Physics Final Exam Review
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Efficiency
A measure of the effectiveness of the input of energy to do work; useful energy or work divided by the total input of energy.
Energy
The ability to do work.
Gravitational Potential Energy
The energy an object has due to its position in a gravitational field.
Joule
SI unit of work and energy, equal to one Newton meter.
Kinetic Energy
The energy an object has by reason of its motion.
Law of energy conservation
The general law that total energy is constant in any process.
Power
The rate at which work is done.
Kilowatt-hour
Unit used primarily for electrical energy provided by electric utility companies.
Watt
SI unit of power (1 W = 1 J/s).
Work-energy theorem
The net work done on an object is equal to its change in Kinetic Energy.
Elastic collision
A collision that conserves internal Kinetic Energy.
Inelastic collision
A collision that does not conserve internal Kinetic Energy.
Impulse
The average net external force times the time it acts; equal to the change in momentum.
Linear Momentum
The product of mass and velocity.
Perfectly Inelastic Collision
A collision in which the colliding objects stick together.
Statics
Branch of mechanics that deals with bodies at rest or forces in equilibrium.
Center of gravity
The point where the total weight of the body is assumed to be concentrated.
Dynamic Equilibrium
Net external force and torque on a system moving with constant velocity are zero.
Mechanical advantage
The ratio of output to input forces for any simple machine.
Static Equilibrium
The net external force and torque acting on a system is zero.
Torque
Turning or twisting effectiveness of a force.
Stable Equilibrium
A system, when displaced, experiences net force or torque in the direction opposite to the direction of the displacement.
Unstable Equilibrium
A system experiences net force or torque in the same direction as the displacement from equilibrium.
Neutral Equilibrium
Independent of a system's displacements from its original position.
Angular Velocity
The time rate at which an object rotates or revolves about an axis.
Angular Acceleration
The rate of change of angular velocity with time.
Angular momentum
The product of moment of inertia and angular velocity.
Moment of Inertia
Mass times the square of the perpendicular distance from the rotation axis; I=mr².
Rotational Inertia
Resistance to change of rotation.
Right Hand Rule
Direction of angular velocity and angular momentum in which the thumb of your right hand points when you curl your fingers in the direction of the disk's rotation.
Radial Acceleration
The acceleration of the object is along the radius, directed towards the center.
Tangential Acceleration
The acceleration in a direction tangent to the circle at the point of interest in circular motion.
Absolute Pressure
The sum of gauge pressure and atmospheric pressure.
Gauge Pressure
The pressure relative to atmospheric pressure.
Adhesive Forces
The attractive forces between molecules of different types.
Cohesive Forces
The attractive forces between molecules of the same type.
Buoyancy
The tendency of an object to float in a fluid.
Archimedes' Principle
The buoyant force on an object equals the weight of the fluid it displaces.
Buoyant Force
The net upward force on any object in any fluid.
Fluids
Liquids and gases; state of matter that yields to shearing forces.
Surface Tension
The cohesive forces between molecules which cause the surface of a liquid to contract to the smallest possible surface area.
Contact Angle
The angle between the tangent to the liquid surface and the surface.
Density
The mass per unit volume of a substance or object.
Specific Gravity
The ratio of the density of an object to a fluid.
Pascal's Principle
A change in pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to all portions of the fluid and to the walls of its container.
Bernoulli's equation
The equation resulting from applying conservation of energy to an incompressible frictionless fluid.
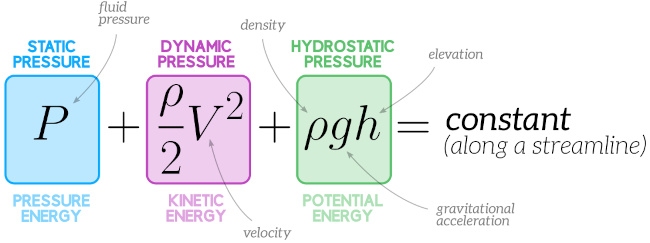
Flow Rate
The volume that flows past a particular point during a time.
Fluid Dynamics
The physics of fluids in motion.
Laminar Flow
Fluid travels smoothly with little to no mixing.
Turbulent Flow
Fluid undergoes irregular fluctuations and mixing.
Turbulence
Fluid flow in which layers mix together.
Viscosity
The friction in a fluid between layers.
Reynolds Number
A dimensionless parameter that can reveal whether a particular flow is laminar, transition, or turbulent.