Comprehensive Guide to Joints: Types, Movements, and Disorders in Anatomy
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Joints
AKA - Articulation or arthrosis
Functional Classification
Based on the type of movement they permit
Synarthrosis
An immovable joint
Amphiarthrosis
A slightly movable joint
Diarthrosis
A freely movable joint; all are synovial joints
General morphology or Structural Classification
Anatomical characteristics; presence or absence of space between articulating bones (synovial cavity); type of connective tissue that binds the bones together
Fibrous
No synovial cavity; bones held together by dense collagen fibers
Cartilaginous
No synovial cavity; bones held together by cartilage
Synovial
Have a synovial cavity; united by dense irregular connective tissue of articular capsule; bones held together by ligaments
Fibrous Joints
Lack a synovial cavity; the articulating bones are held very closely together by dense irregular connective tissue; permit little or no movement
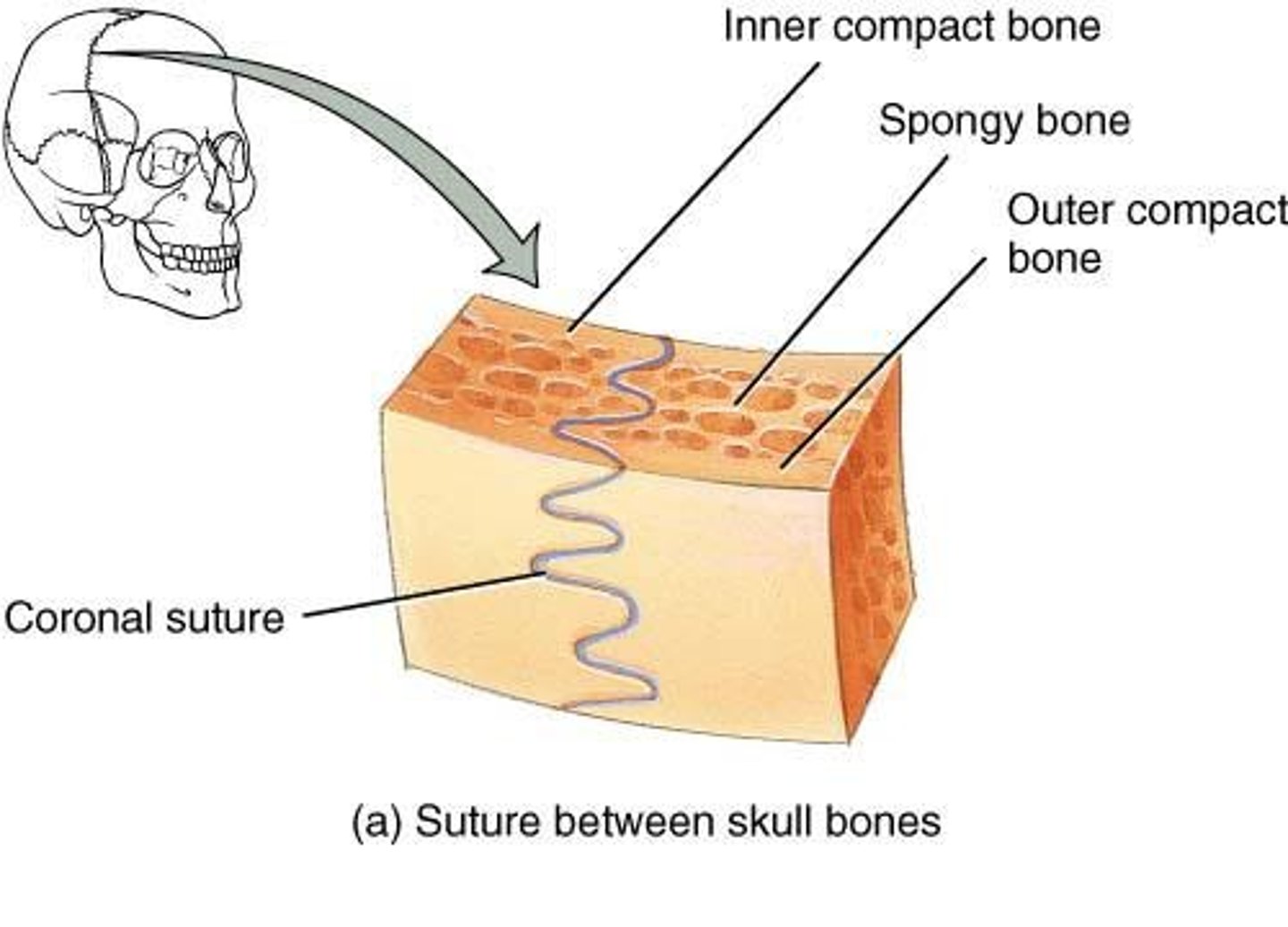
Sutures
Occur only between bones of the skull; adult = immovable; infants & children = slightly moveable
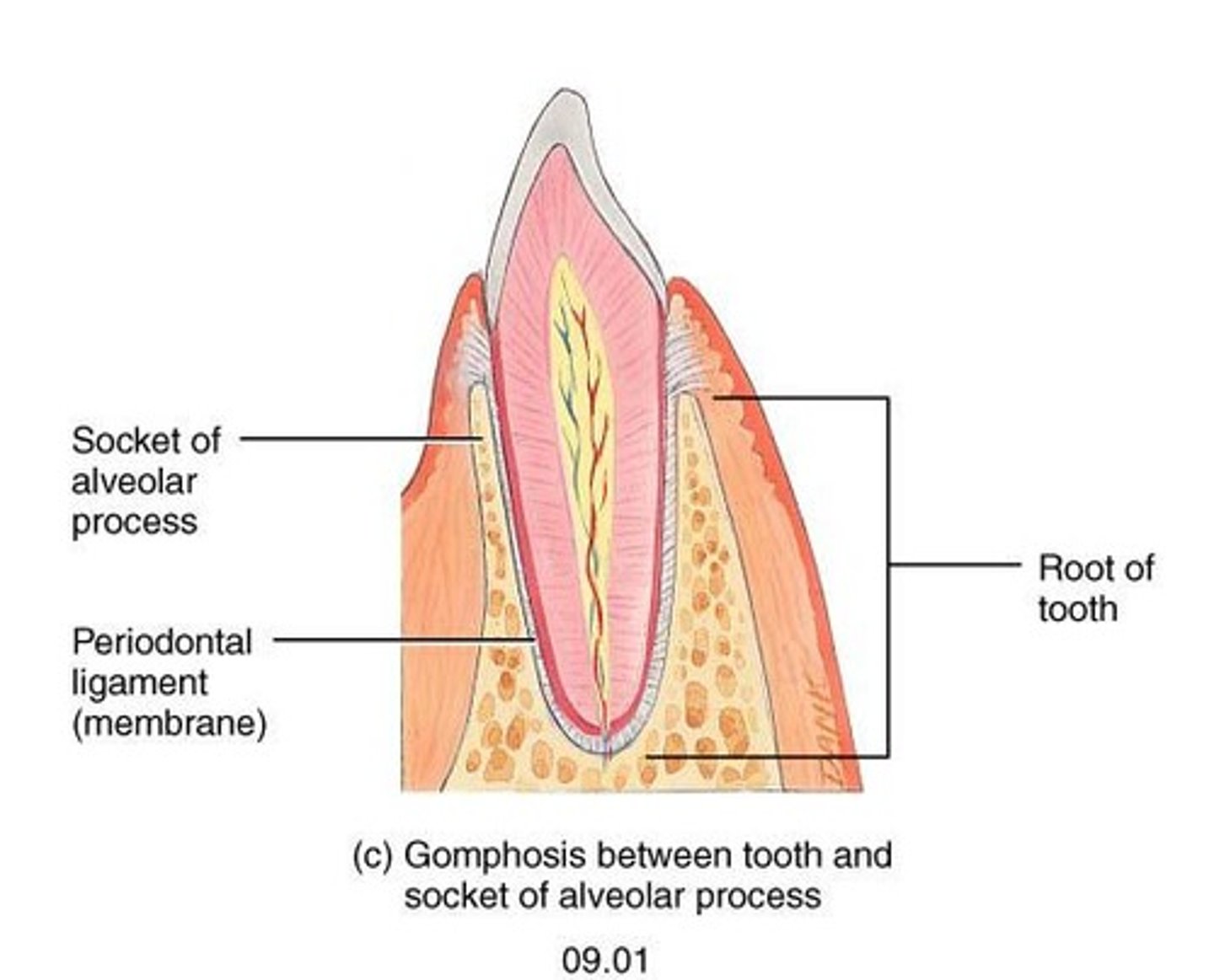
Gomphosis
Immovable joint; joint in which a cone-shaped peg fits into a socket; articulations of the teeth with the sockets of the maxillae and mandible
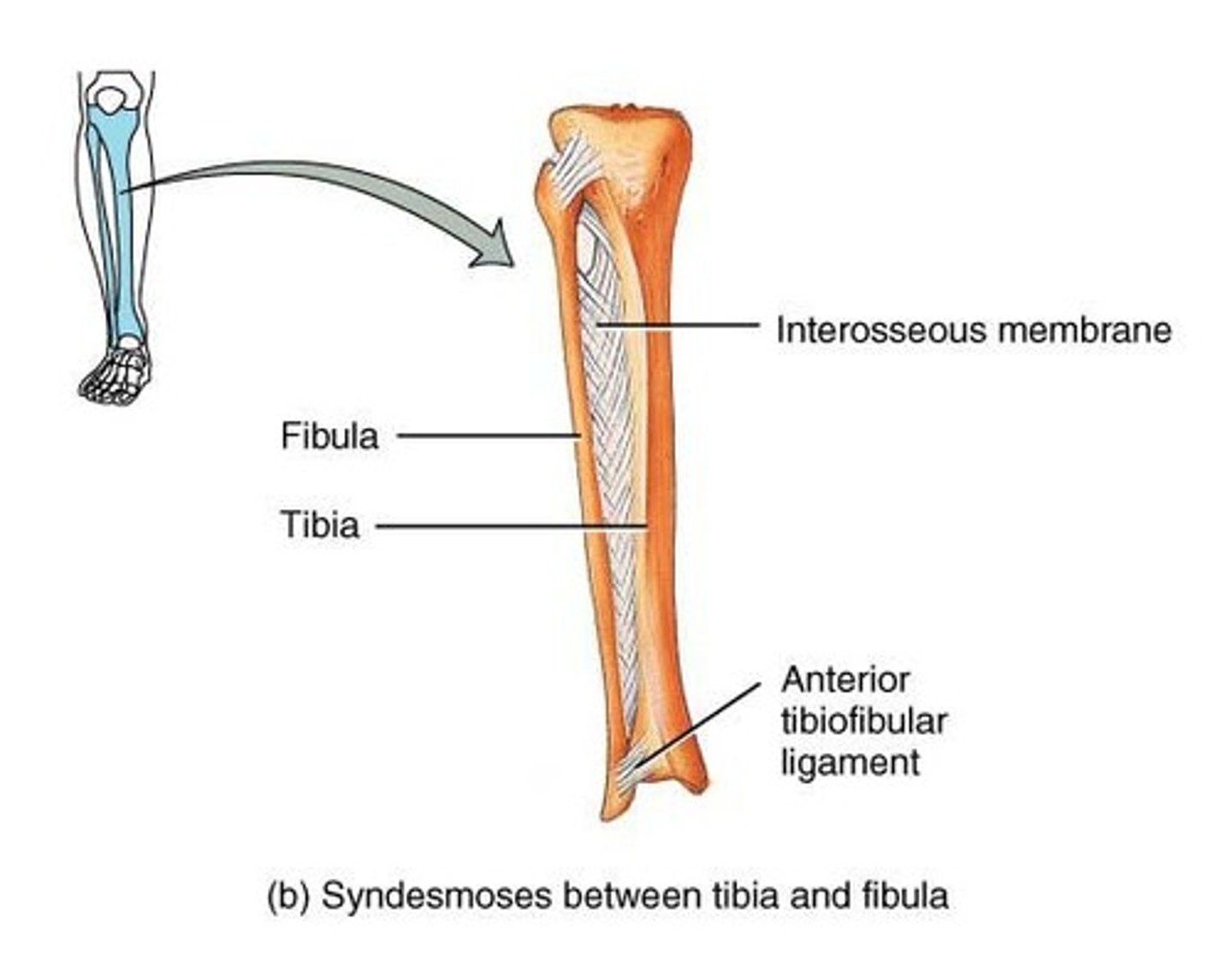
Syndesmoses
2 bones bound by an interosseous membrane; slight movement (amphiarthrosis); between the tibia and fibula in the leg
Cartilaginous Joints
No synovial cavity, allows little or no movement, held together by hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage.
Synchondroses
Connecting tissue is hyaline cartilage, immovable, includes the epiphyseal (growth) plate.
Symphyses
Slightly movable joint where ends of articulating bones are covered with hyaline cartilage and connected by a disc of fibrocartilage.
Pubic Symphysis
Example of a symphysis located between the anterior surfaces of the hip bones.
Intervertebral joints
Example of a symphysis located between the vertebrae.
Articular Cartilage
Reduces friction between bones during movement and helps absorb shock.
Synovial Fluid
Secreted by the synovial membrane, contains hyaluronic acid, reduces friction, absorbs shocks, supplies oxygen and nutrients to cartilage, and removes carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes.
Articular Capsule
A sleeve-like capsule enclosing the synovial cavity, composed of an outer fibrous capsule and an inner synovial membrane.
Ligaments
Fibrous membranes arranged as parallel bundles of dense regular connective tissue that hold bones together in a synovial joint.
Articular Fat Pad
Adipose tissue located between the fibrous capsule and synovial membrane.
Infrapatellar fat pad
Example of an articular fat pad.
Bursa
Fibrous, slightly flattened sacs lined with synovial membrane, found between skin, tendons, muscles, and ligaments, providing cushioning.
Tendon Sheaths
Elongated bursa that wrap around tendons to reduce friction.
Accessory Ligaments
Extracapsular ligaments located outside of the articular capsule, such as the collateral ligaments of the knee.
Intracapsular ligaments
Ligaments located within the articular capsule but excluded from the synovial cavity by folds of synovial membrane, such as the ACL and PCL.
Articular Discs or Menisci
Pads of fibrocartilage between articular surfaces that function in shock absorption, better fit, adapting surfaces for combined movements, and weight distribution.
Labra
Fibrocartilaginous lip that extends from the end of a socket, deepening the joint socket and increasing area of contact.
Nerve endings
Convey information about pain from the joint to the spinal cord and brain, responding to the degree of movement and stretch at a joint.
Types of Synovial Joints
Classified into uniaxial, biaxial, and multiaxial types.
Uniaxial Joints
Include hinge, planar, and pivot joints.
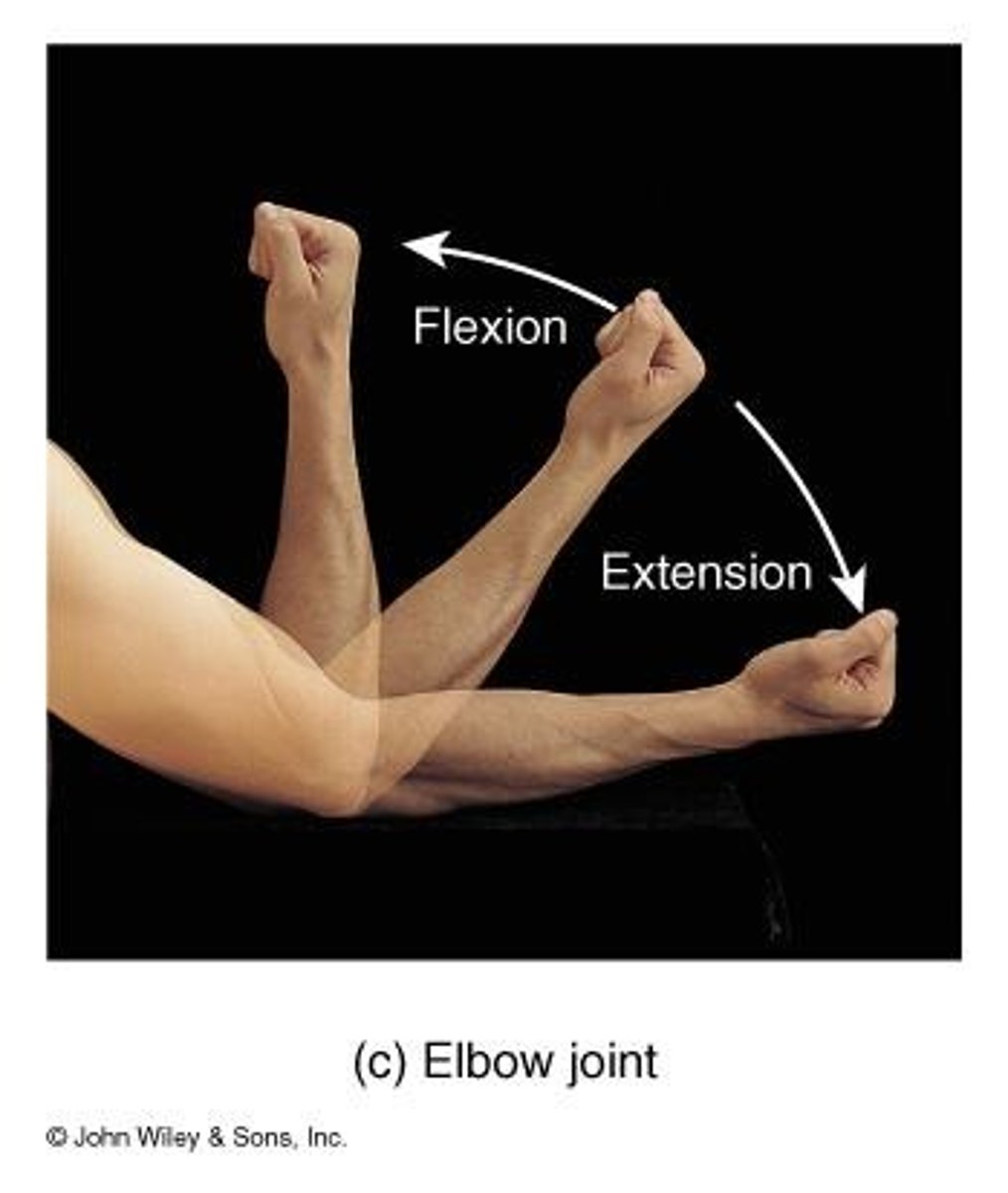
Hinge Joints
Produce an opening and closing motion like that of a hinged door, permitting only flexion and extension, such as the elbow.
Planar Joints
Flat surfaces that primarily permit back-and-forth and side-to-side movements, such as intercarpal joints.
Pivot Joints
Surface of one bone articulates with a ring formed partly by another bone, enabling the palms to turn anteriorly and posteriorly, such as the superior radioulnar joint.
Biaxial Joints
Include condyloid and saddle joints.
Condyloid Joints
The projection of one bone fits into the oval-shaped depression of another bone, such as the wrist.
Saddle Joints
Articular surface of one bone is saddle-shaped, fitting into the saddle of another bone, such as the thumb.
Multiaxial Joints
Include ball-and-socket joints.
Ball-and-Socket Joints
Ball-like surface of one bone fitting into a cuplike depression of another bone, such as the shoulder and hip.

Types of Movement @ Synovial Joints
Grouped into four main categories: Gliding, Angular movements, Rotation, and Special movements.
Gliding
Simple movement back-and-forth and from side-to-side with no significant alteration of the angle between the bones, limited in range, such as intercarpal joints.
Angular Movements
Increase or decrease in the angle between articulating bones, including flexion, extension, hyperextension, lateral flexion, abduction/adduction, and circumduction.
Flexion
Decrease in the angle between articulating bones
Extension
Increase in the angle between articulating bones
Hyperextension
Continuation of extension beyond the normal extension
Lateral flexion
Movement of the trunk sideways to the right or left at the waist
Abduction
Movement of a bone away from the midline
Adduction
Movement of a bone toward the midline
Circumduction
Movement of a body part in a circle
Rotation
A bone revolves around its own longitudinal axis
Elevation
Upward movement of a part of the body
Depression
Downward movement of a part of the body
Protraction
Movement of a part of the body anteriorly
Retraction
Movement of a protracted part of the body back to normal
Inversion
Movement of the foot medially
Eversion
Movement of the sole laterally
Dorsiflexion
Bending of the foot at the ankle in an upward direction
Plantar flexion
Bending of the foot at the ankle in a downward direction
Supination
Movement of the forearm so that the palm is turned upward
Pronation
Movement of the forearm so that the palm is turned downward
Opposition/Reposition
Movement of the thumb in which the thumb moves across the palm to touch the tips of the fingers on the same hand
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Autoimmune disorder causing cartilage attack, inflammation, swelling & pain
Osteoarthritis
Degenerative joint disease characterized by aging and wear & tear
Gouty Arthritis
Condition where urate crystals build up in joints causing pain
Arthroplasty
Surgical replacement of joints with artificial joints
Hip Replacements
Partial or total replacement of the hip joint
Knee Replacements
May be partial or total replacement of the knee joint
Structural Classification
Based on anatomical characteristics and presence or absence of space between articulating bones (synovial cavity)
Synovial Joints
Have a synovial cavity; united by dense irregular connective tissue of articular capsule
Synchondrosis
Connecting tissue is hyaline cartilage; immovable
Gliding Movement
Simple movement back-and-forth and from side-to-side without significant alteration of the angle between the bones
Gliding Movements
Simple movement back-and-forth and from side-to-side without significant alteration of the angle between the bones