Lab F: Fischer Esterification
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Draw the general fischer esterification reaction
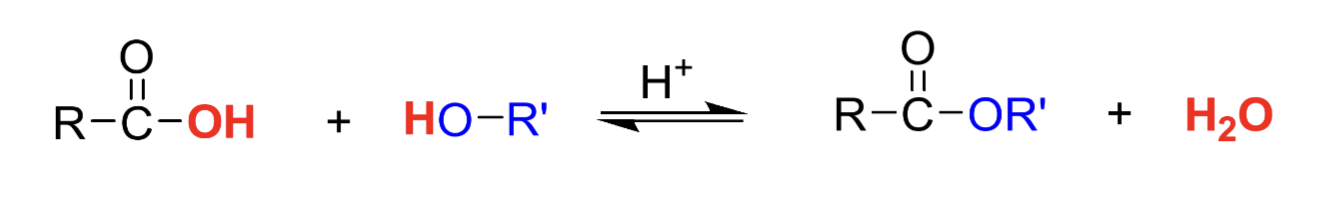
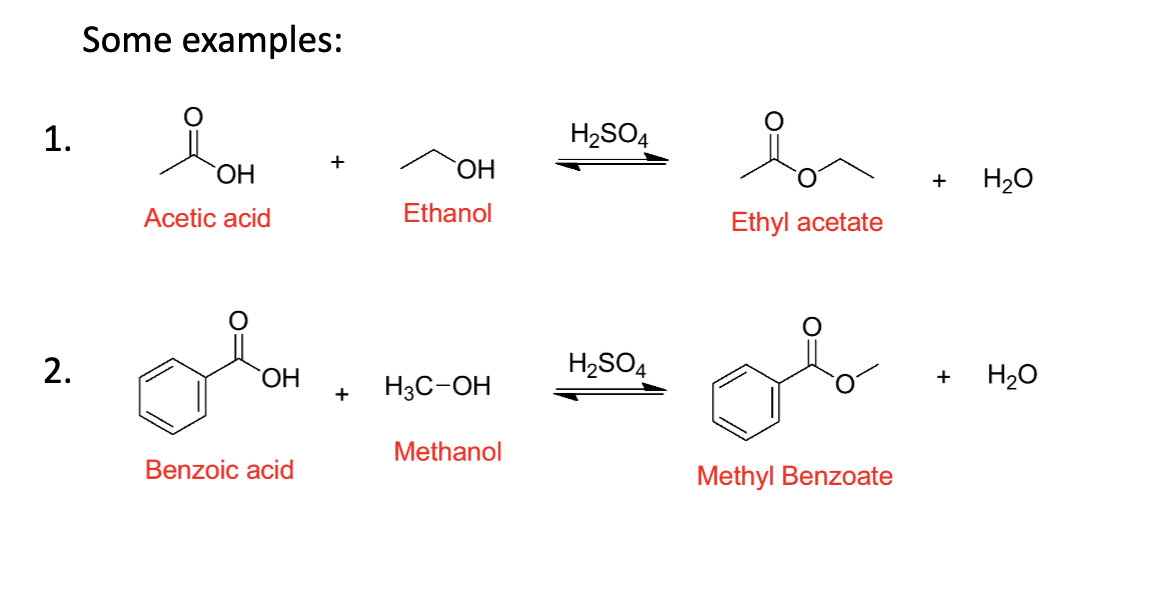
Draw the two examples of fischer esterification reaction
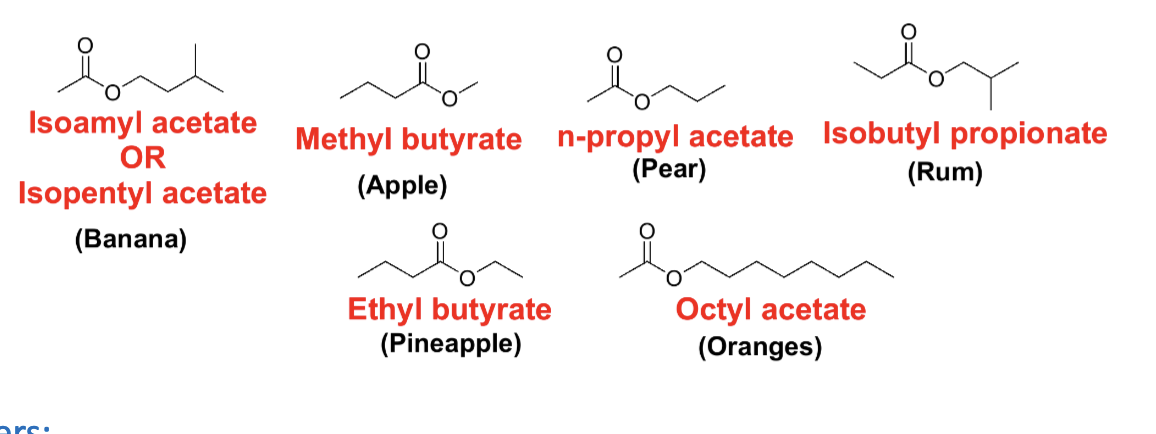
Draw the 6 esters with their fruit fragrance
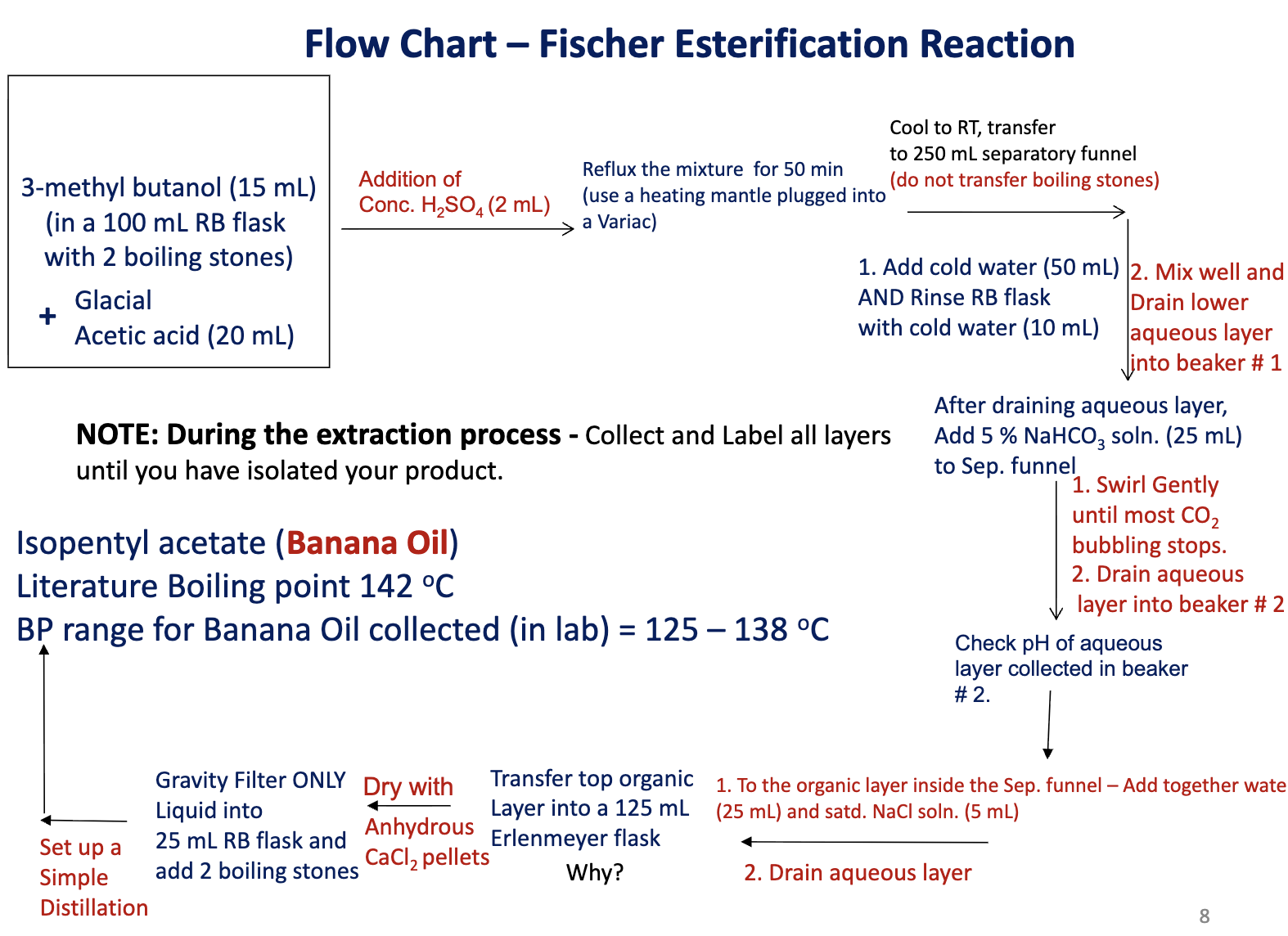
What are the methods used in lab F?
Reflux, extractions, and simple distillation
What are the two traits of ester preperation?
Acid catalyzed reaction, acid is regenerated and never consumed.
Impossible to obtain a 100% yield.
Draw scheme 1 of lab F
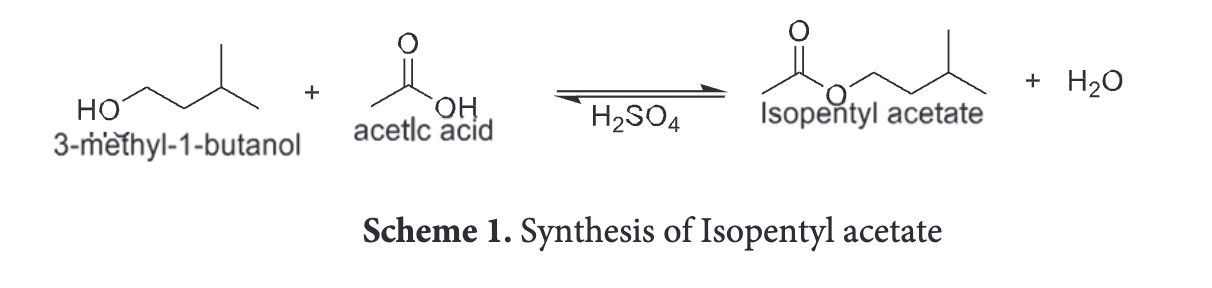
Why is glacial acetic acid named “glacial”?
It is acetic acid that is free of water. On freezing, it creates needle shaped crystals.
What is the boiling point of glacial acetic acid?
118°C
Hazard ratings for glacial acetic acid and sulfuric acid?
Glacial acetic acid - flammable (rating 2), health (rating 3), corrosive
Sulfuric acid - corrosive, health (rating 3)
Why do we use boiling stones?
To avoid bumps + prevent distillation from being choppy.
What is the purpose of a reflux?
To heat a reaction mixture at its boiling temperature (BP of solvent, or in our case the excess reactant) to form the product without losing any material inside the reaction flask.
What are the advantages of a reflux?
Maintains a constant temperature in the reaction flask.
Reaction is able to reach equilibrium with minimal evaporation of material inside the reaction flask.
Draw the flow chart for Lab F
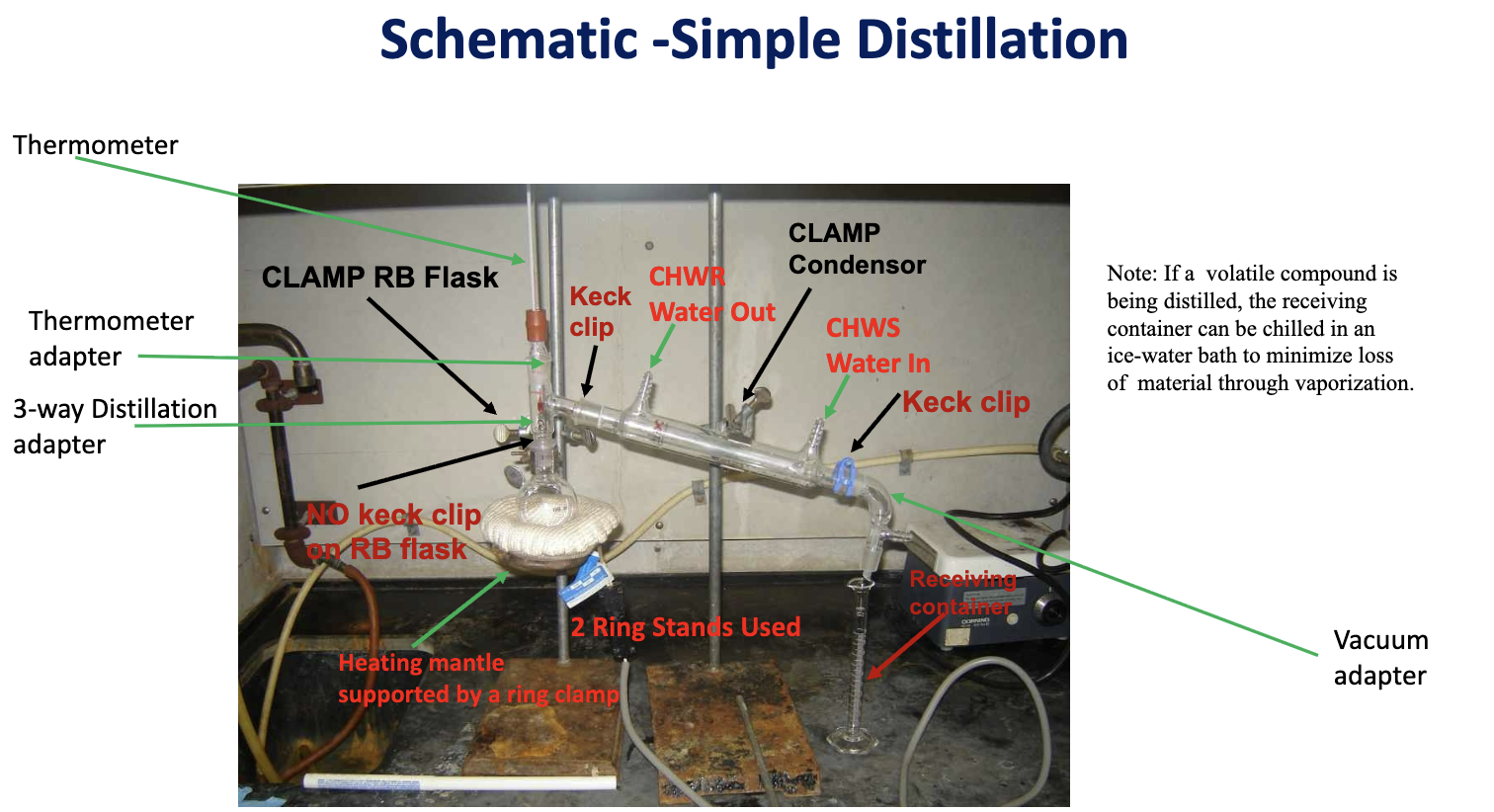
What is simple distillation?
Used to separate liquids where boiling points differ by more than 20-30°C at 1 atm.
The two liquids must be miscible in each other.
What is distillation?
A technique where a liquid is vaporized by heating to its boiling point, then re-condensed back to a liquid (distillate) which is collected in a receiving flask.
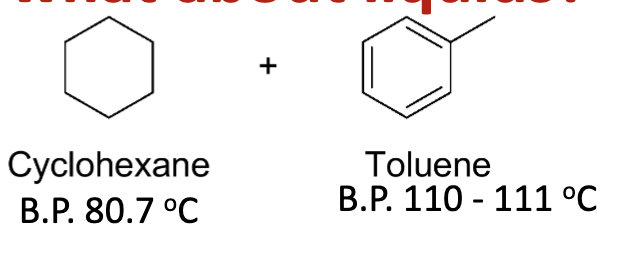
Draw cyclohexane and toluene and list their boiling points.
Draw simple distillation setup
Why should you not distill to dryness?
To prevent overheating and breaking the flask + prevent formation of pyrolytic tars that are difficult to wash out.
Simple distillation reminders?
Cover distilling RB flask w/ foil at the start of distillation.
Make sure ring clamp holds heating mantle flush + firmly against RB flask.
What is vacuum distillation used for?
For compounds that either boil at too high a temperature, or decompose near their boiling points. Under vacuum, compounds can be distilled at temperatures lower than their atmospheric boiling points. Only works for compounds w/ BPs > 200°C
What is fractional distillation used for?
To separate liquid mixtures where the difference in BPs is less than 25°C at 1 atm.
How does fractional distillation work?
A fractionating column (Vigreux column) is inserted b/w the 3-way distillation adapter and the RB flask, providing a larger surface area over which a number of separate liquid-vapor equilibria can occur. Many vaporizations + condensations take place before the distillate is collected. One theoretical plate = one simple distillation cycle.
Why do we use simple distillation over fractional?
With fractional, we will lose a lot of product because it vaporizes + condenses multiple times. A large portion of isoamyl acetate can get stuck in the indentations.
Fractional takes a longer time.
What factors affect boiling points?
Size (molecular weight)
Pentane (35-36°C)
Hexane (69°C)
Heptane (98°C)
Intermolecular Interactions
What does it mean for a solution to boil?
Temperature at which the Vapor Pressure of the liquid = Atmospheric Pressure (surface of liquid). Normal BP = temperature where liquid’s vapor pressure = 1 atm.
Where should the thermometer bulb be positioned?
Right under the arm of the condenser.
When should you start reading the thermometer?
When the material starts collecting, not when the solution starts boiling.
What is a Variac?
A variable voltage transformer - provides a voltage-adjusted source of alternating current. The higher the BP, the grater the voltage required. Start at ~65.