Latin America Since Indpendence-Geography/Leaders
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
The Andean Republics
The Andean Republics, generally recognized as Bolivia, Chile, Ecuador, and Peru, are South American nations defined by their shared geography along the Andes mountains and historical ties to the Inca Empire. These nations share a, primarily Spanish-speaking, cultural heritage, though they often include indigenous languages like Quechua
Bahia
Brazilian State: Bahia is a major state in Northeast Brazil, with its capital, Salvador, known for its extensive coastline and historical significance of Afro-Brazilian Influences
Bolívia pre-1884
Before 1884, the territory now known as Bolivia underwent a significant transformation from a wealthy Spanish colonial center known as
Upper Peru (Alto Perú) to an independent but politically unstable republic that lost its coastline in the War of the Pacific
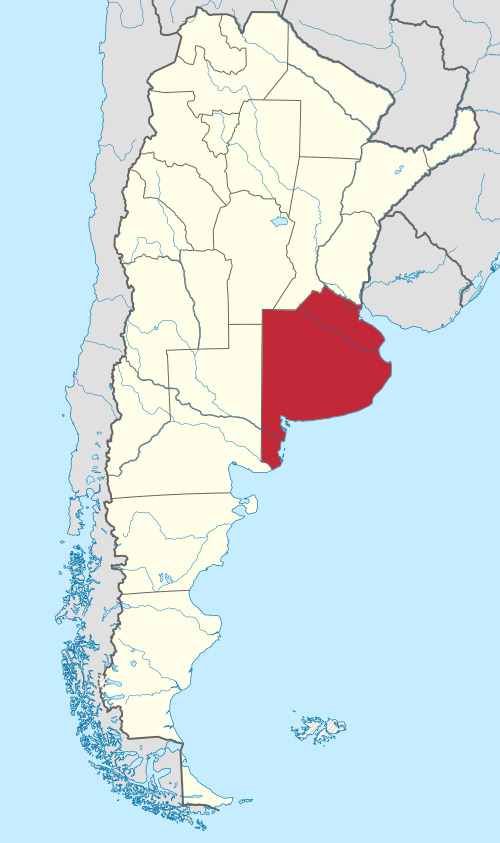
Buenos Aires Provence
Argentina's largest and most populous province, located in the east-central region surrounding—but not including—the autonomous federal capital city of Buenos Aires. Its capital is La Plata, a city known for its planned layout. The province acts as the nation's economic and agricultural heart, dominated by the fertile Pampas, coastal beaches, and industrial, residential suburban zones
Central America
Central America is the isthmian, southernmost region of North America, bridging the continent to South America, comprising seven nations: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. It acts as a land bridge bordered by Mexico, Colombia, the Pacific Ocean, and the Caribbean Sea.
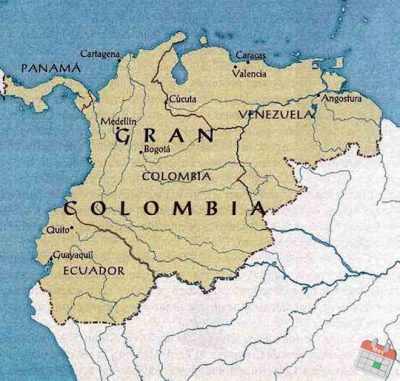
Colombia Prior 1903
Prior to 1903, Colombia experienced intense political instability, evolving from the independent Republic of Gran Colombia (1819–1830)—which included modern-day Ecuador, Venezuela, and Panama—into a series of republics, ultimately becoming the centralized Republic of Colombia in 1886. The nation was characterized by frequent civil wars between liberals and conservatives, culminating in the devastating Thousand Days' War (1899–1902)
Combatants in the War of the Triple Alliance (Paraguayan War)
The War of the Triple Alliance (1864–1870) was fought between Paraguay and the allied forces of the Empire of Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay (the "Triple Alliance"). Triggered by regional power disputes and the Uruguayan War, it was the deadliest inter-state war in South American history, resulting in massive casualties for Paraguay.
Key com
Combatants in the War of the Pacific
The War of the Pacific (1879–1884) was fought primarily between Chile and the allied forces of Peru and Bolivia. Chile emerged victorious, seizing Bolivia's coastal territory (making it landlocked) and Peru's southern province of Tarapacá, driven by control over valuable Atacama Desert nitrate deposits
Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles are a group of the four largest islands in the northern Caribbean Sea—Cuba, Hispaniola, Jamaica, and Puerto Rico—along with the Cayman Islands. They comprise over 90% of the total land area of the West Indies and are characterized by their mountainous terrain, tropical climate, and diverse, rich cultures.
Mercosul/Mercosur Signatories
As of January 2026, the full member signatories of Mercosur (Southern Common Market) are
Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Bolivia, which became a full member in 2024. Venezuela is a founding signatory but has been suspended since 2017. Associate states include Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Panama
Mexico pre-1848
Before 1848, Mexico was a newly independent nation (est. 1821) with a vast territory stretching from modern-day Central America to the northern borders of California, Nevada, and Utah, including all of the current U.S. Southwest. Following independence, this region was characterized by rapid border changes, political instability, and the 1836 loss of Texas
Morelos
Morelos is a landlocked state in south-central Mexico, known as the "Central Breadbasket" and for its consistent, warm climate, often calling its capital, Cuernavaca, the "City of Eternal Spring". It is the second-smallest state in Mexico, with a rich history, indigenous roots, and significant agricultural production.
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historically and culturally distinct region spanning from central Mexico through Central America (Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica). It was home to advanced pre-Columbian civilizations like the Olmec, Maya, and Aztec, known for monumental architecture, complex polytheistic religions, hieroglyphic writing, and intricate calendars
NAFTA Signatories
Mexico was the sole Latin American signatory to the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
, which took effect on January 1, 1994, alongside the United States and Canada. It established a trilateral trade bloc aimed at reducing barriers to goods, services, and investment, and was replaced by the USMCA on July 1, 2020
River Plate Region
The Río de la Plata (River Plate) is a major funnel-shaped estuary on the southeastern coast of South America, forming part of the border between Argentina to the south and Uruguay to the north. It serves as the confluence of the Paraná and Uruguay rivers, stretching roughly 290 km (180 mi) from its head to the Atlantic Ocean
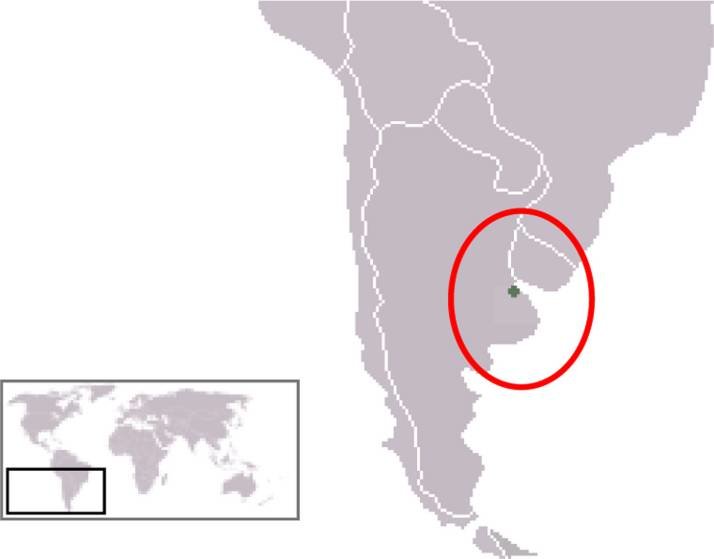
Southern Cone
The Southern Cone (Spanish: Cono Sur, Portuguese: Cone Sul) is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn.
Largest Nation (by total population)
Brazil: With a population of roughly 211-215 million
Smallest Nation (by total population)
Suriname
with roughly 590,000 to 645,000
Highest Life Expectancy at Birth
Chile holds the highest life expectancy at birth in Latin America
with estimates around 81.17 to 81.36 years
Largest Total GDP
Brazil
has the largest total GDP in Latin America, with an estimated nominal GDP of over trillion to $2-2.25 Trillion
Highest Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Per Capita
Guyana has emerged as having the highest GDP per capita in Latin America, driven by massive oil sector expansion
Lowest Projected Infant Mortality Rate
Cuba consistently reports the lowest infant mortality rate in Latin America, with rates often cited around 4–5 deaths per 1,000 live births.
Highest Economic Participation of Women
Bolivia has the highest economic participation of women in Latin America, with a female labor force participation rate of approximately 72.46% in 2024, ranking highest in the region
Highest Literacy Rate
Costa Rica: Frequently leads, with near-perfect youth literacy (e.g., 99.61% female, 99.46% male in 2021). followed closely by countries like Panama, Uruguay, and Cuba
Claudia Sheinbaum
Claudia Sheinbaum is the leader of Mexico
Sheinbaum is a member of the Morena (National Regeneration Movement) party, which is characterized as center-left to left-wing. She is considered the political heir to former President Andrés Manuel López Obrador (AMLO) and continues his "Fourth Transformation" agenda, which focuses on social programs, state-led development, and opposing neoliberal economic policies.
Nayib Bukele
Nayib Bukele is the President of El Salvador
After being expelled from the left-wing FMLN party, he ran with the right-leaning GANA party in 2019. His Nuevas Ideas party, founded later, holds a supermajority in congress.
Daniel Ortega
President of Nicaragua
Identified as a left-wing leader who has allied with other Latin American socialists, though some analyses suggest a shift away from earlier, strict leftist economic principles toward a more hybrid, authoritarian approach.
Gustavo Petro
President of Colombia
left-wing / Progressive
Background: Former member of the M-19 guerrilla group, former Mayor of Bogotá, and former Senator.
Delcy Rodríguez
interim leader of Venezuela
She is a leftist political operator and a hardline socialist, serving as a trusted ally of Nicolás Maduro and a prominent figure in the United Socialist Party of Venezuela
Bernardo Arévalo
Bernardo Arévalo is the President of Guatemala
center-left.
Ideology: Arévalo is a sociologist and former diplomat who leads the Movimiento Semilla (Seed Movement) party. He describes himself as a social democrat and focuses on anti-corruption, strengthening public education, and universal healthcare.
Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva
Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva is the President of Brazil. He is classified on the political spectrum as leftist or center-left, known for prioritizing policies that support the poor, expanding social welfare, and leading the Workers' Party (PT)
Javier Milei
Javier Milei is the President of Argentina He is positioned on the far-right of the political spectrum, characterized as an ultraliberal, libertarian, and anarcho-capitalist who won election by promising drastic cuts to government spending
Jose Antonio Kast
osé Antonio Kast is a politician from
Chile. He is classified on the political spectrum as far-right or ultra-conservative, representing the most conservative, right-wing leadership in Chile since the end of the Pinochet dictatorship. His platform focuses on strict law and order, limiting immigration, and economic deregulation
Miguel Díaz-Canel
Miguel Díaz-Canel is the leader of Cuba.
On the political spectrum, Miguel Díaz-Canel is firmly on the Left (Far-Left/Communist).
Ideology: He leads a one-party communist state based on Marxist-Leninist principles.
Daniel Noboa
Daniel Noboa Equadorian President
While he personally identifies as center-left, he is widely classified by political analysts and international media as center-right or right-wing due to his pro-business policies and conservative security agenda