History of the Atom
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Turn on override answers!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Significance of Aristotle and problem
States matter is continuous and not made of smaller particles
Didn't have evidence
Significance of Democritius and problem
Says the world is made of two things: empty space and tiny particles called atoms (atomus → invisible)
Didn't have evidence
Law of Conservation of Matter
Matter is not created nor destroyed. It's only rearranged
Mass of reactants= Mass of products
Law of Electrical Charges
Opposite charges attract and like charges repel.
Law of Definite Proportions
Atoms must combine in whole number ratios
Father of Modern Atomic Theory
John Dalton
(Dalton’s Atomic Theory) TRUE OR FALSE:
All matter is made up of atoms. Atoms are the smallest fundamental units of matter.
True
(Dalton’s Atomic Theory) TRUE OR FALSE:
All elements consist of atoms which are indivisible and indestructible.
False. Evidence: Nuclear Reactions
(Dalton’s Atomic Theory) TRUE OR FALSE:
All atoms of the same element are identical in size, shape, and mass
False. Evidence: Isotopes
(Dalton’s Atomic Theory) TRUE OR FALSE:
Atoms of different elements are different in size, shape, and mass.
True.
(Dalton’s Atomic Theory) TRUE OR FALSE:
In a chemical reaction, atoms are rearranged, never created nor destroyed and they combine in whole number ratios.
True
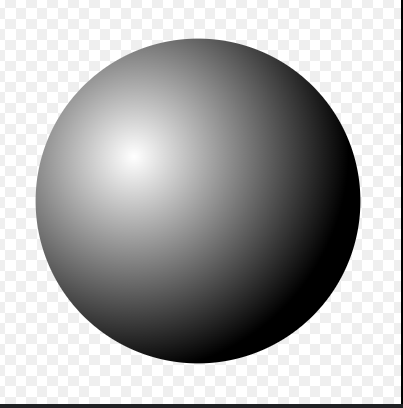

A solid sphere, everything else is empty space. Who’s atomic model fits this description?
John Dalton
Who theorized the atom structure MIGHT be related to electricity… it might have a charge,
Michael Faraday
Who discovered there are positive charges and negative charges
Benjamin Franklin

Who’s responsible for the plum pudding model
JJ Thomson
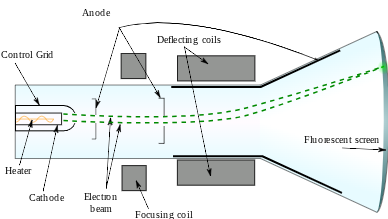
All atoms contain electrons. Since all atoms were neutral, there must be some positive charge spread throughout the atom to balance the negative and keep the atom neutral.
This conclusion was drawn from the ______ experiment
Cathode Ray Tube
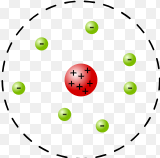
Who’s atomic model?
Ernest Rutherford
The ______ experiment proved all protons aren’t spread throughout the atom, they’re clumped together in the middle (nucleus).
Gold Foil
Provide the explanation for the following observation from the Gold Foil Experiment:
Most positive charges passed through because…
the atom is mostly empty space
Provide the explanation for the following observation from the Gold Foil Experiment:
Some of the positive charges deflected because…
the atom contains some positive charge
Provide the explanation for the following observation from the Gold Foil Experiment:
Some of the positive charges deflected straight back because…
there is a concentrated area of positive charge
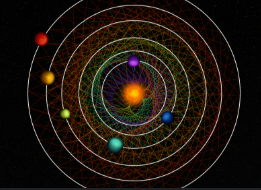
Who is responsible for the Solar System Model
Niels Bohr
Problem with the Solar System Model
It only worked for hydrogen, all other elements failed
the more precisely the location of an electron is determined the less precisely speed is known
Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle
Found that electrons sometimes act like waves or particles. aka ______
Lous de Brogile, wave particle duality
lamda (𝜆), distance from crest to crest or trough to trough (meters or nanometers)
Wavelength
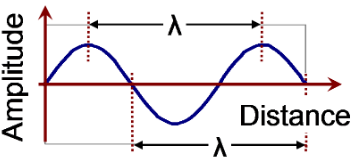
nu, the # of wave cycles that pass a given point (hertz or 1/s or s^-1)
Frequency
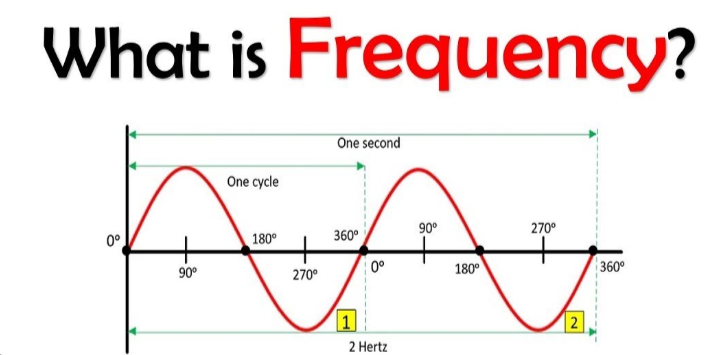

The _______ spectrum
electromagnetic
Shorter wavelength = _____ frequency, _____ energy
higher frequency, higher energy
Longer wavelength = _____ frequency, ______ energy
lower frequency, lower energy
λ x 𝜈 = c
(lambda x nu = speed of wave)
what does c =
c= speed of light = 2.99 × 108m/s
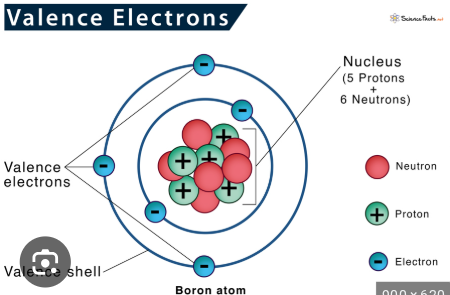
Outermost electrons in an atom
Valence electrons
Any amount of E(energy) could be gained or lost by any object
This would result in a continuous line spectrum
What is this theory called?
Classical Theory Physic
Any amount of E(energy) could be gained or lost by any object
This would result in a continuous line spectrum
True or false, If false what theory disproves
False, Quantum Theory
_______ Theory
When atoms or molecules absorbs or emits energy, it must be a specific amount called a quanta
Quantum