IGCSE Combined Science Physics
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Brownian motion
Motion of small particles suspended in a liquid or gas caused by molecular bombardment
thermal expansion
An increase in the volume of a material when the temperature is increased
Infrared radiation
Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths that are longer than visible light but shorter than microwaves.
Wave motion
the transfer of energy without transferring matter
real image
An upside-down image formed where rays of light meet.
conventional current
Current that flows from the positive side of the battery to the negative side. This is the way current is drawn in circuit diagrams, even though it is wrong.
Ampere
unit of electric current
D.C. supply
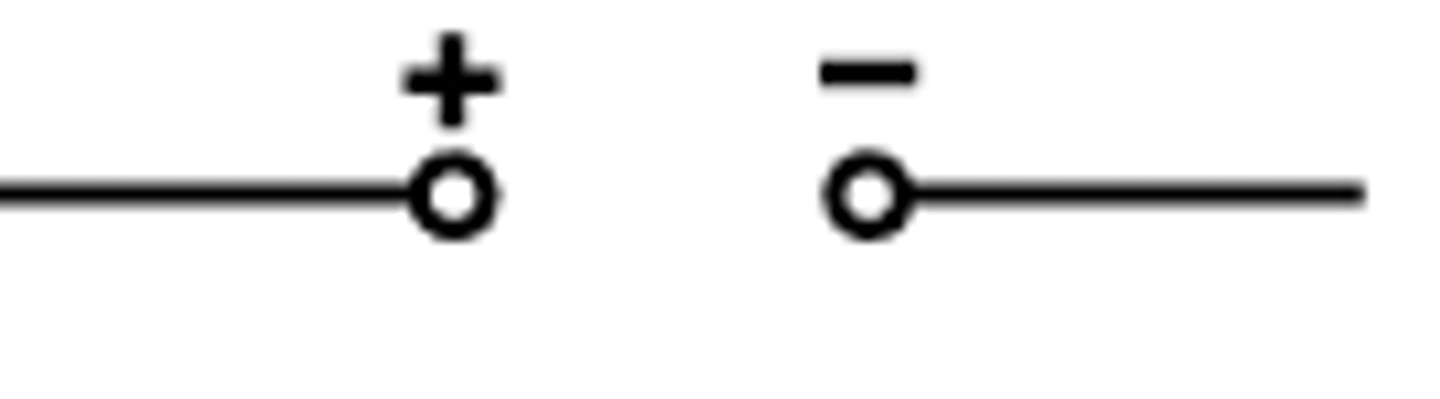
Density formula
mass/volume
Gravitational Potential Energy formula
m x g x change in h
power unit
Watts (W)
Speed unit
m/s (meters per second)
Acceleration unit
m/s^2
boiling
The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas
Solidifying
liquid to solid
longitudinal wave
a wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of wave motion
Refraction
the change in direction of a ray or wave when it passes from one medium to another

angle of incidence
the angle between the incident ray and the normal
angle of refraction
the angle between the refracted ray and the normal
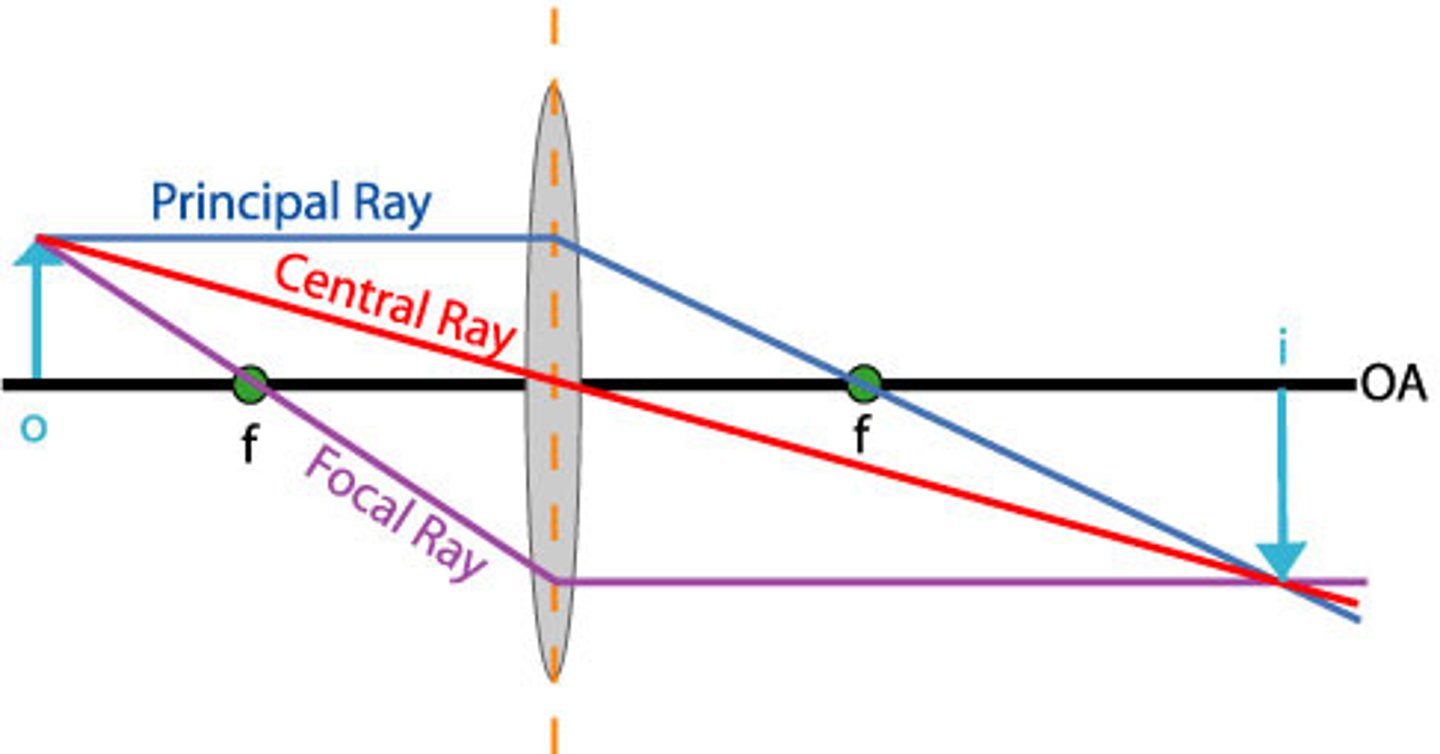
converging lens (convex)
a lens that bends exiting light rays toward the focal point
inverted
upside down
Current
Rate at which electric charge passes a point in a circut
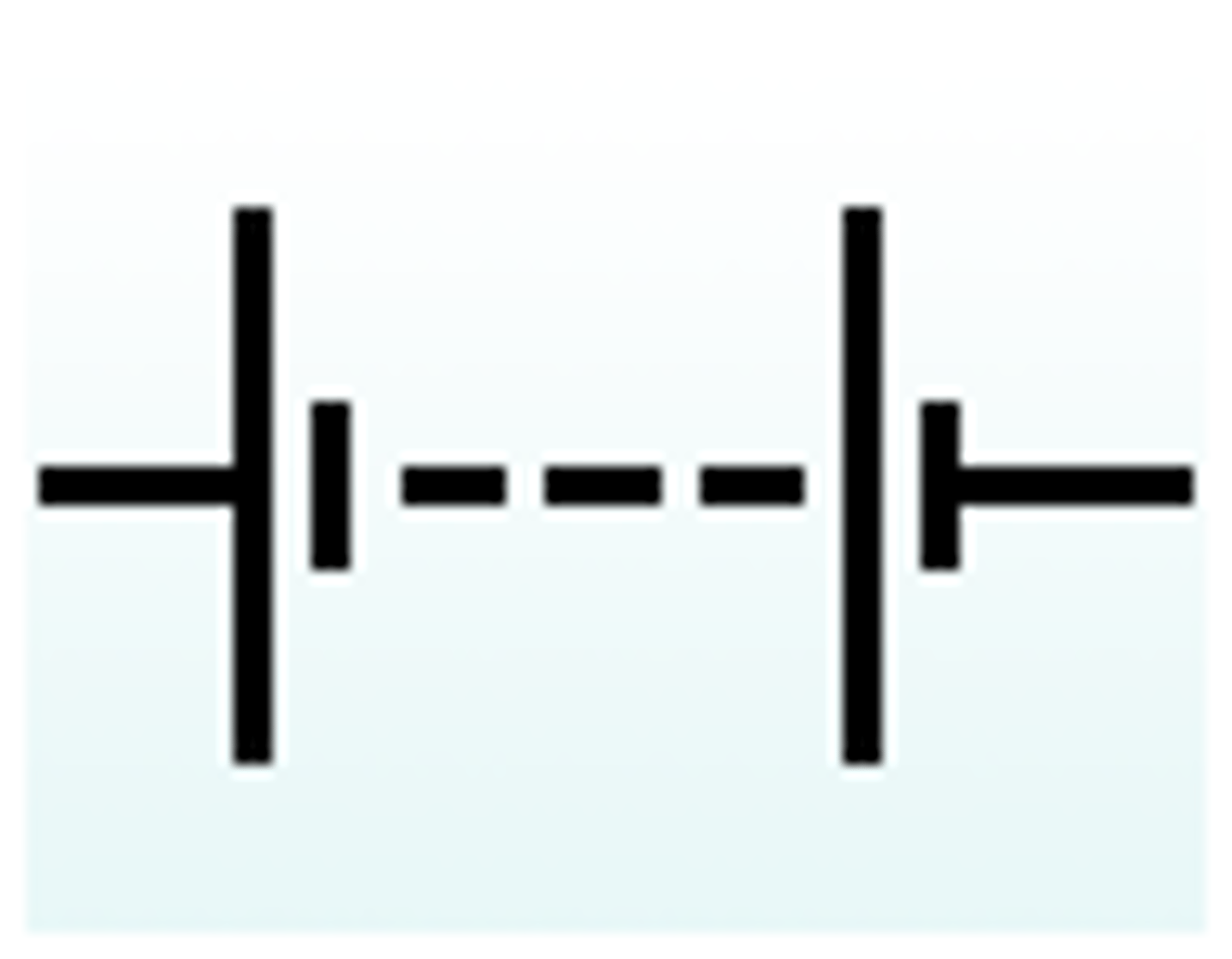
Battery
Voltmeter
Closed switch
Weight formula
mass x gravity
Acceleration formula
final velocity-initial velocity/time
speed formula
distance/time
Force formula
mass x acceleration
Pressure formula
force/area
kinetic energy formula
1/2mv^2
Work formula
force x distance
Power formula
work/time
Work & Energy unit
Joules (J)
Force unit
N (newtons)
Pressure unit
Pascal (Pa)
States of matter
solid, liquid, gas
melting
The change in state from a solid to a liquid
Evaporation
The change of a substance from a liquid to a gas
Condensing
The change of state from a gas to a liquid
Atom
Smallest particle of an element
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Attractive forces
the force by which one object attracts another, fixed position in solid and close together in a liquid
melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid
boiling point
The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas
thermal conduction
the transfer of thermal energy from one substance to another through vibration of molecules
thermal conductor
a substance that conducts thermal energy well
thermal insulator
a substance that conducts thermal energy poorly
Convection
The transfer of thermal energy through a material by the movement of the material
convection current
The transfer of thermal energy by the motion of a fluid
electromagnetic spectrum
All of the frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation
crest
Highest point of a wave
trough
Lowest point of a wave
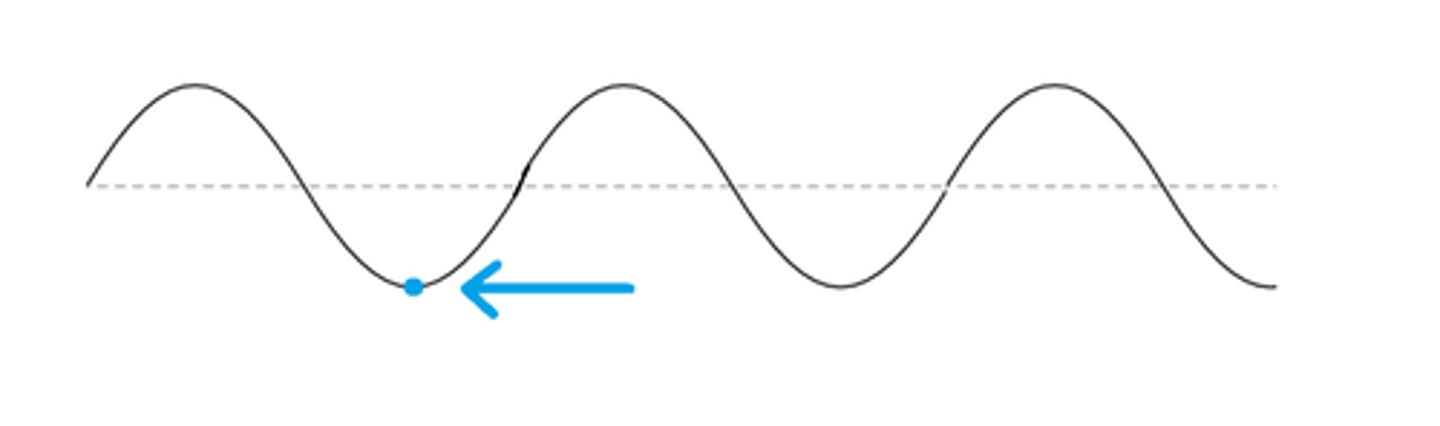
Wavelength
Horizontal distance between the crests or between the troughs of two adjacent waves

Amplitude
For a wave, the maximum displacement on either side of the equilibrium (midpoint) position.
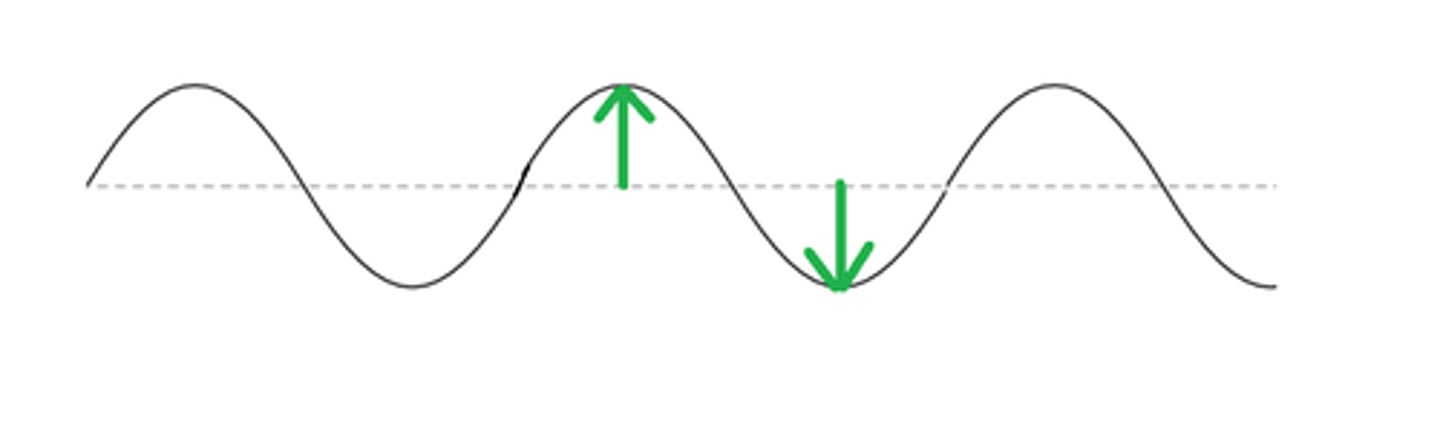
Frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a second
Hertz (Hz)
Unit of measurement for frequency
transverse wave
A wave that moves the medium in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels
wave speed=
frequency x wavelength
Reflection
the change in direction of a ray or wave when it strikes a surface without passing through it

angle of reflection
The angle between the reflected ray and the normal
normal
the line drawn at right angles to a surface at the point where a ray hits the surface
ray diagram
a diagram showing rays that can be drawn to determine the size and location of an image formed by a mirror or lens
plane mirror
a mirror with a flat surface
incident ray
The Ray that strikes a surface
reflected ray
The Ray that is reflected from a surface
virtual image
a reflected optical image (as seen in a plane mirror)
focal length
the distance from the center of a lens to the focal point/principal focus
principal focus or focal point
the point at which rays of light parallel to the principal axis converge after passing through a converging lens
spectrum
waves, or colours, separated out in order according to their wavelengths
Dispersion
the separation of different wavelengths of light because they are refracted through different angles
ultrasound
Sound waves with frequencies above 20,000 Hz.
Positive charge
Type of electrical charge carried in nucleus of an atom
Negative charge
Type of electrical charge carried in electrons
Direct Current (DC)
Electric current that flows in only one direction
Alternating Current (AC)
A flow of electric charge that regularly reverses its direction.
Ammeter
A device used to measure current in a circuit
Current=
charge/time
volt (V)
unit for measuring voltage
electrical force (e.m.f.)
Voltage across the terminals of a source or the electrical work done by a source (cell, battery, etc)
potential difference (p.d.)
the work per unit charge from electrical energy into other energy forms by a device
resistance=
Potential difference/current
ohm
unit of electrical resistance
Energy transferred=
current x p.d. x time
power=
current x potential difference
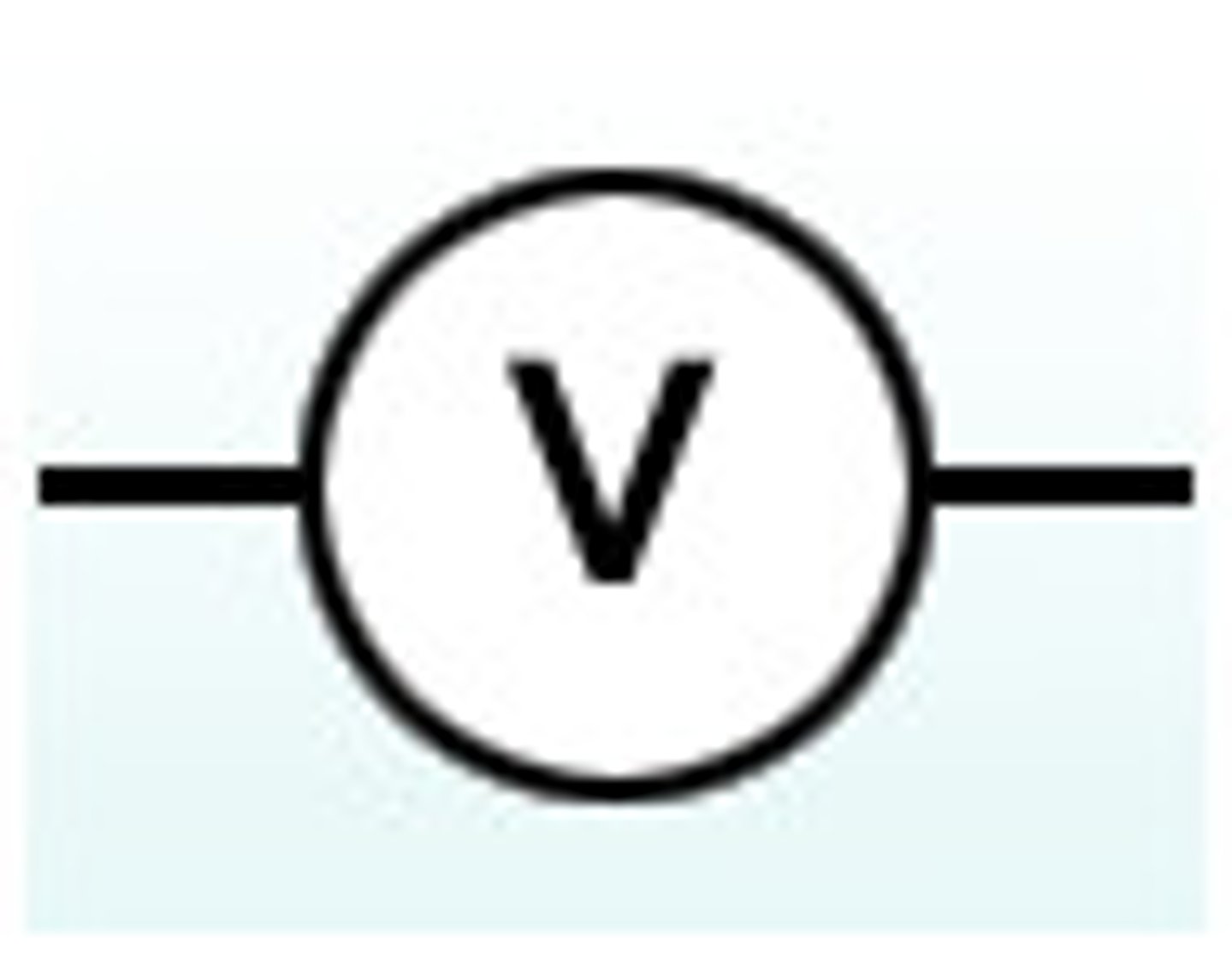
voltmeter
a device used to measure p.d. (voltage) between 2 points
charge=
current x time
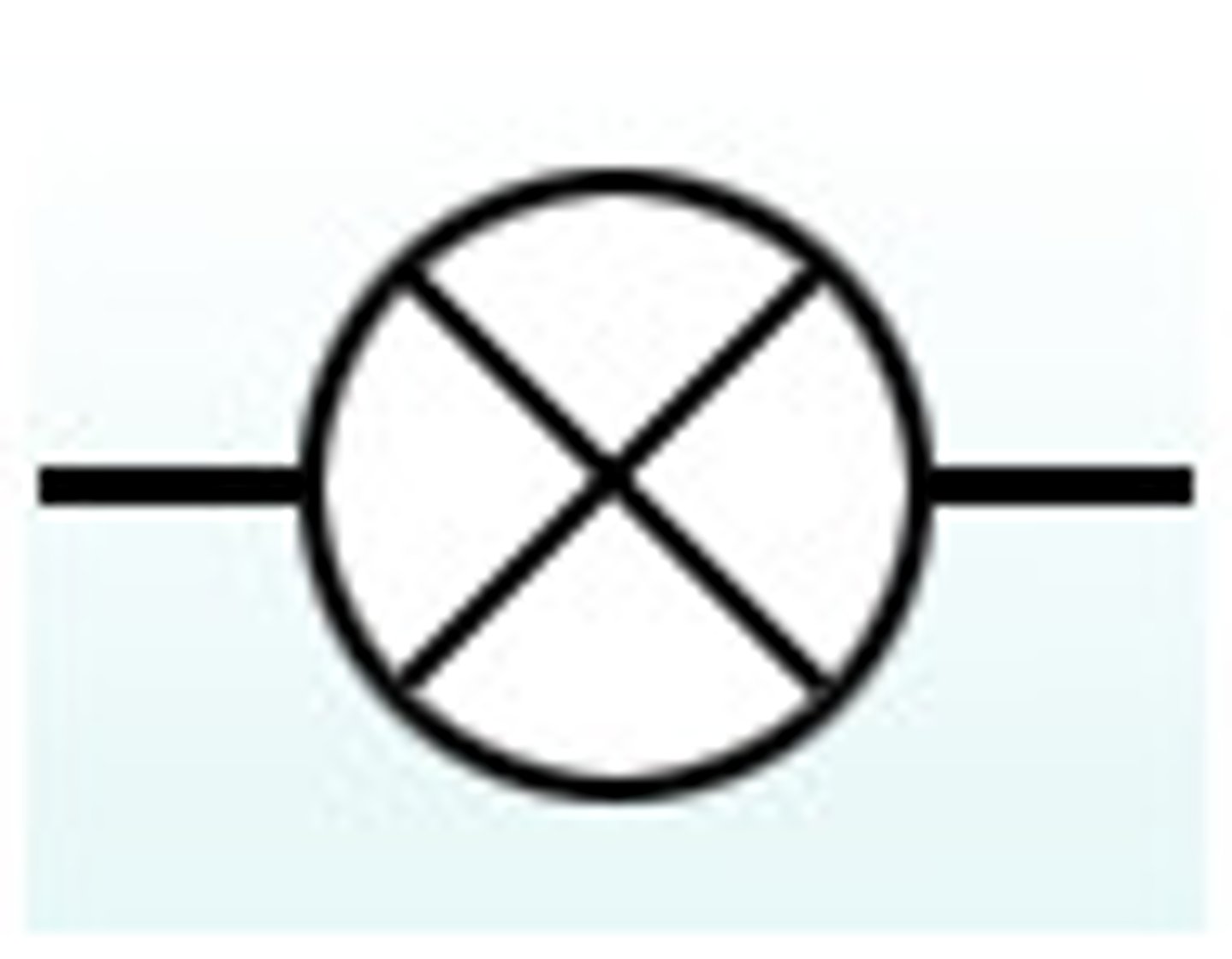
Lamp
LED
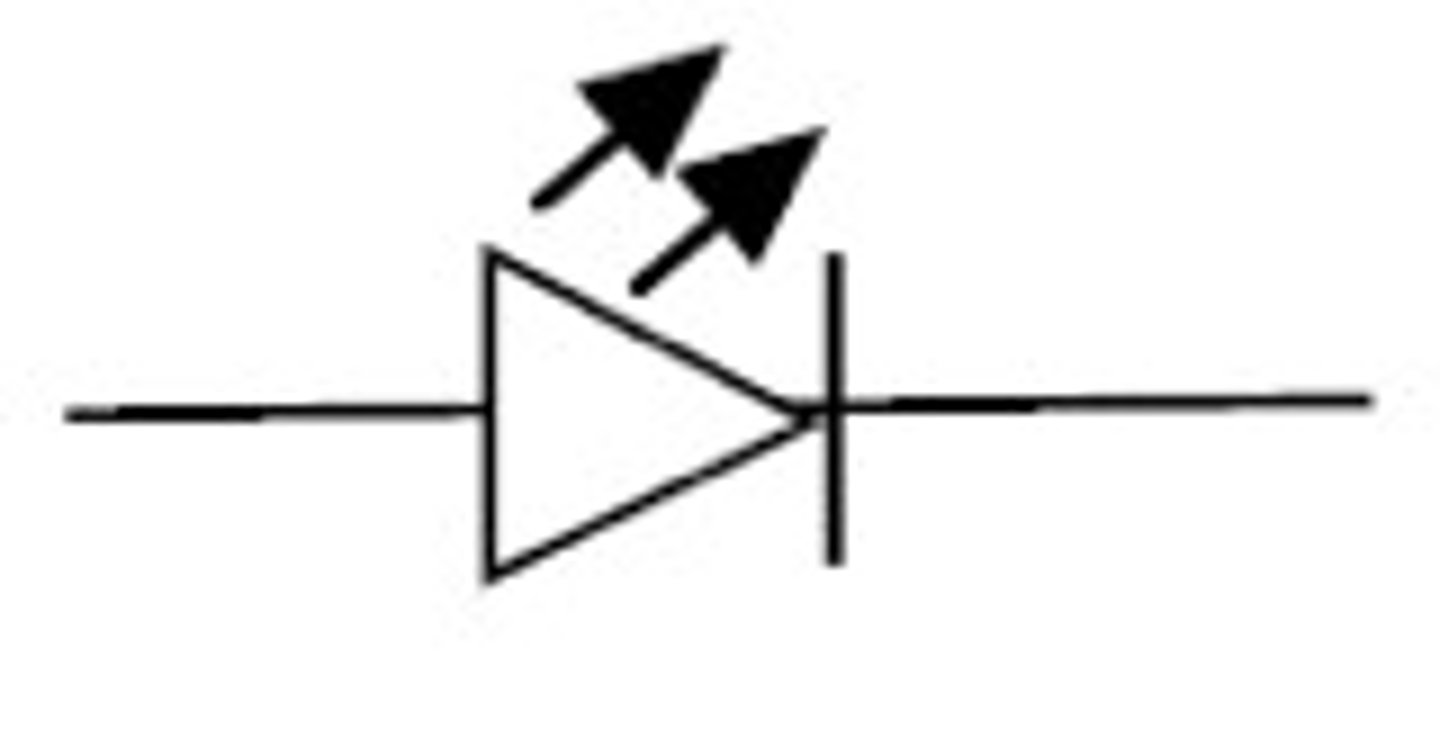
Fuse
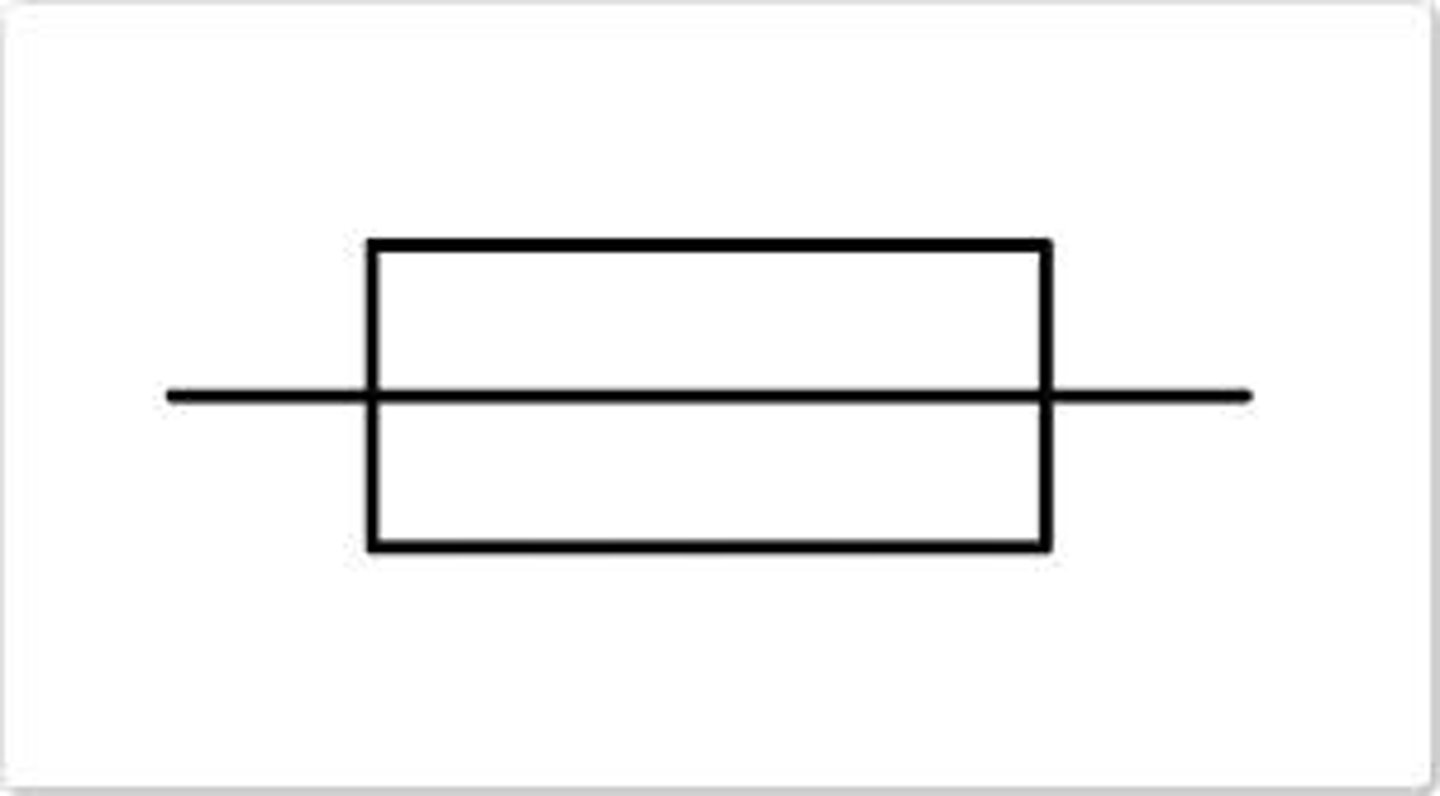
LDR
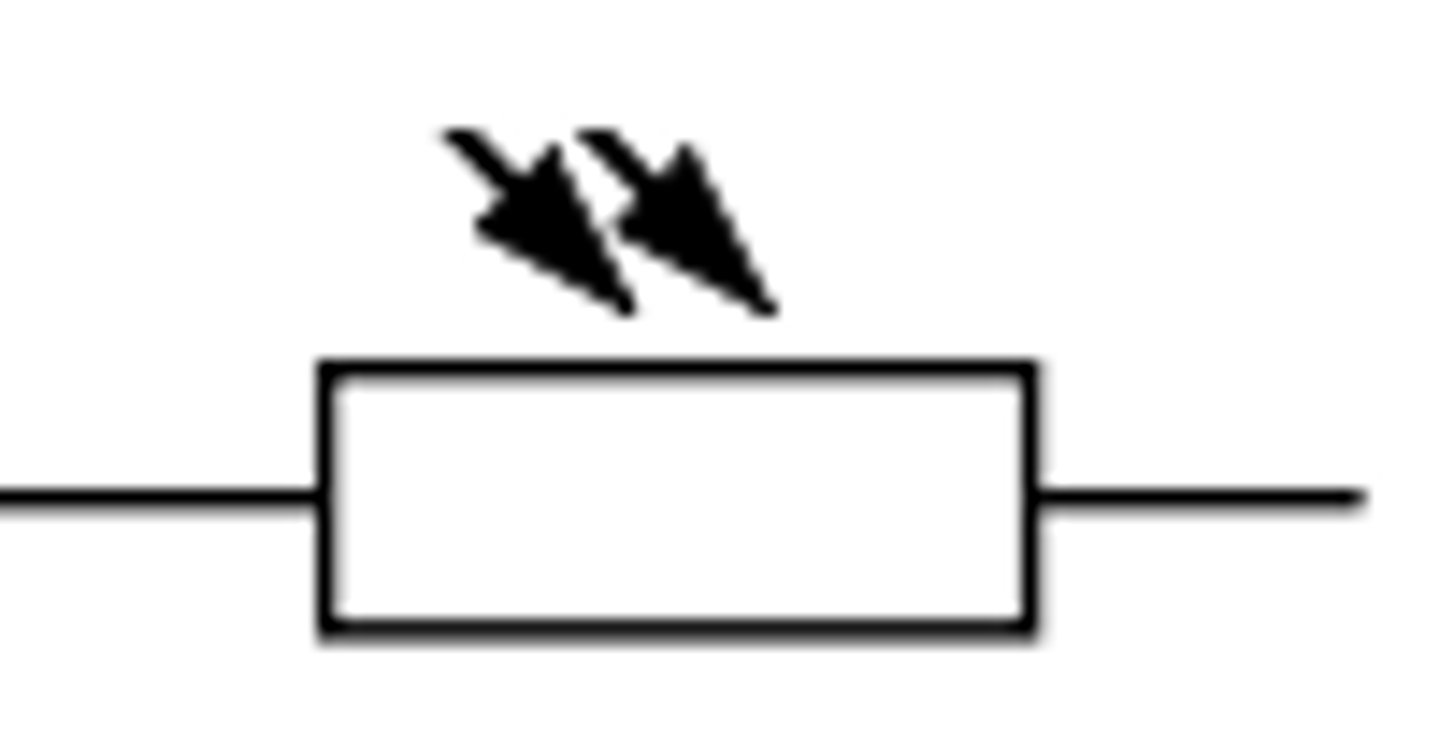
Ammeter
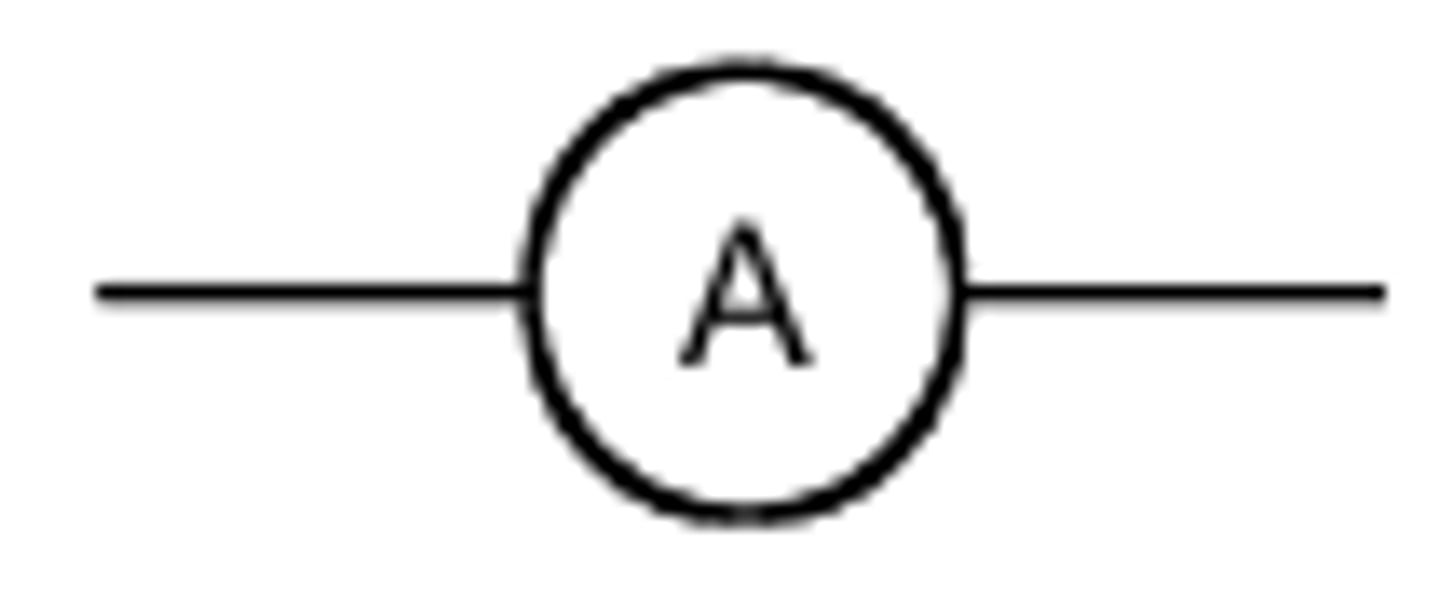
Motor

Fixed Resistor
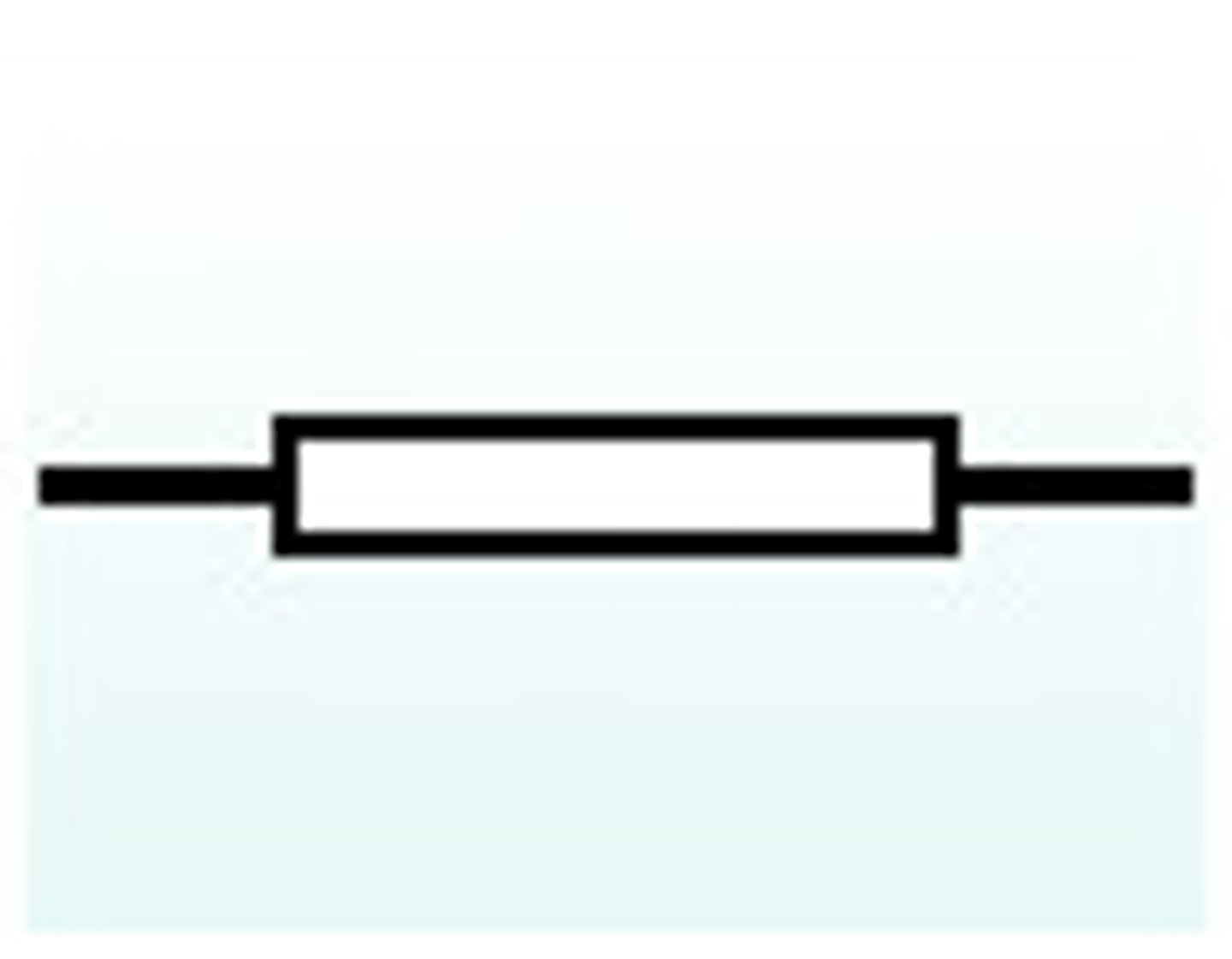
Variable resistor
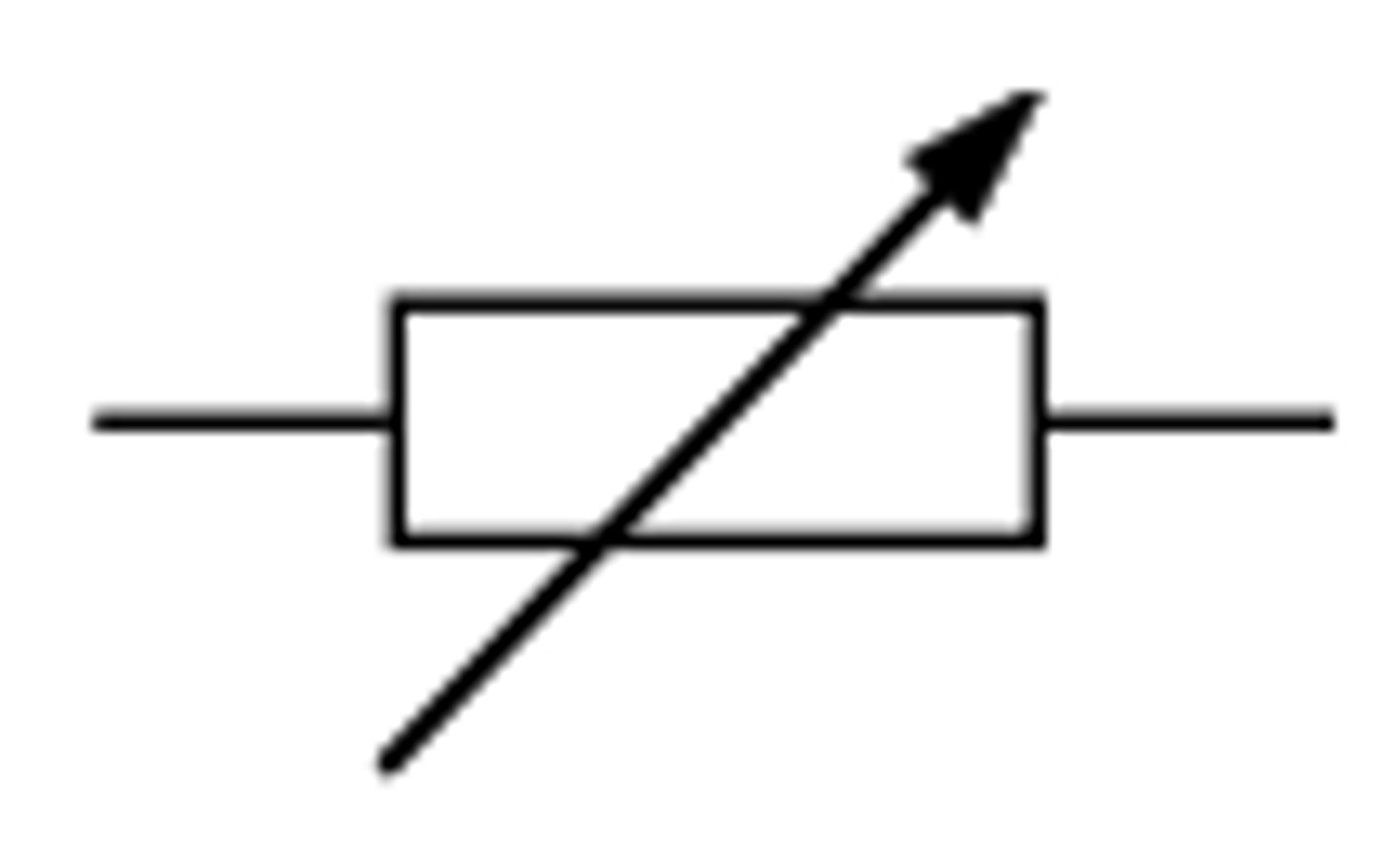
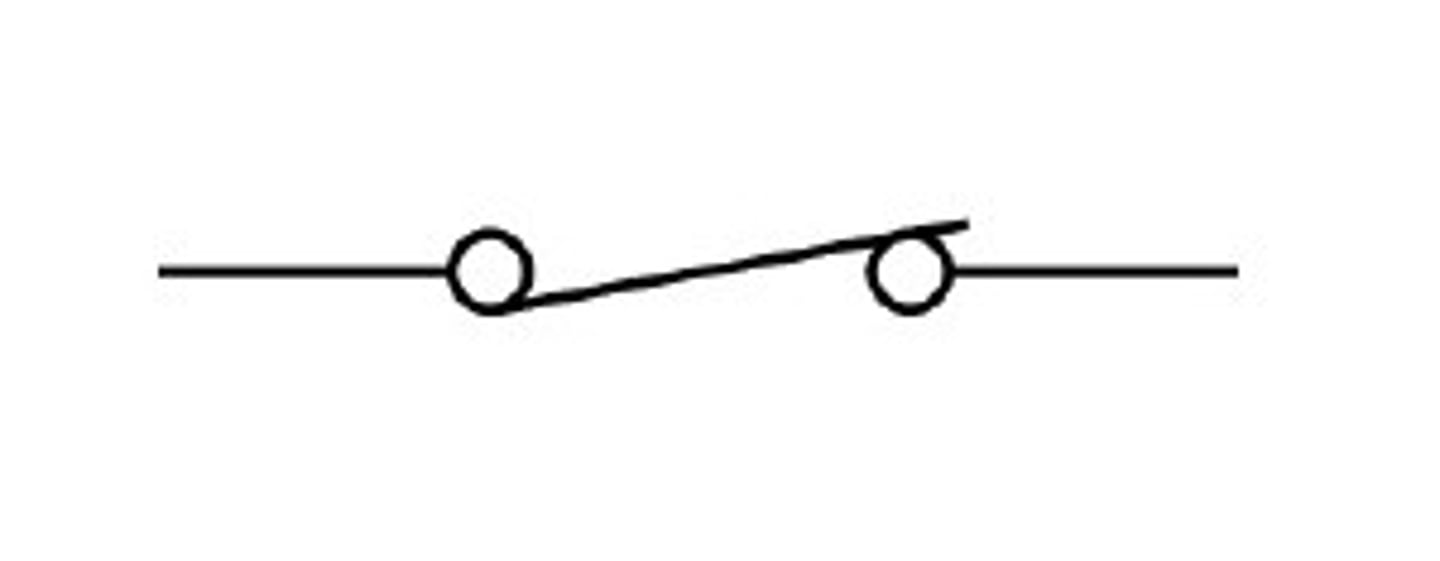
Open Switch
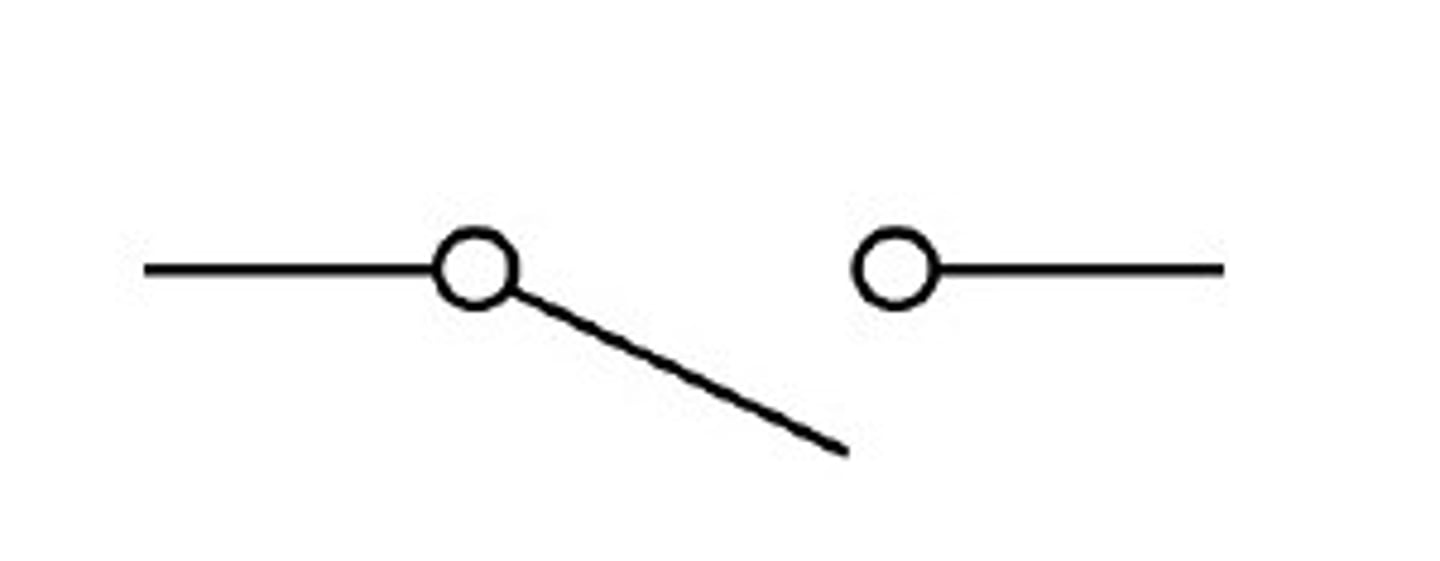
A.C. supply

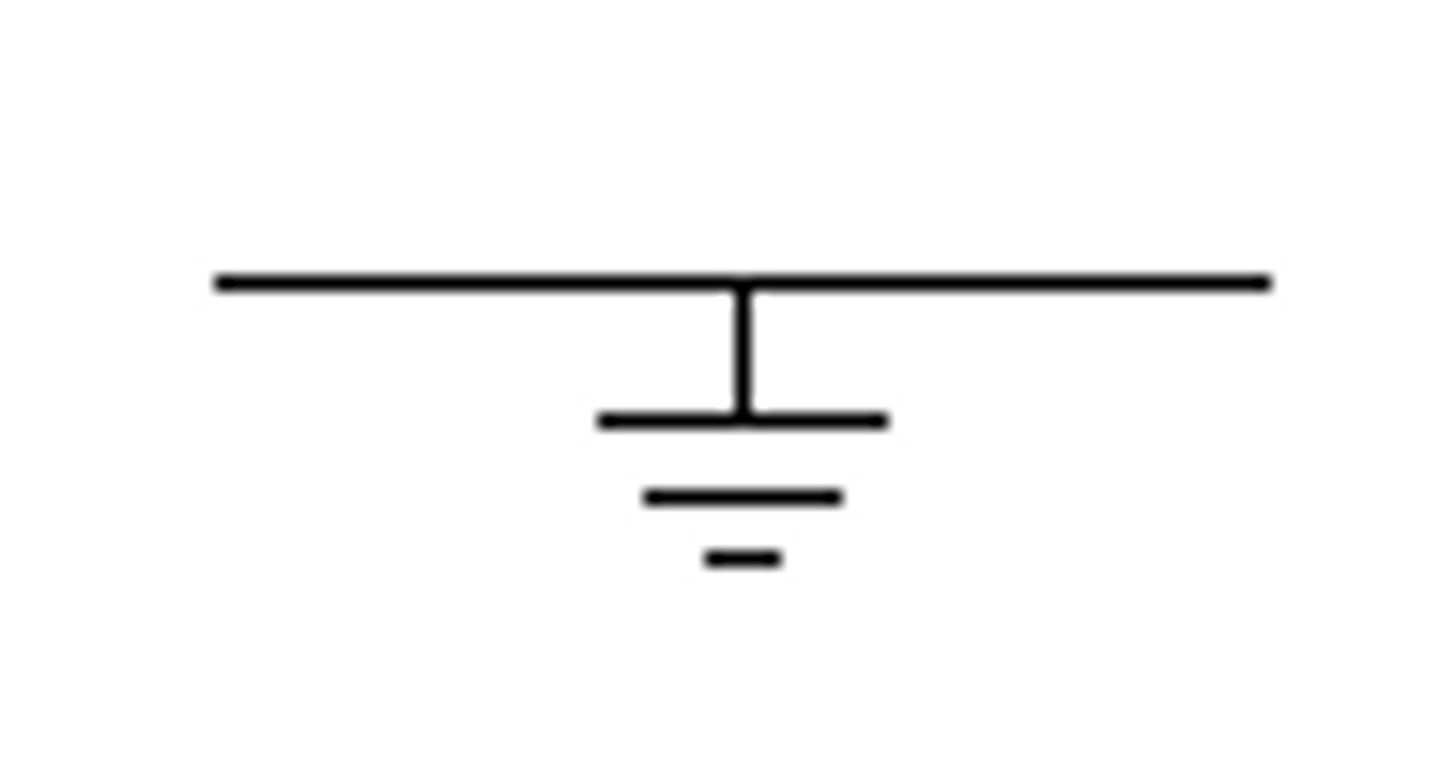
Earth/Ground
Still learning (25)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!