Neurology Physio OSCE
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What are some Treatment Exercises to address/improve: Decreased pelvic control in stance phase
Weight shift exercise
Abductor strength exercise
Side walking exercise
1-foot disc lateral sliders
Stepping up onto cones
What are some Treatment Exercises to address/improve: No trunk rotation or arm swing
Single step hand-to-target
^ same as above, but touch further across body
reach and grab task
marching on spot with exaggerated arm swing
hold patients hand and passively swing their arm
opposite arm to leg touches (good strength patient only)
What are some Treatment Exercises to address/improve: Impaired sequencing and activation
marching/walking on spot
mirroring
queuing
tactile tapping of muscle to activate it
opposite arm to leg touches (good strength patient only)
What are some Treatment Exercises to address/improve: Decreased knee control in mid stance
manual assistance
walking over obstacles
weight transfers
What are some Treatment Exercises to address/improve: Foot drop during swing phase
step over obstacles
weight transfers anteroposterior
address strength/length deficits
Dorsiflexion ROM
What are some Treatment Exercises to address/improve: No heel strike or roll over to push off
heel strike exaggeration
wedge-block to step onto
heel taps
What are some Treatment Exercises to address/improve: Decreased step length
step to target on ground
single leg forward step rocking
step goal within distance (decrease step goal within distance as patient improves)
work on step propulsion -> increase power
What are some Treatment Exercises to address/improve: Decreased walking speed
walking with metronome/ beat to match
must achieve a certain distance in a certain time
pace setting with therapist
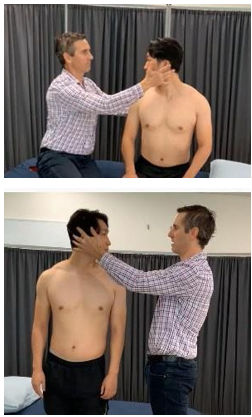
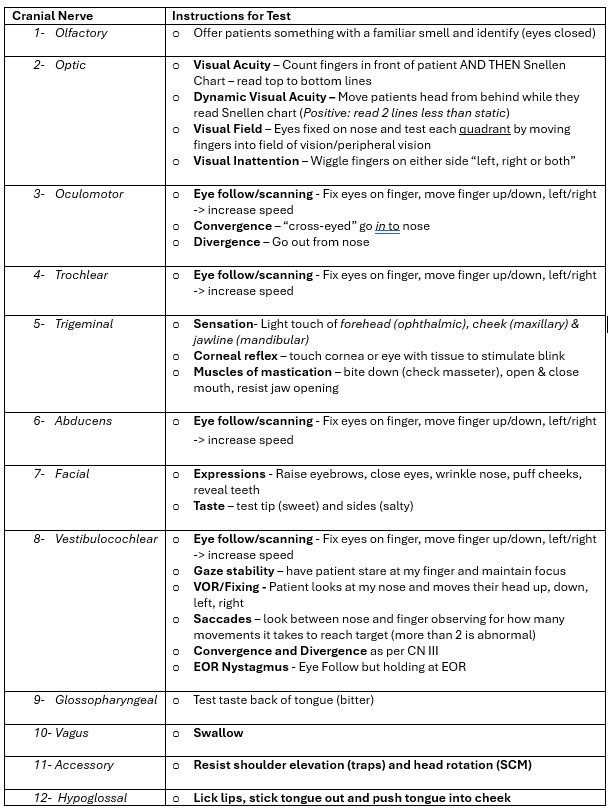
Station 3: Cranial Nerve Assessment
(will test cranial nerves 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 (excluding taste), 8, 11)
Station 4: Coordination Tests - Upper and Lower Limb + Grading
Upper Limb: (Ataxia)
Finger chase - finger to finger
Finger to nose - their nose, my index finger
Forearm supination/pronation - alternating opposite movements on thighs
Finger strumming- tap each finger in order
Lower Limb:
Heel-shin slide - run opposite heel down shin from knee to ankle, repeat looking for ataxia
Leg cycling - in supine
Heel or toe tapping (alternating to make harder)
Alternating hip flexion
Alternating prone knee flexion
Grading:
0- no tremor or dysmetria
1- tremor with amplitude <2cm, dysmetria <5cm
2- tremor with amplitude <5cm, dysmetria <15cm
3- tremor with amplitude >5cm, dysmetria >15cm
4- Unable to perform 5 pointing movements/task
Station 4: Tardieu Scale for Reflex/Spasticity
Testing the movements and reflexes in joints
move elbow flexors slowly (PROM) and then quickly (V3)
move ankle dorsiflexors slowly (PROM) and then quickly (V3)
Key points to notice
Quality of muscle reaction at V1and V3
Spasticity is present if there is a “catch” at V3
Clonus present (Quality 4 or 5)
Hyperreflexia or Hyporeflexia
V1: As slow as possible (measure PROM)
V2: Speed of limb segment falling under gravity (measure spasticity)
V3: As fast as possible (measure spasticity)
Deep tendon reflexes (usually associated)
Assess using a reflex hammer
Biceps tendon/elbow flexion (C5, C6) in supine
Triceps tendon/elbow extension (C6, C7) in prone with towel propped under pec
Quadriceps tendon/ leg extension (L3, L4) off edge of bed
Achilles tendon/plantar flexion (S1, S2) in prone
Cutaneous Reflex
→ Babinski → CNS lesion
Clonus
→ rhythmic oscillation between opposite directions of movement
more than 10 beats is “infatigueable”
Station 6: CTSIB Balance Test
*All stances are arms crossed on shoulders and feet together
Eyes open, hold for 30 seconds
Eyes shut, hold for 30 seconds
Eyes open, rotate head R/L
Eyes open, stand on foam mat, hold for 30 seconds
Eyes shut, stand on foam mat, hold for 30 seconds
Eyes open, rotate head R/L, on a foam mat, hold for 30 seconds
Left hemisphere controls:
Motor function of R side of body
receives sensory info from R side of body
language, interpretation and expression
science, math, logic, reasoning
Right hemisphere controls:
motor function of L side of body
receives sensory info from L side of body
Interpretation of perception
Abstract and creation
Art, music, imagination, intuition and insight
Upper Motor Neuron Lesions
Paralysis
fine-motor-skill impairment
Increased tone (inability for a muscle to relax)
Altered reflexes → Hyper-reflexia/Babinski
Altered soft tissue length
Altered sensation
Lower Motor Neuron Lesions
Paralysis
Muscle wasting
Fasciculations
decreased tone
hypo-reflexia
altered sensation
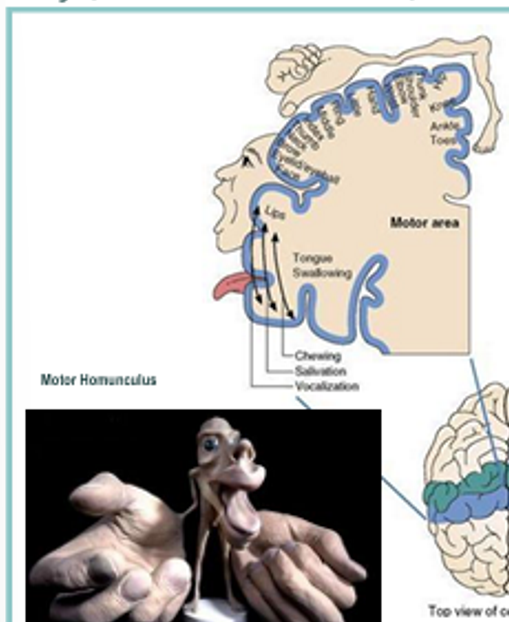
Motor Areas in Somatosensory
Located in frontal lobe of both hemispheres
(Left side of Homunculus)
controls the contralateral side of body
Arranged topographically (motor homunculus)
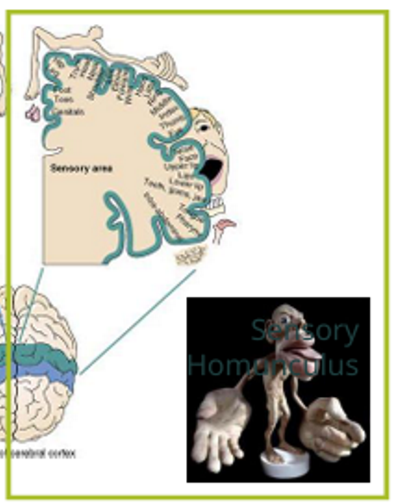
Sensory Areas in Somatosensory
located in parietal, temporal and occipital lobes of both hemispheres
(Right side of homunculus)
receive and process information from sensory receptors
arranged topographically (somatosensory homunculus)
Spinothalamic Tract
Ascending central pathway for pain, temperature, tickle, crude/touch and pressure
Anterolateral system
^crosses immediately for pain
^crosses near brainstem for touch
Spinocerebellar Tract
Ascending central pathway for unconscious proprioception, postural control, balance, coordination.
Corticospinal Tract
Descending motor central pathway concerned with control of voluntary, fine motor and skilled movements of distal limbs
Pyramidal tract
Issues related? Muscle weakness, spasticity, clonus, hyperreflexia
Rubrospinal Tract
Descending motor pathway controlling motor control, flexor muscle tone in upper limbs, inhibits extensor muscles
Tectospinal Tract
Descending motor pathway that coordinates head and neck movements in response to auditory and visual stimuli
Vestibulospinal Tract
Descending motor pathway that works with the reticulospinal tract to modulate muscle tone, and coordinate head and eye movements
related to vestibular systems role in balance
Reticulospinal Tract
Descending motor pathway that influences posture, locomotion, muscle tone, gait and balance by controlling activity of both alpha and gamma motor neurons
^ specialises in trunk and proximal limb movements
Corticobulbar Tract
control of voluntary movement of head and neck muscles, facial expression, chewing/swallowing/speech
Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscus Tract
Ascending central pathway carrying conscious, proprioception and discriminative/fine touch
Motor, Sensory and Motor/Sensory Nerves - Which ones are which?
Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter Most
Motor: 3, 4, 6, 11, 12
Sensory: 1, 2, 8
Both: 5, 7, 9, 10
Station 1: Dermatome Assessment
C2- 3cm behind ear
C3- supraclavicular fossa
C4- AC joint
C5- anterolateral elbow
C6- dorsal thumb
C7- dorsal middle finger
C8- dorsal little finger
T1- anteromedial elbow
T2- axilla
T3- 3rd intercostal space
T4- level of nipples
T5- xiphoid→ sternum upper
T6- xiphoid → sternum lower
T7- quarter way to umbilicus
T8- half-way to umbilicus
T9- three-quarter way to umbilicus
T10- umbilicus
T11- between umbilicus and inguinal ligament
T12- inguinal ligament
L1- proximal thigh
L2- anteromedial thigh
L3- medial femoral condyle
L4- medial malleolus
L5- dorsal 3rd metacarpal
S1- lateral calcaneus
S2- popliteal fossa
S3- ischial tuberosity
S4/5- next to asshole
^ to be done for a spinal cord injury
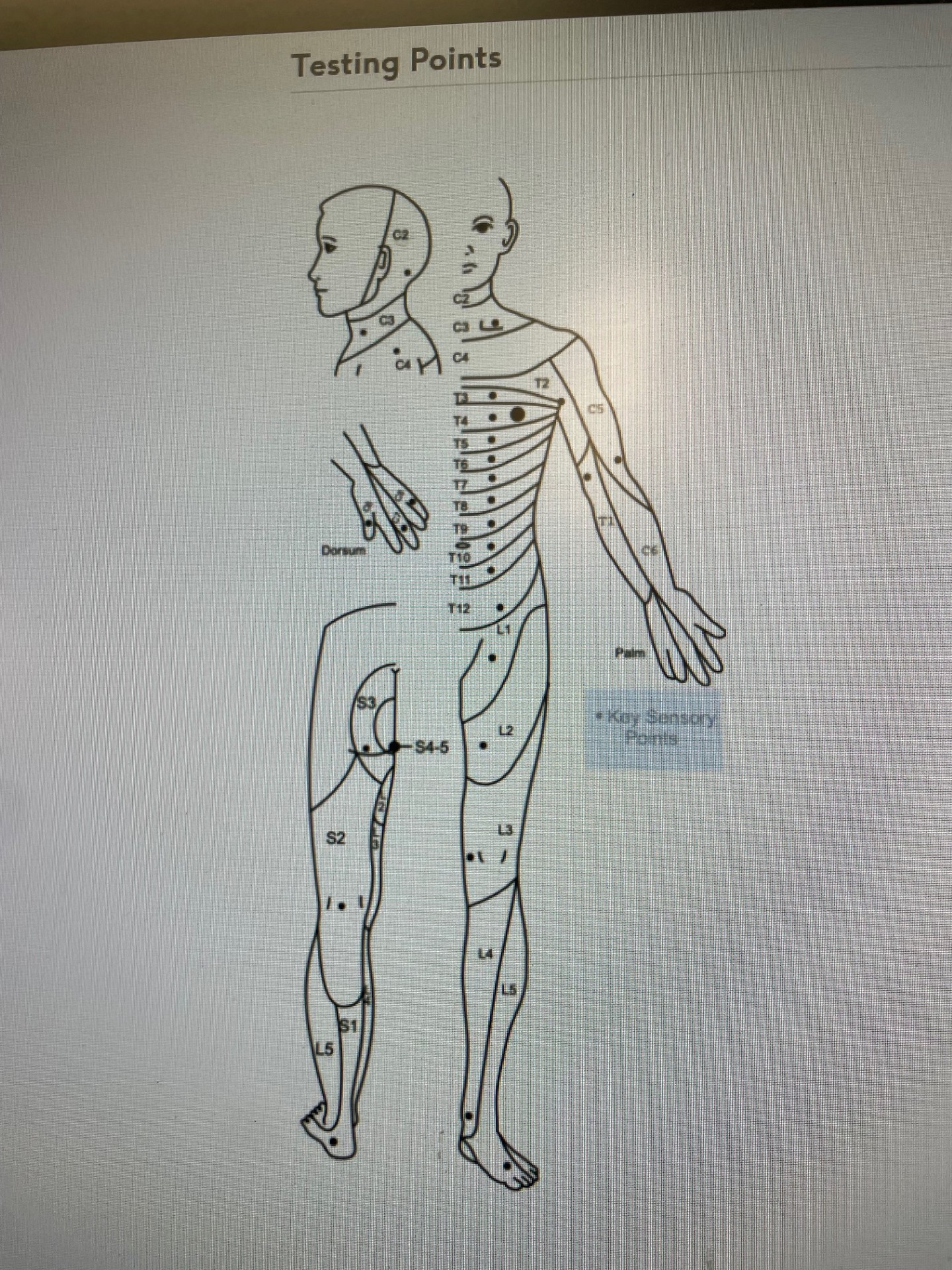
For a spinal cord injury patient, what sensation testing should be done?
Follow the dermatome pattern as outlined by the ASIA scale (specific spots on the body) as were trying to determine the level injured
For a brain injury patient, what sensation testing should be done?
Assess random alternating areas on the upper arm, lower arm, several areas on the hands and multiple spots on the fingers
largely driven by the homunculus representation in the cortex—meaning there are more sites to test.
5 Grades for Motor Scoring
0 - No muscle contraction
1 - Palpable or visible contraction
2 - Active movement; full ROM; gravity eliminated
3 - Active movement; full ROM; against gravity
4 - Active movement; full ROM, against gravity; + moderate resistance
5 - Normal active movement; full ROM; against gravity; + full resistance
5+ - Normal active movement; full ROM; against gravity; + sufficient resistance with no pain
NT - Not testable → severe pain, amputation, >50% ROM
Station 6/7: Essential Components of Reaching
Shoulder forward flexion
Shoulder abduction
Elbow flexion
Forearm supination/pronation
Wrist extension
Wrist radial/ulnar deviation
Station 6/7: Essential Components of Grasp & Manipulation
Thumb abduction
MCP/IP extension
Thumb to 4th & 5tg digit
Force throughout 2nd digit
Force modulation
Individuation of fingers
Station 6/7: Essential Components of sit to stand
Initial foot placement - ankle DF
Forward trunk + trunk extension
Anterior translation of knees
Hip/Knee/Ankle PF extension
Station 6/7: Essential Components of Side-lying to Sitting
Neck and trunk lateral flexion
Pushing of abducted arm
Extension of elbow/wrist
Hip/knee flexion
Lower feet to floor
Station 1: What are some examples of upper limb tactile assessments for a patient with a brain injury?
Using a cotton tip (light touch)
Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscus pathway
Pin prick test (sharp/dull)
Spinothalamic pathway
Paperclip 1-or-2 sides (two-point discrimination) deep touch
Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscus pathway
Hot and Cold test tubes (temperature)
Spinothatlamic pathway
Important Tips:
Start with baseline tester on facial cheeks
Compare both sides
Test proximal to distal
Ask patient to close their eyes
Example: Demonstrate a muscle strength test of shoulder extension for a person with a L) brain injury/CNS lesion?
Motor weakness or spasticity on the right side, but will check left side first as this is unaffected
Can be done prone or sitting
Muscles Assessed: Lats, teres major, post deltoid
Looking for: Right sided weakness, spasticity,
2 Signs of Dysfunction in each Cranial Nerve
CN 1 - Olfactory
Loss of smell & distorted smell
CN 2 - Optic
Vision loss & impaired pupillary light reflex
CN 3 - Oculomotor
Drooping eyelids & eye deviated
CN 4 - Trochlear
Vertical diplopia & head tilt away from lesion
CN 5 - Trigeminal
Facial numbness & weak jaw muscles
CN 6 - Abducens
Inability to abduct eye & horizontal diplopia
CN 7 - Facial
Facial weakness & loss of taste
CN 8 - Vestibulocochlear
Hearing loss & balance disturbance
CN 9 - Glossopharyngeal
loss of gag reflex & impaired taste
CN 10 - Vagus
Voice change & uvular deviation away from lesion
CN 11 - Accessory
Weak shoulder shrug & weak head turn
CN 12 - Hypoglossal
Tongue deviation towards lesion & atrophy of tongue
Station 1: How to perform Somatosensation testing
Light touch:
Compare both sides by dabbing a pulled cotton tip
Spinal cord → dermatomal
Brian injury → comparable random sides
Start with a baseline on face
Pain/Pinprick: Deep touch
Use a pin prick for the sharp and dull sides
Alternate dull & sharp and ask patient to differentiate between sides → dermatomal pattern
Compare left and right alternatingly at same location
Start with a baseline on face
Temperature:
Using a hot and cold test tube
Compare left and right alternatingly at same location
Start with a baseline on face
Proprioception:
Dynamic: Move limb and get patient to identify direction
Static: Move the unaffected joint and as patient to repeat action on their affected side
(testing the Spinocerebellar pathway)
2-Point Discrimination:
Use paperclip to either touch 1 side or both and ask which one they feel
Start with a baseline on face
What would be some abnormal findings?
Inability to differentiate, oversensitivity, absent/reduced sensation, mislocalizes
Station 2: Myotome testing (UL and LL)
Upper Limb:
C1 → Head flexion
C2 → Head extension
C3 → Lateral flexion
C4 → Shoulder elevation
C5 → Shoulder abduction
C6 → Elbow flexion + wrist extension
C7 → Elbow extension + wrist flexion
C8 → Finger flexion + thumb extension
T1 → Finger abduction
Lower Limb:
L2 → Hip flexion
L3 → Knee extension
L4 - Ankle dorsiflexion
L5 → Great toe extension
S1 → Ankle plantar flexion + knee flexion
^ Alternate sides each time
Voluntary movement is executed by corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts
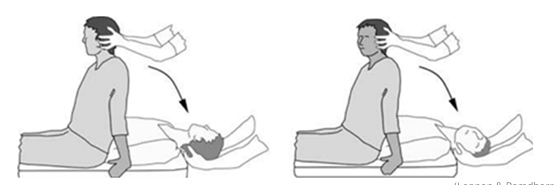
Station 5: How to perform the Hall-Pike test?
Assessment for Anterior and Posterior Canal BPPV
Warn patient of possible symptom reproduction, nausea, sickness, and that there is a vomit bag nearby if needed*
Instruct patient where you’re going to grip them and what movement is going to be done.
Rotate head 45deg to affected side
Patient’s gaze fixed to examiners nose or recommended target
Lie down patient swiftly, placing head into 30deg extension and off the bed
Observe for nystagmus and other symptoms
Interpretation:
Posterior canal → Affected rotational and up beating
Anterior canal → Affected rotational and down beating
For a peripheral nerve injury patient, what sensation testing should be done?
Follow the peripheral nerve distribution
Median, ulnar, radial, axillary, musculocutaneous, brachial
i.e. altered sensation of the pinky, most likely going to be ulnar nerve
For a CNS lesion injury patient, what sensation testing should be done?
Test body segments that correlate with the sensory homunculus
This helps identify where in the brain (or nervous system) a problem might be occurring.
If someone has numbness in the hand and face (which are next to each other in the sensory homunculus), it might point to a problem in a specific part of the brain
If a patient has an unknown lesion, what sensation testing should be done?
Comprehensive circumferential testing of the whole body
Station 2: Grading strength
Grade 0 → total paralysis, no contraction
Grade 1 → no movement but contraction observed
Grade 2 → full ROM, gravity eliminated
Grade 3 → full ROM, against gravity only
Grade 4 → holds against moderate resistance
Grade 5 → holds against maximum resistance
Station 4: Rigidity vs Spasticity
Rigidity: increased resistance throughout ROM and is present in all muscles.
Spasticity: jerky and clonus movements
Station 2: Muscle Strength Assessment
Get patient to complete movement by self first
Check unaffected side first
Upper Limb:
Shoulder abduction (GE= supine)
Elbow flexion (GE= upright along a bed)
Elbow extension (GE= upright along a bed)
Wrist extension/flexion (GE= along a bed)
Lower Limb:
Hip flexion (GE= side lying)
Knee extension (GE= side lying)
Ankle dorsiflexion (GE= side lying)
Ankle plantar flexion (GE= side lying)
Knee flexion (GE= side lying)
GE = Gravity Eliminated
Station 2 Muscle Strength: If the person has a R) brain injury, what side do we test first?
The R) side because that would mean the left is affected and we always start with the unaffected side first
Station 4: What are some abnormal findings for coordination, reflexes and muscle tone assessments?
Dysmetria (over or under shooting)
Tremor
Can’t perform rapid alternating movements
Poor coordination
Absent reflexes
Babinski sign/Hoffmans sign
Clonus
Jerky resistance
Station 5: How to perform the Supine Roll test?
Assessment for Horizontal Canal BPPV
Patient lying supine with 30deg head flexion → on pillow
Rotate patients head 90deg to affected side. Observe nystagmus and symptoms, hold for 1 minute.
Turn head back to midline. Hold for 1 minute
Rotate patients head 90→ to unaffected side. Observe again. Hold for 1 minute
Horizontal Canalithiasis→ geotropic and greater nystagmus intensity
horizontal Cupulothiasis→ apogeotropic and lesser nystagmus intensity
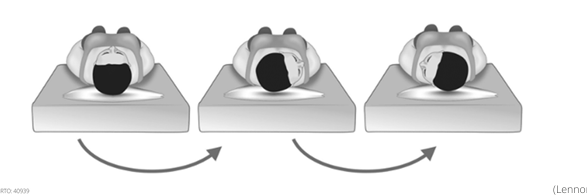
Station 5: How to perform the Epley Maneuver?
Located in the posterior canal BPPV
Head rotated 45deg to affected side and swifty brought down into 30deg extension off the edge of bed. Hold for 1 minute and observe.
Rotated 90deg to other side. Hold for 1 minute and observe. Symptoms should relieve.
Roll patient onto unaffected shoulder. Hold for 1 minute. Guide patient back up.
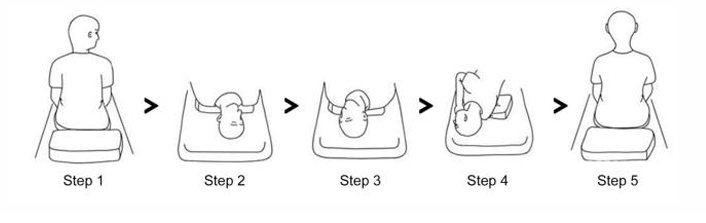
Station 5: How to perform the 360 BBQ Head roll?
Located in the horizontal canal
In supine with 30deg flexion, head turned 45deg toward affected ear and held for about 1 minute
Head rolled slowly back to neutral, pause for 1 minute
Continue toward unaffected ear and stop at 45deg. Hold for about 1 minute
Roll in same direction until patient is prone resting on elbow, chin tucked towards chest. Hold for 1 minute.
Return patient back to supine, and then sitting
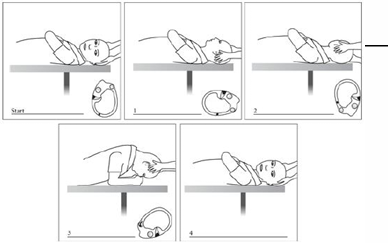
Station 5: What are screening tests to be done before conducting vestibular tests?
VBI screening test
Cervical AROM screening
Recent surgery, cardiovascular and vision history ± medications
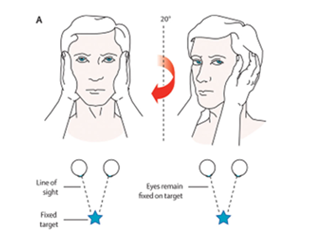
Station 5: How to perform the Head Impulse Test?
Position patient upright fixating gaze on nose whole time
Hold patients head with both hands
Move head slowly side to size for a baseline
Give a small. quick and unpredictable thrust to one side and return to midline. Repeat on other side.
Repeat 2-3 times on each side
Positive test: unable to maintain fixation
differentiate peripheral vs central vertigo and VOR
“Saccade = Side of lesion”
Abnormal finding: Patients eyes move with their head and then make a corrective saccade back to nose
Result | Suggests |
|---|---|
Abnormal HIT (with corrective saccade) | Peripheral cause (e.g., vestibular neuritis) |
Normal HIT (no corrective saccade, despite vertigo) | Central cause (e.g., stroke) |
Station 7: What are some parameters to change to influence grasp parameters?
Add a visual target (like tape)
Change object to grasp
Change distance, size, shape, weight, texture etc
Alter height or support conditions
Station 8: How to facilitate a person’s gait for a person with Gr2 LL strength? + GR3 and GR4
~ Instruct examiner to use belt to hold patient up and on affected side ~
Stand phase: 1 hand pushing hip forward, 1 hand pushing knee back
Swing phase: 1 hand pulling foot up, 1 hand pushing knee up/through
^ use a wheel-stool to follow patient along
GR3 - Without examiner holding belt but still facilitating
GR4 - Tactile tapping while they walk normally
Introduction
Wash Hands…
“Hi Sarah, my name is Emily Grace, and I am a second year Physio student. Just before we begin, I am just going to need 3 points of ID including your first and last name, date of birth and address….So today we are going to be conducting a few tests in regard to your level of function and some of these will be pretty hands on, is that okay with you? So were going to get started with…”
VBI Screening
Performed first in sitting and then standing
Rotated EOR and held for 10 seconds → observing for signs of VBI/CAD
Bought back to neutral for 10 seconds → repeated in opposite direction