cue competition?
Latent inhibition refers to the decreased ability to learn about a stimulus that has previously been experienced without any consequences, while cue competition involves the interaction of multiple cues that can affect learning.
What are the executive functions related to attentional shifting?
Executive functions include working memory, response inhibition, cognitive flexibility, attentional set-shifting, rule or strategy-shifting, and reversal learning.
How can cognitive flexibility be measured?
Through tasks designed to assess attentional shifting and reversal learning.
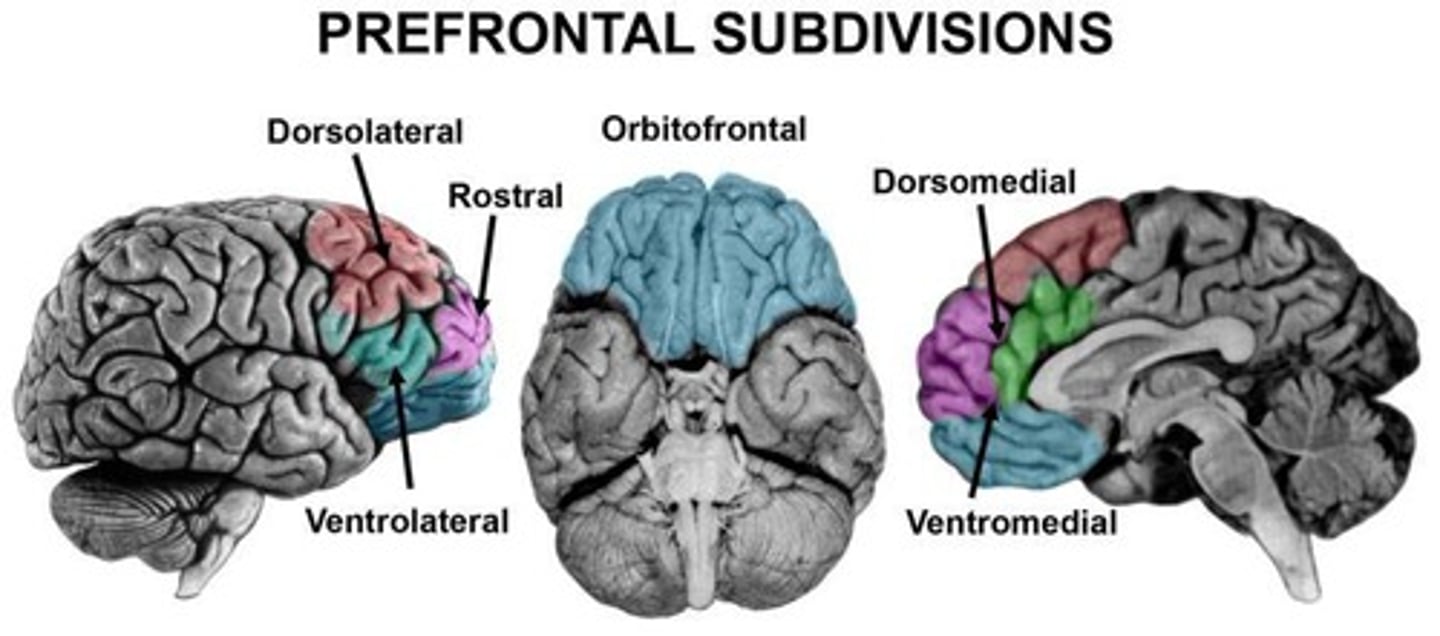
What brain regions are associated with attentional shifting?
The prefrontal cortex (PFC) in rats, monkeys, and humans is particularly involved in attentional shifting.
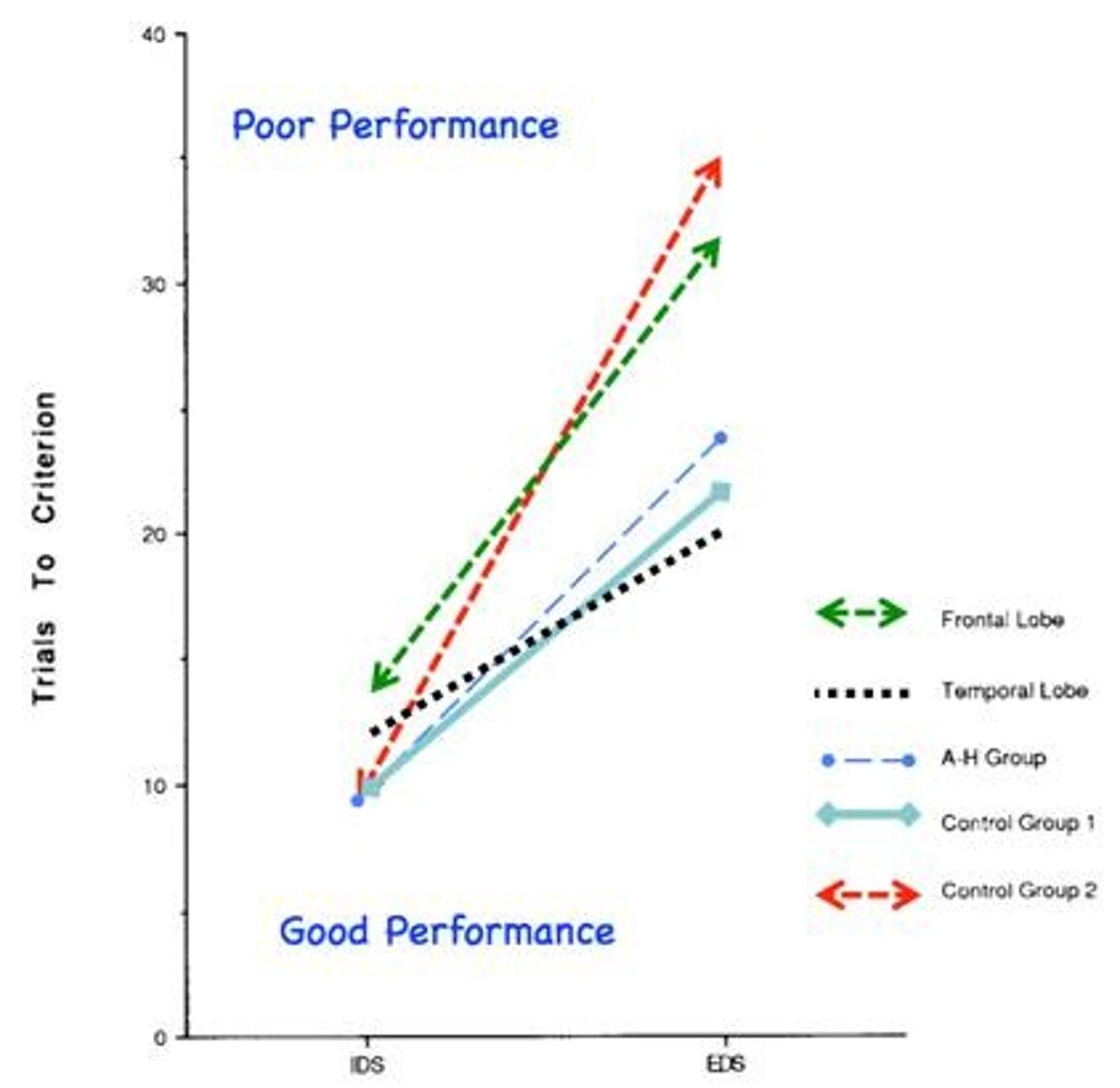
What types of brain lesions were studied by Owen et al. (1991)?
Unilateral and bilateral frontal lesions, unilateral temporal lobe lesions, and amygdalo-hippocampectomy.
What was a key finding from Owen et al. (1991) regarding set shifting performance?
The study found differences in extra-dimensional versus intra-dimensional set shifting performance following various types of brain excisions.
What conditions were compared in the studies by Sahakian et al. (1991) and Downes et al. (1989)?
Patients with Parkinson's Disease (PD) and Dementia of Alzheimer's Type (DAT) were compared, focusing on attentional and mnemonic functions.
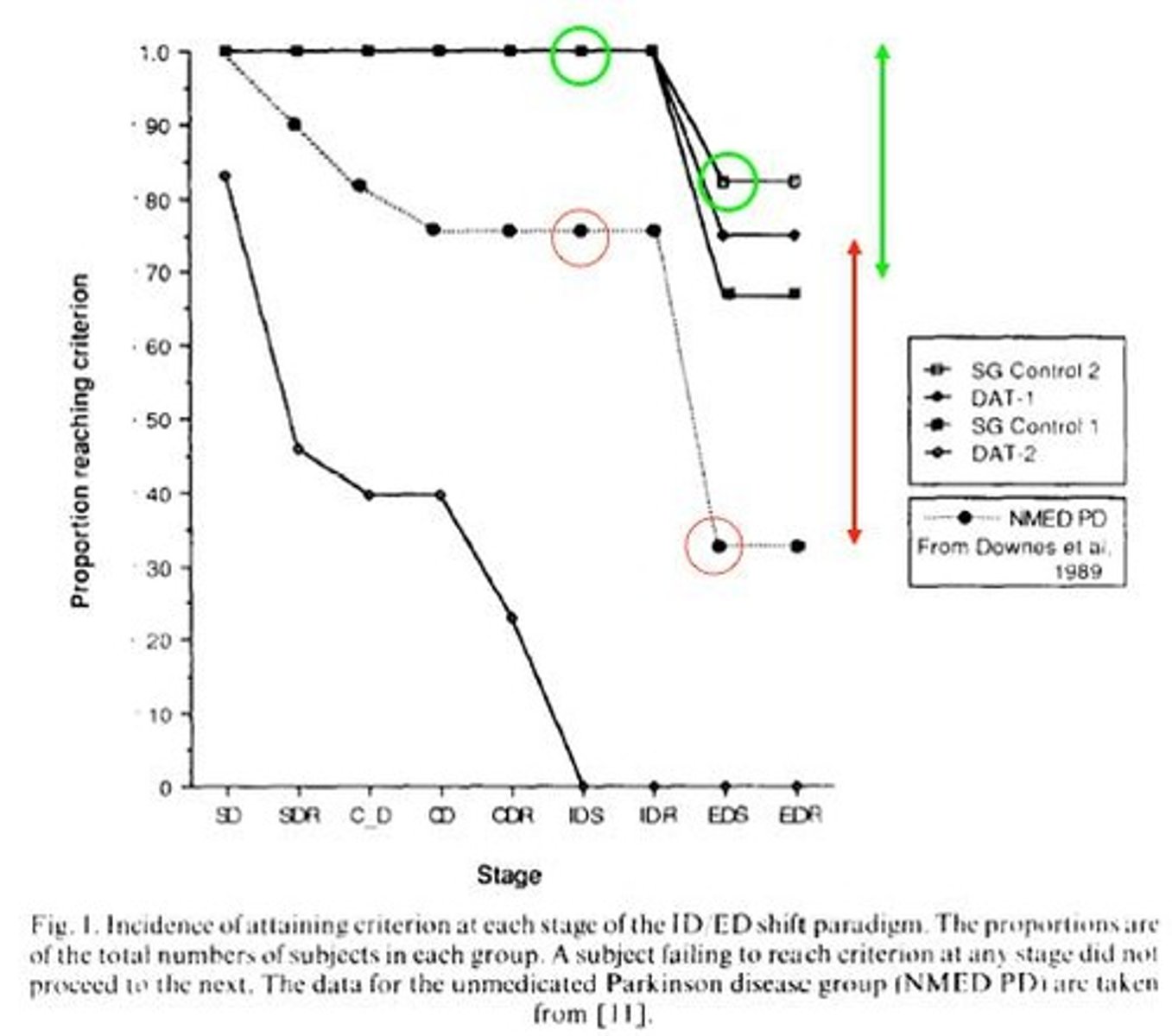
What is the difference between DAT1 and DAT2?
DAT1 refers to mild dementia of Alzheimer's Type, while DAT2 refers to moderate dementia.
What is the significance of the control subgroups in the studies?
Control subgroups (SG) were used to compare attentional functions in patients with different severities of dementia and in non-medicated Parkinson's patients.
What did Sahakian et al. (1990) find regarding attentional function in Alzheimer's patients?
They found sparing of attentional function relative to mnemonic function in a subgroup of patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type.
What are the advantages of the optional-shift design?
It allows for a more nuanced assessment of attentional processes using fewer stimuli.
What are the drawbacks of the optional-shift design?
The design may still have limitations in fully capturing the complexity of attentional mechanisms.
What is the relevance of studying attentional processes in psychology?
Understanding attentional processes is crucial for insights into learning, memory, and cognitive flexibility.
What is the role of cognitive flexibility in attentional shifting?
Cognitive flexibility allows individuals to adapt their thinking and behavior in response to changing environments or rules.
What is reversal learning?
A type of learning where an individual learns to reverse a previously learned response or rule.
What is the relationship between attentional set-shifting and executive functions?
Attentional set-shifting is a component of executive functions that involves the ability to switch focus between different tasks or rules.
How does the optional-shift design contribute to understanding attentional processes?
It provides a framework for assessing how attentional mechanisms operate in discrimination learning across different species.
What is the significance of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in attention studies?
It is the analogue of the rodent medial prefrontal cortex and is a key brain region in attentional set.
What did Sahakian et al. (1990) find regarding attentional and mnemonic functions in Alzheimer's patients?
They found sparing of attentional relative to mnemonic function in a subgroup of patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type.
What was the focus of the study by Dias et al. (1996)?
They investigated the dissociation in the prefrontal cortex of affective and attentional shifts.
What did Birrell & Brown (2000) conclude about the medial frontal cortex?
They concluded that it mediates perceptual attentional set shifting in rats.
What role does the orbital prefrontal cortex play according to McAlonan & Brown (2003)?
It mediates reversal learning but not attentional set shifting in rats.
What are the four criticisms of the frontal/attentional analysis discussed in the notes?
1. Locus Specificity: Damage to non-frontal structures affects attentional set. 2. Pathology Specificity: PD is not the only disorder affecting attentional set. 3. Counterbalancing: Many experiments may show effects of stimulus generalization rather than attentional-set effects. 4. Comparison of ID/ED transfer at different times.
What types of evidence support the role of the frontal cortex in attention?
Evidence from human clinical studies and animal lesion work.
What is the difference between fMRI and the evidence provided by animal studies?
fMRI provides correlational evidence, while animal studies provide causal evidence.
What are intra-dimensional and extra-dimensional shifts in attention?
They refer to the transfer of attention based on the relevance of stimuli, with intra-dimensional shifts focusing on relevant dimensions and extra-dimensional shifts involving shifts to new dimensions.
How do excitotoxic brain lesions contribute to attention research in animals?
They can be directed accurately, causing minimal collateral damage, allowing for clearer insights into brain function.
What are the implications of the findings from Sahakian et al. (1990) for understanding dementia?
They suggest that attentional functions may remain intact even as mnemonic functions decline in Alzheimer's patients.
What is the significance of studying attention in non-human animals?
It allows researchers to gain general information about attention without the complexities of clinical human populations.
What is the role of the medial prefrontal cortex in rodents according to the notes?
It is analogous to the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in primates and is involved in attentional set.
What is the relevance of the study by Dias, Robbins, and Roberts (1996)?
It highlights the distinction between affective and attentional processes in the prefrontal cortex.
What does the term 'attentional set' refer to?
It refers to the mental framework that influences how attention is directed and prioritized.
What are some examples of selective attention mentioned in the notes?
Sustained attention and cue competition are examples of selective attention.
What is the significance of the findings from Birrell & Brown (2000) for understanding attentional processes?
They indicate that specific brain regions are responsible for different aspects of attentional shifts.
What are the potential drawbacks of attentional-set experiments mentioned?
Many experiments may not have been adequately counterbalanced, leading to confounding effects.
What is the relationship between Parkinson's Disease (PD) and attentional set?
PD is one of the disorders associated with alterations in attentional set, but not the only one.
What is the focus of the lecture outline provided in the notes?
The lecture covers various aspects of attention, including its importance in psychology, examples, measuring methods, neural basis, and criticisms.
What is the significance of using a 'complete-change design' in attentional set studies?
It requires comparison of ID (intradimensional) vs. ED (extradimensional) at different times, which may reveal time-related artifacts affecting results.
What is locus specificity in the context of attentional set?
Damage to non-frontal (temporal) structures can affect attentional set, as evidenced by patients with temporal lobe lesions (Owen et al., 1991).
What did Oswald et al. (2001) demonstrate regarding rats and attentional modulation?
They showed that rats trained with multiple configural discriminations could shift attention based on relevant stimuli, such as walls or floors in their environment.
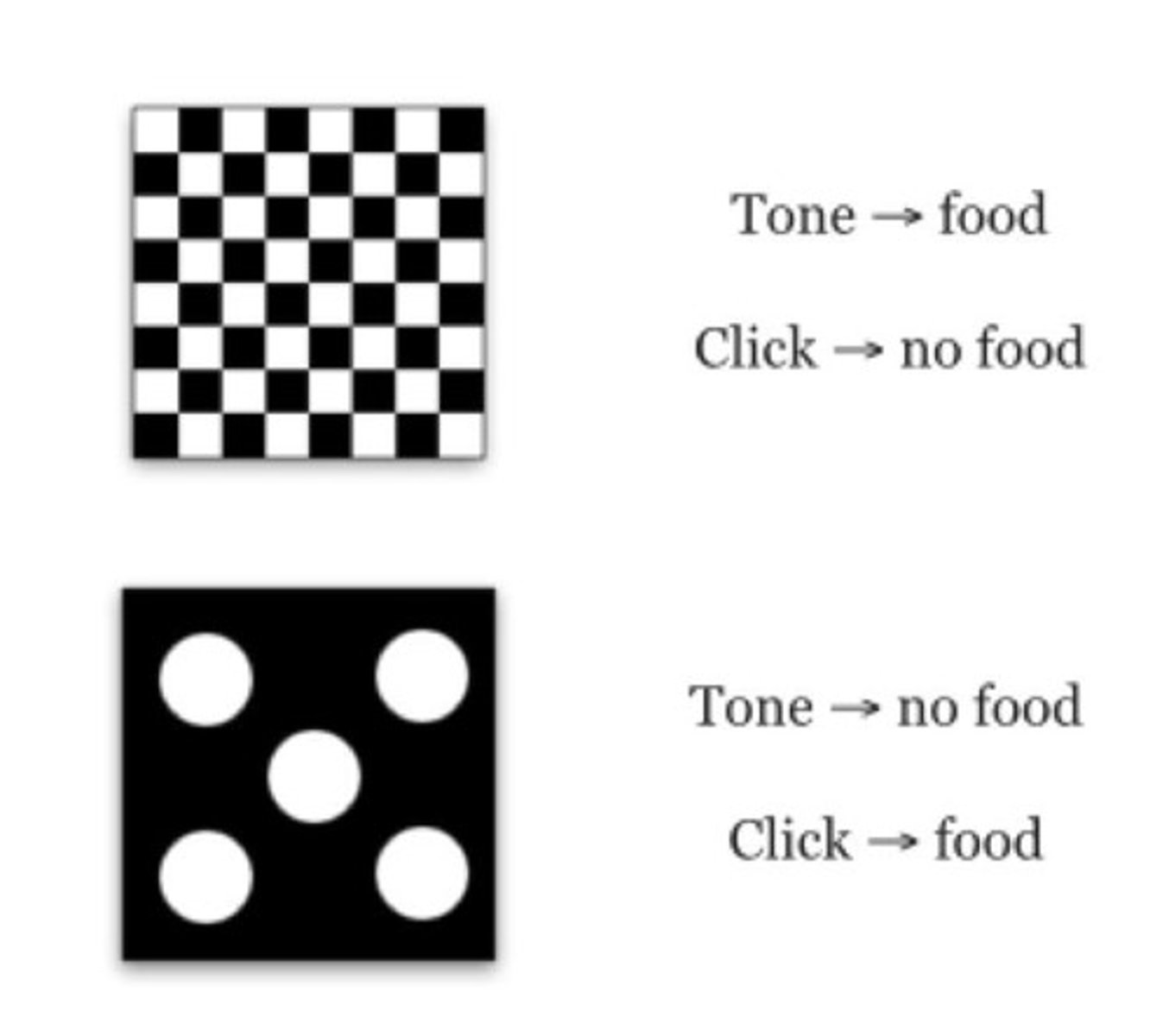
What are the implications of entorhinal cortex lesions in attentional modulation?
Lesions in the entorhinal cortex affect the ability to modulate attention, as shown in the IDS/EDS procedure by Oswald et al. (2001).
Which disorders are associated with alterations in attentional set according to the notes?
Schizophrenia, depression, violent offenders, mania, and OCD are linked to changes in attentional set.
What evidence did Rogers (2003) provide regarding WCST deficits?
He cited evidence of WCST deficits in participants with non-frontal damage and the absence of such deficits in known frontal patients.
What is the importance of counterbalancing in attentional set experiments?
Many experiments may not have been adequately counterbalanced, potentially leading to stimulus generalization effects rather than true attentional-set effects.
What were the four main experimental groups identified by Mackintosh & Little?
1. Colour (red vs yellow) --> Colour (blue vs green); 2. Orientation (-- vs |) --> Orientation (/ vs "); 3. Colour (red vs yellow) --> Orientation (/ vs "); 4. Orientation (-- vs |) --> Colour (blue vs green).
What potential issues arise from the comparison of ID/ED transfer in a complete-change design?
ID discrimination occurs before ED, which may lead to collateral differences in performance due to factors like attention set shifts or boredom.
What are the benefits of ID/ED and optional shift designs in attentional studies?
They ensure that attentional comparisons are made at the same time point, addressing potential issues with time-related artifacts.
What are some examples of attention types mentioned in the lecture outline?
Sustained attention and selective attention.
What is latent inhibition in the context of attentional processes?
Latent inhibition refers to the reduced ability to learn about a stimulus that has previously been presented without any consequences.
What is cue competition in attentional studies?
Cue competition occurs when multiple cues are present, leading to competition for attention and potentially affecting learning and discrimination.
What is the significance of measuring selective attention?
It helps in understanding how attention is allocated and shifted in response to different stimuli.
What are some drawbacks of attentional set-shifting studies?
Drawbacks may include difficulties in controlling for confounding variables and ensuring that results are not influenced by external factors.
What types of evidence exist regarding attentional processes in different species?
Evidence exists in humans, marmosets, and rodents, indicating the evolutionary significance of attentional processes.
