A&P - Lab quiz 3 notes + tissues
1/251
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
252 Terms
This tissue type allows movement & is made of long, contractile protein-packed cells
Muscle Tissue
The spleen is the location of _________
Reticular connective
The function of _____ is to filter & remove old blood cells or microbes.
Reticular connective tissue
The walls of the organs of the urinary tract (like the bladder and the ureters) are the location of
smooth muscle tissue
This tissue type is made almost entirely of cells. It covers & lines body cavities and forms glands
Epithelial
his tissue type is the main component of the brain, spinal cord, & nerves. It conducts impulses and has branching cells with long extensions
Nervous
This tissue type is the most abundant in the body. It is made of cells, fibers, & ground substance.
Connective
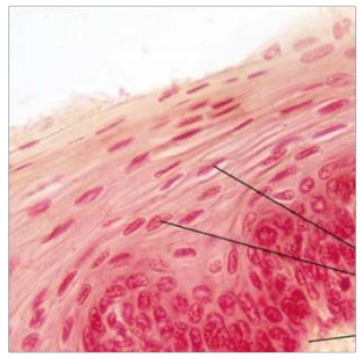
Identify the tissue type based off the image
Epithelial
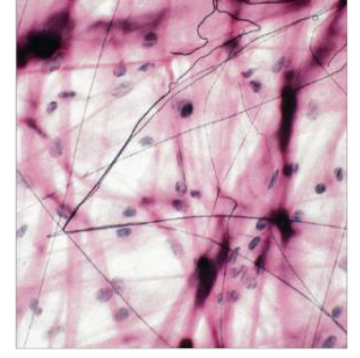
Identify the tissue type based off the image below
Connective
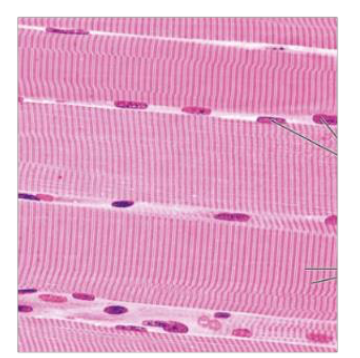
Identify the tissue type based off the image below
Muscle
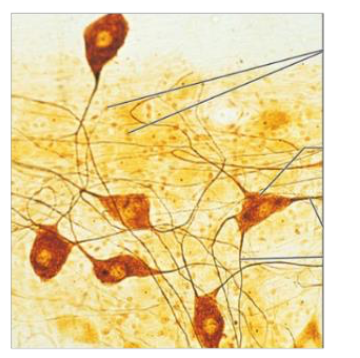
Identify the tissue type based off the image below
Nervous
The number of cell layers in epithelial tissue varies. In the space below, identify how many layers are found in each of these kinds of epithelial tissue:
1) Simple Epithelium:
2) Stratified Epithelium:
3) Pseudostratified epithelium:
1) 1 layer (+ basement)
2) 2+ layers (+ basement)
3) 1 layer (+ basement)
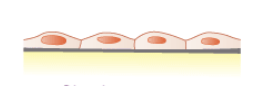
What is the cell shape and where is it typically found?
simple Squamous cells of the epithelial tissue
Found in the lining of blood vessels (endothelium), body cavities (mesothelium), the air sacs of the lungs (alveoli), and the kidney's filtration system (glomeruli)
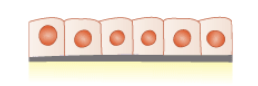
What is the cell shape and where is it typically found?
simple Cuboidal cells of the epithelial tissue
it lines the ducts of various glands (like salivary and mammary glands), the kidney tubules (including the proximal and distal convoluted tubules), the surface of ovaries, and within the thyroid gland (forming thyroid follicles)
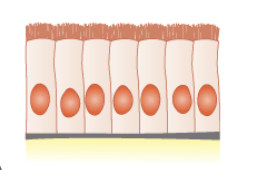
What is the cell shape and where is it typically found?
simple columnar cells of the epithelial tissue
What is the function of cillia and where is it typically found?
movement of substances across the epithelial surface
Epithelial tissue
What is the function of microvilli and where is it typically found?
increases surface area to enhance absorbtion
what type of tissue would be best at Protecting the body against abrasion (like the rubbing of your feet in your shoes)
stratified epithelium
what type of tissue would be best at Allowing substances (like gases) to diffuse through
simple epithelium
what type of cells would be best at moving substances (like dust & debris) out of the body
cells w/ cilia
what type of cells would be best at absorbing nutrients and water
cells with microvilli
Describe the layers and shape of the cell: simple cuboidal epithelium
1 layer (+ basement) and it is cube shaped
Describe the layers and shape of the cell: Stratified squamous epithelium
2+ layers (+ basement) and it is flat/scale like
Describe the layers and shape of the cell: pseudostratified columnar epithelium
1 layer (+ basement) and rectangle shape.
Appears to have more that one layer due to the varying positions of the nuclei
the type of cells found in keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Keratinocytes
the type of cells found in cartilage tissue
Chondrocytes
the type of cells (found in some epithelial tissue types) that make mucus
Goblet cells
the type of cells found in bone connective tissue
Ostecytes
the type of cells in blood connective tissue that initiate immune reactions
Leukocytes
the type of cells in blood connective tissue that transport oxygen
Erthrocytes
the type of cells found in adipose connective tissue
Adipocytes
the type of cells found in most connective tissues that make protein fibers
Fibroblasts
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Simple squamous Epithelium
Location: The alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs
Function: Gas exchange (diffusion)
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Simple cuboidal Epithelium
Location: Ducts of glands, kidney tubuels
Function: Secretion of products
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Non ciliated simple columnar epithelium
Location: GI tract (stomach, S and L intestine)
Function: Absorption of nutriens, secretion of enzymes/mucus
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Ciliated simple columnar epithelium
Location: Fallopian tubes, bronchiole, tubes of lungs
Functions: movmeent of mucus and foreign objects out of throat, movement of eggs to uterus
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Location: Trach, upper resp tract
Function: serection of mucus, propulsion of mucus and foreign objects of throat
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Non-keratinized squamous epithelium
Location: Lining of the mouth and espohagus
Function: protection against abrasion, water loss, and microbe invasion
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Location: The epidermis (superficial layer of the skin)
Function: Protection from abrasion, pathogens, UV radiation, microbes and water loss
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Stratifed cuboidal epithelium
Location: sweat glands
Functions: Secretion and abosrption
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Stratified columnar epithelium
Location: salivary glands
Function: secretion
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Transitional epithelium
Location: urinary bladder, ureters
Function: allowing organs to stretch
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Areolar loose connective tissue
Location: papillary layer of the dermis
Function: wraps and cushions organs
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Adipose loose connective tissue
Location: Subcutaneous layer of the skin (hypodermis)
Function: Energy reserve, prevents heat loss, supports and protects organs
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Reticular loose connective tissue
Location: lymph nodes, spleen
Functions: Filters and removes old blood cells or microbes
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Dense regular connective tissue
Location: Tendons and ligaments
Functions: Attachment and withstoodstands pulling
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Dense irregular connective tissue
Location: reticular layer of the dermis
Functions: provides strength in multiple directions
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
DEnse elastic connective tissue
Location: Walls of large arteries, trach and bronchial tubes
Function: returns organs to shape after stretching
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Hyaline cartilage (connective tissue)
Location: Embryoninc and fetal skeleton, at the end of long bones, costal cartilage
Function: provides smooth surface for movement, cushions and resists compression stress
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Fibrocartilage (connective tissue)
Location: Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis
Function: Shock absorption, joining structures together
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Elastic cartilage (connective tissue)
Location: external ear,epiglottis
Function: Maintains the shape of structures
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Compact bone connective tissue
Location: Outside of boney structures
Functions: supports and protects body organs, enables movement
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Spongy bone connective tissue
Location: Inside of boney structures
Functions: Stores bone marrow
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Blood connective tissue
Location: inside blood vessels
Function: transports resp gases, nutrients and wastes. Enables blood clotting
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Skeletal muscle tissue
Location: Skeletal muscles
Function: Motion, posture, heat production
The GI tract, urinary tract, and blood vessels are all types of?
Hollow internal organs
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Smooth muscle tissue
Location: Walls of hollow internal organs (GI tract, urinary tract, blood vessels, etc)
Function: movement of substances (like food, urine, blood, etc)
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Cardiac muscle tissue
Location: walls of the heart
Function: Pumps blood to the rest of the body
Where is this type of tissue found and what is its function:
Nervous tissue (there is 2)
Location: Neurons are located at the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Function: send electrical signals
Location of neuroglia: these are also located at the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Function: These provide structural support for neurons, protects and nourishes neurons
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Simple squamous
In the epithelium
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
simple cuboidal
Epithelium
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Non-ciliated simple columnar
Epithelium
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Ciliated simple columnar
Epithelium
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Ciliated psedostratified columnar
Epithelium
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Non-keratinized stratified squamous
epithelium
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Keratinized stratified squamous
Epithelium
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Stratified cuboidal
Epithelium
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Stratifed columnar
Epithelium
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Transitional
Epithelium
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Areolar loose
Connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Adipose loose
Connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Reticular loose
Connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Dense regular
Connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Dense irregular
connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Dense elastic
Connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Hyaline cartilage
Connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Fibrocartilage
Connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Elastic cartilage
Connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Compact bone
Connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Spongey bone
Connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Blood
connective tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Skeletal
Muscle tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Smooth
Muscle tissue
What type of major tissue type is this found at?:
Cardiac
Muscle tissue
Where are neurons and neuroglia typically found?
in the nervous tissue
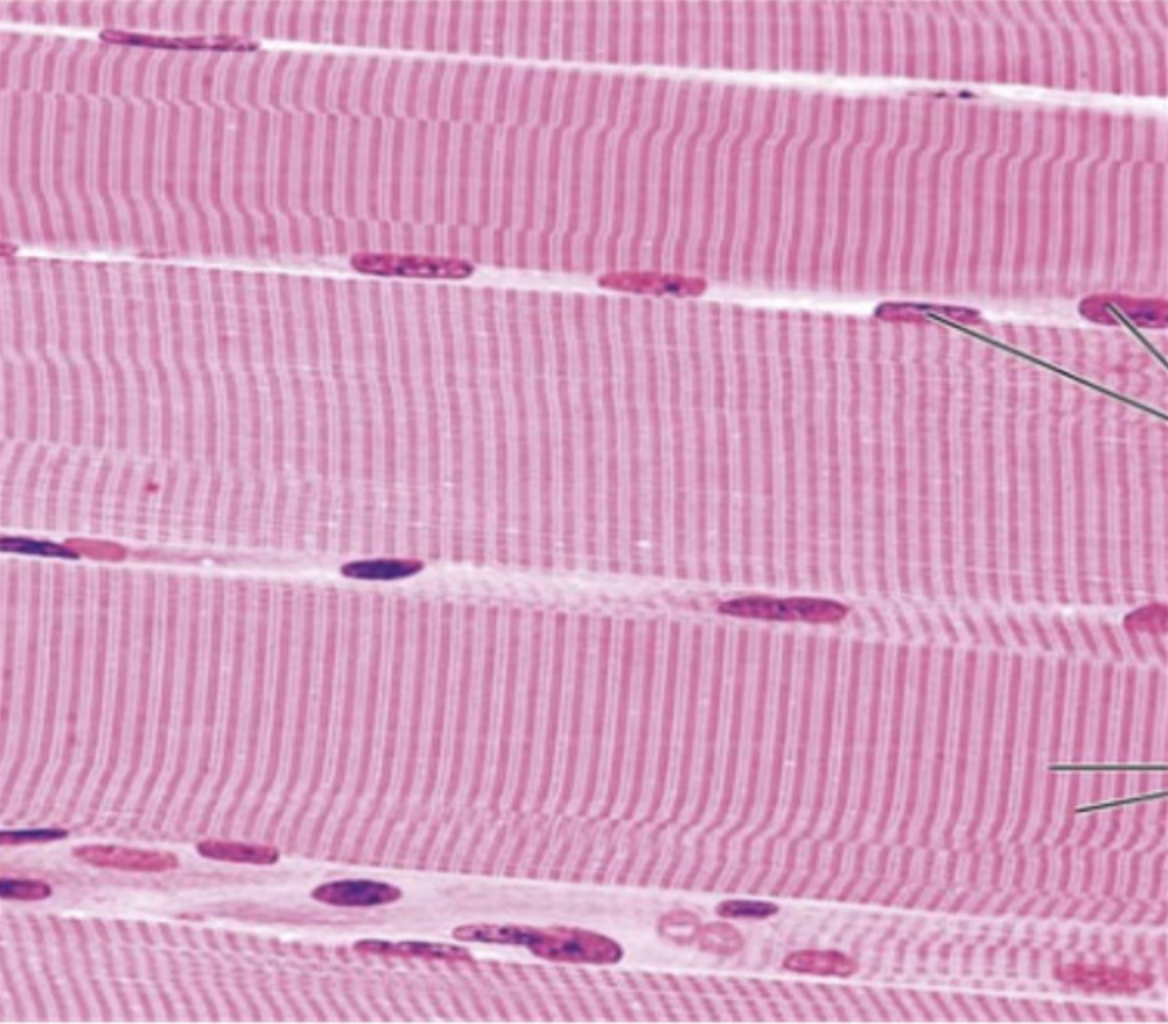
What type of tissue is this?
Skeletal muscle tissue
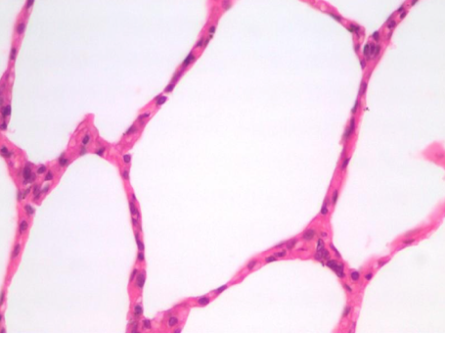
What type of tissue is this?
Simple squamous epithelium
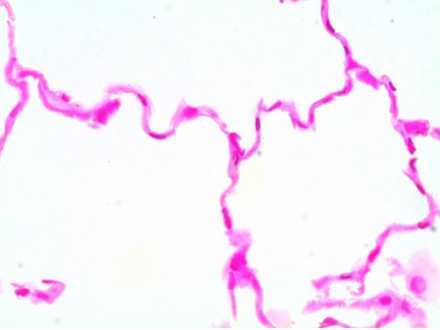
What type of tissue is this?
Simple squamous epithelium
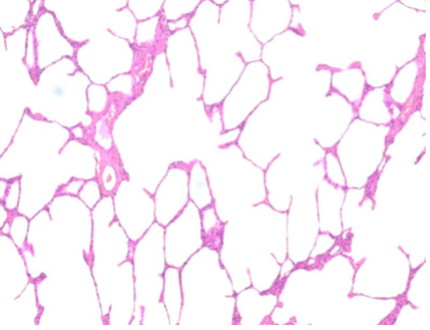
What type of tissue is this?
Simple squamous epithelium
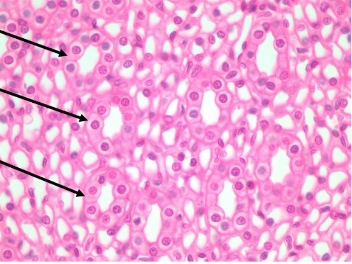
What type of tissue is this?
Simple cuboidal epithelium
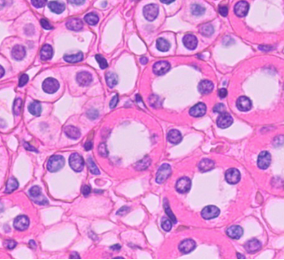
What type of tissue is this?
Simple cuboidal epithelium
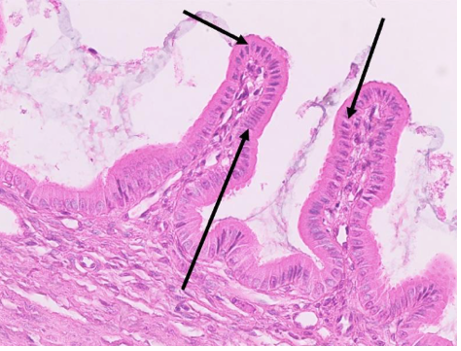
What type of tissue is this?
non-ciliated simple columnar epithelium
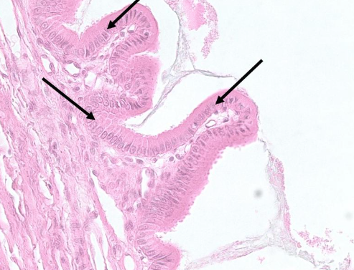
What type of tissue is this?
non-ciliated simple columnar epithelium
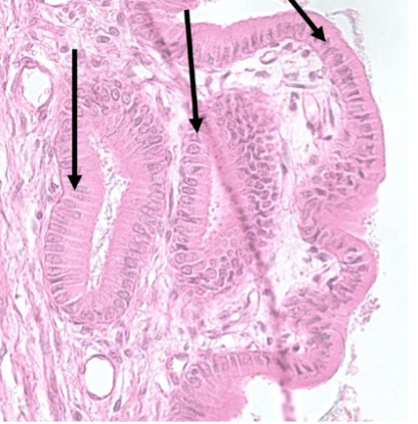
What type of tissue is this?
non-ciliated simple columnar epithelium
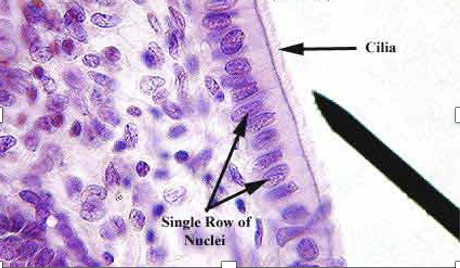
What type of tissue is this?
ciliated simple columnar epithelium
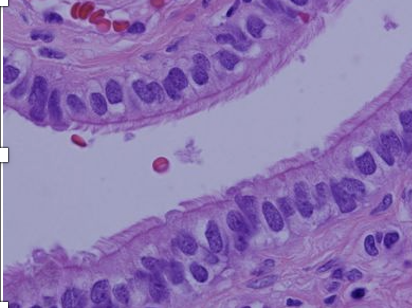
What type of tissue is this?
ciliated simple columnar epithelium
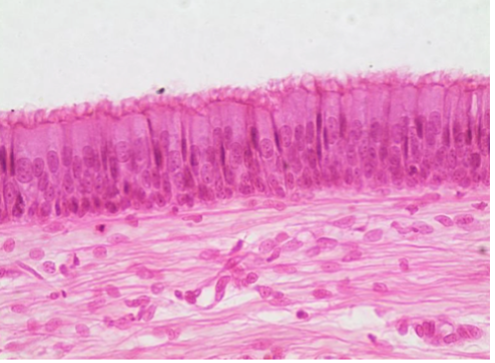
What type of tissue is this?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
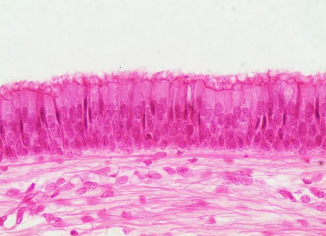
What type of tissue is this?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
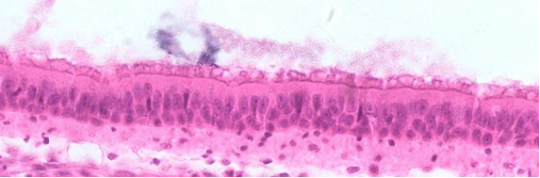
What type of tissue is this?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
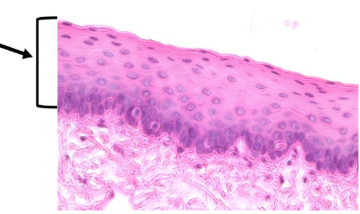
What type of tissue is this?
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium