Pre-formulation of Solid Dosage Forms
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 1 and 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms

What is preformulation?
The first step in the rational development of dosage forms of a drug into a medicine.
Main aim of dosage-form design?
To convert a new chemical entity into a medicine that delivers drug safely, efficiently, reproducibly, and conveniently.
Difference between solubility and dissolution rate?
Solubility is a constant; dissolution rate is a variable.
Why is solubility constant?
Once this maximum amount of drug that can dissolve in a solvent is reached, no more will dissolve if you wait longer.
Why is dissolution rate variable?
Because how fast a drug dissolves can change depending on things like:
Particle size (smaller = faster)
Tablet formulation
Stirring/agitation in the gut
Surface area exposed
If the drug is coated
Whether the tablet is compressed tightly or loosely
Whether excipients (like disintegrants) are present
So dissolution rate can be manipulated and is not fixed.
Why are solubility and dissolution rate critical for oral drugs?
A solid drug must dissolve before it can permeate the gut wall. Basically solubility and dissolution rate control absorption rate and bioavailability.
What is dissolution rate?
The speed at which the drug dissolves.
It describes how fast the solid turns into dissolved molecules.
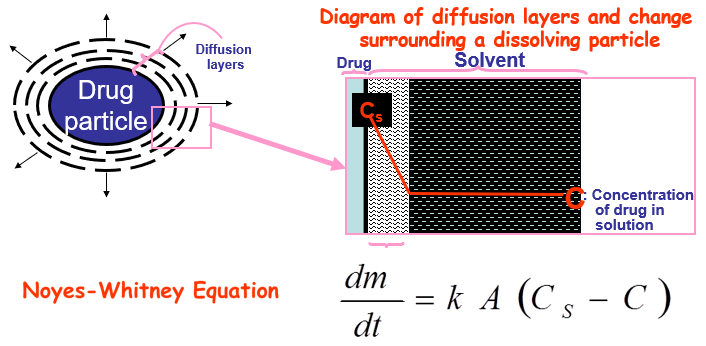
Why does solubility and dissolution rate matter in pharmacy?
Low solubility → poor absorption (low bioavailability)
Slow dissolution rate → delayed or incomplete absorption
Which equation describes dissolution rate?
The Noyes–Whitney equation.
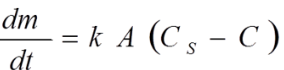
Noyes Whitney Equation for Dissolution Rate
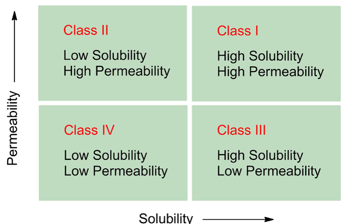
What is BCS?
Biopharmaceutical Classification System
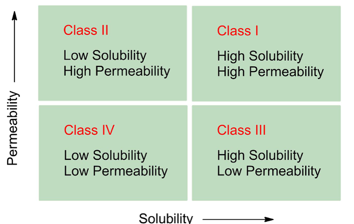
What is BCS only applicable for?
Oral dosage forms
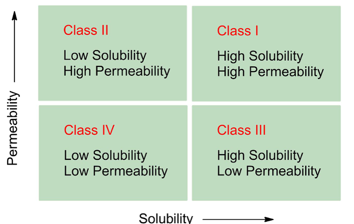
What do we do using the information of BCS?
We can only modify the solubility of the compound, we can’t do much with permeability
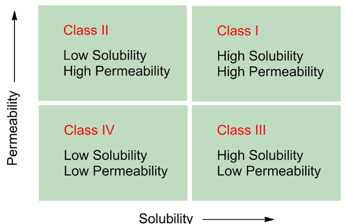
Which BCS classes are high risk?
Class II and Class IV (poorly soluble).
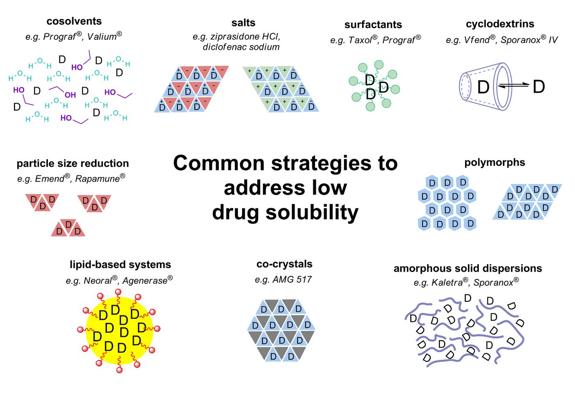
Common strategies to address low drug solubility and to make a drug more soluble:
Amorphous forms
Metastable polymorphs
Solid dispersions
Lipid-based formulations (e.g., soft gel capsules).
Why is early preformulation critical?
Because only small amounts of drug are available, and changing salt or polymorph later causes major delays.
Why are pharmaceutical salts important today?
Many modern drugs are lipophilic and poorly soluble; salts can improve physicochemical and biopharmaceutical properties.
In order for a salt to be formed, the acid and base must have a pKa difference of roughly….
pKa = 3
If your drug is a weak acid, you need a base 3 pKa units higher
If your drug is a weak base, you need an acid 3 pKa units lower
When is salt formation useful?
When a drug is poorly soluble and is a weak acid or weak base.
When choosing a salt form of a drug, scientists must consider:
Structure of the drug
pKa
Stability
Related compounds
Dosage form
What is meant by the physical form of a drug?
The solid-state form of a drug (e.g. crystalline, polymorphs, hydrates/solvates, chiral forms, amorphous).
Advantages of Pharmaceutical Salts
Enhance solubility
Increased dissolution rate
Easier synthesis and purification
Better taste
Improved photostability
High bioavailability
Higher melting point
Disadvantages of Pharmaceutical Salts
Decreased percentage of drug
Increased hygroscopicity
Additional manufacturing steps
Increased toxicity
Decrease chemical stability
No change in solubility at different pH in GI tract
Increased number of polymorphs
Which drug properties are influenced by physical form?
Solubility
Stability
Bioavailability
Formulation design strategy

What is an amorphous solid?
A solid with no long-range molecular order (non-crystalline).
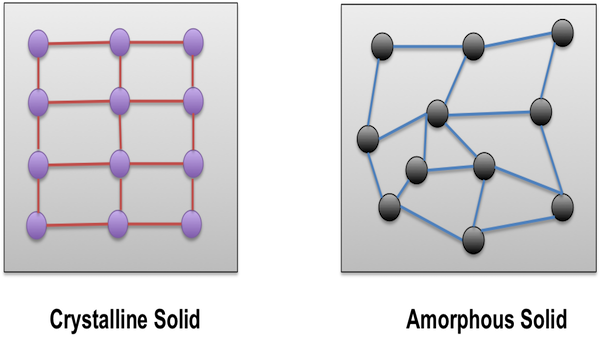
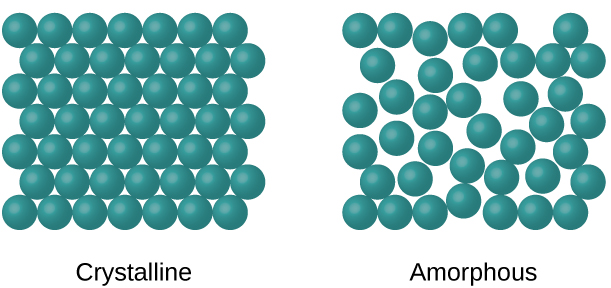
What is a crystalline solid?
A solid with molecules arranged in a regular, repeating lattice (unit cells).
Amorphous Vs Crystalline
Amorphous:
Molecules arranged in disordered manner
High internal energy
High solubility
Faster dissolution
Crystalline:
Molecules are arranged in an ordered repeating lattice
Sharp melting point
Higher density
Lower solubility
Slower dissolution rate
What is a unit cell?
The smallest repeating structural unit of a crystal lattice that defines the crystal structure and symmetry.
There are a total of 7 types of crystal systems and all can be defined by the lengths and angles between each side of the unit cell. What are the 7 primitive unit cells?
Cubic
Tetragonal
Orthorhombic
Trigonal
Monoclinic
Triclinic
Hexagonal

Which crystal systems are most common for drugs?
Triclinic, monoclinic, and orthorhombic.
What are Bravais lattices?
The 14 possible 3D lattice arrangements of unit cells.
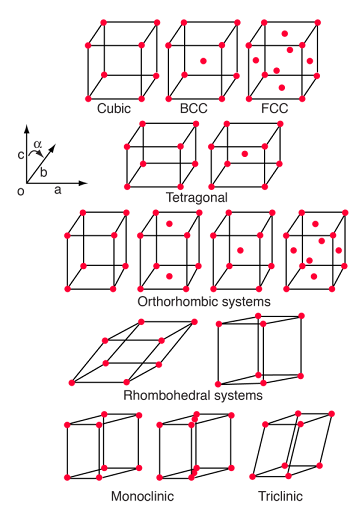
What is a crystal habit?
The external shape of a crystal
Which face dominates the crystal habit?
The slowest growing face.
Why is crystal habit important pharmaceutically?
It affects flowability, compressibility, stability, and solubility.
What are Miller indices?
A system used to identify crystal faces and describe molecular ordering at the surface.
Why are Miller indices important?
They help predict surface energy, growth behaviour, and interactions with excipients.
Which crystal shape is preferred for injectables?
Plate-like crystals (pass through needles more easily).
Why are needle-shaped crystals problematic for tableting?
They show poor compressibility and increased capping and lamination.
Which habit is beneficial for dry powder inhalers (DPIs)?
Needle-like crystals (better fine particle fraction).
What does crystal form refer to?
Molecular ordering within the lattice, not particle shape or habit.
It does not mean outer appearance (habit) of the crystals/particles
There are 2 crystal forms. What are they called?
Polymorphism
Enantiomorphism
What is polymorphism?
When the same chemical compound exists in more than one crystal form.
What are the 2 pseudopolymorphs?
Special cases of polymorphs are pseudopolymorphs, called:
solvates (solvent molecules in crystal lattice) or
hydrates (water molecules in crystal lattice)
What is enantiomorphism?
When chiral molecules crystallise as mirror-image crystal forms.
Enantiomorphism racemic mixture. What is a racemic mixture?
A mixture of D and L crystal forms in equal amounts are known as a racemic mixture
What is an enantiotropic transition?
A reversible solid-state transition between polymorphs below the melting point.
What is a monotropic transition?
An irreversible polymorphic transition below the melting point.
Which properties vary between polymorphs?
Melting point
Dissolution rate
Compressibility
Density
Flowability
Surface properties
Habit and crystal shape
Hardness
Stability
How do higher lattice energy polymorphs behave?
Higher P
Lower solubility
Slower dissolution
Why is polymorphism important in preformulation?
Different polymorphs have different physical and biopharmaceutical properties, and less stable forms may convert during scale-up, processing, or storage (e.g. moisture- or solid-state transitions), affecting product performance and safety.
Regulatory authorities require assurance that all crystalline forms are identified and characterised, and specific polymorphs may also be protected through subsidiary patents.
Why must the most stable polymorph be selected early?
Less stable forms may convert during processing or storage.
What regulatory concern exists regarding polymorphism?
Manufacturers must prove no undiscovered crystalline forms exist.