Lecture #6 - Compartments, connectivity, & membrane transport
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
voltage-gated channel
open or close depending on an electrical change in the membrane
ligand-gated channel
open or close depending on the binding of a ligand (hormone)
mechanically-gated channels
open or close depending on physical stimuli like stretching of the membrane
True or False: Active transport goes with the concentration gradient.
False: Active transport goes against the concentration gradient.
Where are most active transports at?
through transporters (pumps)
List the 3 types of carriers or transporters.
Uniporter: 1 molecule one direction
Symport: 2 molecules in one direction
Antiport: 2 molecules in different directions
What is the difference between primary active transport and secondary active transport?
Primary active transport → energy derived directly from ATP
Secondary active transport → derived secondarily from energy that has been used in the form of a concentration gradient
Can you have a secondary active transporter without a primary active transporter?
No → primary AT generates concentration gradient needed to drive secondary AT
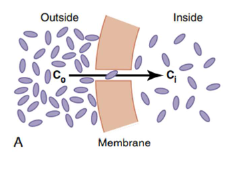
What is this image an example of?
Passive transport (down its concentration gradient)
What is another form of active transport?
vesicular transport →
What is exocytosis?
Intracellular vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and leave the cell
What are two forms of endocytosis?
Phagocytosis: engulfing larger molecules (macrophages, neutrophils)
Pinocytosis: engulfing smaller molecules
Receptor-mediated endocytosis: specific
True or False: Symporters use energy to transport chemicals across a membrane
True
Define Transepithelial transport.
the movement of chemicals across an epithelium
ex: intestine, kidney, glands
What transepithelial transport happens between the epithelial?
paracellular
What transepithelial transport happens through both membranes of the epithelium?
transcellular
Why are tight junctions important?
Tight junctions act as security to make sure molecules and ions do not enter the cell or leave the cell through epithelium cells.
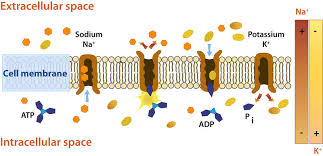
What is the importance of the Na+/K+ pump?
establishing different electrical and concentration gradients outside and inside the cell (production of ATP)
anions
nutrients
water
other solutes in the lumen
The Na+/K+ ATPase creates a ____________. This is used as a _________ type of _________ transport.
concentration gradient
secondary
active transport
Draw out the Na+/K+ ATPase pump.
True or False: Active transports go with the concentration gradient.
False: Active transports go against the concentration gradient.