AICE Language Paper 1 Breakdown and Analysis Guide
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
AICE Language
An examination that lasts for 2 hours and 15 minutes.
Directed Response
A type of question that requires a specific answer based on the original text.
Key conventions
The standard practices or norms that are expected in a particular form of writing.
Structural devices
Techniques used in writing to organize and present ideas effectively.
Language devices
Tools used in writing to enhance meaning and impact, such as figurative language.
Form
The overall structure and style of a piece of writing, including audience, tone, and purpose.
Structure
The arrangement of elements within a text, including introduction, paragraphs, and punctuation.
Language
The choice of words and style used in writing, which can include rhetorical devices and lexical fields.
Rhetorical devices
Techniques used to persuade or impact the audience, such as metaphors and similes.

Lexical fields
Groups of words related in meaning that create a specific atmosphere or context.

Figurative language
Language that uses figures of speech to convey meaning beyond the literal.

Anaphora
The repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of successive clauses.
Epistrophe
The repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses.
Comparative Analysis
The examination of similarities and differences between two texts.
Examiner report
A document summarizing the performance and observations of candidates in an exam.
Key messages
Important points highlighted in the examiner report regarding candidate performance.
Integrated approach
A method that combines different elements for a more effective analysis.
Textual evidence
Quotations or references from the text used to support an argument or analysis.
Chiasmus
A rhetorical device in which words or concepts are repeated in reverse order.
Weaker response analysis
An evaluation of why some candidates did not perform well in the exam.
Formal letter
A letter that follows a structured format and is typically used for professional communication.
Informal letter
A letter that is more casual in tone and structure, often used for personal communication.
Purpose
The reason for writing, which influences the tone and structure of the text.
Text Analysis
A critical examination of a text's form, structure, and language to understand how it achieves its purpose and conveys meaning to the audience.
Stronger Responses
Responses that demonstrate awareness of travel writing conventions, including chronological structure, location-focused descriptions, and integration of experiential content.
Weaker Responses
Responses that struggle to identify textual features and their effects, often lacking clarity and precision in terminology.
Quotation Precision
Quotations from the text should be precise, concise, and linked to explanatory comments to enhance analysis.
Higher Marks Suggestions
Candidates should use quotations, evidence, and evaluation to produce precise, meaningful commentaries and ensure coherent and effectively structured analysis.
Features of Higher-Level Responses
Coherent and effectively structured analysis that integrates quotations and evidence into a cohesive argument.
Chronological Structure
A narrative structure that presents events in the order they occur, commonly used in travel writing.
Anecdotal Content
Personal stories or experiences included in writing to engage the reader and provide a relatable context.
Figurative Language
Language that uses figures of speech, such as metaphors and personification, to create vivid imagery and convey deeper meanings.

Metaphor
A figure of speech that describes an object or action in a way that isn't literally true, often to suggest a similarity.
Personification
Attributing human characteristics to non-human entities to create relatable imagery.
Rhetorical Questions
Questions posed for effect rather than answers, inviting the reader to reflect on the content.
Lexis
The total stock of words in a language or a particular field of study, often used to convey specific meanings.
Positive Connotations
Words or phrases that evoke a favorable or pleasant association.
Negative Connotations
Words or phrases that evoke an unfavorable or unpleasant association.
Cohesive Argument
An argument that is logically structured and flows smoothly, making it easy for the reader to follow.
Textual Features
Elements of a text, such as style, mood, and vocabulary, that contribute to its overall meaning and effect.
Evidence Selection
The process of choosing specific examples or quotations from a text to support an analysis.
Integration of Quotations
The practice of seamlessly incorporating quotations into an analysis to support claims and arguments.
Experiential Content
Content that draws from personal experiences to enhance the narrative and engage the reader.
Geographic Features
Natural characteristics of a landscape, such as mountains and rivers, that can influence the content of travel writing.
Gastronomic Delicacies
Special or unique food items that are highlighted in travel writing to enhance the cultural experience.
Whole Text Approach
An analytical method that considers the entire text to provide a comprehensive understanding of its themes and techniques.
Audience Engagement
The process of capturing and maintaining the reader's interest through effective writing techniques.
Author's Purpose
The reason WHY an author wrote something.
Possible Effects of Author's Purpose
Depending on the type of purpose, a text might impact the reader by convincing them to do something or think a certain way, teach them something new, or make them feel entertained.
Bias
Being heavily in favor of (positive bias) OR heavily opposed to (negative bias) an idea or thing, usually in a way that is close-minded, prejudicial, or unfair.
Possible Effects of Bias
Sends a message to readers about specific prejudice and is sometimes used to create prejudice. Can spin the text in a positive or negative light, depending on the positive or negative bias.
Genre Elements
Text features and unique elements that make up fiction and nonfiction texts.
Possible Effects of Genre Elements
For fiction, the effect of genre elements might be to help readers better understand the story or to create suspense. For nonfiction, it might be to provide meaningful information or make that information easier to understand.
Asyndeton
A literary tool that can speed up the pace of a text, create a sense of chaos or unease, or create a sense of abundance or intensity.
Polysyndeton
A literary tool that can slow down the pace of a text, imply that the items are linked in an equal way, and create a sense of breathlessness.
Anaphora
The repetition of certain words or phrases at the beginning of sentences that follow each other.
Possible Effects of Anaphora
Increasing the emotional impact and memorability of the message, establishing a rhythm and pattern, and emphasizing the repeated word or phrase.
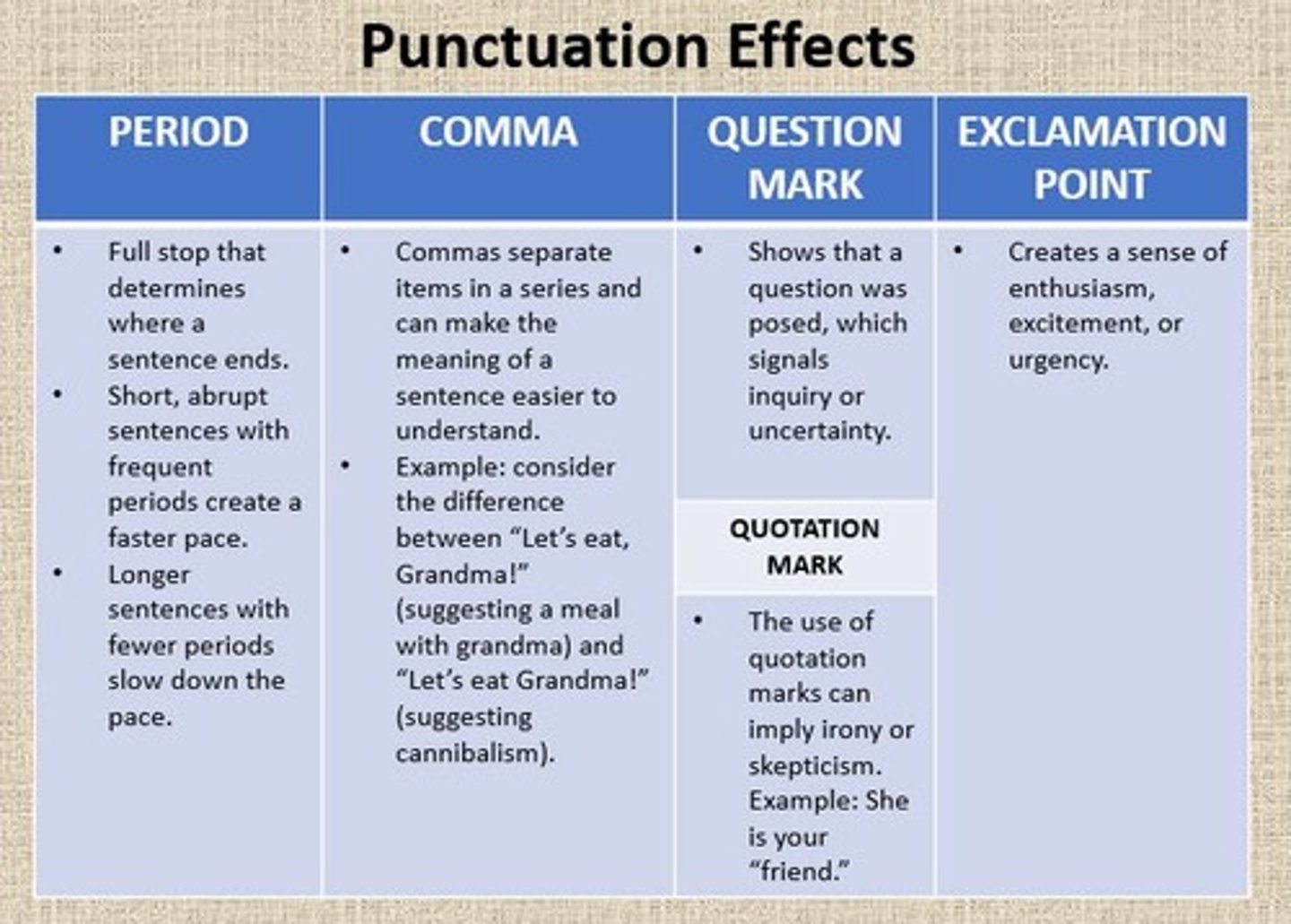
Punctuation
The marks or symbols used in writing to improve the clarity, meaning, and structure of sentences and texts.
Possible Effects of Punctuation
Effects depend on the type of punctuation. Punctuation can contribute to the register of a text.
Example of Punctuation Effects
Using semicolons and colons creates a more formal register while dashes and ellipses can create a more casual or conversational register.
Repetition
The repeating of a specific word or phrase. Repetition in a general sense can repeat anywhere in a text.
POSSIBLE EFFECT(S)
Provides clarity, creates emphasis, highlights deeper meanings, makes portions of a text more memorable, increases persuasive effects, and creates a rhythm and flow.
MEANING (Sentence Length)
The length of a given sentence, which can impact the overall effect.
POSSIBLE EFFECT(S) (Sentence Length)
Sentence lengths can influence the rhythm and pace of a text as well as its overall tone.
SHORT sentences
Including Staccato sentences can create a sense of urgency, excitement, or suspense.
LONG sentences
Help slow the pace and pack in more details.
VERY short sentences
1-2 words.
Short sentences
5-10 words.
Medium sentences
11-20 words.
Long sentences
21+ words.
MEANING (Sentence Type)
Establishes the purpose of a sentence (to tell something, ask something, give a command, or show strong emotion).
POSSIBLE EFFECT(S) (Sentence Type)
Sentence type can create specific tones, moods, and intentions, which can have a significant impact on how the reader perceives and engages with a text.
DECLARATIVE sentences
Make a statement and are usually used to present facts, describe events, or express opinions in a neutral, informative way.
INTERROGATIVE sentences
Ask a question and are usually used to create a sense of curiosity, engagement, or suspense.
IMPERATIVE sentences
Give a command and are usually used to create a sense of urgency, authority, or persuasion.
EXCLAMATORY sentences
Show strong emotion and are usually used to create a sense of surprise, excitement, or enthusiasm but can also show a heightened sense of joy or anger.
Syntax
The arrangement of words and phrases in a specific order.
POSSIBLE EFFECT(S) (Syntax)
Syntax helps to effectively convey a message and influences the way that readers interpret and respond to a text.
Triadic Structure (Rule of 3's)
A sentence containing a series of three words, phrases, or clauses.
POSSIBLE EFFECT(S) (Triadic Structure)
Creates a sense of completeness and harmony that makes the text more engaging, persuasive, and memorable.
Alliteration
The repetition of two or more letters or sounds at the BEGINNING of words that are adjacent or closely connected to each other.
POSSIBLE EFFECT(S) (Alliteration)
Depending on how it is used, and in which type of text, alliteration can create various effects like creating a certain rhythm/flow, making something more memorable or catchy, emphasizing or reinforcing specific words, creating a comedic effect, or adding richness and depth to the language of a text.
Allusion
A reference to another work, person, event, place, or thing in pop culture.
POSSIBLE EFFECT(S) (Allusion)
It can enrich the meaning of a text by connecting it to a larger cultural or historical context.
Allusion (continued)
It can create depth and complexity by tapping into collective cultural references that make it more likely to resonate with readers on a psychological, emotional, or intellectual level.
Allusion (further note)
For an allusion to make sense, the reader must have background knowledge about it. Otherwise, it won't make sense.
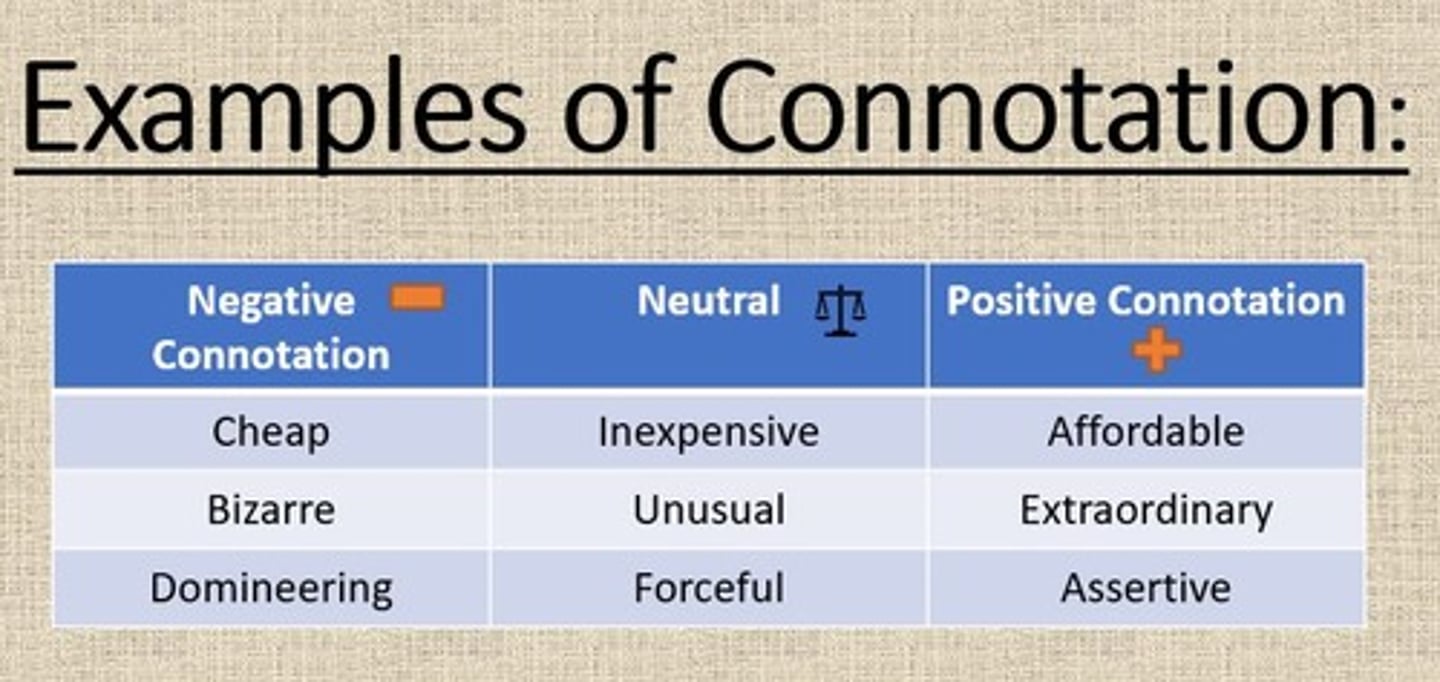
Connotation
Refers to the feeling or emotion associated with a word. It can be positive, negative, or neutral.
Possible Effects of Connotation
Adds layers of depth and complexity to a text that helps influence readers' emotional responses, imagery, characterization, theme development, and overall engagement with the text.
Denotation
Refers to the literal, dictionary definition of a word.
Possible Effects of Denotation
Can help improve clarity and understanding of a text, can help maintain an objective/impartial tone, and can support juxtaposition by making sharp contrasts between words with contrasting denotations.
Diction
Refers to the choice and use of words that authors use in their writing. It involves selecting and arranging words deliberately to create specific effects.
Possible Effects of Diction
Diction can enhance or hinder the clarity of a message. It can set the tone or mood, determine the register (formal/informal), enhance persuasiveness, reflect cultural norms, create vivid imagery, and deepen symbolism.
Hyperbole
Refers to the deliberate exaggeration of a truth or point for emphasis or dramatic effect.

Possible Effects of Hyperbole
It can capture the readers' attention, present something common in an intense manner, emphasize a point, enhance imagery, trigger an emotional response in the reader, make a point more persuasive or memorable, and add some humor to a text.
Imagery (Descriptive Language)
Refers to the use of vivid and descriptive language to create mental pictures, sensations, or experiences in the minds of readers.
Possible Effects of Imagery
It can appeal to readers' senses, emotions, and imaginations. It can make a text far more engaging and memorable and can also help establish the setting, mood, and atmosphere.
Irony
Refers to a contradiction or disconnect between what is expected and what happens.
Possible Effects of Irony
It can appeal to readers' senses, emotions, and imaginations. It can make a text far more engaging and memorable and can also help establish the setting, mood, and atmosphere. Irony is often used for humor, satire, social commentary, or dramatic effect.
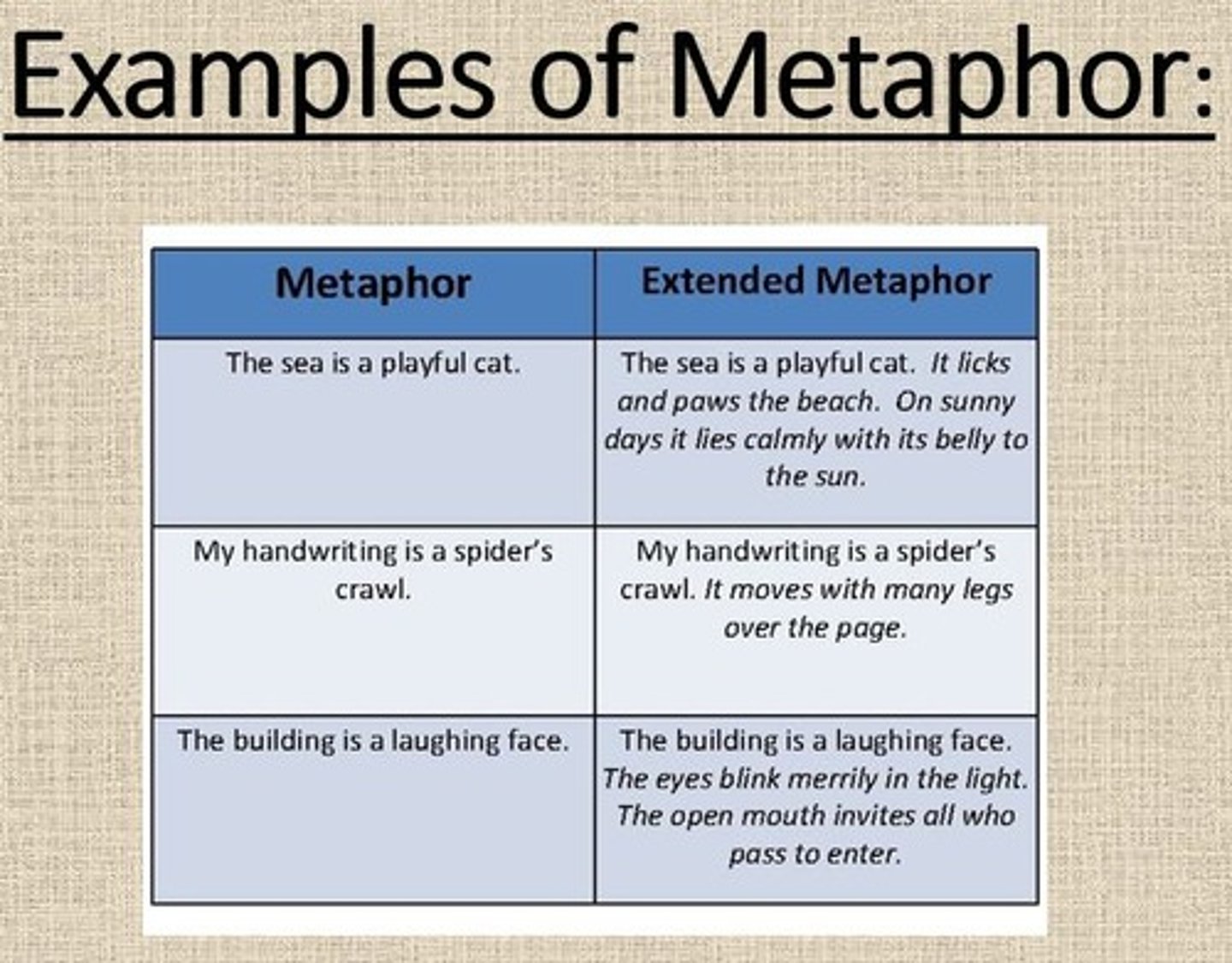
Metaphor
A METAPHOR makes a comparison between two unrelated things WITHOUT using 'like' or 'as' to make the comparison.
Extended Metaphor
An EXTENDED METAPHOR extends/continues the comparison for several lines, paragraphs, or pages.