APES - Unit 6 - Human Populations
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
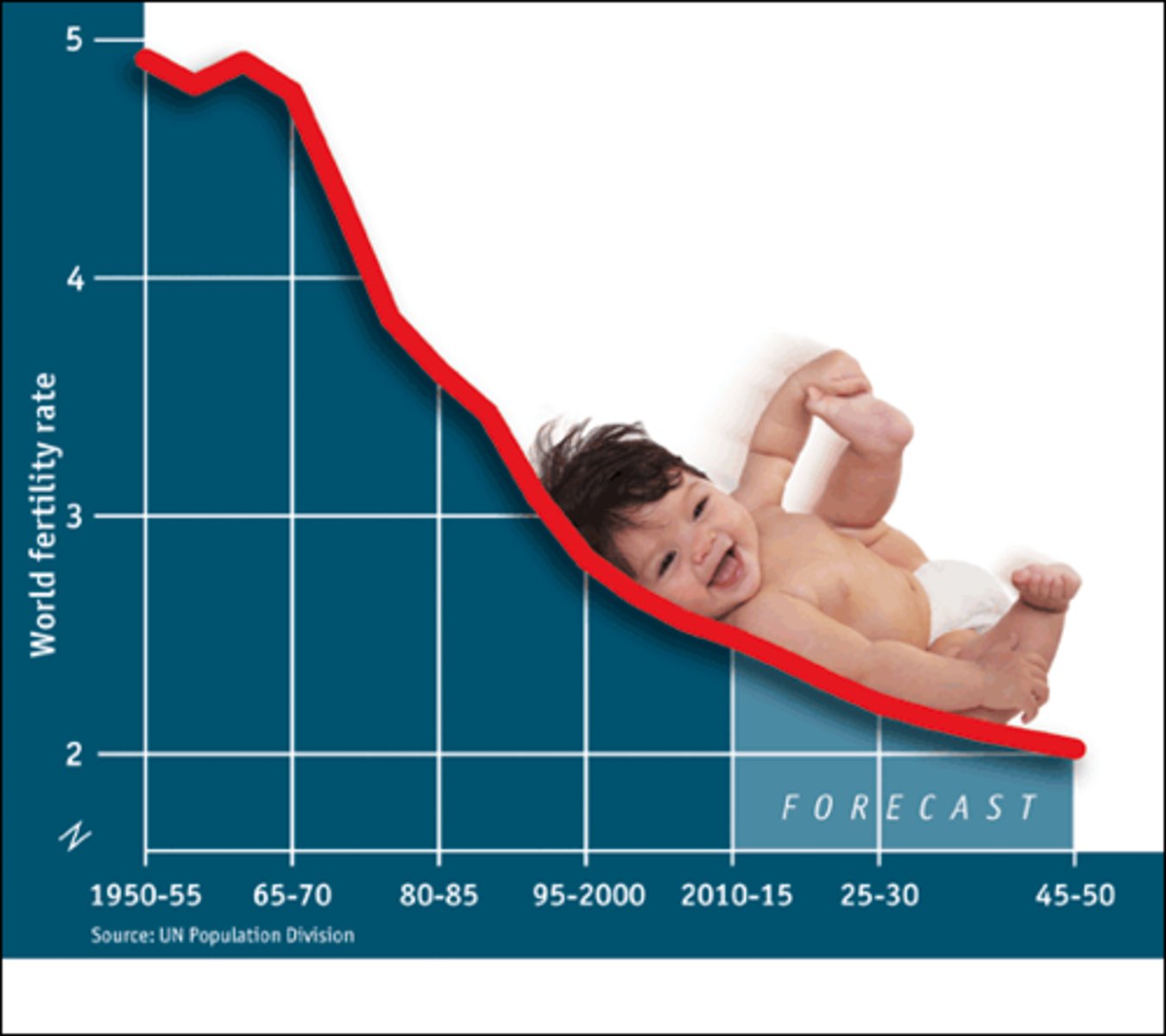
fertility rate
number of children a woman has during her lifetime
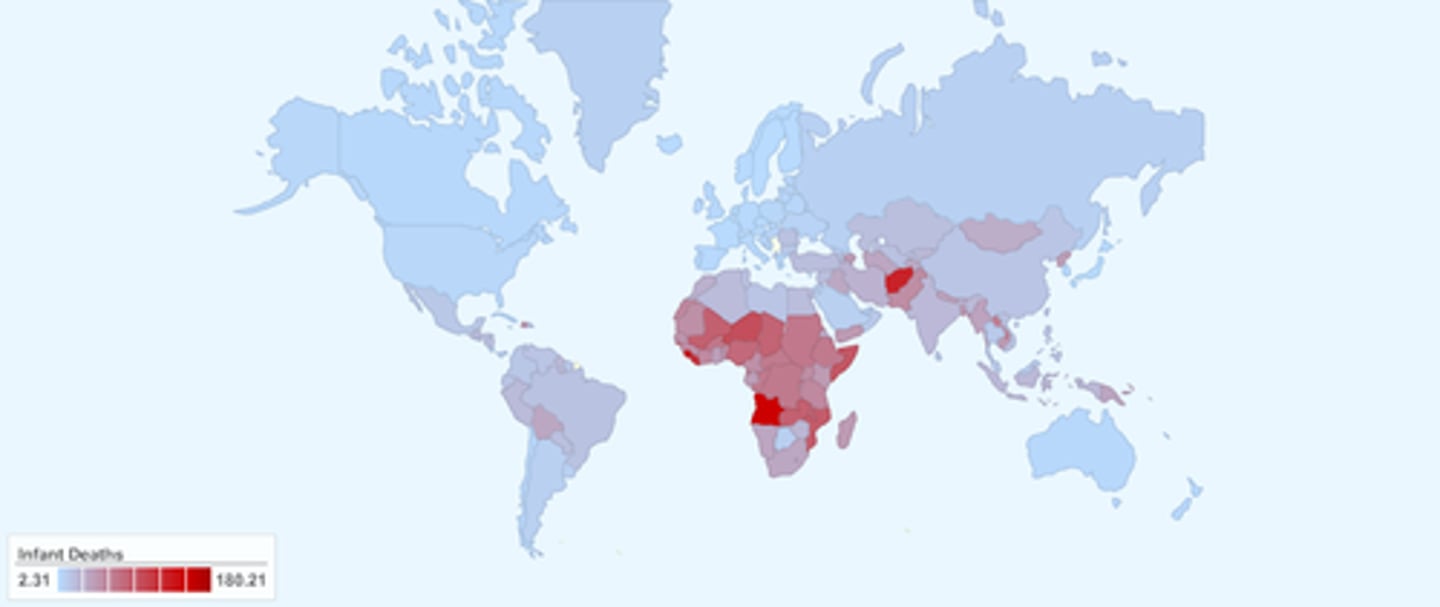
infant mortality
number of children who die before age 5, higher in less-developed countries
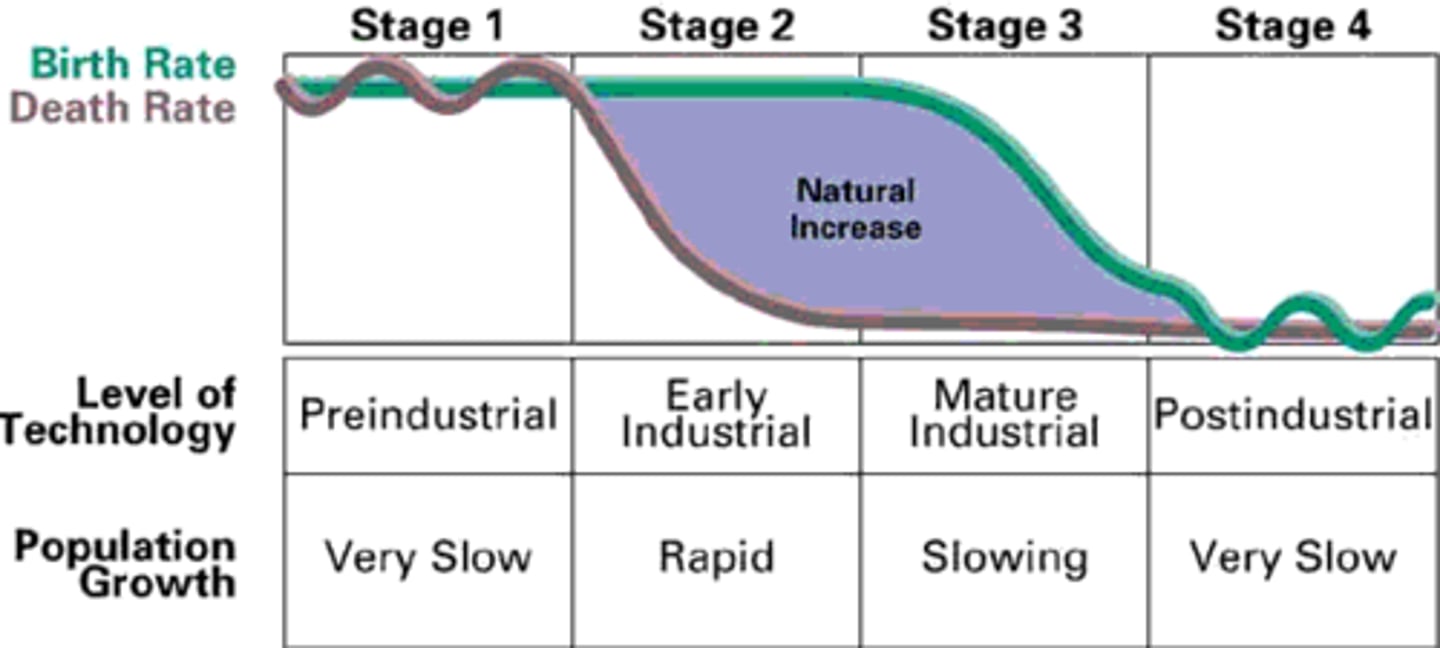
demographic transition
four-stage process from high birth and death rates, to declining death rates thanks to better medical care, and eventually lower birthrates due to better education and family planning
developed country
high GDP (income), highly educated and industrialized, long life expectancy, and generally low birthrate

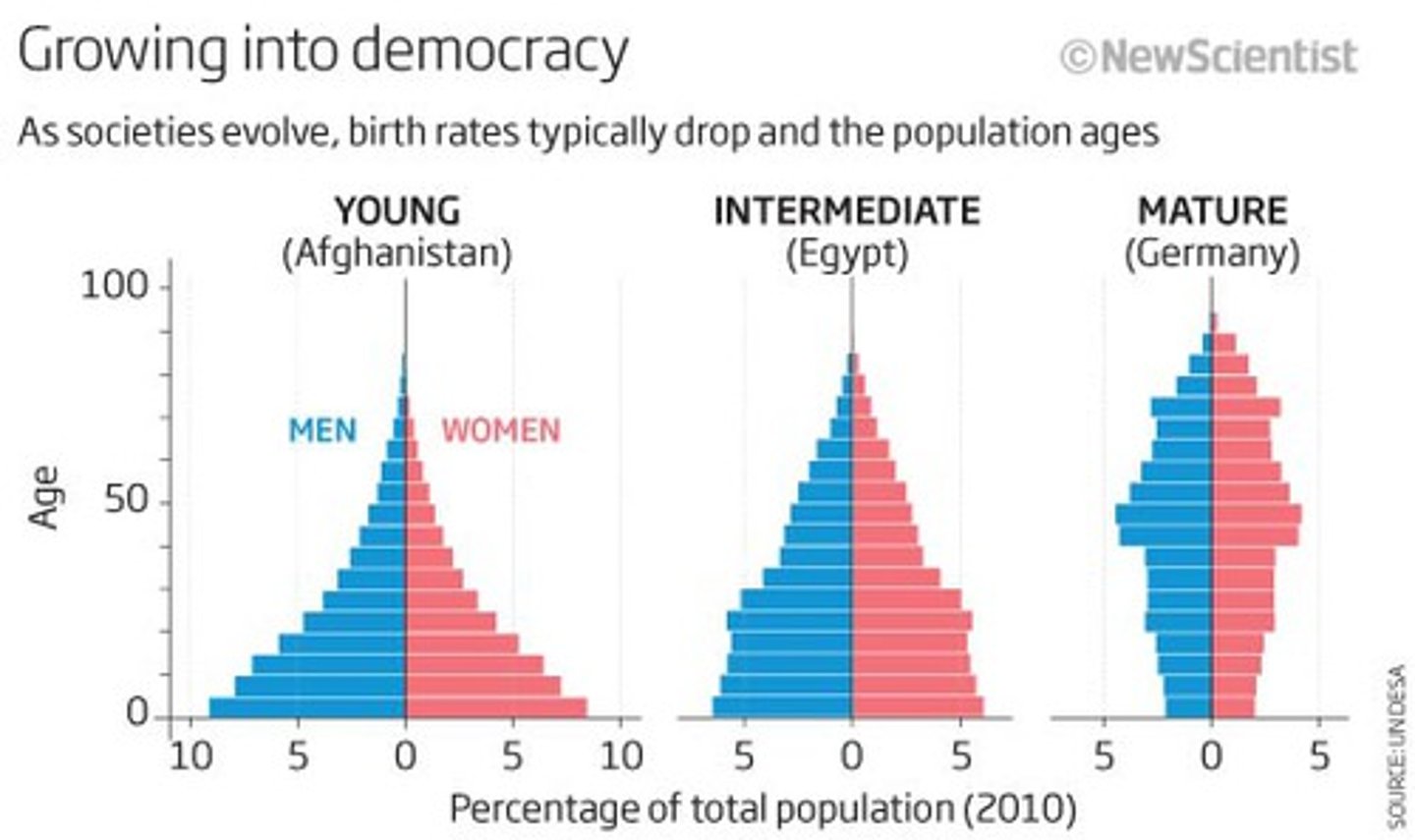
age structure diagram
pyramid that shows the percentage of the population in different age groups
developing country
a country in demographic transition, that is industrializing but still has a very high birth rate. Consumption is lower than in a developed country
rapid growth
more people will be having children in 20 years than are now. Typical of under-developed and early developing countries
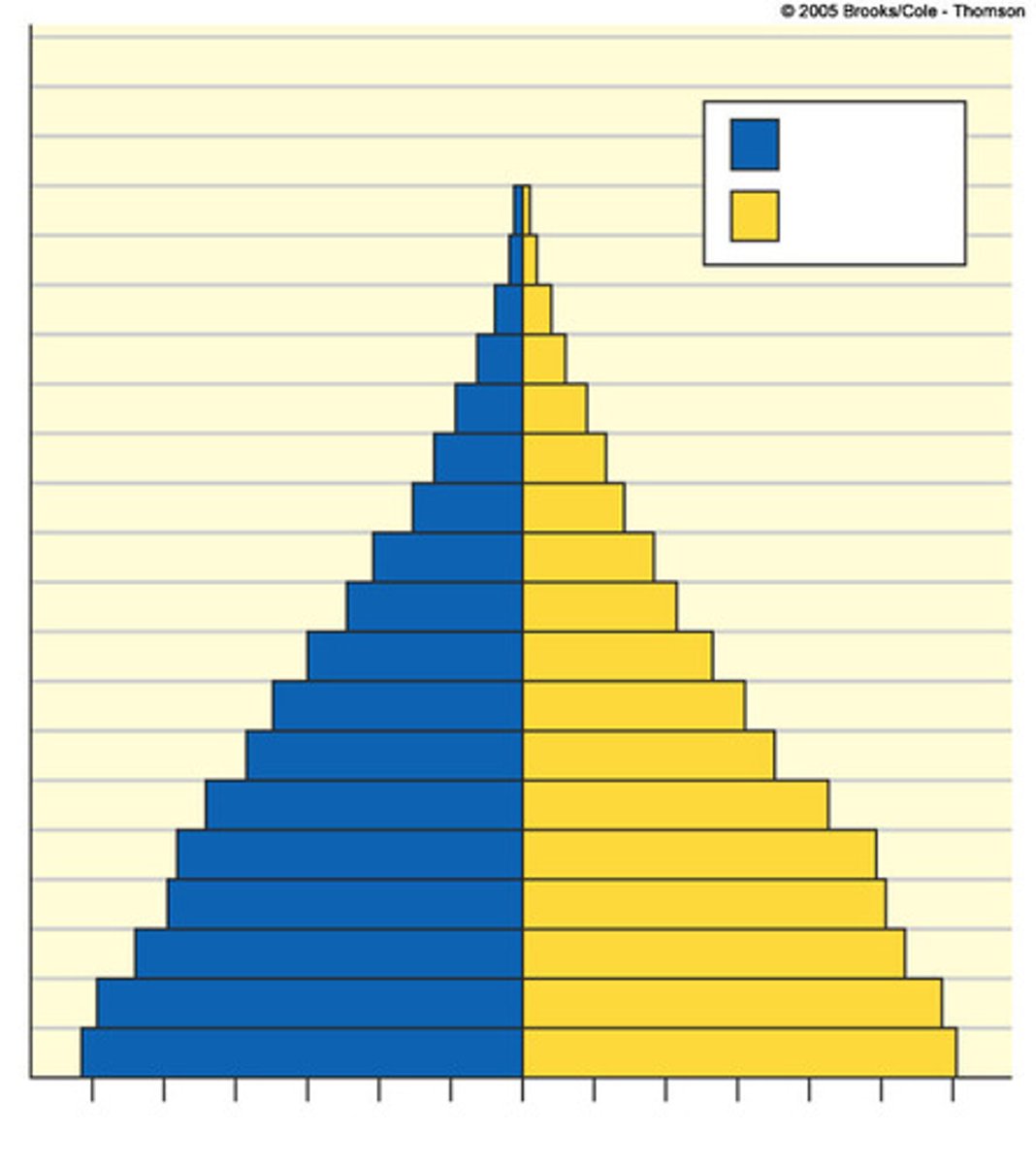
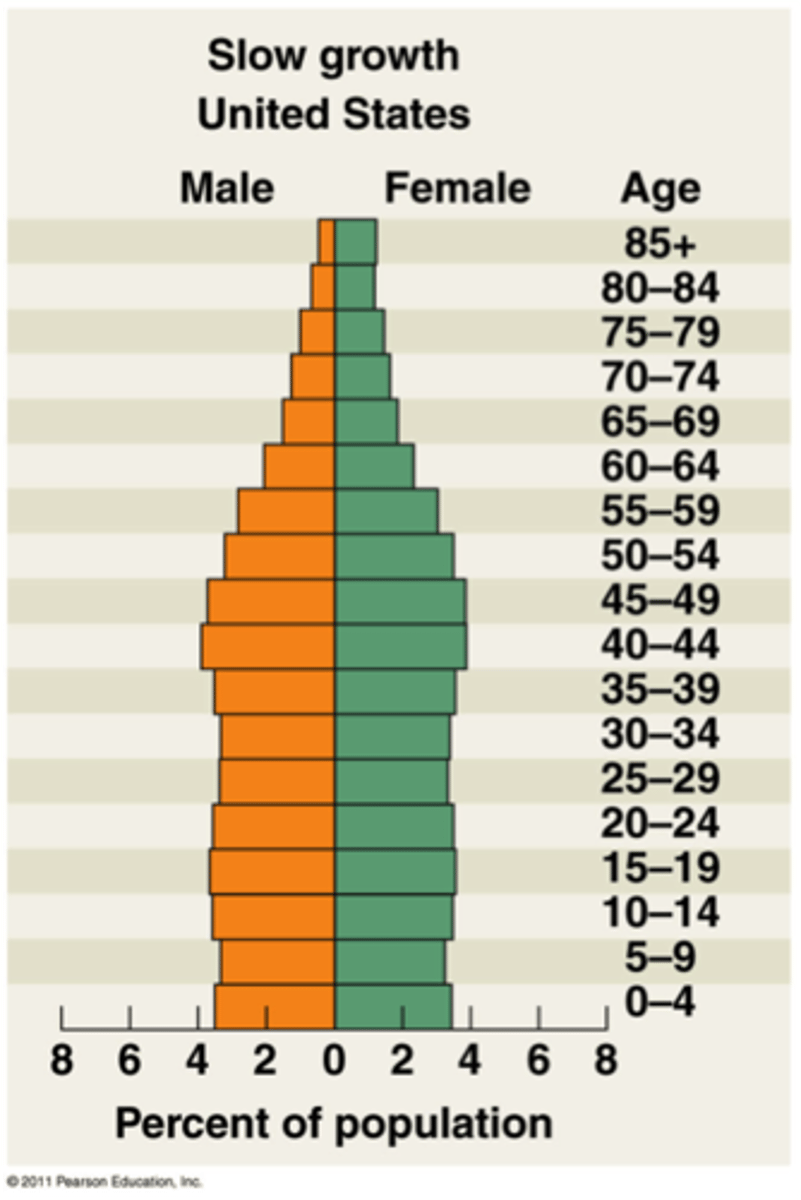
slow growth
typical of later developing countries. Growth rate is still increasing
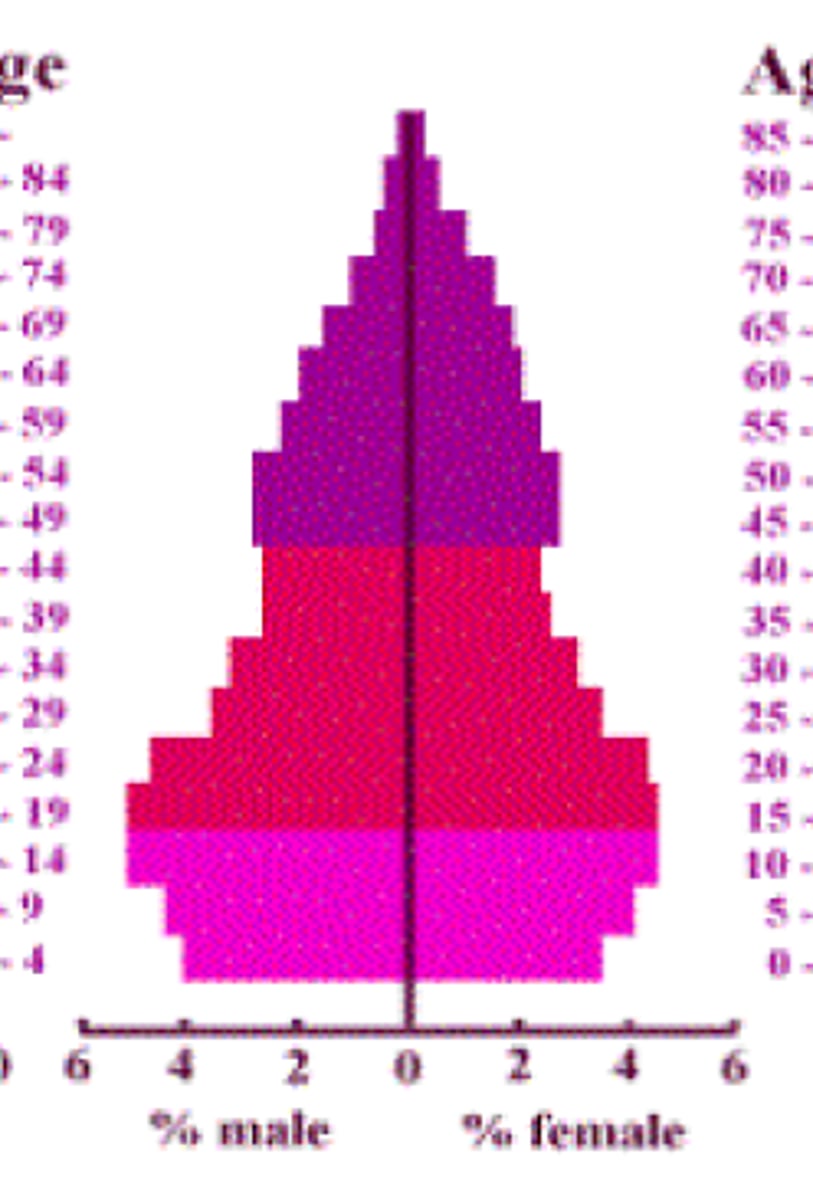
zero growth
same number of people will be having children (ages 0-14) in 20 years as now. No change.
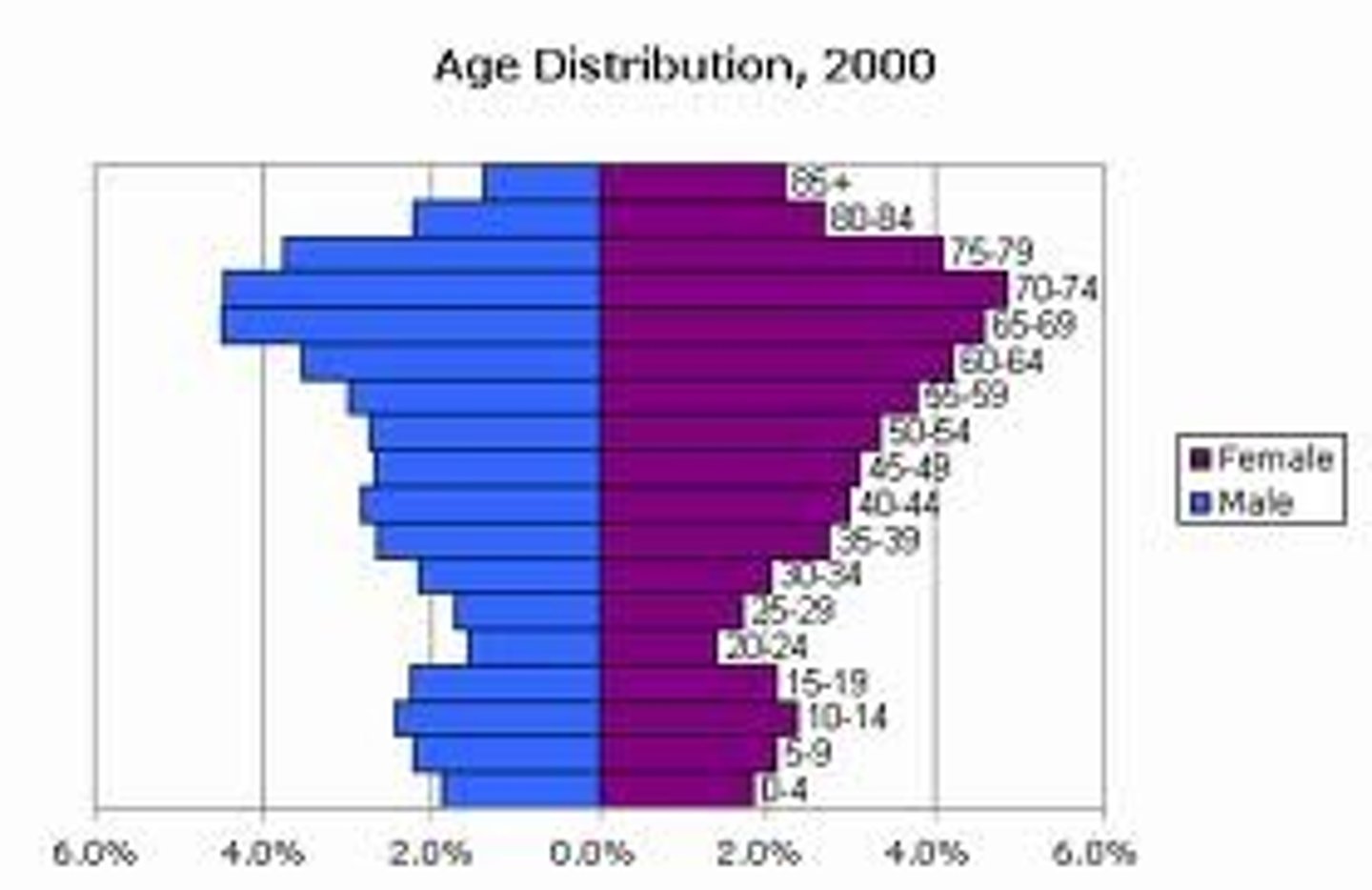
negative growth
fewer people will be having children (ages 0-14) in 20 years than are now. Population will decrease.
What problems are associated with increasing population growth?
Lack of resources, lack of jobs, not enough sanitation, pollution, lack of housing, lack of or increased costs of food and other resources.

What problems are associated with decreasing population growth?
Lack of workers, lack of space in nursing homes, increased costs of healthcare, slow economic growth

demography
study of human populations and how they change over time
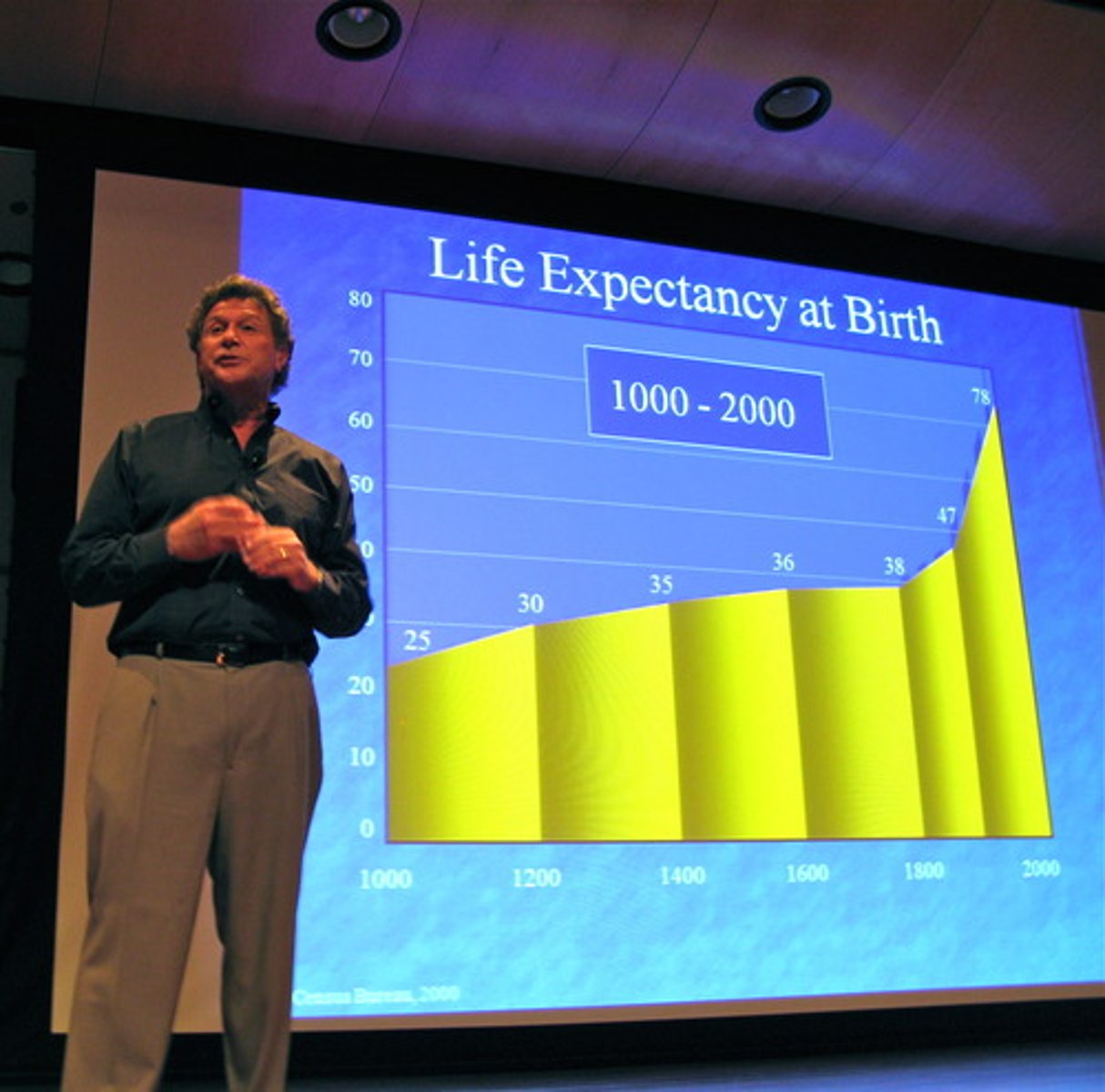
reasons population growth increased in the 1800s
Industrial revolution-- better medicine and increased food (death rates declined)
reasons population growth slowed since the 1970s
increased job opportunities for women and family planning

industrialization
amount of a country's income that comes from manufactured goods that they export

replacement rate
number of children each family needs to have in order to replace the parents and have zero population growth (about 2.1 because not every person has children)
Urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements.

What are diseases that are caused by unclean water
typhoid fever, dysentery, cholera
infrastructure
the basic physical and organizational structures and facilities (e.g., buildings, roads, and power supplies) needed for the operation of a society or enterprise.

TFR (total fertility rate)
The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years.
cultural carrying capacity
The limit on population growth that would allow most people in an area or the world to live in reasonable comfort and freedom without impairing the ability of the planet to sustain future generations.

Replacement level fertility rate
the number of children a couple must have to replace themselves
GDP
Gross Domestic Product- the total market value of all final goods and services produced annually in an economy
life expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions. Life expectancy at birth is the average number of years a newborn infant can expect to live.
Demograph Transition
a model that describes how economic and social changes affect population growth rates
Agricultural Revolution
The time when human beings first domesticated plants and animals and no longer relied entirely on hunting and gathering
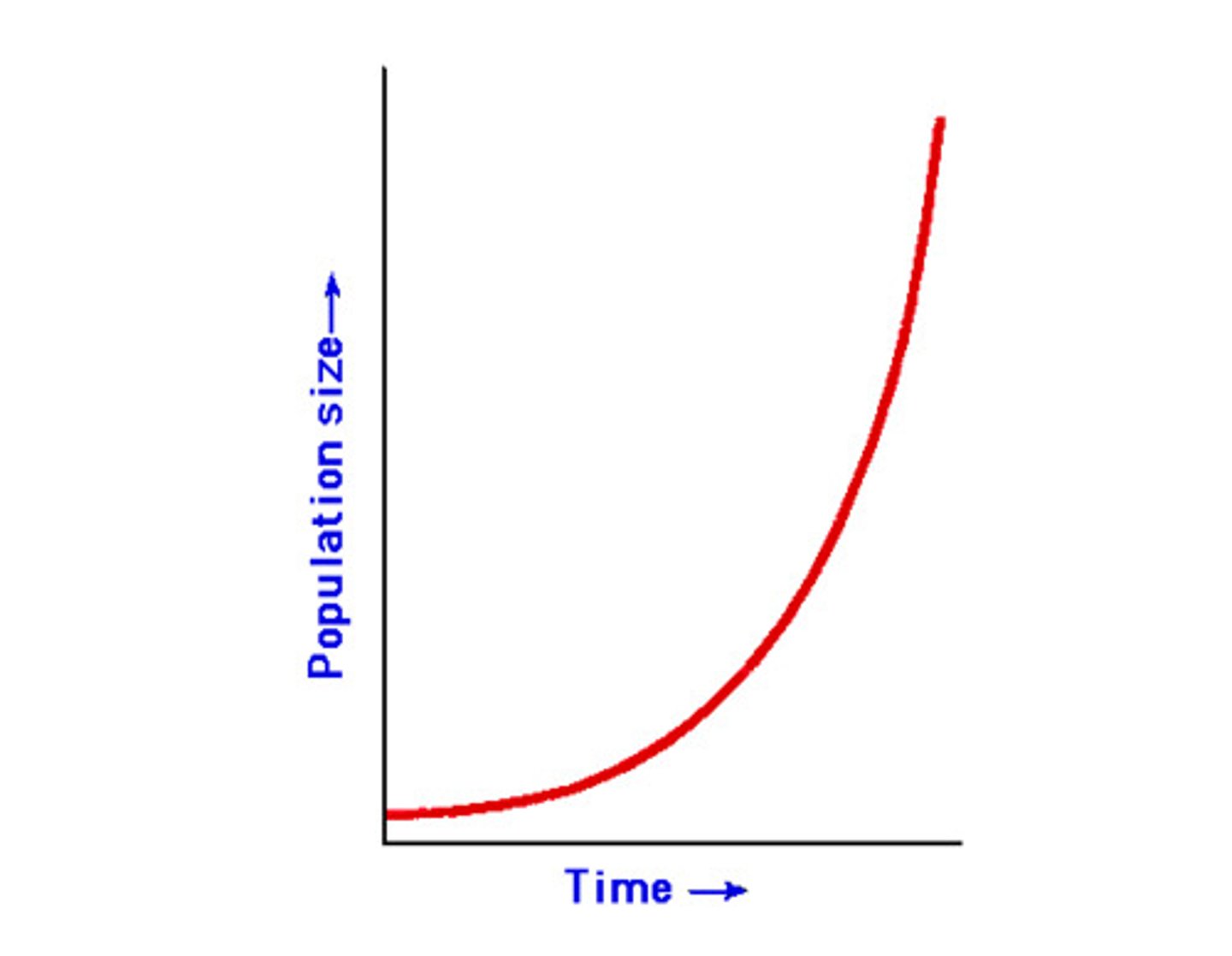
exponential growth
Growth pattern in which the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate
doubling time
70 / (Current % Growth Rate)
Demographics
statistical data relating to the population and particular groups within it.
total fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
Migration
movement of people from one place to another
Emigration
movement of individuals out of an area
Immigration
Movement of individuals into a population
age structure
number of males and females of each age in a population
Demographic Transition Model
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moves from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time.
pronatalist policies
government policies that encourage child birth such as tax breaks and flexible work hours
antinatalist policies
seek to reduce birth rates and strongly encourage or require that women limit their fertility
pre-industrial stage
birth and death rates high, population grows slowly, infant mortality high
early transition stage
Access to food and medicine improve, leading to a rapid drop in death rates
late transition stage
- Birth control and sex education, woman play a greater role in family planning, Improved diet
- Birth Rates - falling
- Death rates - falls slow
- population: increases slowly
Industrial stage
decline in birth rate, population growth slows
post-industrial stage
the fourth and final stage of the demographic transition model, in which both birth and death rates have fallen to a low level and remain stable there, and populations may even decline slightly