Chapter 7 & 8: The skeletal system
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Components of the axial skeleton
skull
Vertebrae
Sternum
Ribs
Hyoid bone
Components of the appendicular skeleton
pectoral girdle
Upper limbs
Lower limb
Pelvic girdle
Appendicular skeleton - pectoral girdle
clavicle
Scapula
Appendicular skeleton - upper limbs
upper arm
Forearm
Wrist
Hand
Fingers
Appendicular skeleton - Pelvic girdle
Coxal bones
Appendicular skeleton - Lower limbs
upper leg
Lower leg
Ankle
Foot
Toes
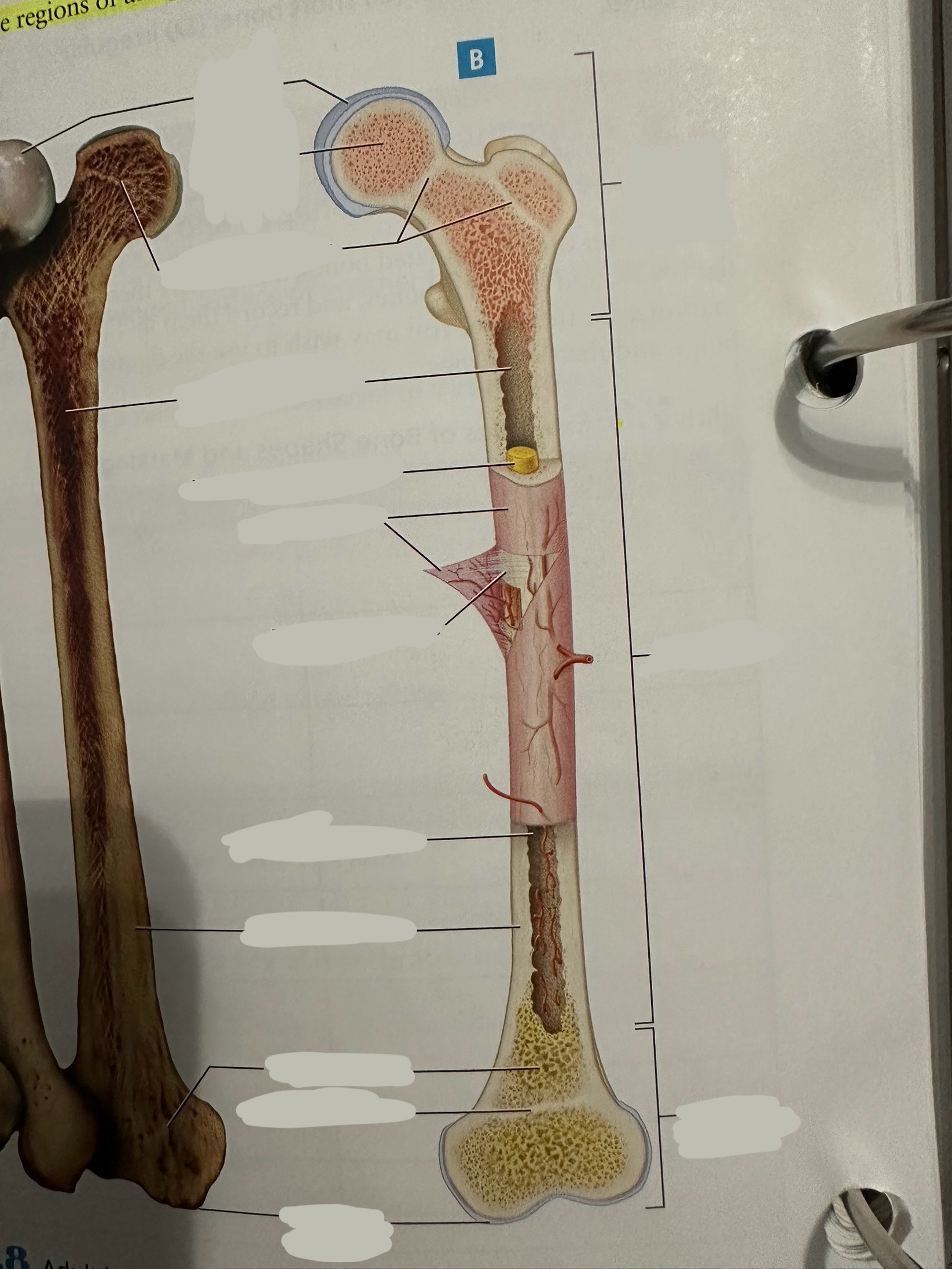
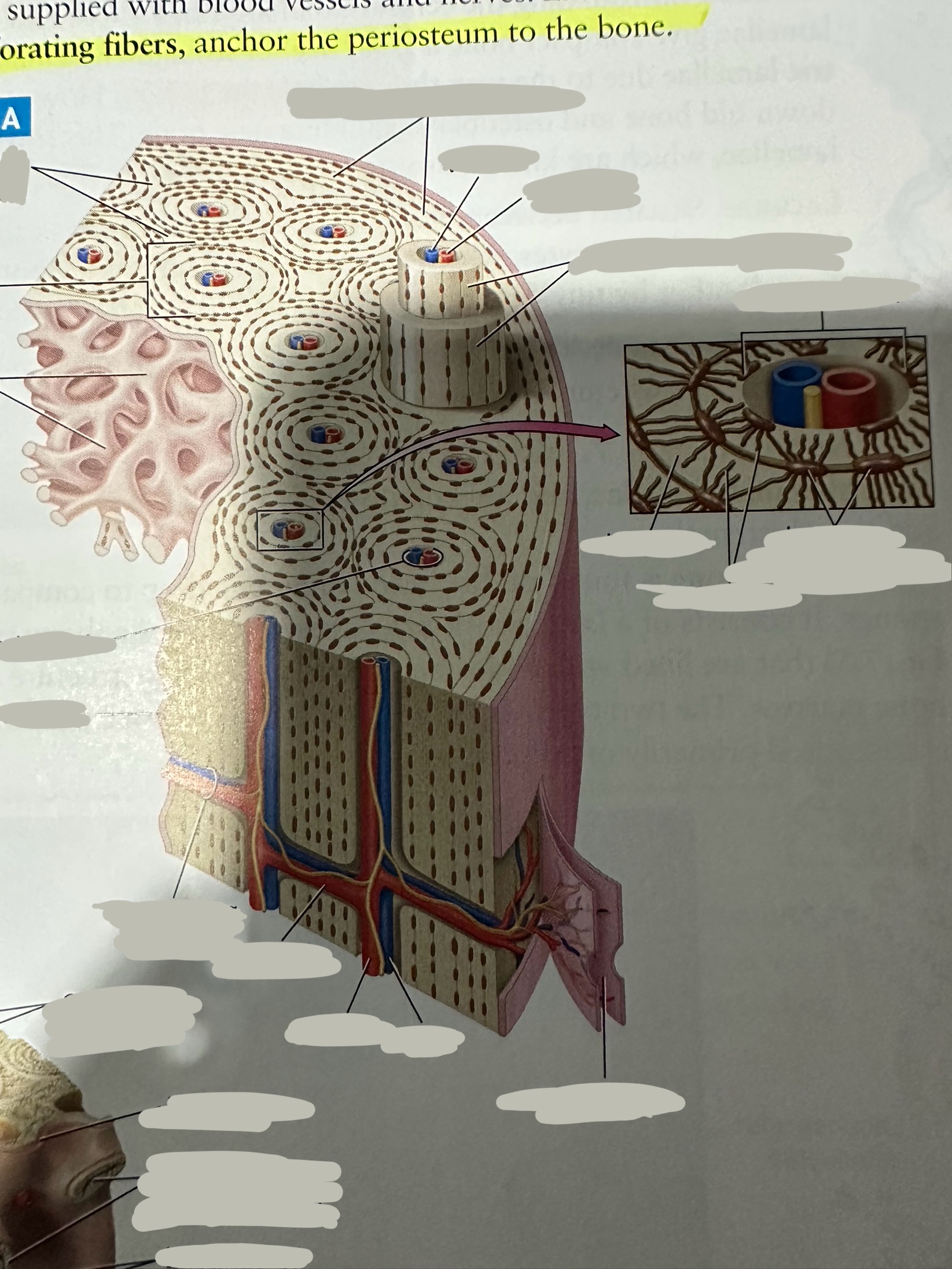
Periosteum
The most superficial tissue of the bone
growth, repair, and protection.
provides a source of osteoblasts for bone formation, supports fracture healing, and nourishes the bone tissue through its rich vascular network.
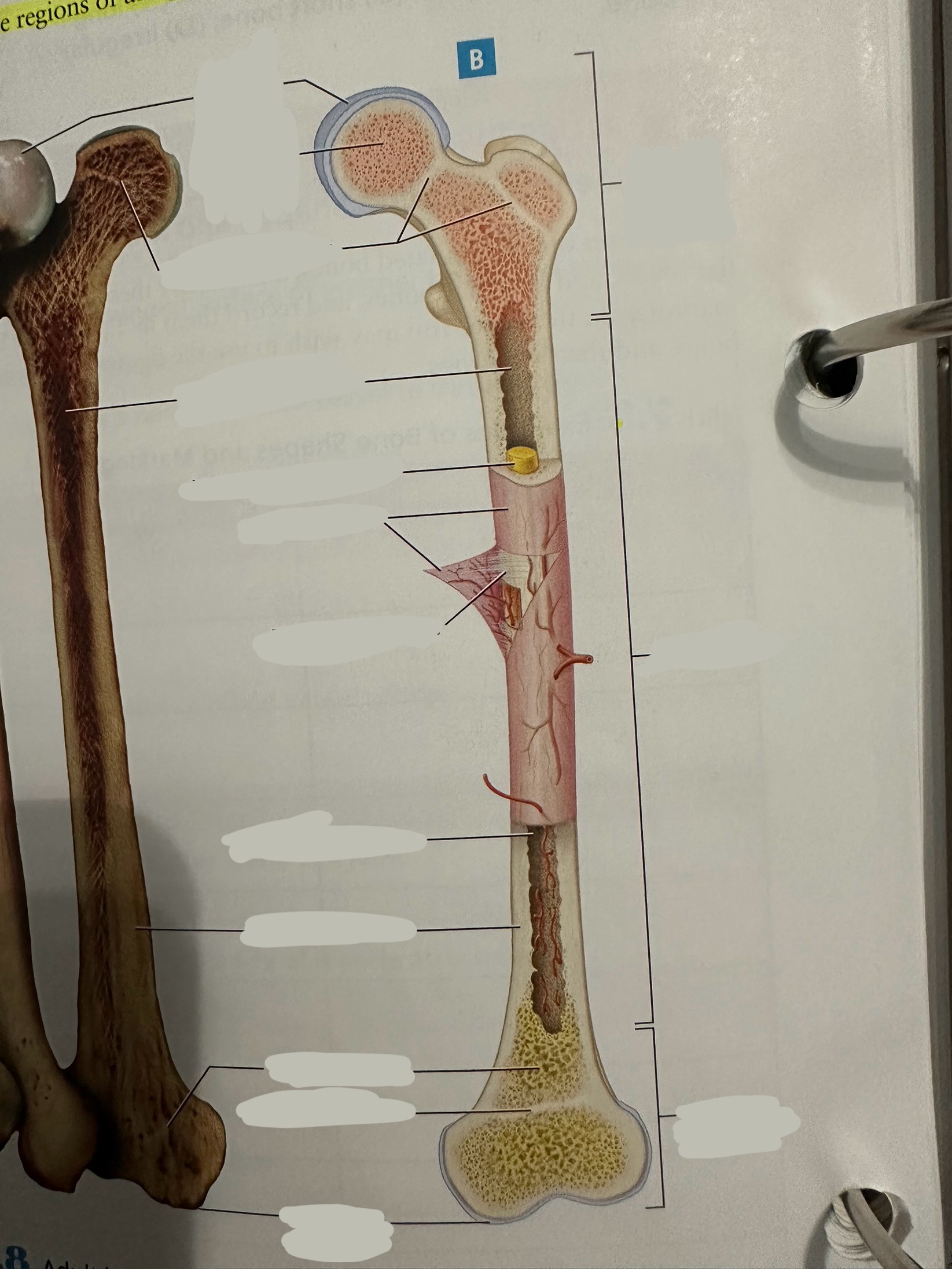
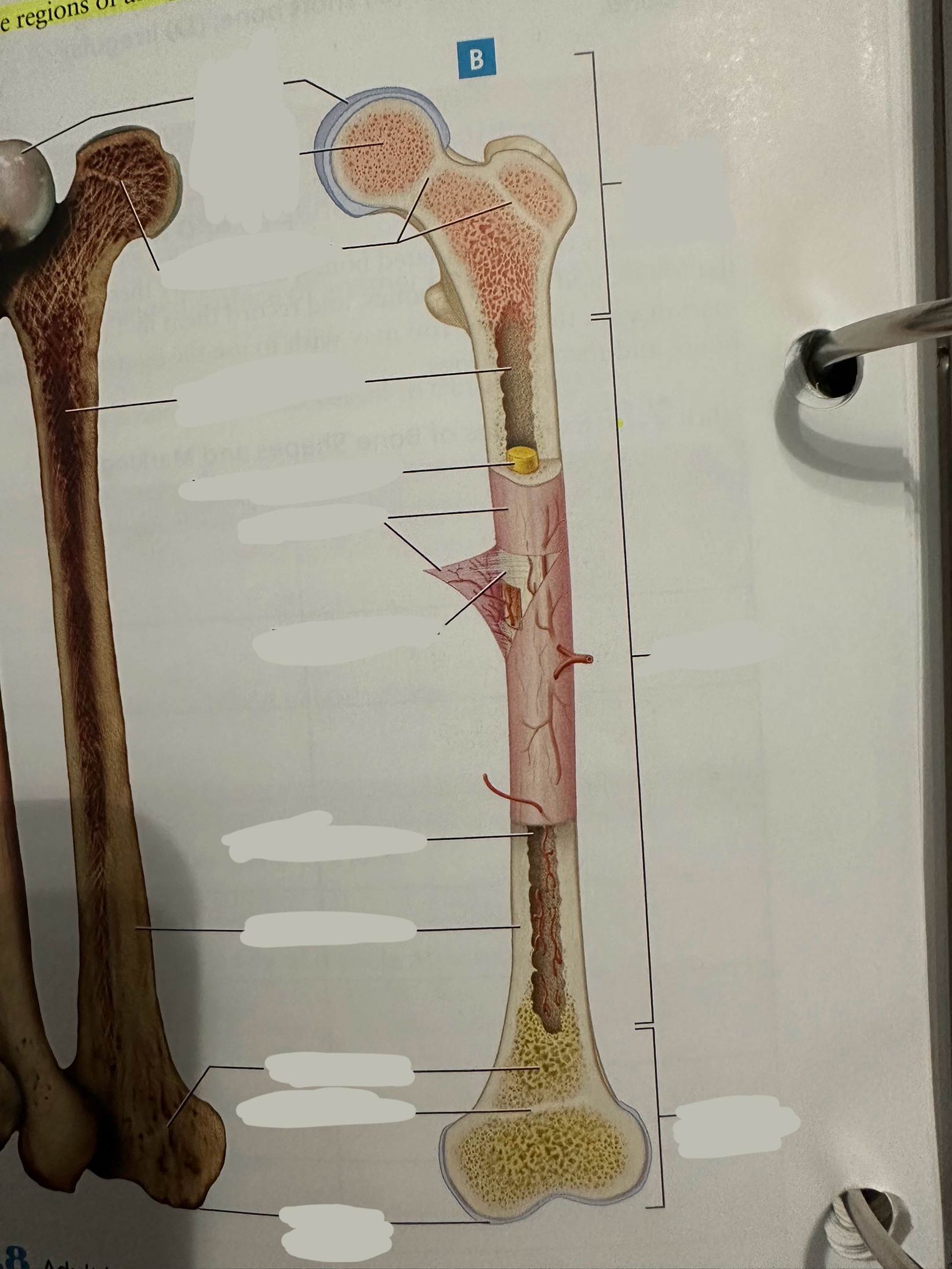
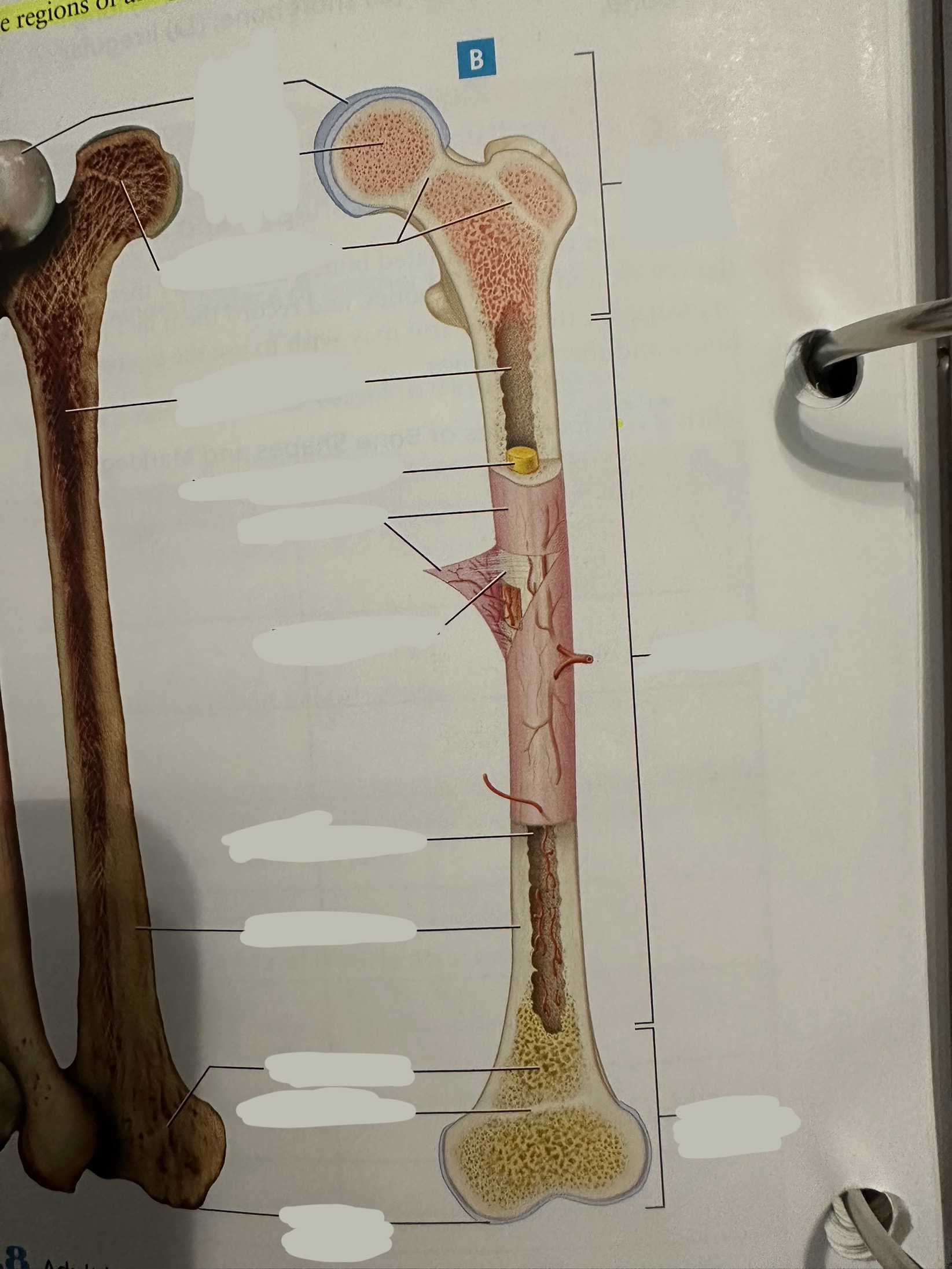
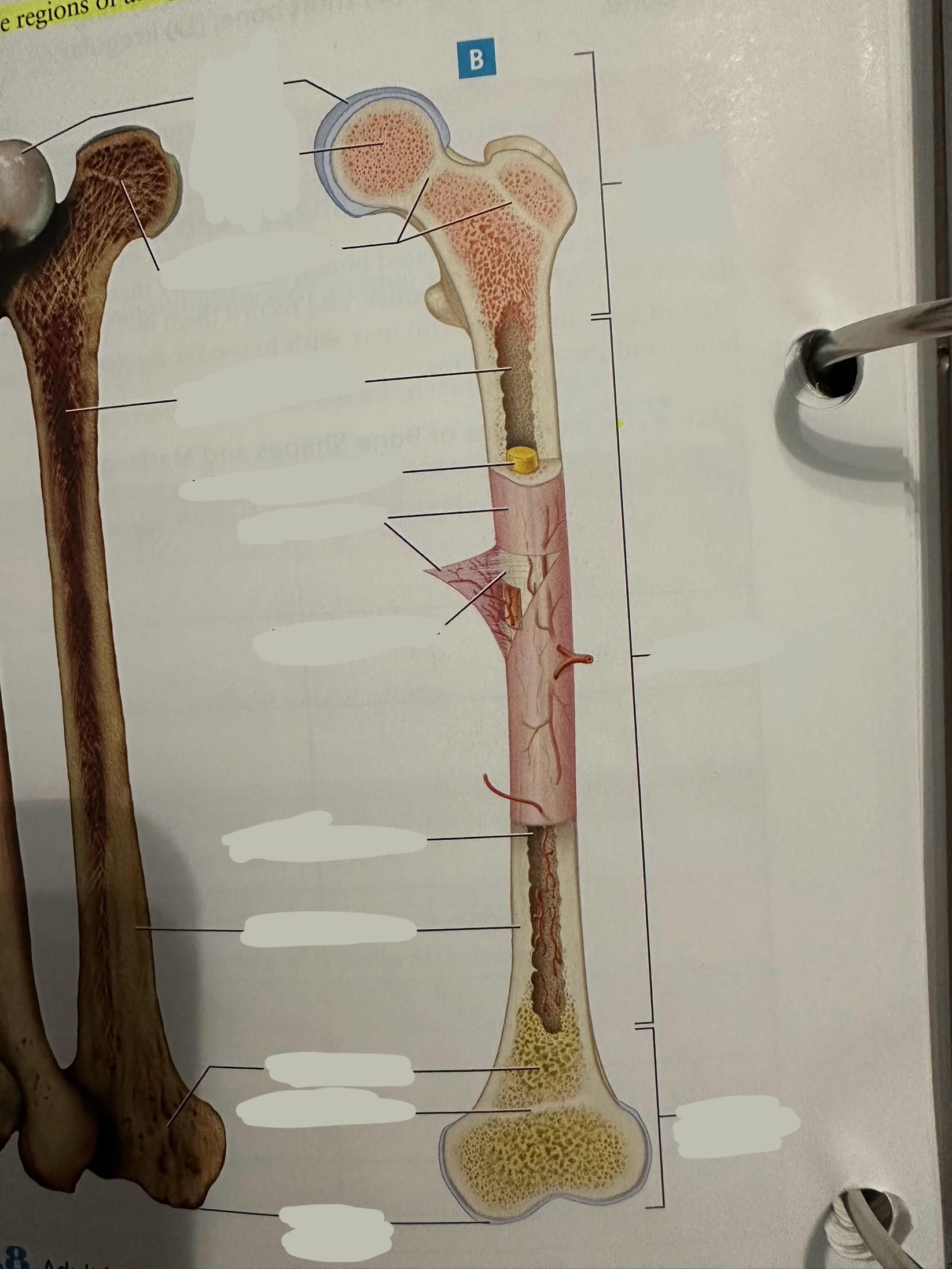
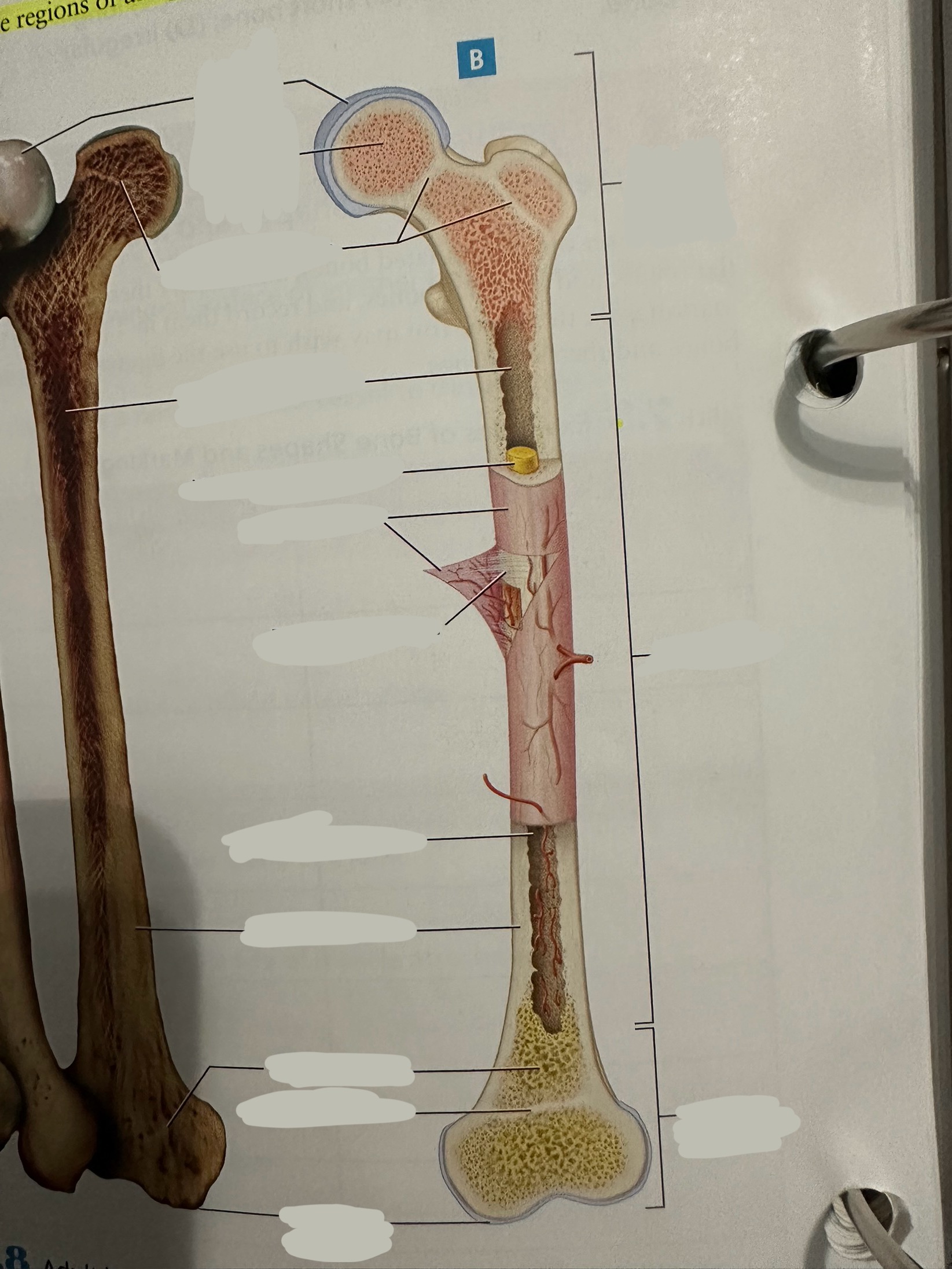
Diaphysis
The shaft of the long bone
provide structural support, strength, and allow for movement. It is primarily made of compact bone and houses the medullary cavity, which contains bone marrow
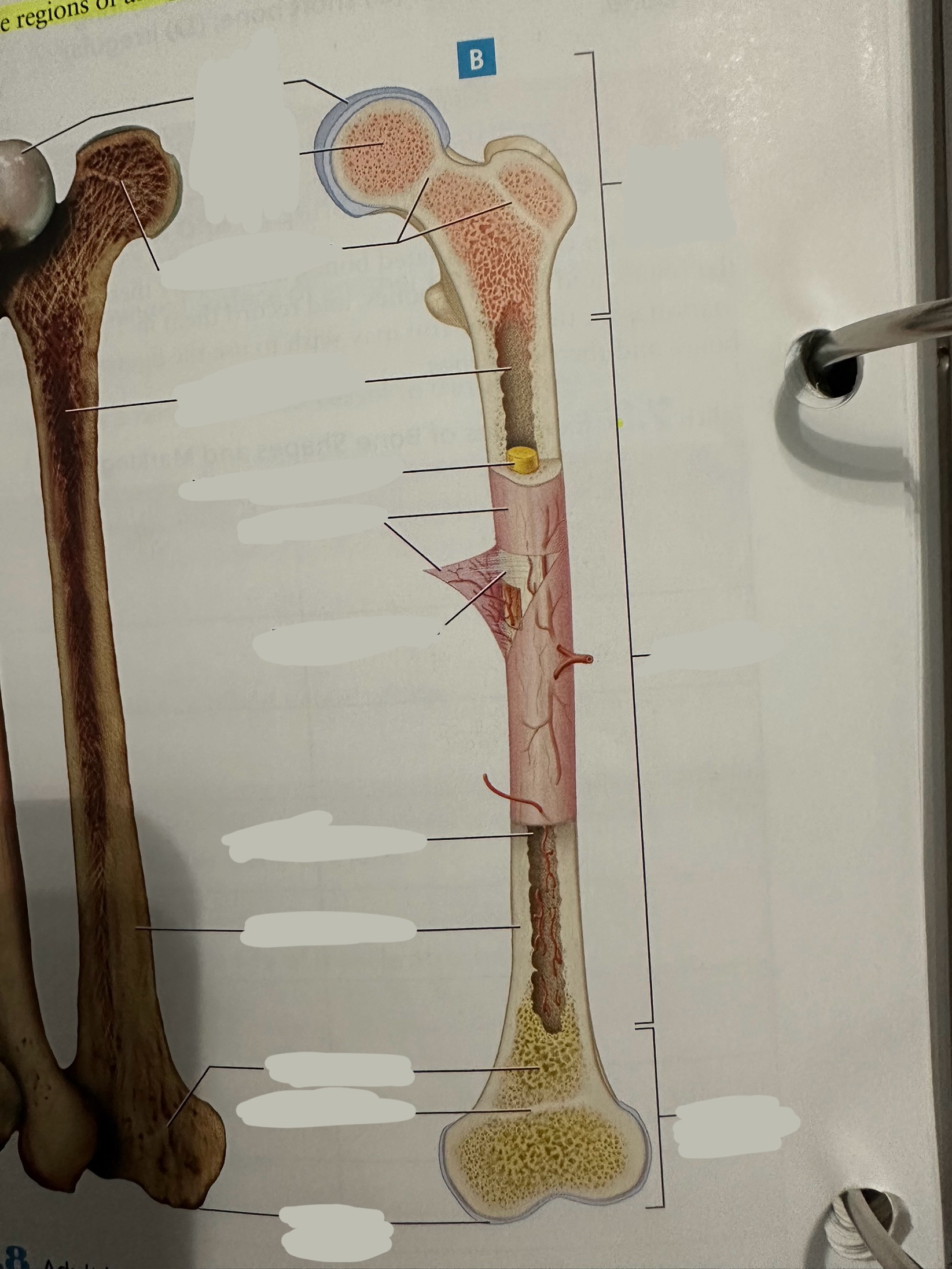
Diaphysis - medullary/marrow cavity
Hollow area that has sparse trabeculae and generally is filled with yellow bone marrow in adult bones
houses bone marrow, which plays a crucial role in blood cell formation and fat storage.
Diaphysis - Yellow marrow
composed primarily of adipose tissue
Fat storage
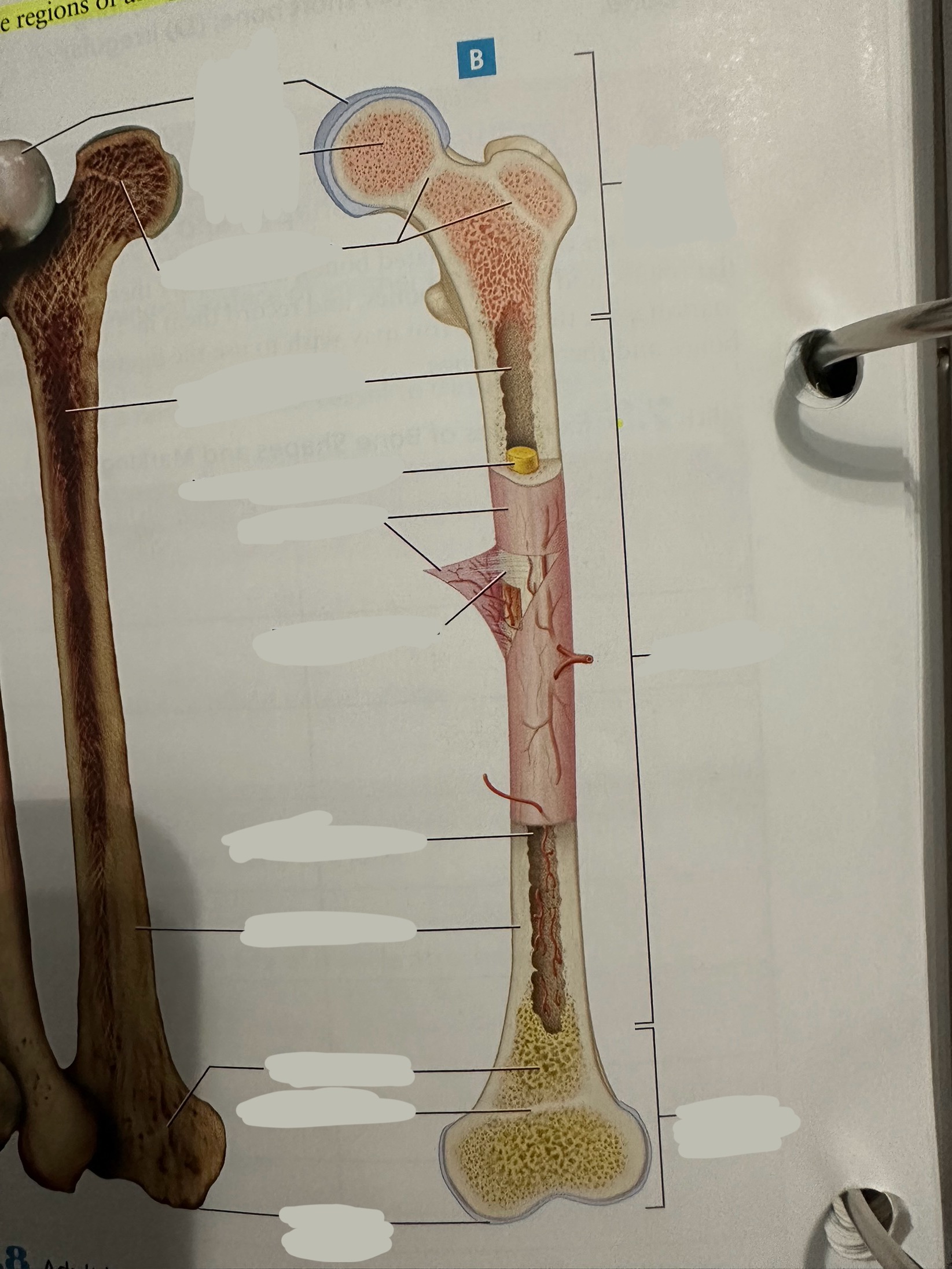
Epiphysis
Contains a shell of compact bone surrounding the inner spongy bone
Ends covered with articular cartilage
primarily functions in joint formation, weight distribution, and bone growth
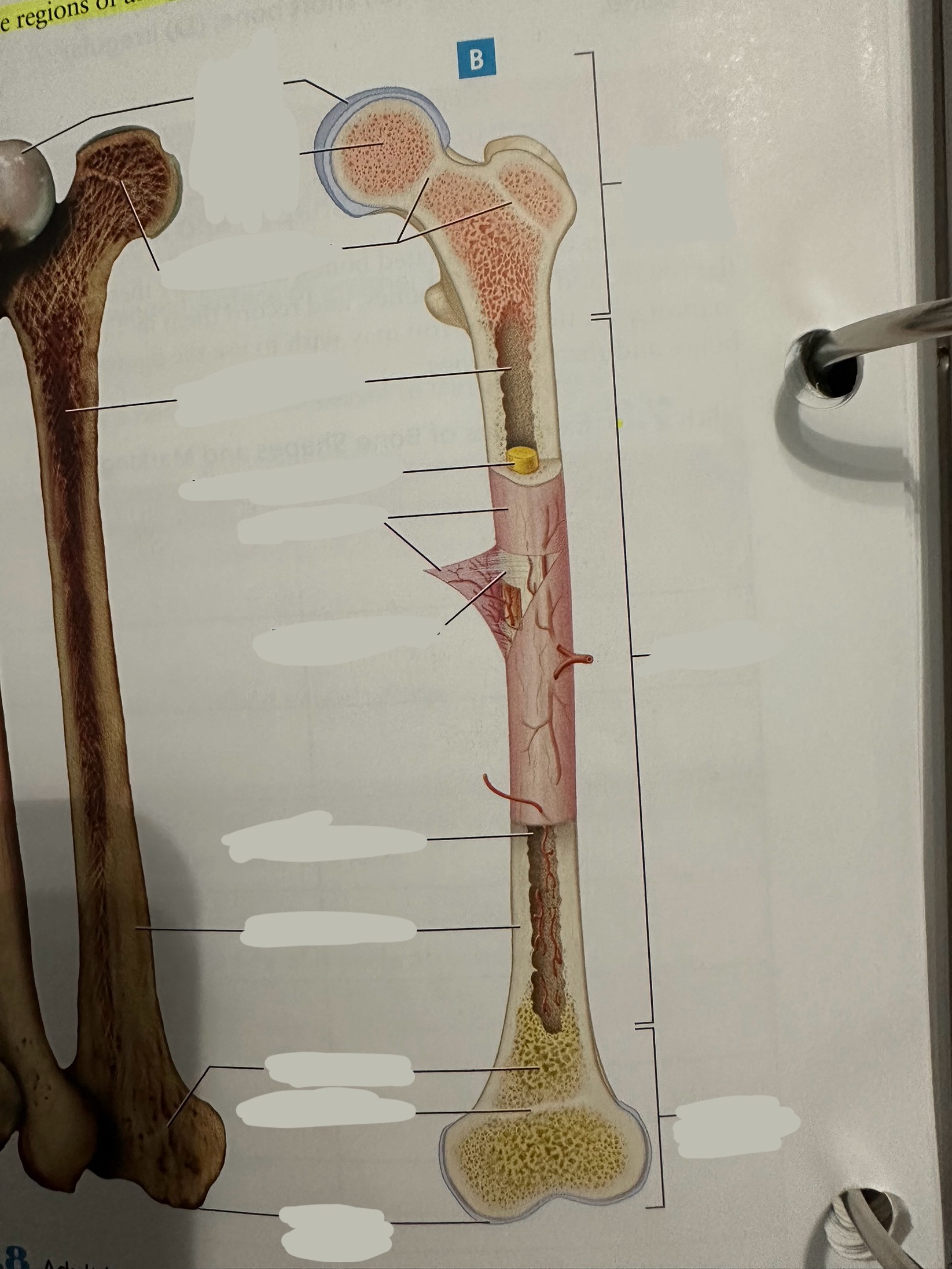
Epiphysis - proximal epiphysis
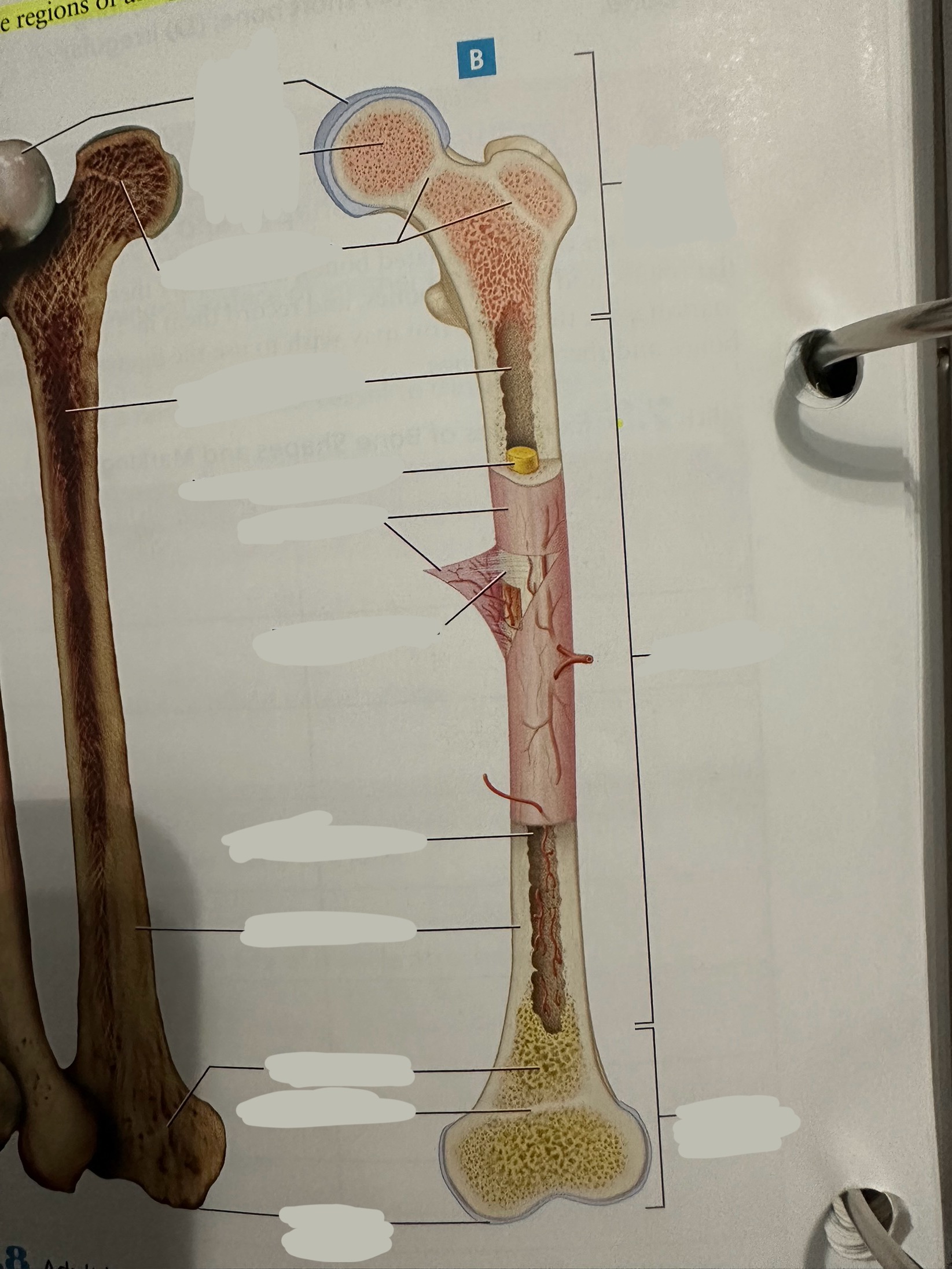
Epiphysis - distal epiphysis
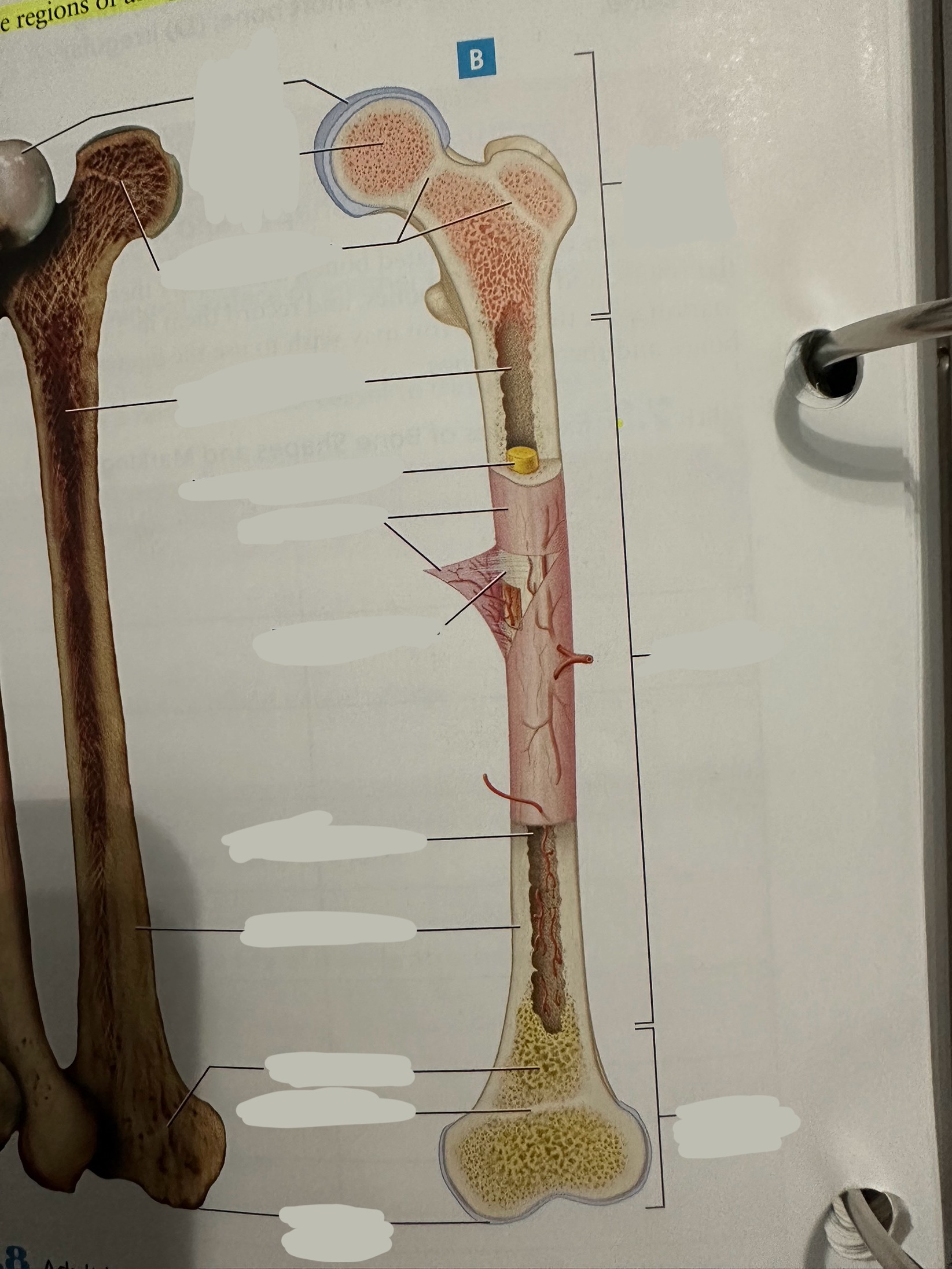
Epiphysis - epiphyseal plate/line
Plate - band of hyaline cartilage from which long bones grow in length in children and young adults
Line - thin calcified line that is a remnant of the epiphyseal plate
Spongy bone
Deep to compact bone
provides structural support and lightness to bones while also housing bone marrow, where blood cells are produced.
Compact bone
Hard, dense bone tissue found immediately deep to the periosteum
provides strength, support, and protection to bones.
Articular cartilage
Allows two bones in a joint to move around one another with minimal friction
Endosteum
thin layer of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of bones
contains osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and osteoclasts (bone-resorbing cells). These cells work together to maintain the balance of bone formation and resorption, ensuring that bones are strong and adaptable.
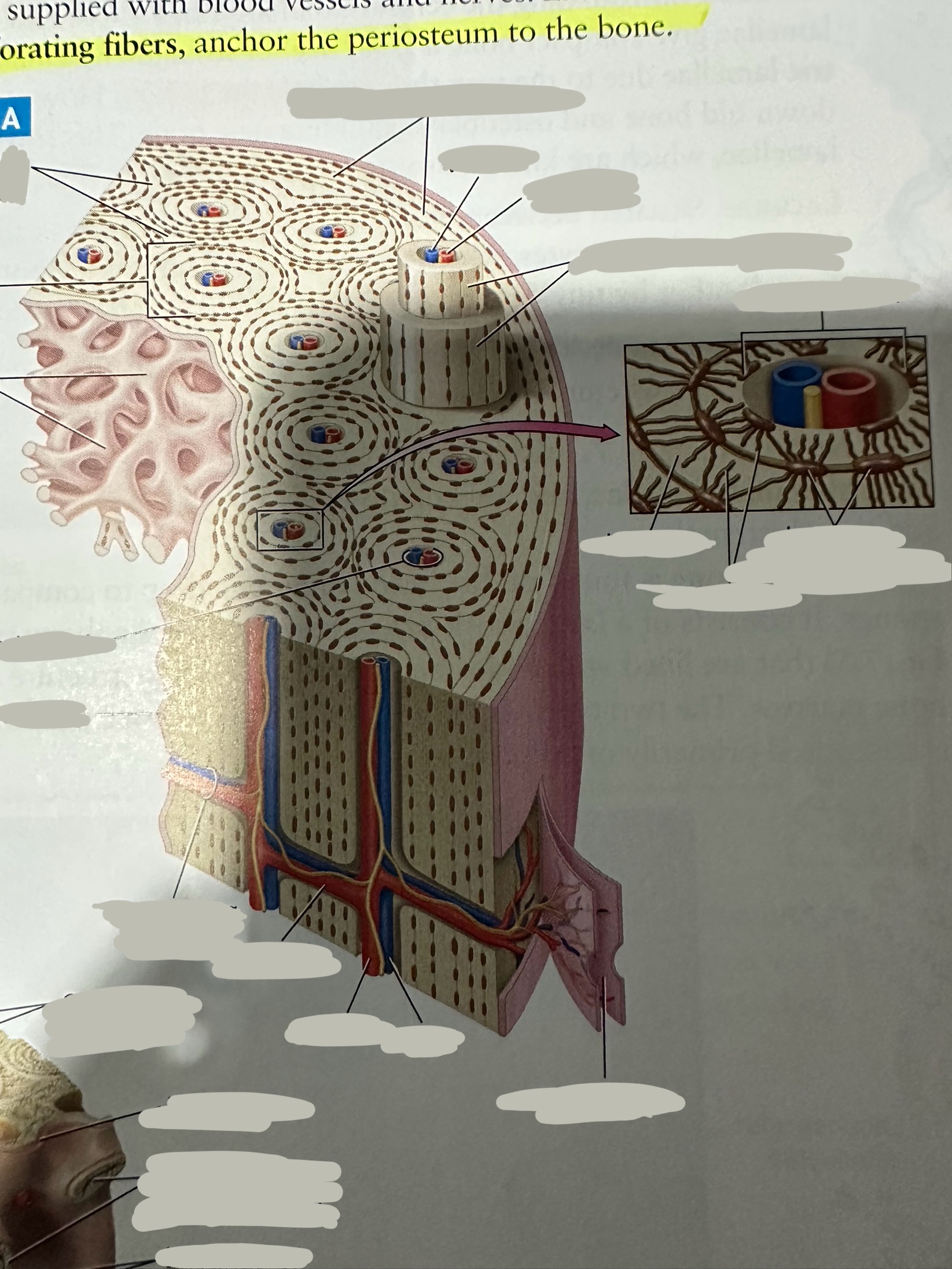

Osteon
Repeating, densely packed subunits
the strength of the bone, the influx of nutrients into the bone, and waste removal from the bone
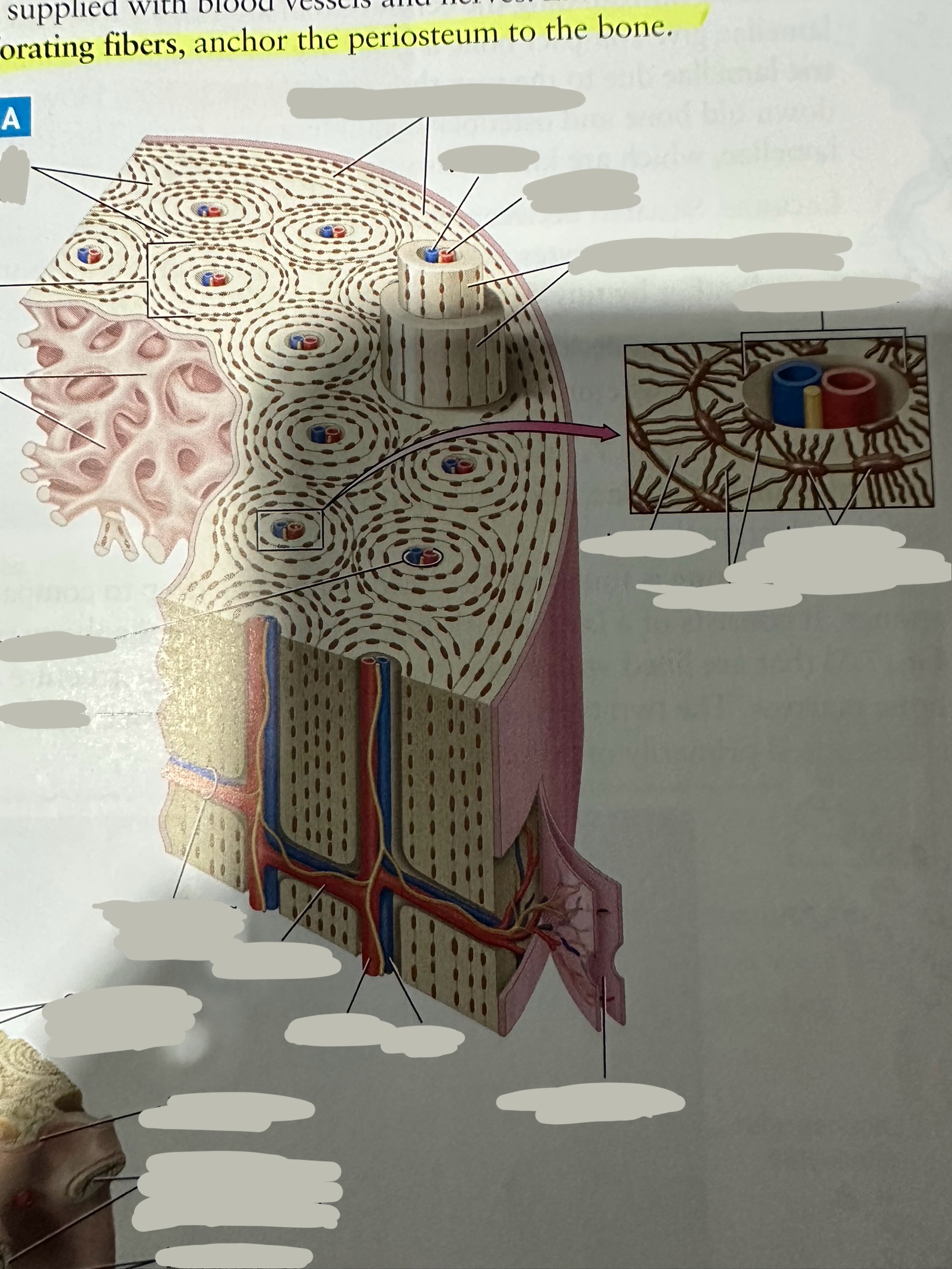

Lamellae
Rings of bone ECM surrounding the central canal
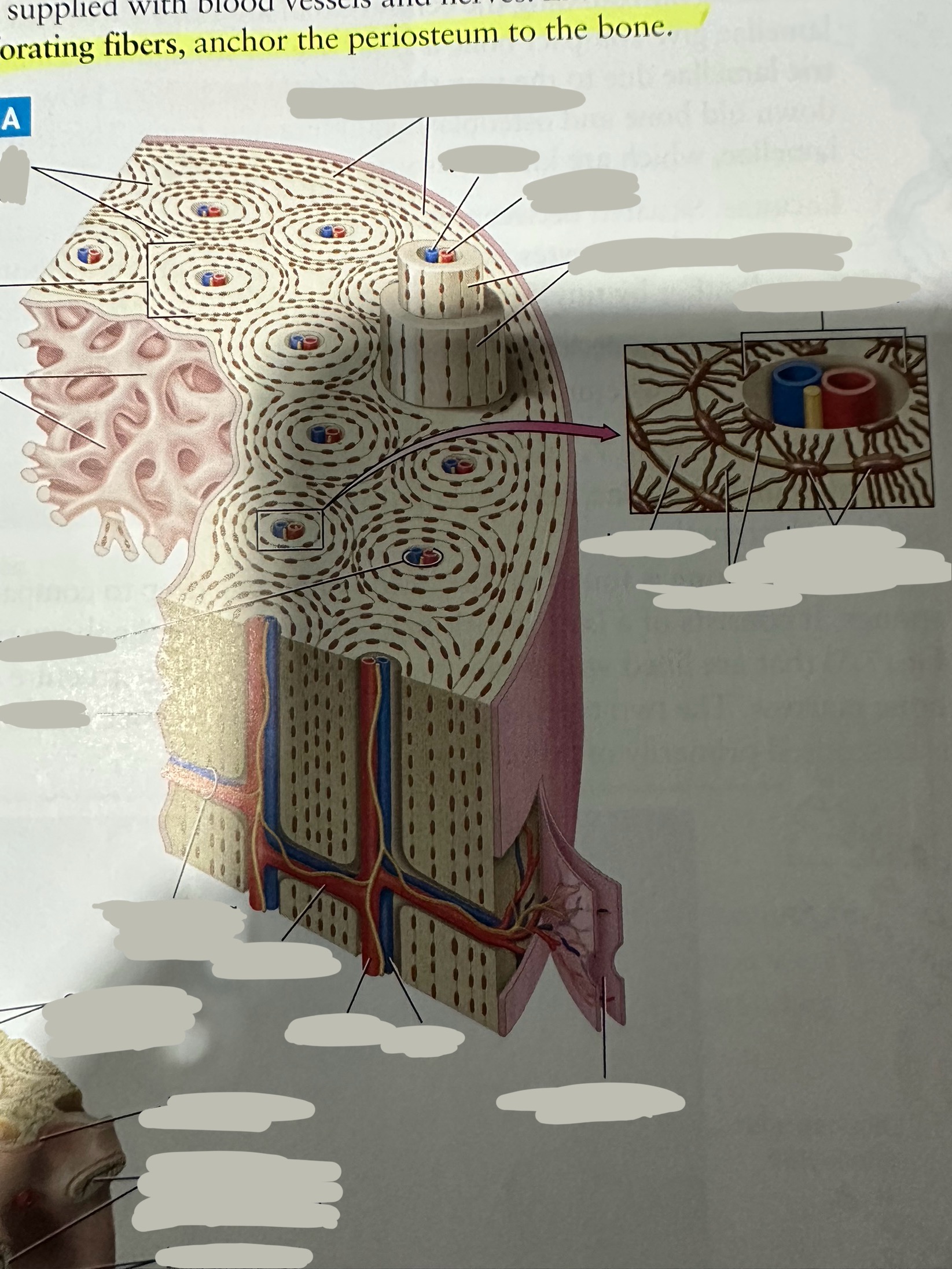

Concentric lamellae
The lamellae in ostensibly
Encircle the osteon
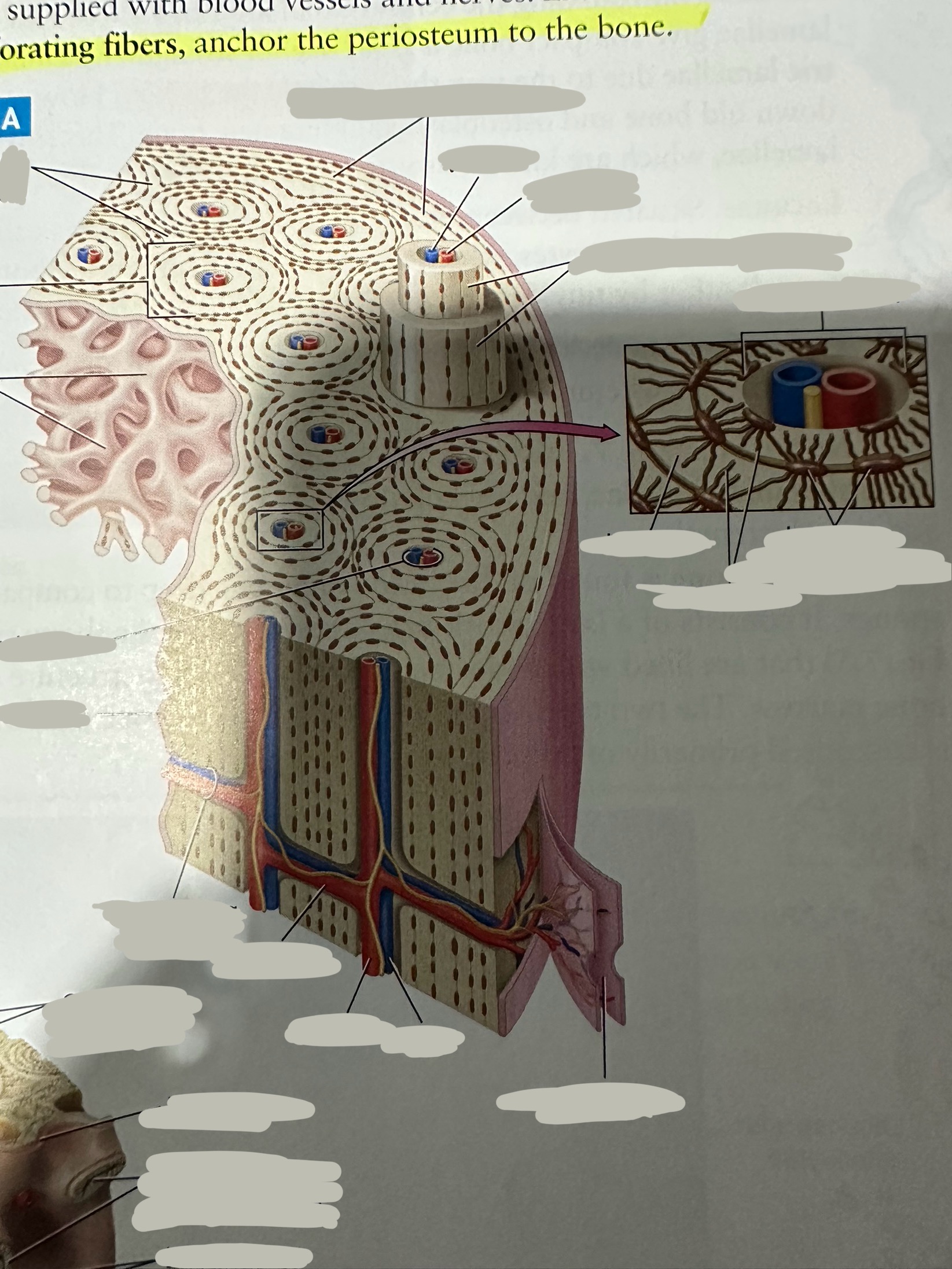

Circumferential lamellae
Lining the outside of the compact bone laid down by the osteoblasts in the periosteum and the endosteum
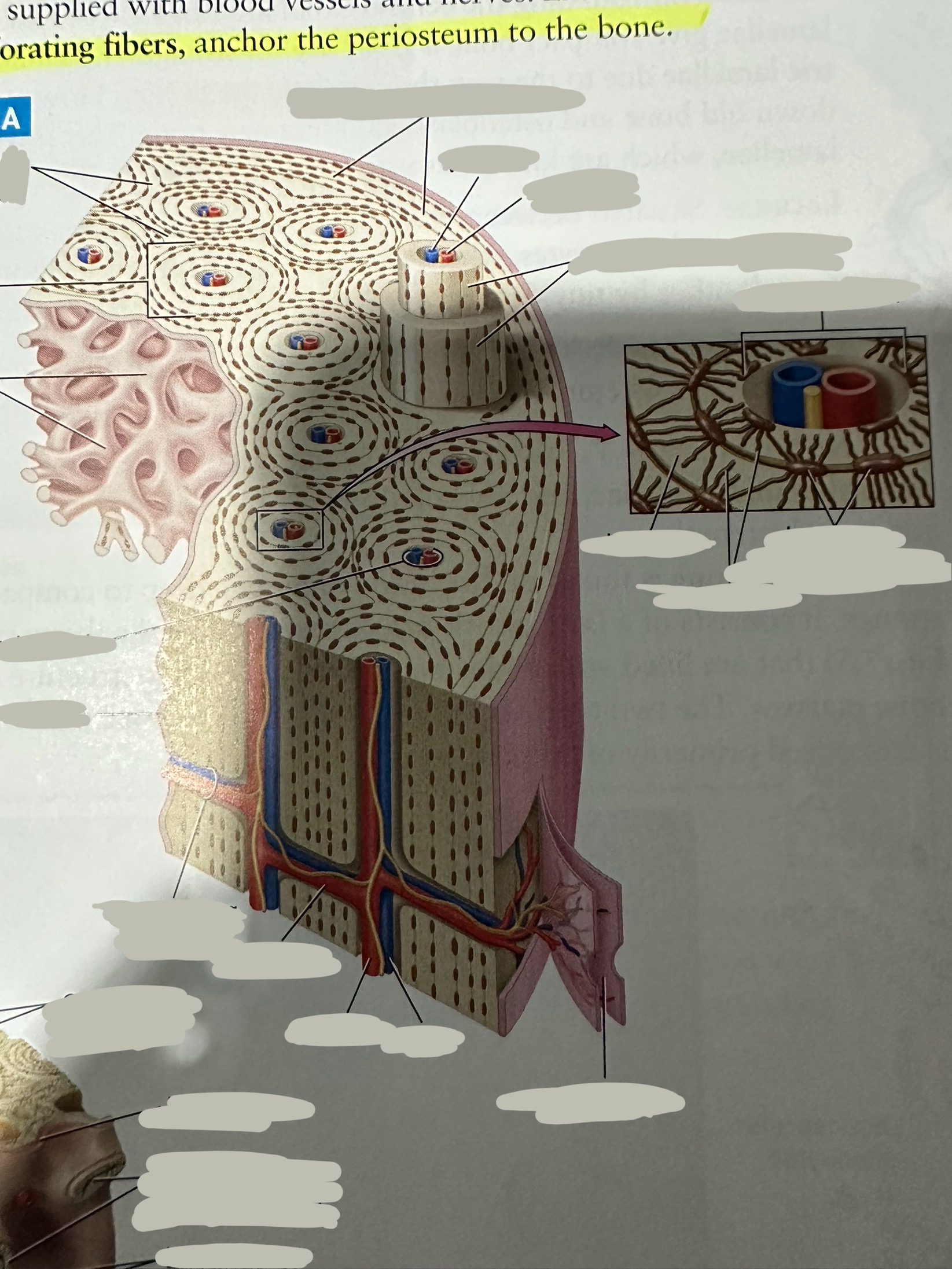

Interstitial lamellae
Old lamellae located between osteons
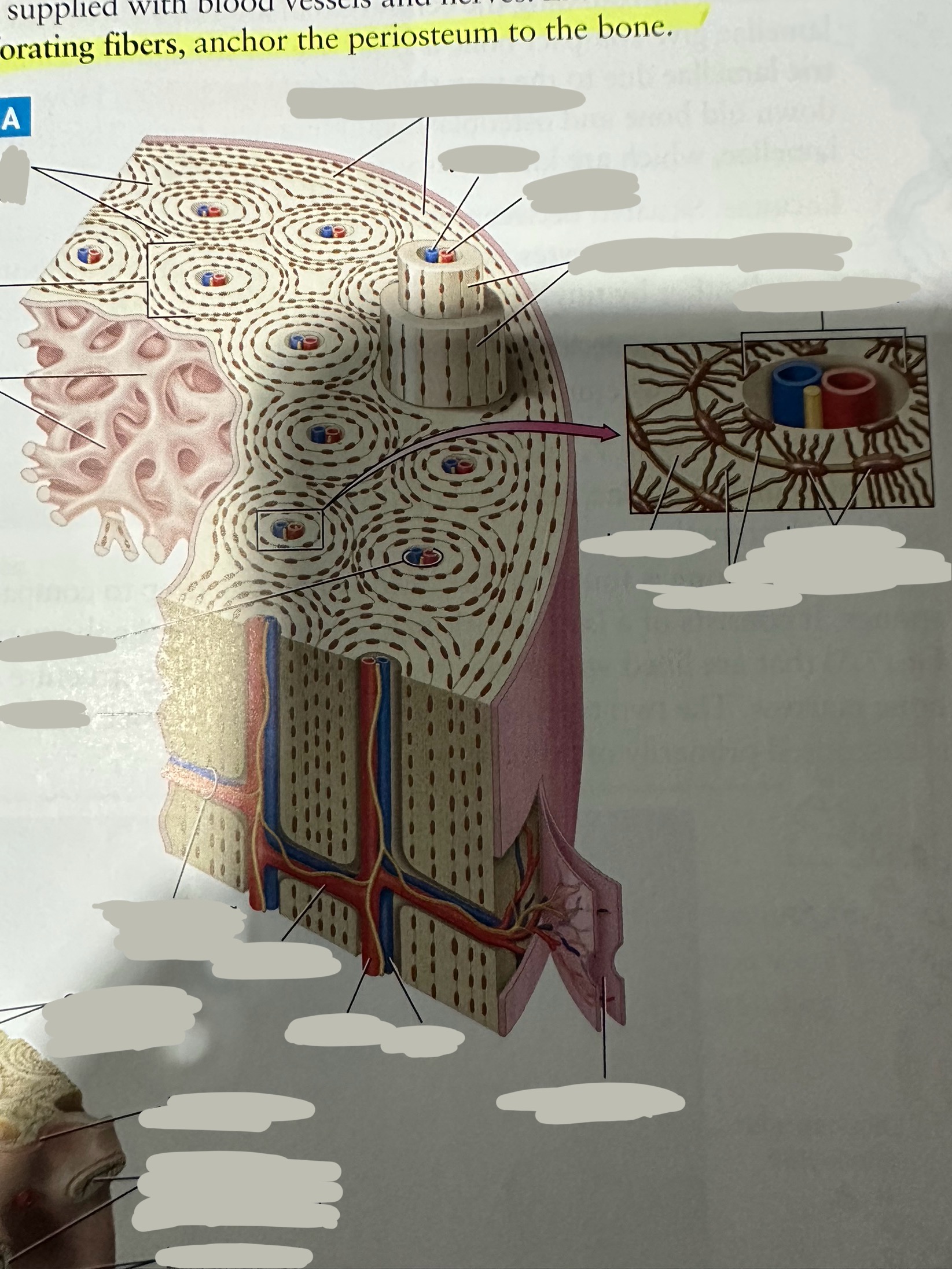

Lacunae
Small cavities situated between the lamellae
; contain mature osteocytes
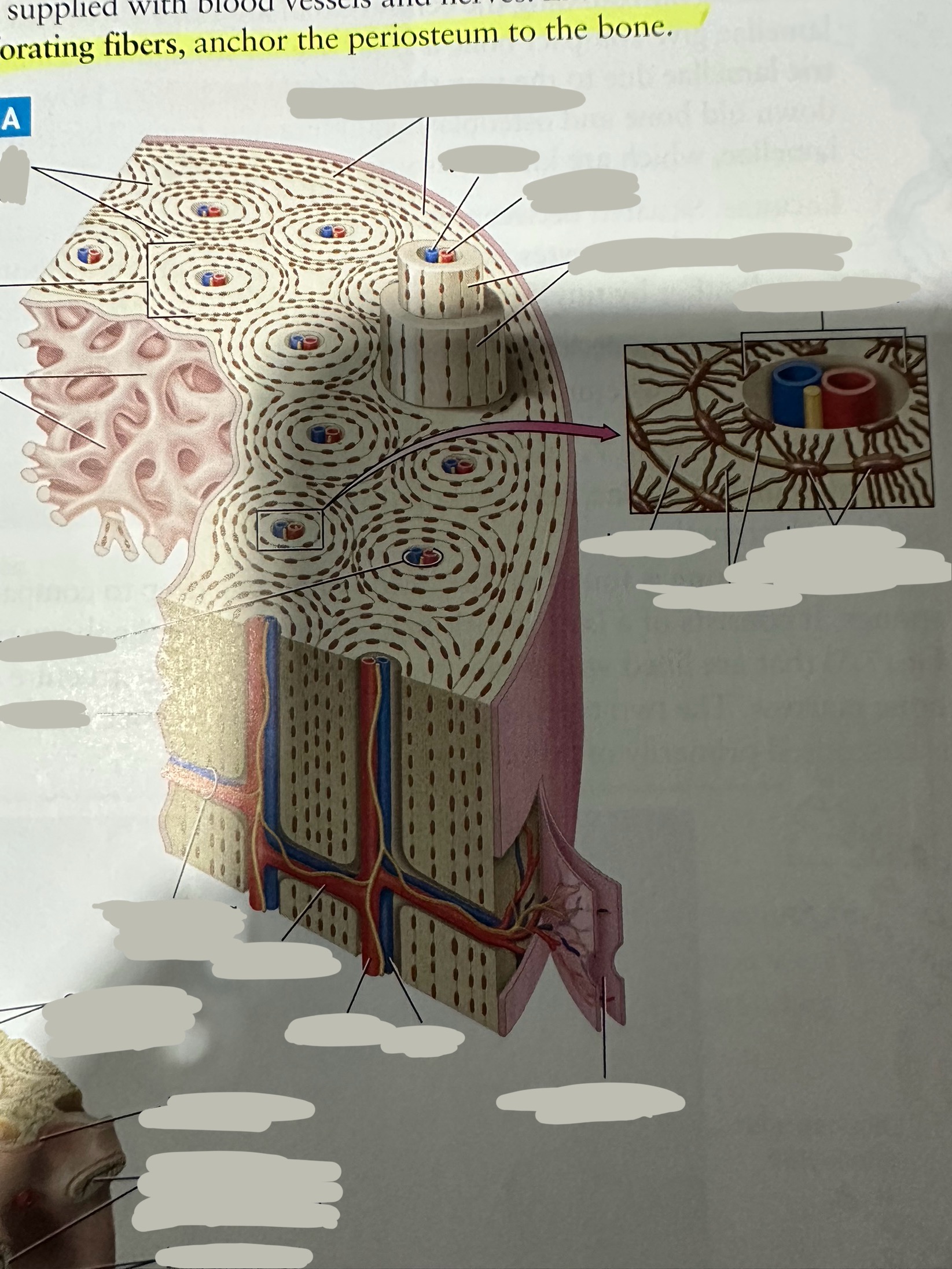

Osteocyte
Maintain and monitor bone ECM; located in lacunae
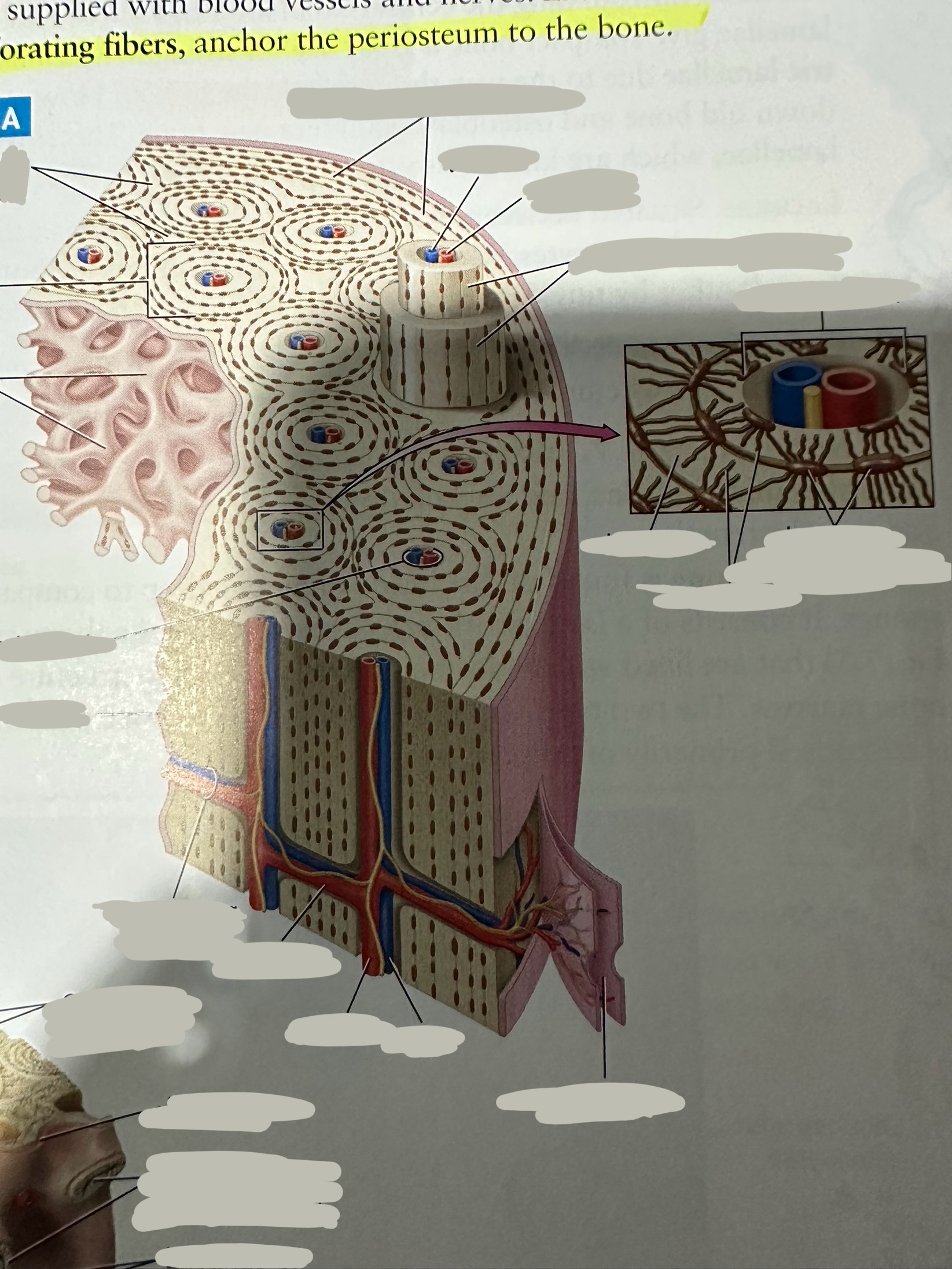

Canaliculi
Connect neighboring lacunae and osteocytes to each other
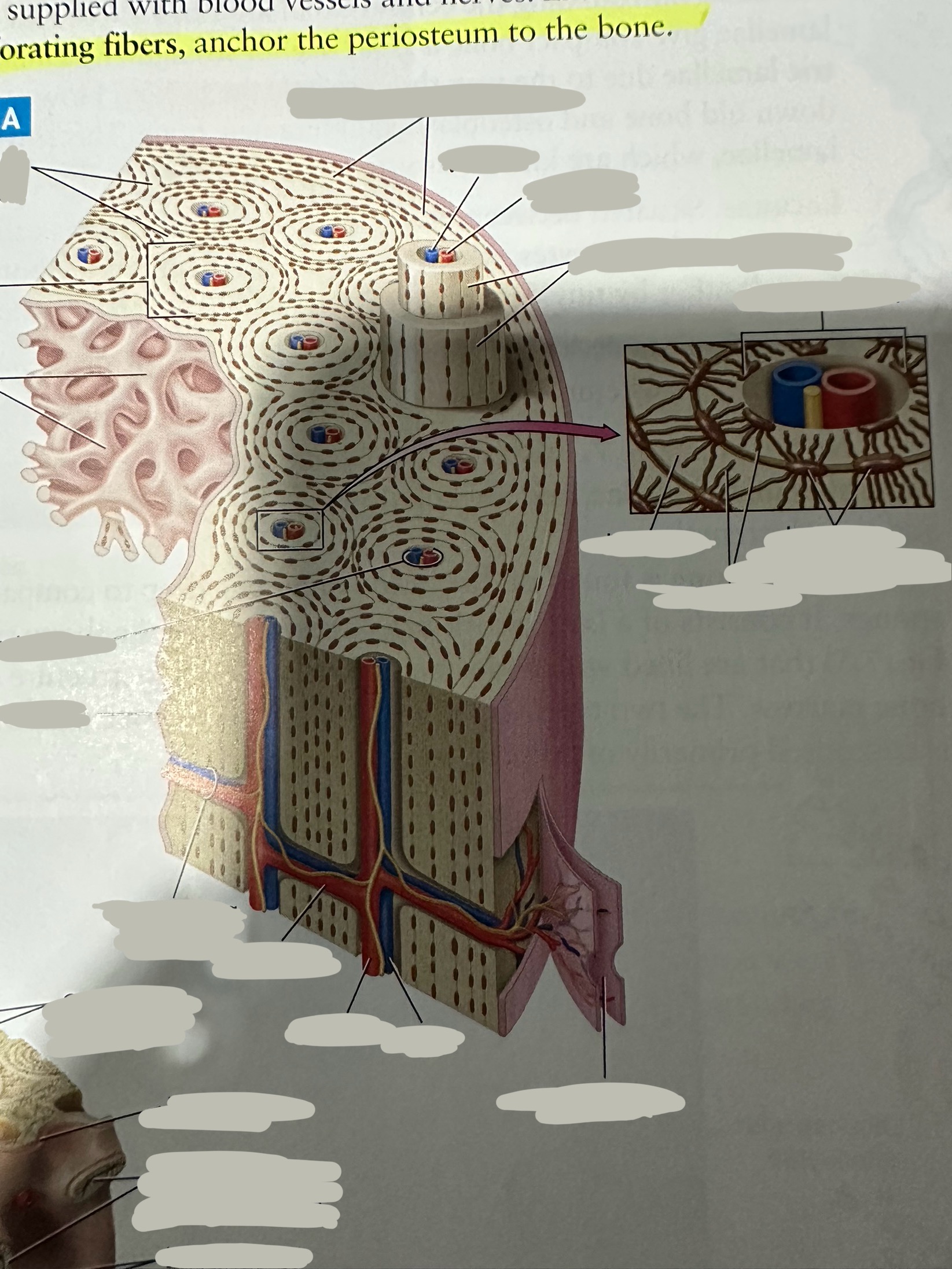

Central canal
Running down the center of each osteon
Contains blood vessels and nerves lined with endosteum
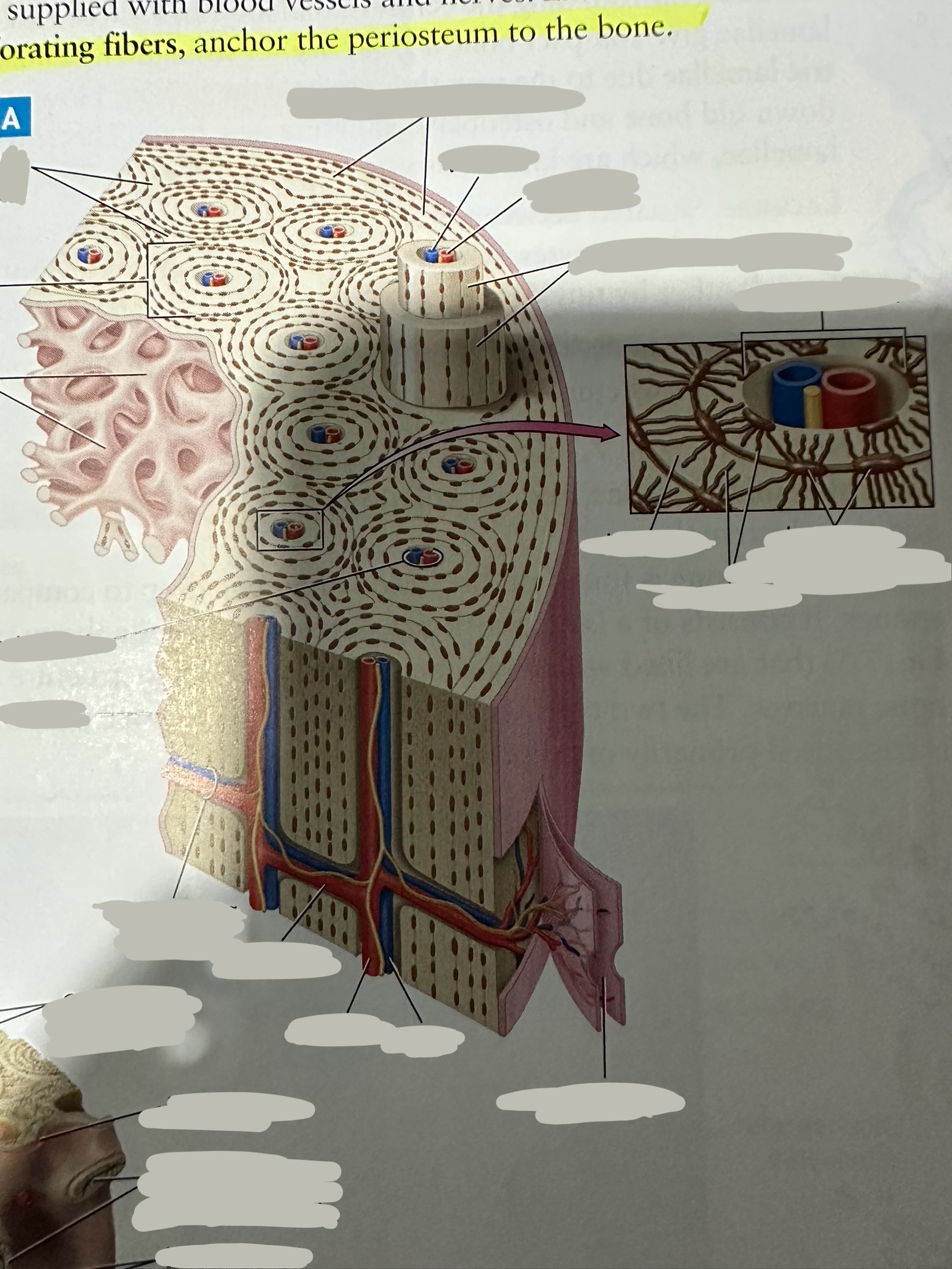

Perforating canal
Run perpendicular to lamellae and carry blood vessels deep into the bone from the periosteum
Lined by the endosteum

Depressions
Provide pathways along which blood vessels and nerves travel, or allow two bones to come together to form a joint
Openings
House and protect structures such as blood vessels and special sensory organs
Projections
Provide points of attachment for ligaments and tendons
Long bone
Longer than they are wide
upper and lower limbs
Flat bones
Flat
ribs, sternum, hip bones, and certain skull bones
Short bones
About as long as they are wide
wrist and ankle
Irregular bones
Shape doesn’t fit into any of the other classes
vertebrae, sacrum, and certain bones of the skulls (sphenoid)
Sesamoid hones
Roughly oval shaped bones within tendons
patella
Suturas bones
Small bones located between the flat bones of the skull
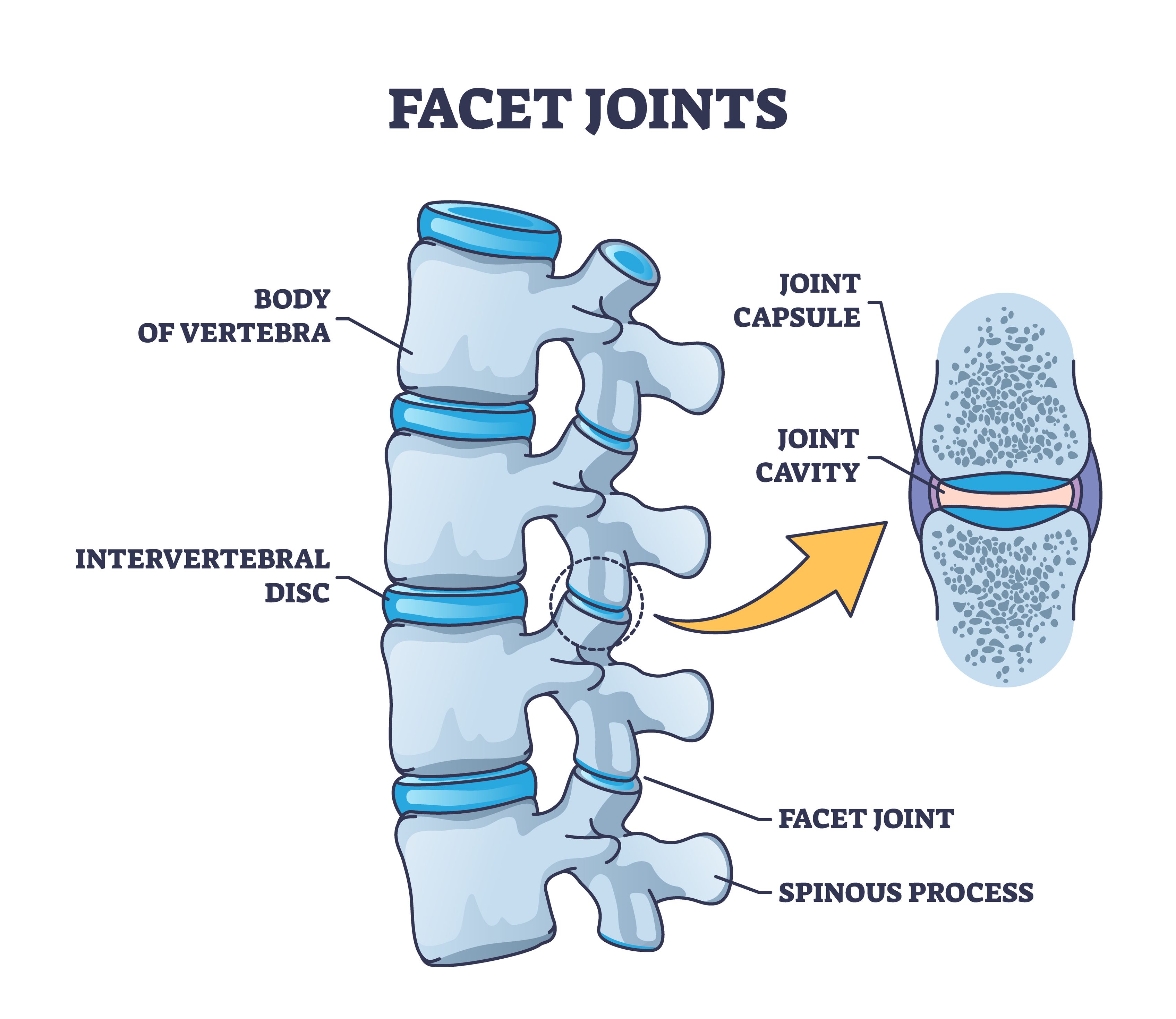
Depressions - facet
Shallow indented surface where two bones meet to form a joint
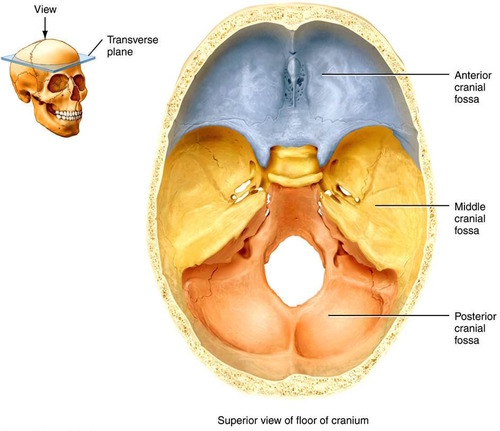
Depressions - Fossa
Deeper indented surface in a bone; usually a rounded surface of another bone to fit inside of it
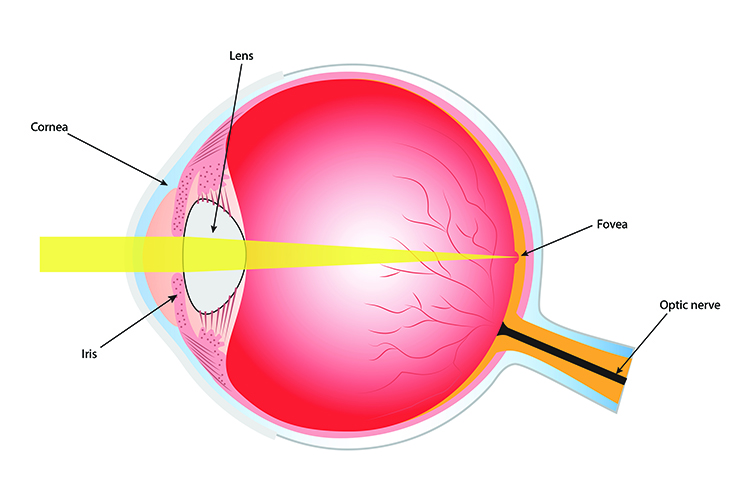
Depressions - Fovea
Shallow pit; often a site for attachment of a ligament
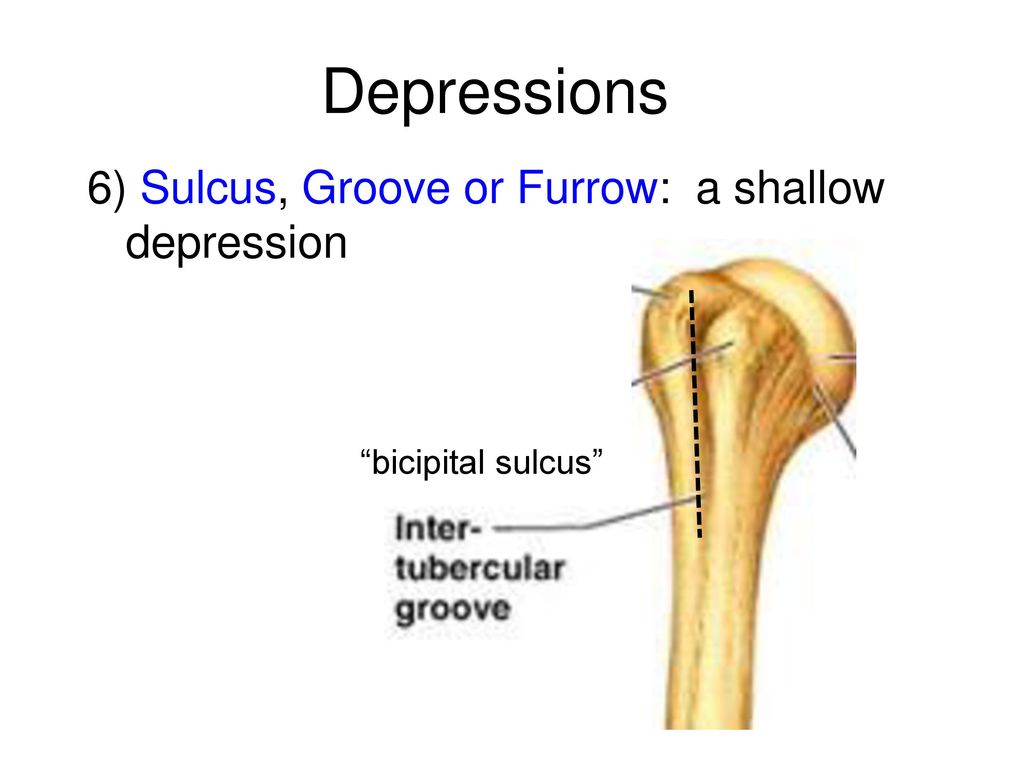
Depressions - groove/sulcus
long, typically shallow depression that usually allows a nerve or blood vessel to travel along the bone’s surface
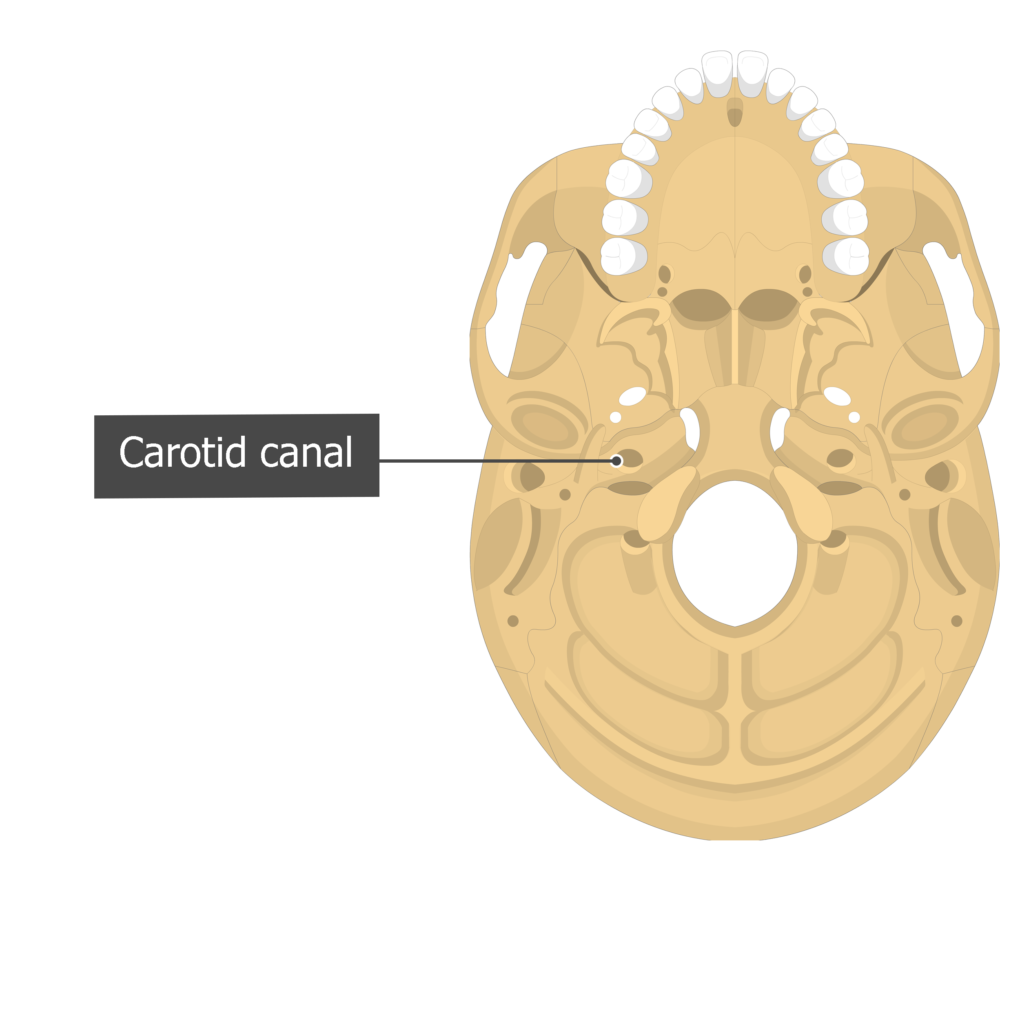
Openings - canal
Passageway through a bone
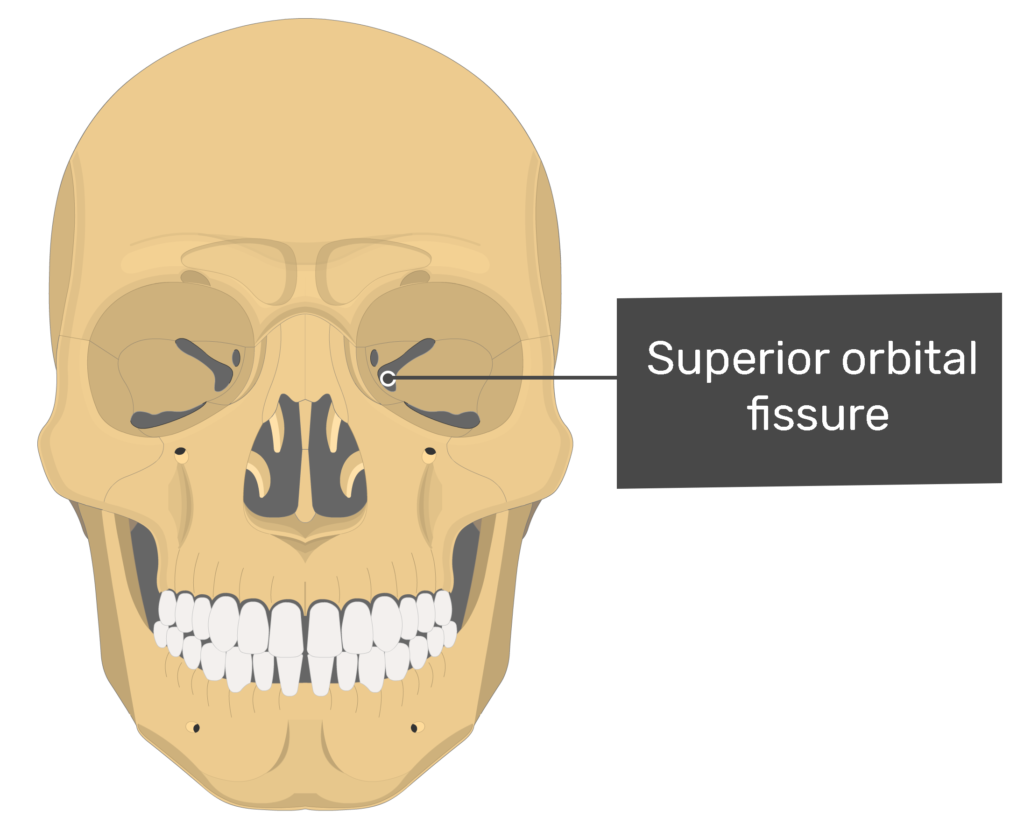
Openings - Fissure
Slit within a bone or between bones
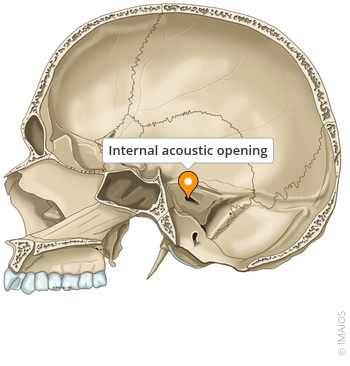
Openings - foramen
Hole in a bone through which a structure such as a nerve or blood vessel passes

Opening - Meatus
Another name for canal
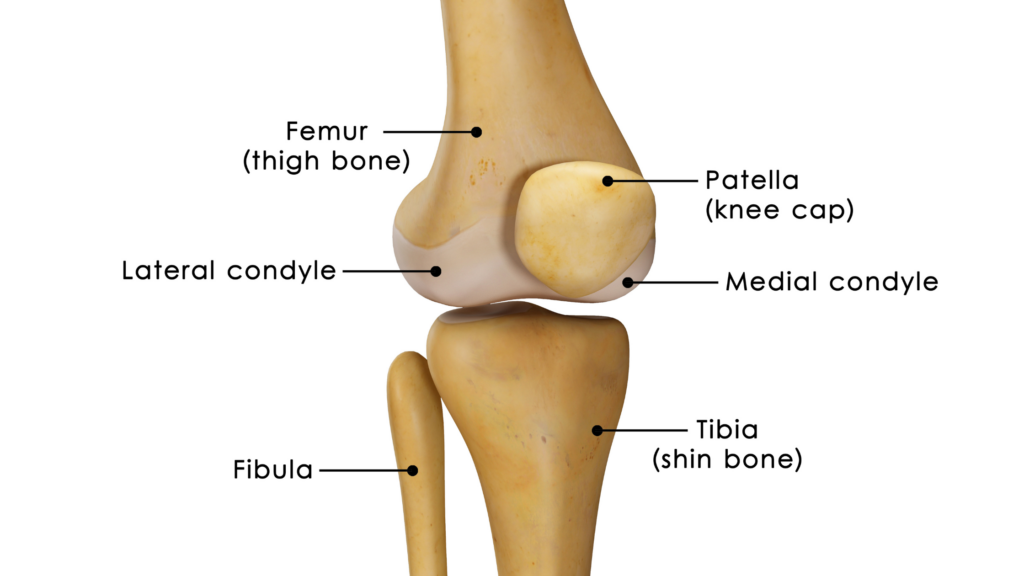
Projections - Condyle
Round end of a bone that fits into a fossa or facet of another bone at a joint
Projections - Crest
Ridge along a bone; generally a site of muscle attachment
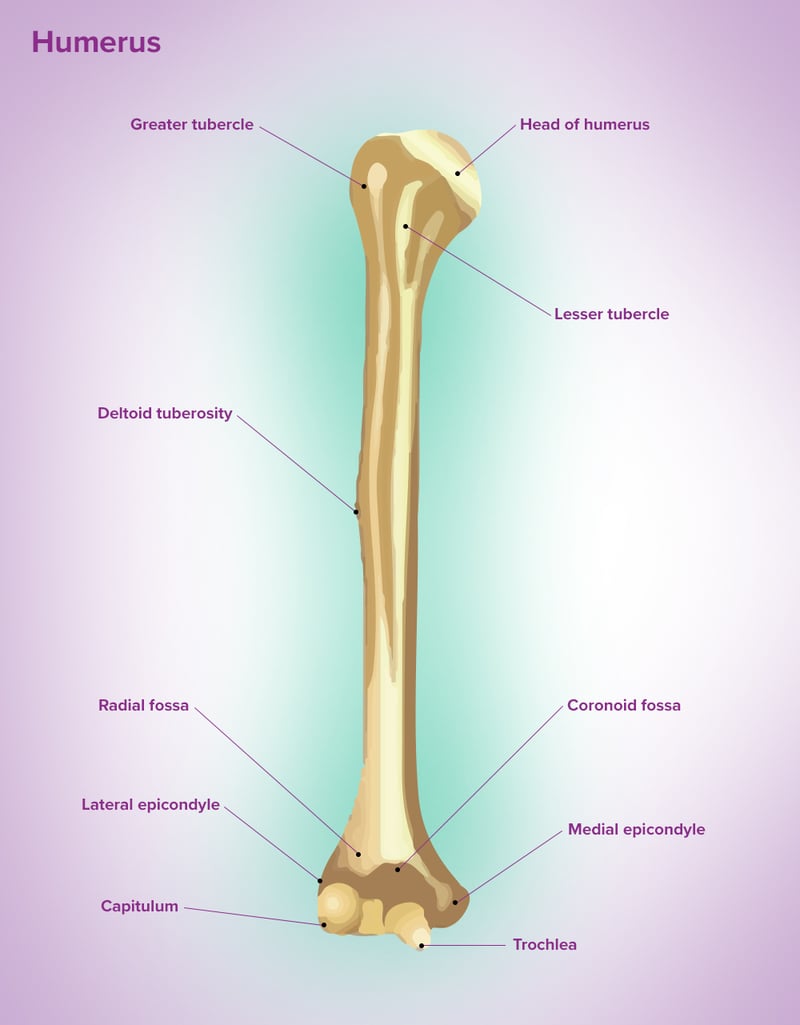
Projections - Epicondyle
Small projection usually proximal to a condyle; generally the site of a muscle attachment
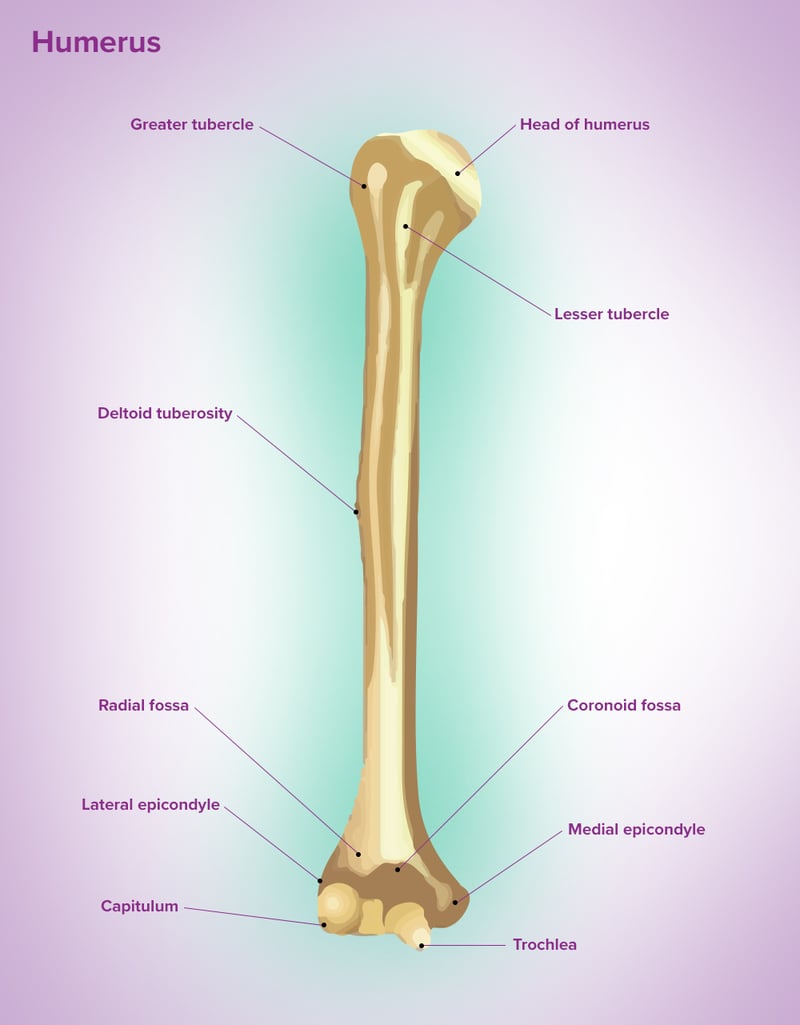
Projections - Head
Rounded end of the bone that fits into a fossa to form a joint
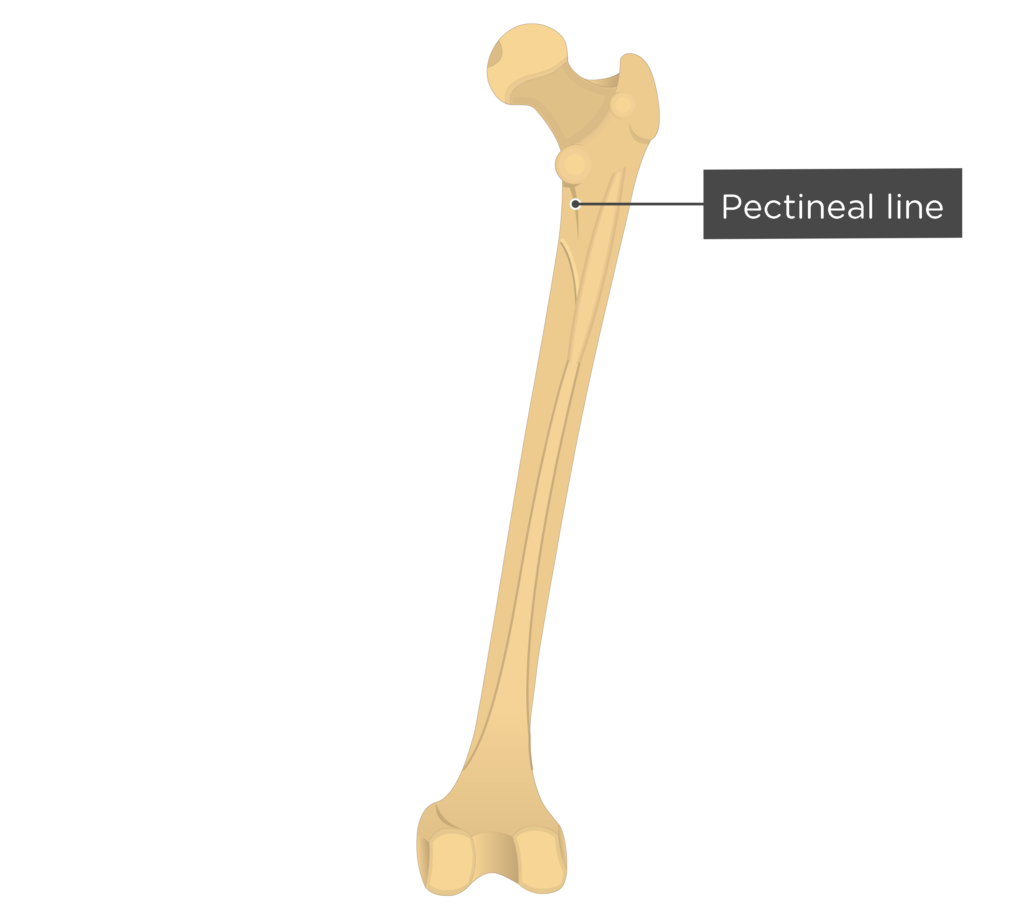
Projections - Line
Ridge along a bone where a muscle attaches
Projections - Process
Any bony projection; generally the site of muscle attachment
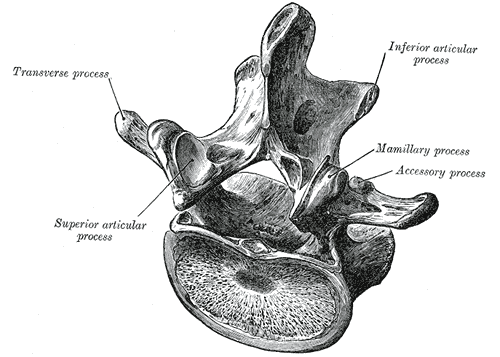
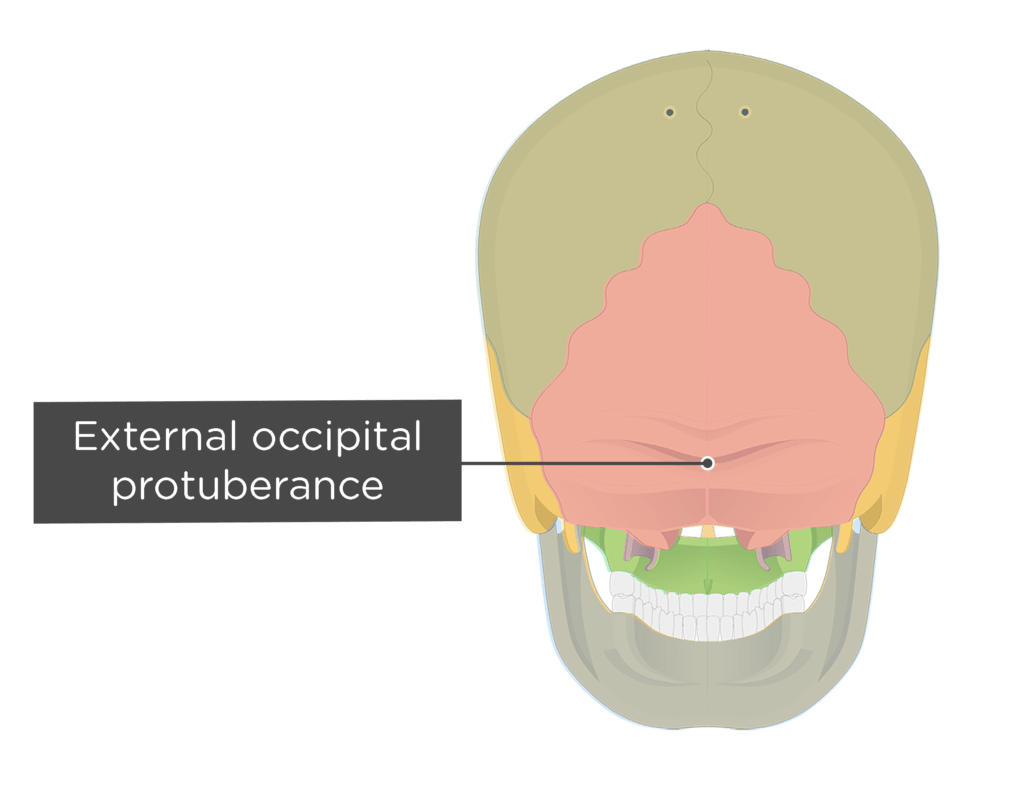
Projections - Protuberance
An outgrowth from a bone due to repetitive pull from a muscle
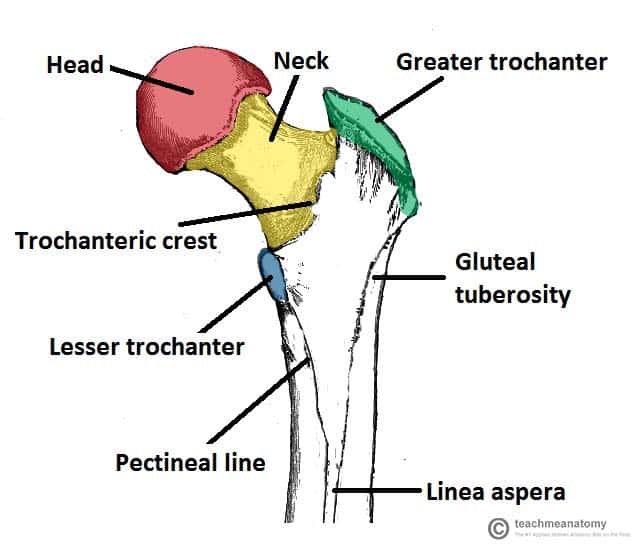
Projections - Trochanter
Large bony projection to which muscles attach; only examples are in the femur
Projections - Tubercle
Small rounded projection where muscles attach
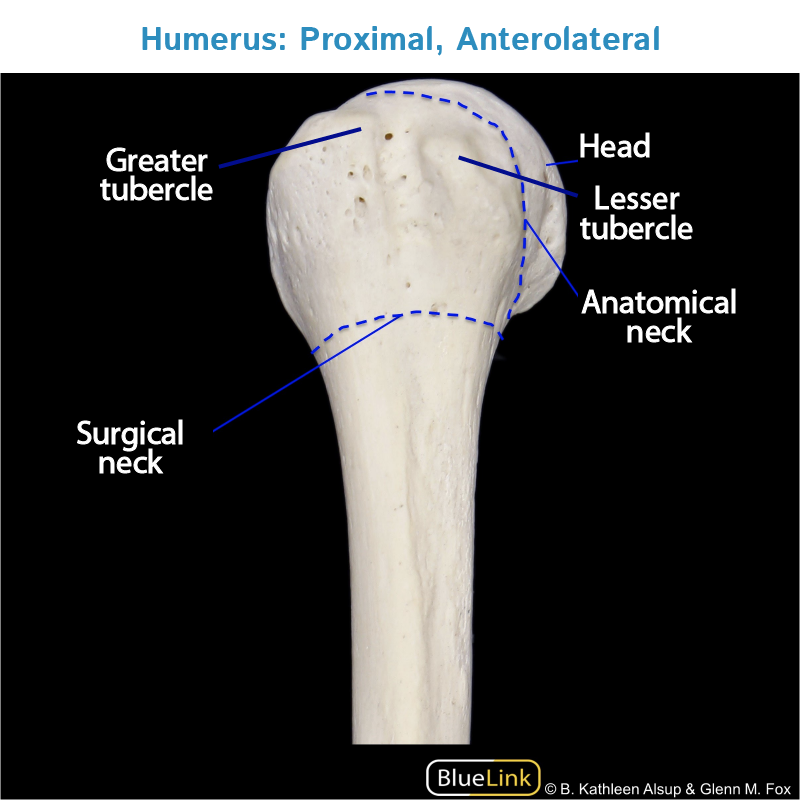
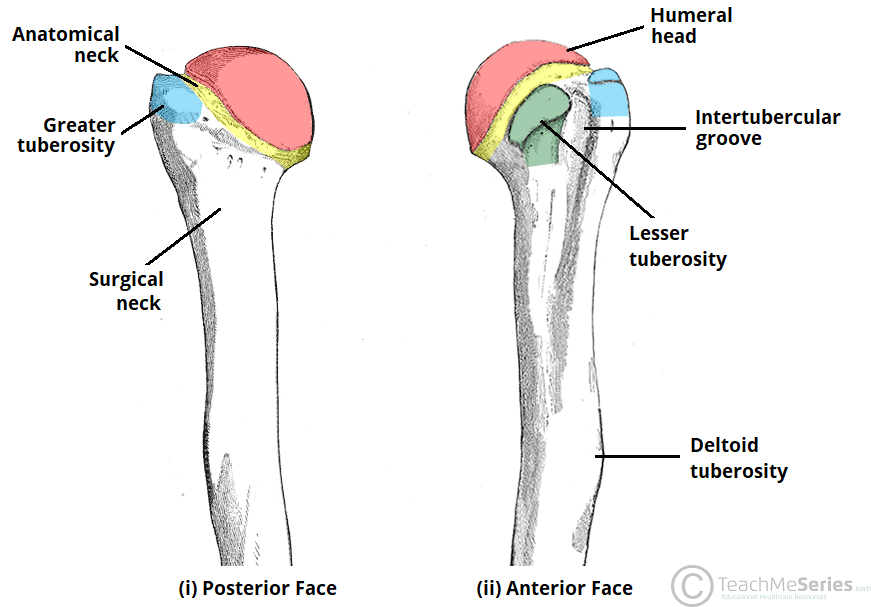
Projections - Tuberosity
A larger, more prominent tubercle
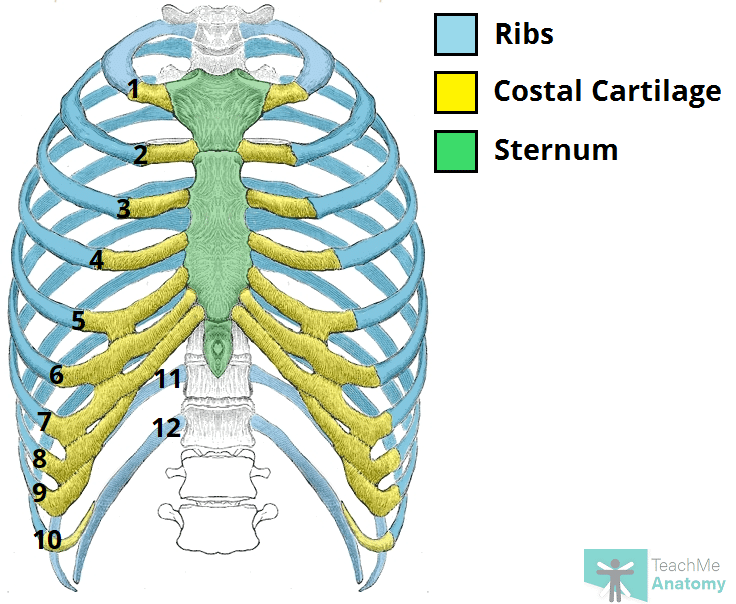
Costal cartilage
flexible, cartilaginous structures that connect the ribs to the sternum
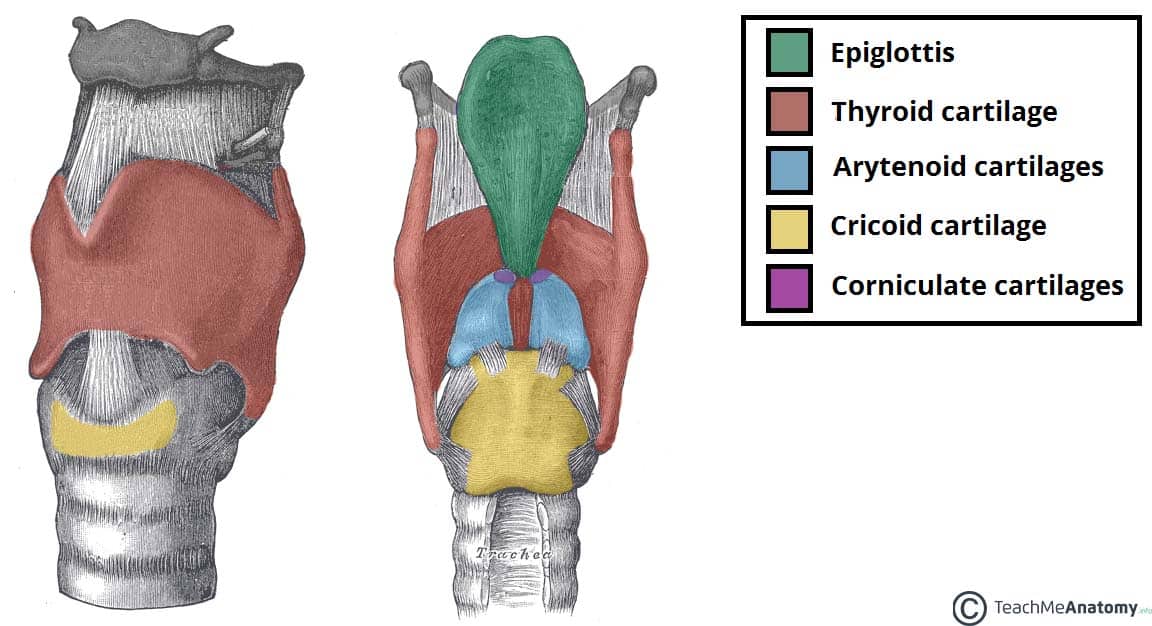
Laryngeal cartilage
make up the larynx (voice box), primarily protect the lower respiratory tract and enable speech. They provide structural support, prevent food from entering the trachea during swallowing, and, through their connection to muscles and ligaments, allow for vocal cord movement and sound production.
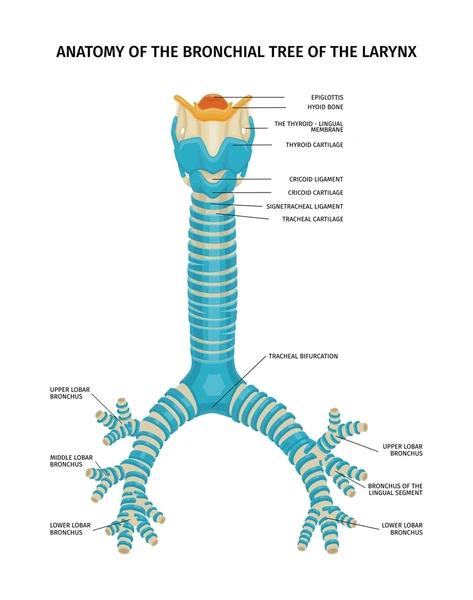
Tracheal & bronchial cartilage
providing structural support to these airways, preventing them from collapsing during breathing. This support is essential for maintaining airflow to and from the lungs, ensuring efficient gas exchange.
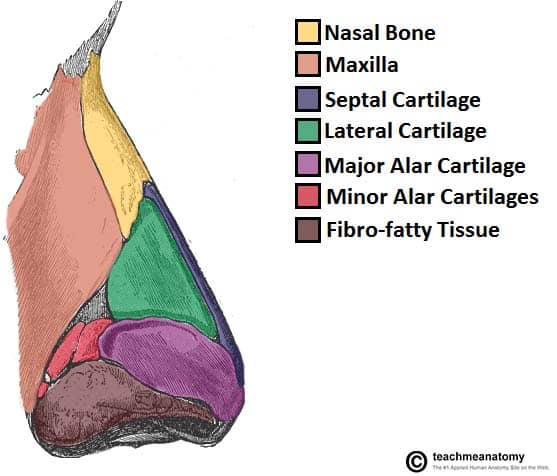
Nasal cartilage
crucial for maintaining the structure and function of the nose. They provide flexibility and support to the nasal framework, ensuring proper airflow and shape. The cartilages also play a role in regulating airflow, contributing to the nose's ability to warm, humidify, and filter inhaled air.
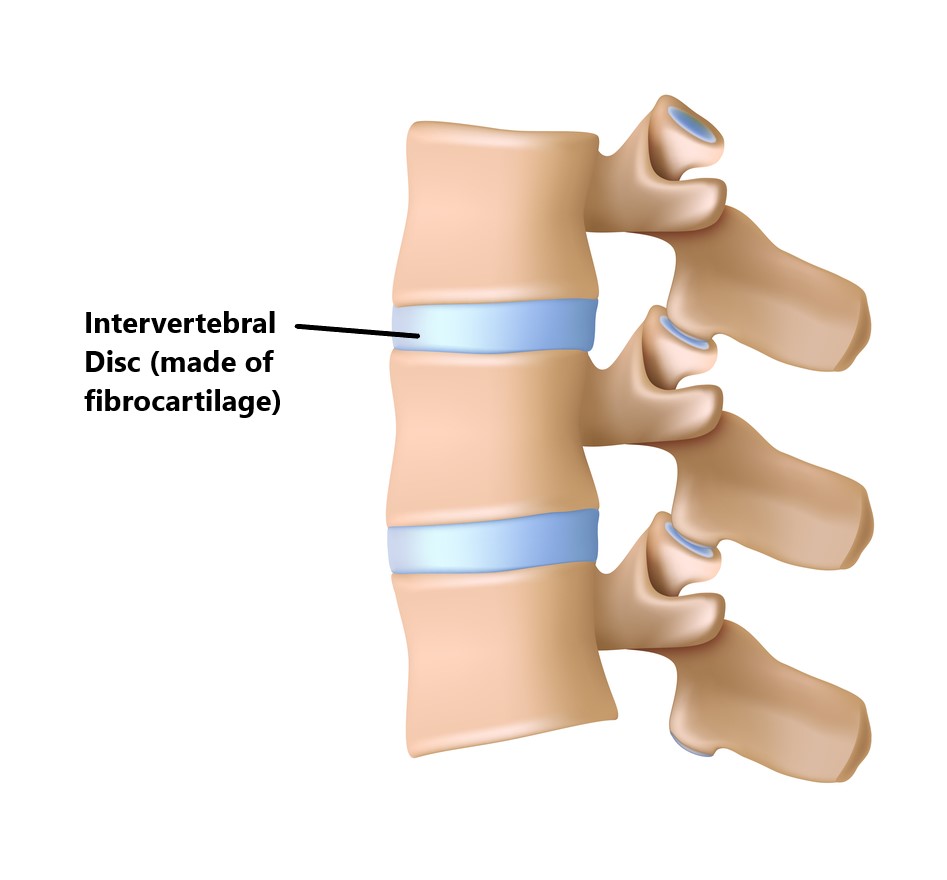
Intervertebral discs cartilage
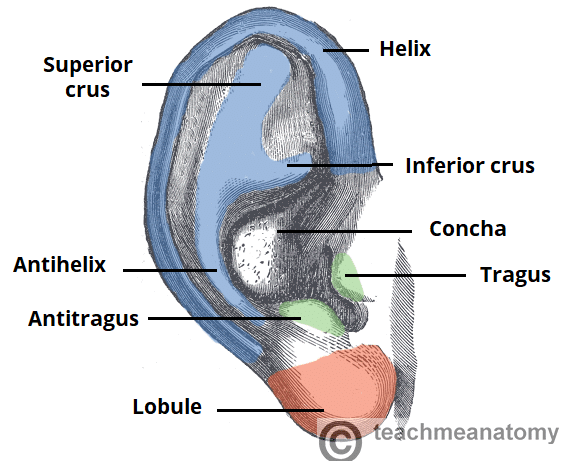
Cartilage of external ear
primarily composed of elastic cartilage covered by skin. This cartilage gives the ear its shape and flexibility.