Chem 101 3rd Exam
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Condensation
Gas to Liquid
Evaporation
Liquid to Gas
Freezing
Liquid to Solid
Melting
Solid to Liquid
Sublimation
Solid to Gas
Deposition
Gas to Solid
Calories
(Specific Heat)(Mass)(Difference of Temp) or (Heat of fusion or vaporation)(Mass)
More Vapor Pressure
Higher temp = ?
Ionic Solids
High melting point, very hard, many soluble in H2O, crystal structures, Ex. NaCl, K2O, CaCl2
Covalent Network Solid
Ex. diamond, solid is one molecule, cannot melt
Molecular Solids
discreet molecules are in the corners, very easy to melt, ex. dry ice, ice,
Metallic Solids
Simple Metals, Ex. Al, Cu, Fe, Mg
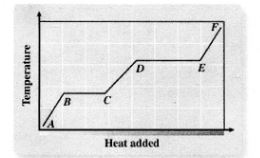
Heating
A - B
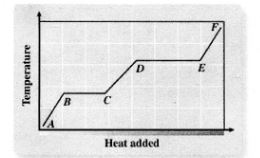
Melting
B - C
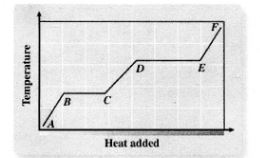
Liquid Heating
C - D
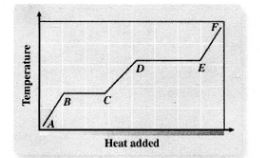
Boiling
D - E
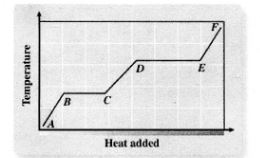
Heating Up Steam
E - F
False
The Melting Point of metallic sodium is 97.83 C so at a temp of 25 C, it is a liquid
True
The solvent in an aqueous solution is always water
True
Network covalent substances have one of the highest melting points of all substances
False
Water is a liquid at room temp, due to its very small mass
True
When heat is first added to an ice/water mixture at 0 C, the temp of the water will not increase until all the ice has melted
False
Adding a non-volatile solute to water will cause the vapor pressure to increase
False
At the same temp, all liquids have the same vapor pressure
False
Dialysis membranes have smaller pores than osmotic membranes
True
Glucose (a small polar molecule) can move through a dialysis membrane but not an osmotic membrane
False
All reactions are reversible
False
When we say that an equilibrium lies to the left, it means that the concentration of the reactants is less than that of the products
True
The larger the energy of activation, the slower the reaction
False
If the chemical energy of the products is less than the chemical energy of the reactants, the reaction is always very fast
exothermic
Steam becoming boiling water (endothermic, exothermic, cannot tell)
exothermic
Metabolizing of chocolate donut (endothermic, exothermix, cannot tell)
endothermic
Photosynthesis (endothermic, exothermix, cannot tell)
cannot tell
A reaction with a very high energy of activation (endothermic, exothermix, cannot tell)
endothermic
Melting iron to molten iron (endothermic, exothermix, cannot tell)
endothermic
Electrolysis of water (to H2 and O2) (endothermic, exothermix, cannot tell)
endothermic
A reaction where the products have more chemical energy than the reactants (endothermic, exothermix, cannot tell)
endothermic
A reaction with a + delta H (endothermic, exothermix, cannot tell)
Precipitation
The process where an insoluble solid separates from the solution
dissolving
The process where a soluble solid goes into solution
Condensation
Name of the process of converting a gas to a liquid
freezing
The process of a liquid going to a solid
evaporation
Name of the process of converting a liquid to a gas
melting
The process of converting a solid to a liquid
sublimation
The process of converting a solid directly to a gas
heat of vaporization
The heat needed to convert 1 gram of a substance from a liquid to a gas
miscible
The term used for two liquids that make a uniform solution when mixed together
alloy
What is a solution of two or more metals called?
specific heat
the heat needed to raise the temp of 1 gram of substance 1 C
viscosity
What is the resistance to flow for a liquid called?
heat of fusion
the heat needed to convert 1 gram of substance from a solid to a liquid
osmotic membranes
type of semi-permeable membrane where only solvent molecules can move through
dialysis membrane
the kidneys are what type of membrane
isotonic
two solutions with equal concentration of solutes are called this
osmols
what is the term for moles of particles
dialysis membrane
type of semi-permeable membrane where the solvent and very small molecules can move through
equilibrium
the situation when the rate of a forward reaction equals the rate in the reverse reaction