Heart - AP and Circulatory system
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Neurogenic heart
beat under control of nervous system
Myogenic heart
Contraction initiated within the heart and the nerves going to the heart only regulate the rate of he heart beat
Cardiac muscle cells
branched, connected to one another via intercalated discs that harbor gap
Junction
allow action potentials to spread between the cardiac cells, producing uniform depolarization of the heart muscle. muscle contraction and synchronized heartbeat.
Pacemaker cells
contain a specialized cell membrane that allows Na, K, and Ca, to cross and trigger their electrical impulses. These are located in the SA node.
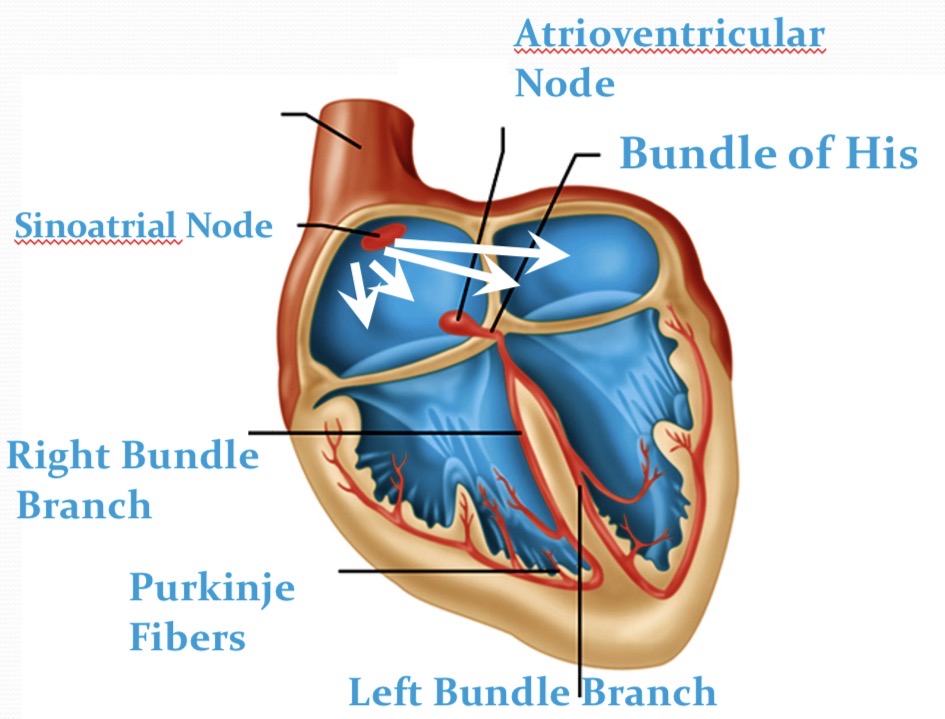
Cardiac Conduction system
transmits electrical impulses to cause atrial and ventricles contractions. Spreads from the SA node → atria/cardiac muscles→ AV reliefs the Bundle of His→ Purkinje fiber → ventricular heart muscle cells.
What effect does the small diameter of the conducting fibers on the velocity of the AP?
The small diameter of the conducting fibers decreases the velocity of the action potential (AP) transmission. This slower conduction rate allows for more effective timing of cardiac muscle contractions.
Why do we want a slow AP between the atria to the ventricles?
A slower action potential (AP) between the atria and ventricles ensures sufficient time for the atria to fully contract and empty blood into the ventricles before they begin to contract. DELAY
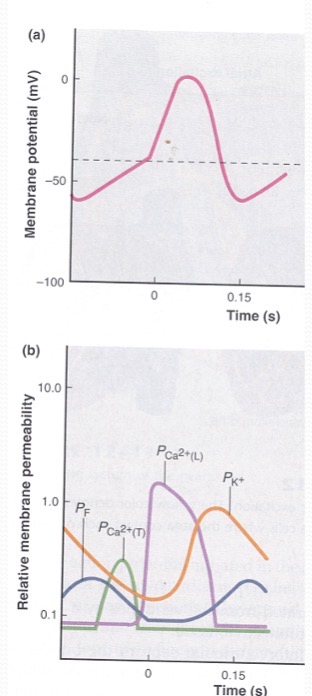
How is the heart beat generate in the SA node?
Permeability of K decreases, Pf are open with low Pm and close with rising Pm - permeable to Na. Pf close and transient Ca open, allowing Ca in → reaching the threshold. Repolarization occurs with K channels reopening.
Pf - Funny Channels
funney current mixed with sodium potassium current. It has dual activation by voltage and by cyclic nucleotides
ECG (EKG)
Electrocardiogram is a measure of the electrical activity that is measured at the surface of your body.
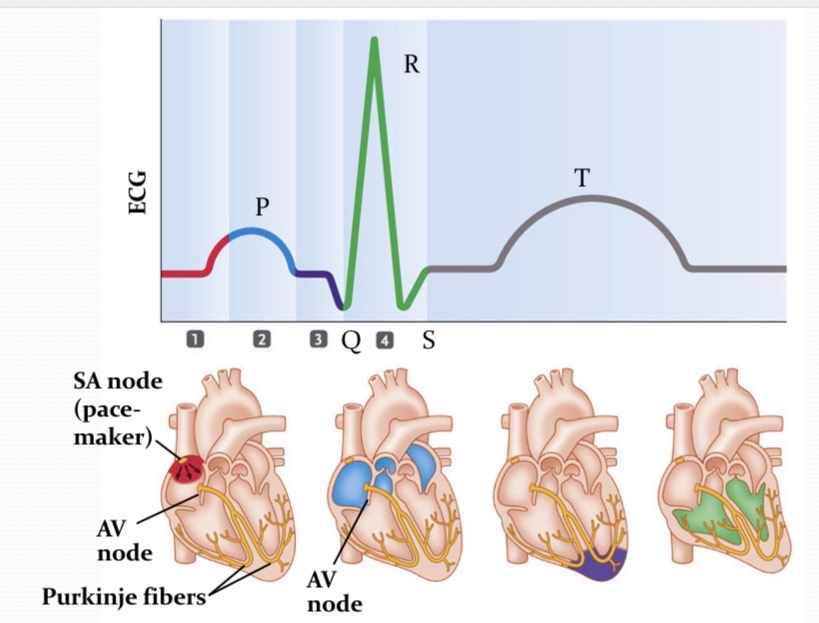
What is happening at 1?
pacemaker generates a wave of signals to contract
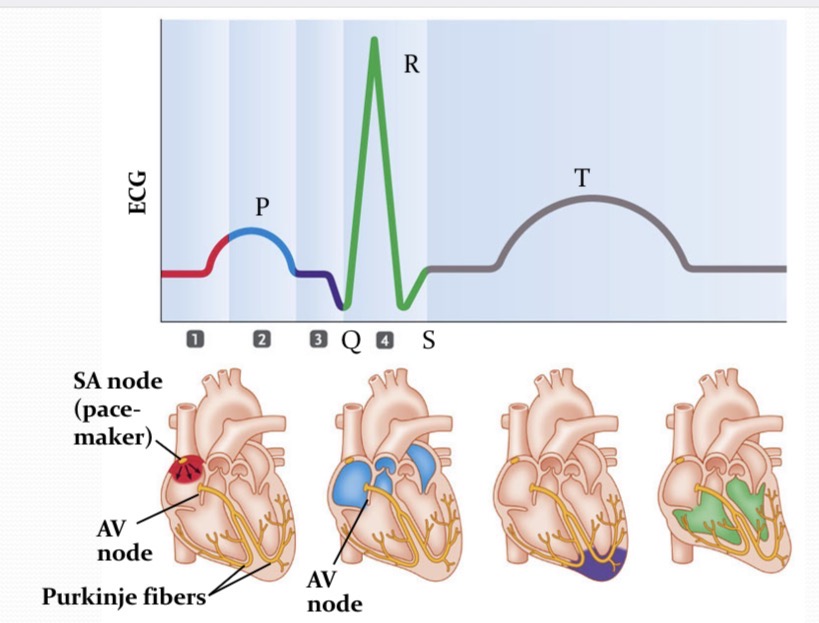
What is happening at 2?
Signal are delayed in the region between the atria and ventricles
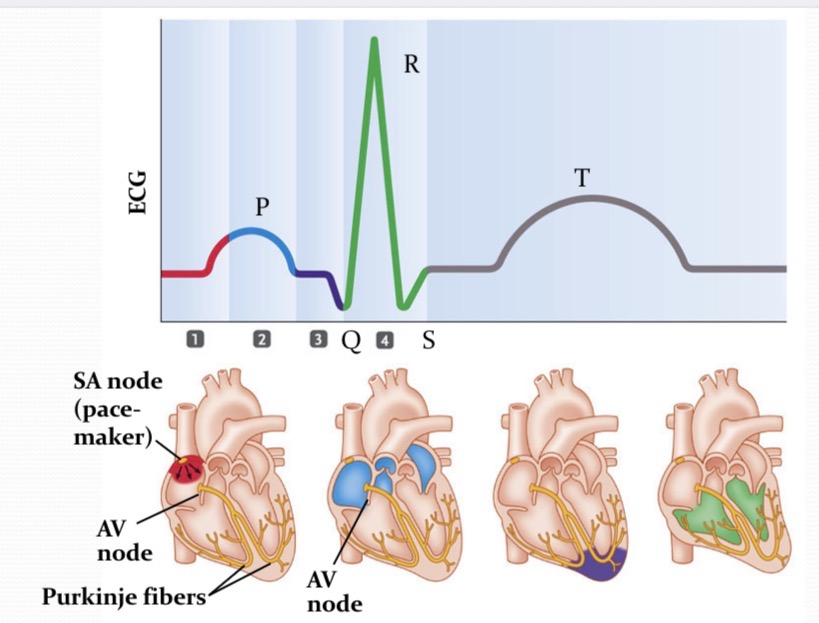
What is happening at 3?
AV node cells are stimulated to produce a signal that travels down the bundle of his, alms the purkinje fiber, to the bottom of the heart
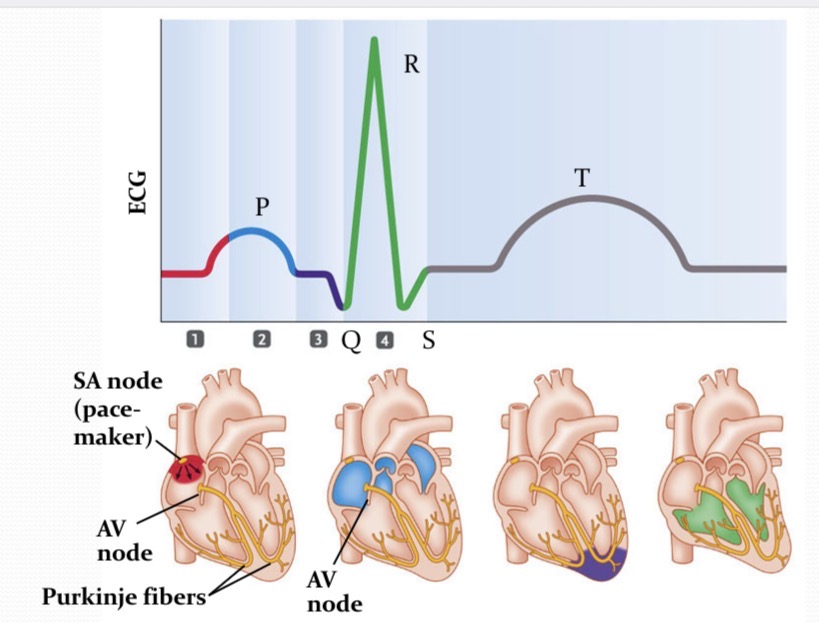
What is happening at 4?
Signals spread from the bottom of the heart upward→the ventricles contract
P wave
wave of depolarization that spread from the SA node throughout the atria
QRS
the time in which the impulse in traveling within the AV node and the bundle of His. depolarization of ventricles
PR interval
time betwen the onset of atrial depolarization and the onset of ventricular depolaization
T wave
ventricles repolarize
ST interval
ventricles are COMPLETELY depolarized
QT interval
time for the ventricular depolarizations and repolarization to occur - “ventricular action potential”
Aterioles
deliver blood to capillaries
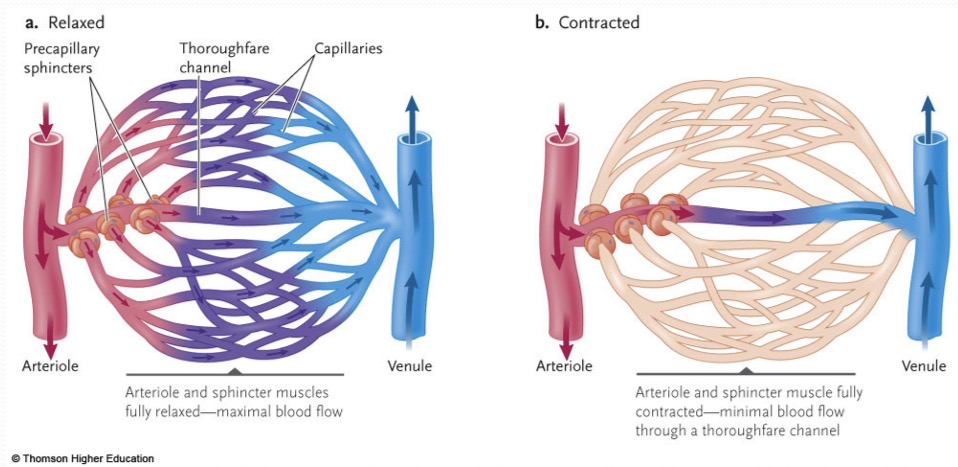
Capillaries
exchange material with interstitial fluid. Thinnest walls and has NO smooth muscle. Precapillary sphincters controls blood flow through the inside.
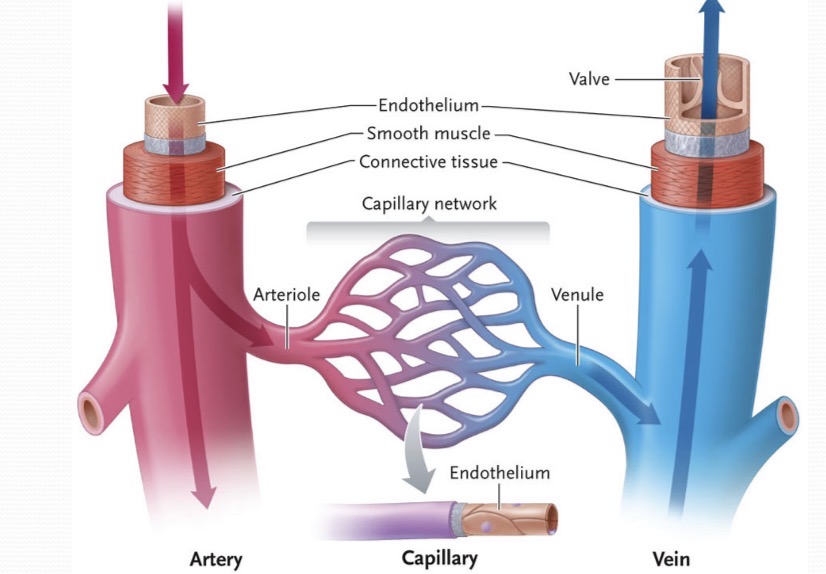
Arteries
carry blood away from the heart - oxygenated blood. Has three layers and can constrict and dilate the blood. Regulates the blood flow and pressure of blood that going into the capillaries
Venules
collect blood from capillaries
Veins
return blood to the heart - deoxygenation blood. They have thin walls and act as a reservoir. Contain one way valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards
Arteriole end
Pressure of blood (hydrostatic pressure) higher than the pressure of the interstitial fluid at the hypertrophic end of the capillary bed → water and small solutes are forced out of the capillaries
Venous end
Hydrostatic pressure is dropped and is pulling fluid back into the blood. Distributes fluids between the flood and extracellular
Starling forces
The forces that regulate the movement of fluid across capillary membranes, including hydrostatic and oncotic pressures - net filration pressure and oncotic pressure.
Net filtration pressure…
is equal to the hydrostatic pressure of the blood in the capillaries - the hydrostatic pressure of the tissue fluid outside the capillaries
Oncotic pressure
difference between colloid osmotic pressure in the plasma and interstitial fluid
Colloid osmotic pressure
osmostic pressure exerted by plasma proteins such as albumin. Greater in the plasma than in the interstitial fluid
Lymphatic system
collects excess interstitial fluid transports it to lymph ducts that empty into veins. It plays a crucial role in immune function and maintains fluid balance in the body. Acts as filter for immune response.
Tissues and organs in the lymphatic system
lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils → remove viruses/debris etc and defend the body against infection
Blood moves through veins in response to…
Numeration of smooth muscle in the walls of the veins and skeletal muscles surrounding the veins
Maintaining blood flow and pressure is regulated by…
cardiac output, degree of contribution of arterioles, and total blood volume
Autonomic nervous system and endocrine system…
interact to coordinate the mechinsims of Nitric oxide and Endothelin
Nitric oxide
is a major inducer of vasodilation
Endothelin
peptide responsible and is a major inducer vasoconstriction
Vessel control
Contains local and central controls that help the body maintain homeostatis
Local control
helps meet the needs of a particular tissue. Will regulate the arteriole diameter
mechanism of regulating arteriole diameter
In low O2, high CO2 → concentrations in tissues dilate arteriole walls to increase the blood flow and diameter
In high O2, low CO2→ concentrations opposite
NO is released by arterial endothelial cells to increase arteriole diameter and blood flow
Central controls
MORE IMPORTANT because they meet the needs of the whole body such as maintaining blood pressure or maintaining the body temperature
Anyone hyperemia
increase in the metabolism of the tissue which makes O2 used faster→ metabolites increase→ arterioles are dilating to achieve more blood flow
Flow Autoregulation
response to a drop in blood pressure; metabolites build up→O2 depleting-.vessel walls are not as stretched→ smooth muscle surrounding the arteriole will contract less strongly → arteriole dilates → flow restores