Biology - 2D Movement of substances into and out of cells
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the three main ways that molecules can pass through a cell membrane?
Most molecules move by diffusion.
Water molecules move by osmosis.
Some molecules move by active transport
What is diffusion?
The net movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, down a concentration gradient
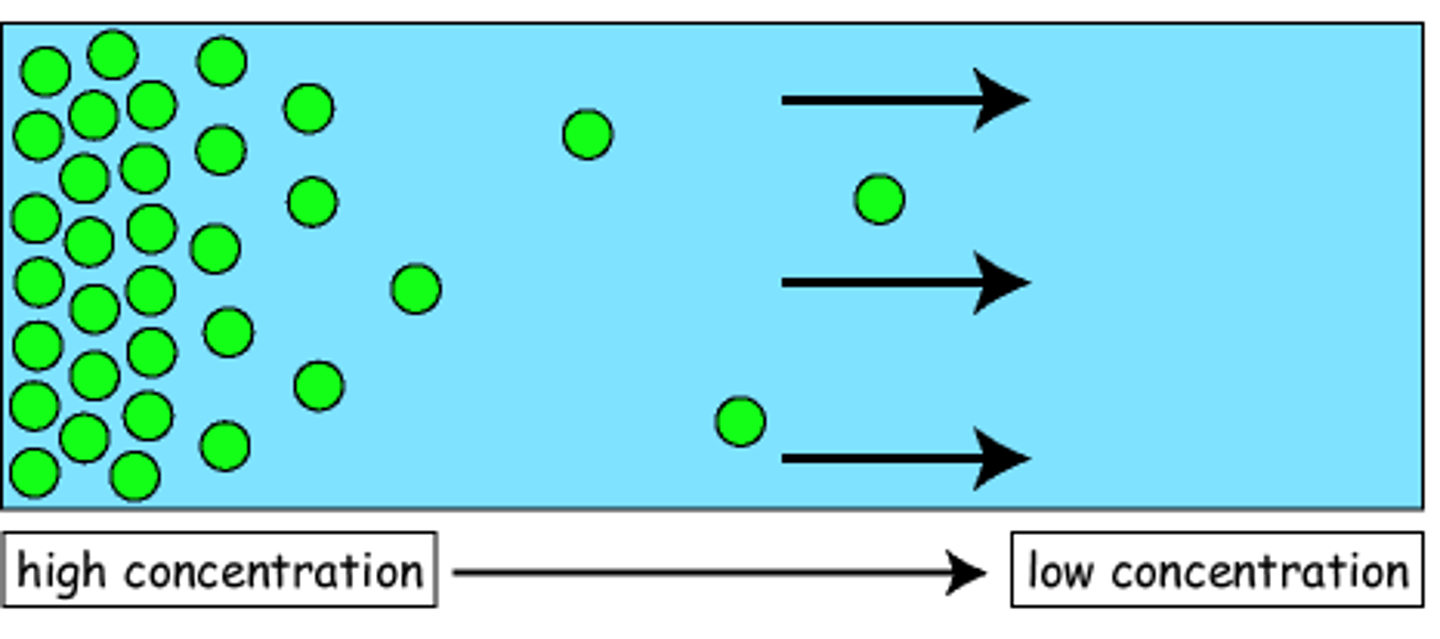
Which states of matter does diffusion occur?
Liquids and gases.
What can you say about the movement of molecules?
They are random
Describe diffusion in cell membranes.
cell membrane is partially permeable, as it controls or only allows some substances to move into and out of the cell based on their size
What type of process is diffusion?
a passive process as the movement of molecules does not require energy from the cells
What is a concentration gradient?
the difference in the concentrations of a solute in two different regions
What is diffusion like in unicellular organisms?
They are in direct contact with the external environment. So, food, oxygen and water are absorbed and waste products released directly by diffusion

What is diffusion like in multicellular organisms?
They are larger, more complex and all the cells are not in direct contact with the external environment. Diffusion is a slow process and is insufficient to meet the food and oxygen requirement of all millions of cells in our body. So multicellular organisms have organ transport systems
What is osmosis?
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential/concentration to a region of lower water potential/concentration across a partially permeable membrane.
What is a solution?
Solution = solute (dissolved substance) + solvent (liquid that the solute is dissolved in)
Describe the water and solvent molecules in a dilute solution.
HIGH concentration of water molecules
LOW concentration of solute molecules
Describe the water and solvent molecules in a concentrated solution.
HIGH concentration of solute molecules
LOW concentration of water molecules
What are the similarities of osmosis and diffusion?
Both involve the net movement of molecules down a concentration gradient.
Both are passive processes (do not require energy from the cell)
What are the differences of osmosis and diffusion?
Diffusion: Involves movement of all molecules (in liquids and gases only) Can take place with or without a partially permeable membrane.
Osmosis: Only involves movement of water molecules. Can only take place if there is a partially permeable membrane
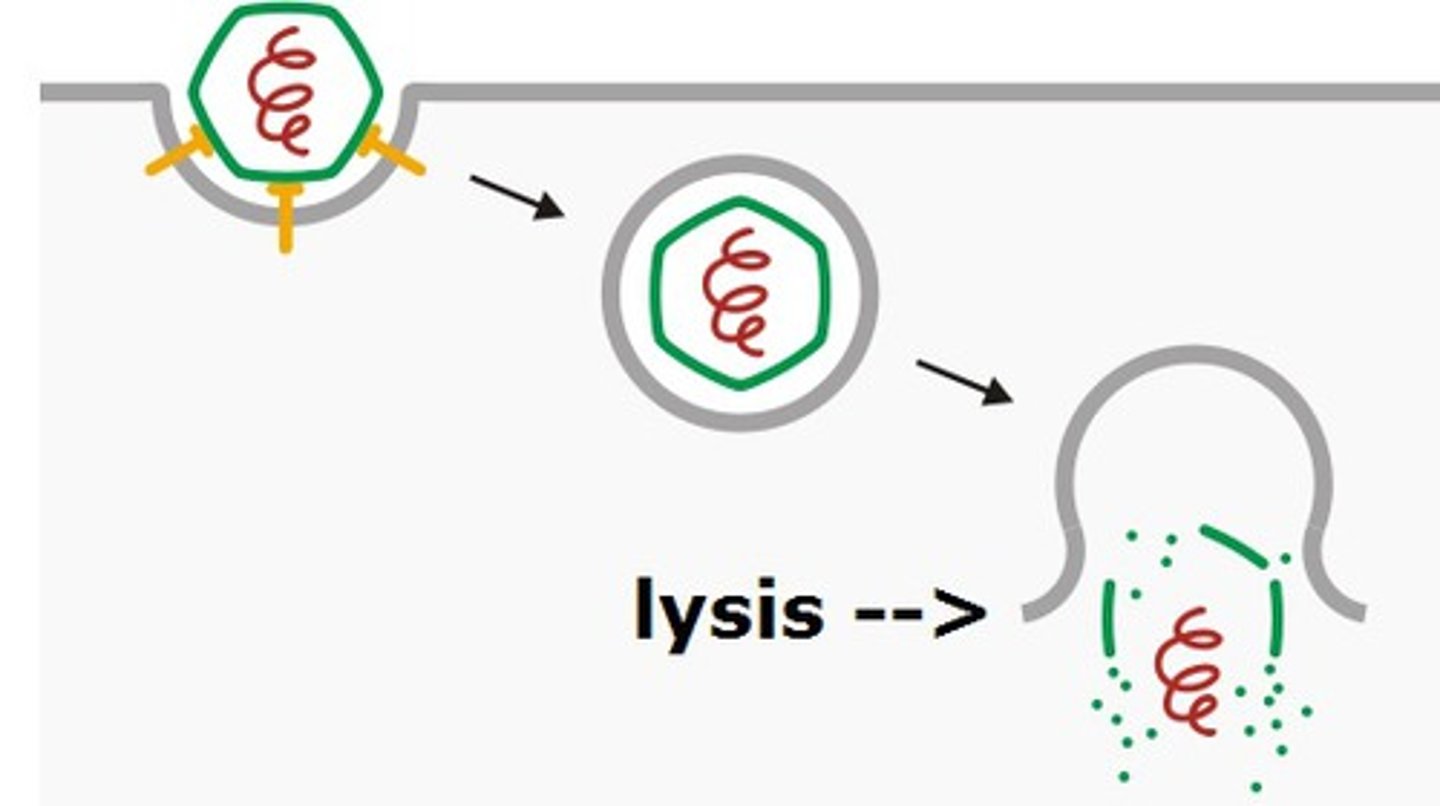
What happens when there is an animal cell surrounded with higher water potential?
Water enters the cell by osmosis
Since the animal cell does NOT have a cell wall for support, the movement of water into the animal cell causes it to swell and eventually burst (cell lysis)
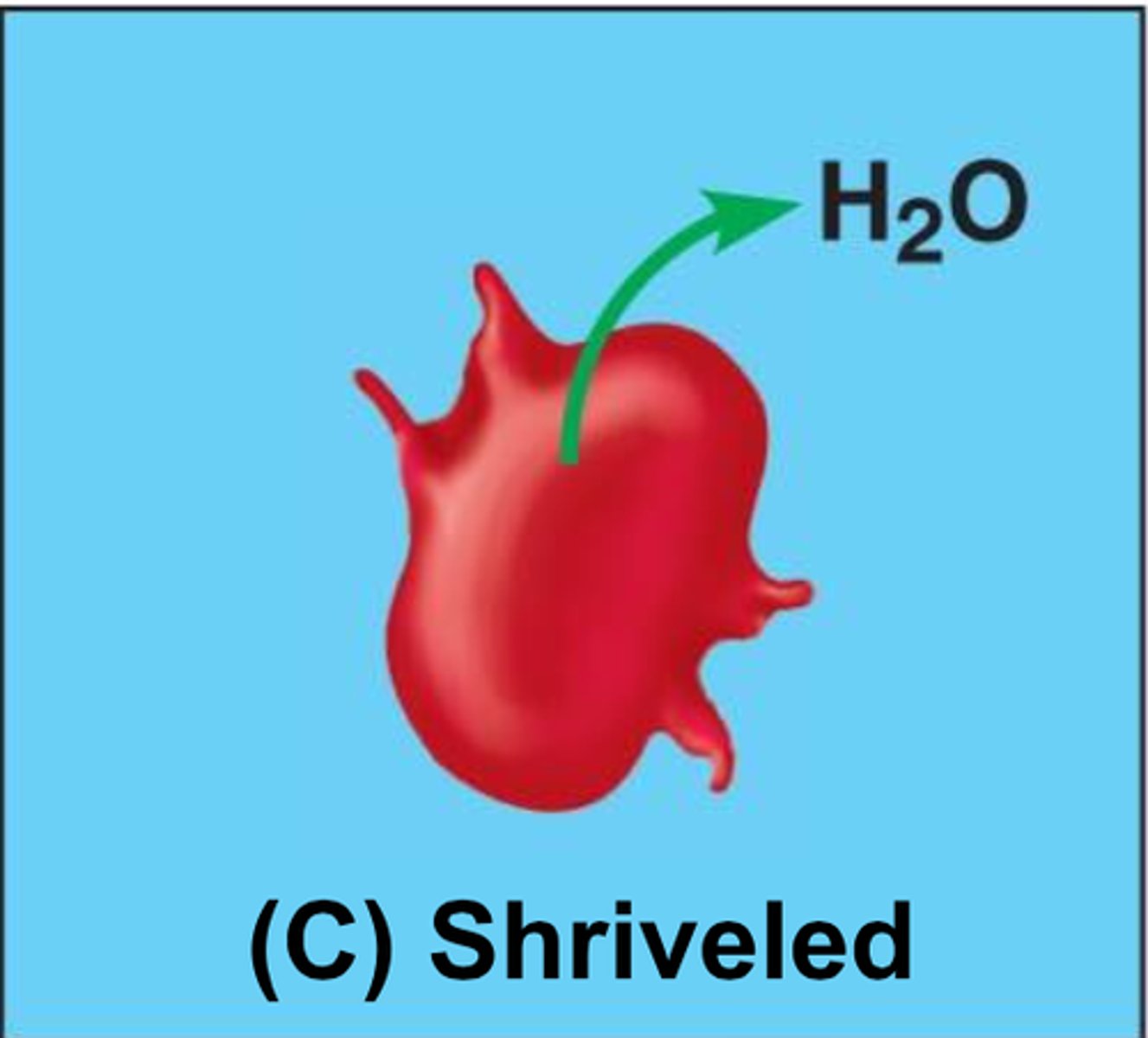
What happens when there is an animal cell surrounded with lower water potential?
Water leaves the cell by osmosis
This causes the animal cell to shrivel and shrink (cell crenation)
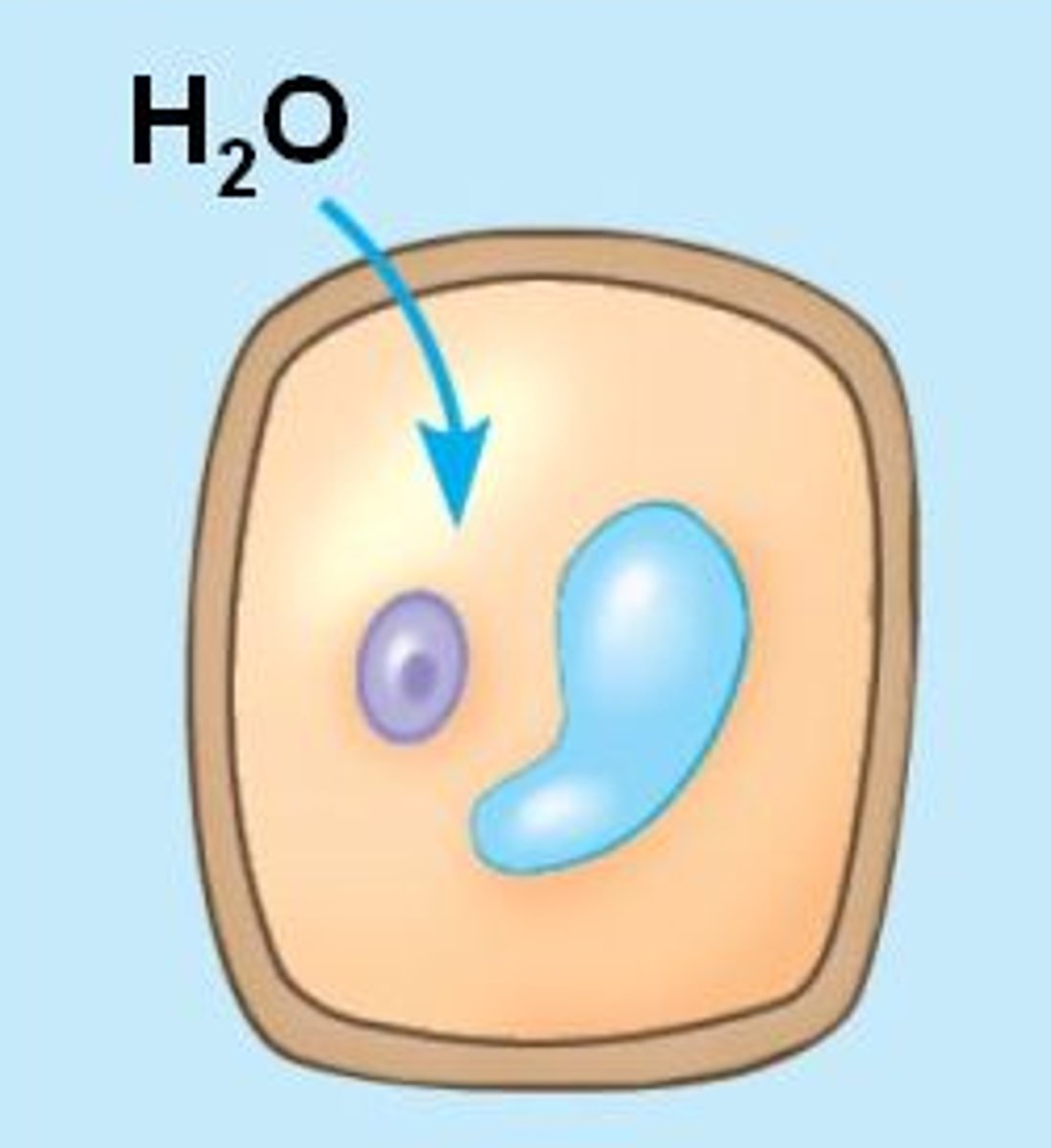
What happens when there is a plant cell surrounded with higher water potential?
Water enters the cell by osmosis.
This causes the cytoplasm and vacuole to push against the cell wall. The plant cell becomes turgid
What happens when there is a plant cell surrounded with lower water potential?
Water leaves the cell by osmosis.
The cell contents shrink and pull away from the cell wall.
The plant cell becomes flaccid.
In highly concentrated solution, more water molecules leave and the plant cell undergoes plasmolysis
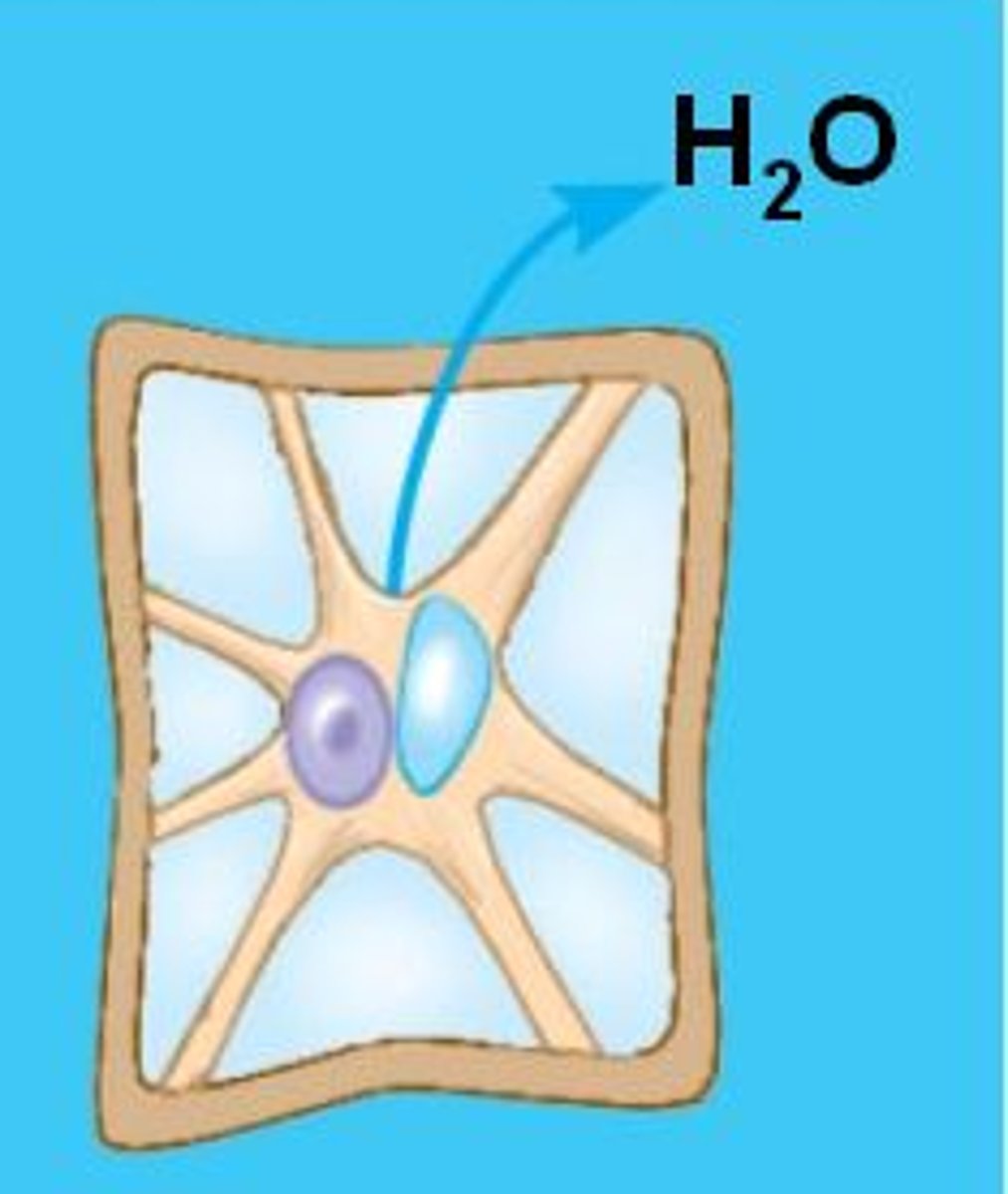
What are the factors that affect rate of diffusion?
Diffusion distance
Concentration difference (gradient)
Surface area to volume ratio
Temperature
What is the relationship between the factor of diffusion distance and diffusion?
The smaller the distance molecules need to move across, the faster the rate of movement
What is the relationship between the factor of concentration gradient and diffusion?
The higher/steeper the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion
What is the relationship between the factor of surface area to volume ratio and diffusion?
The larger the surface area to volume ratio, the faster the rate of diffusion.
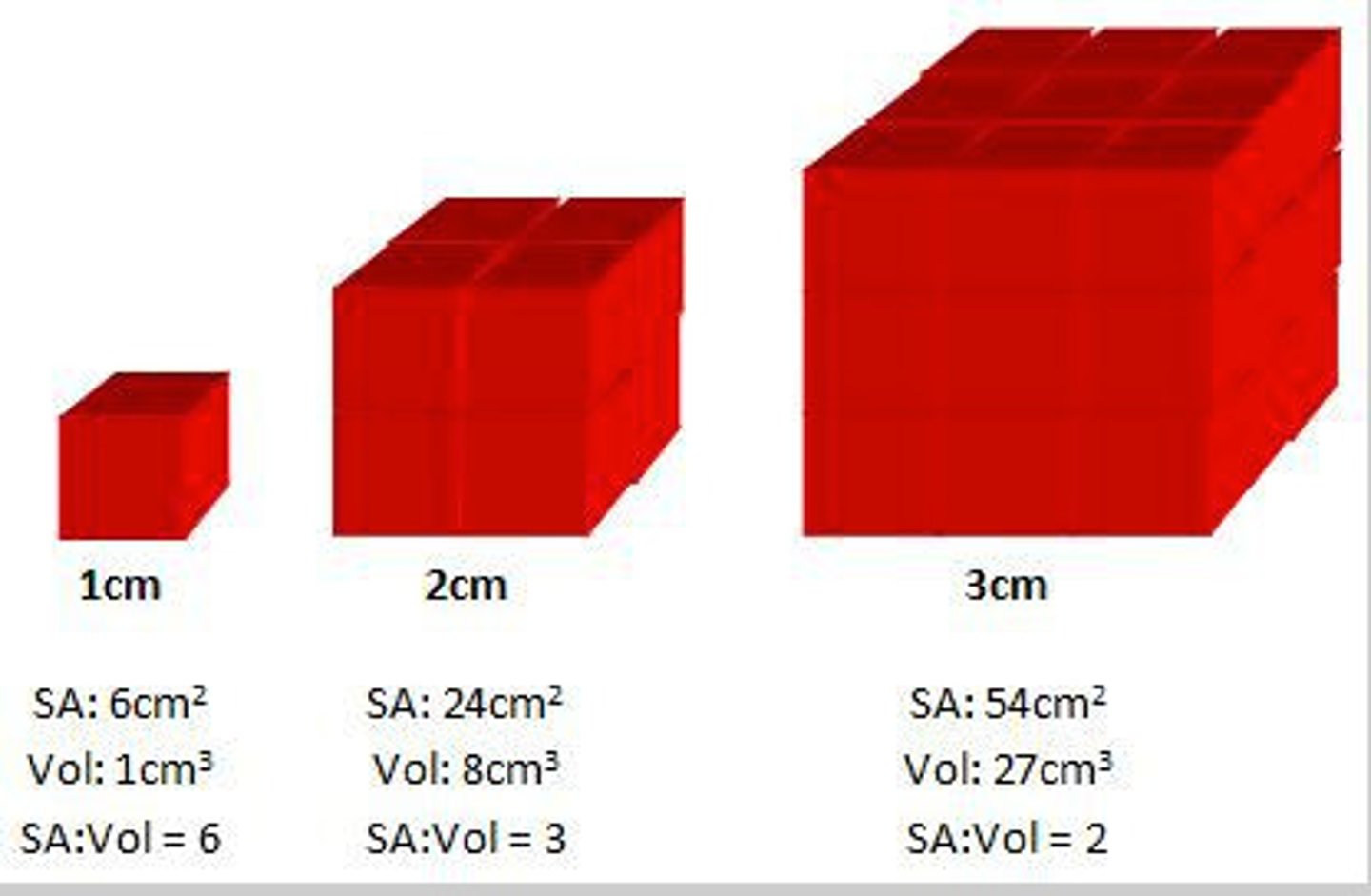
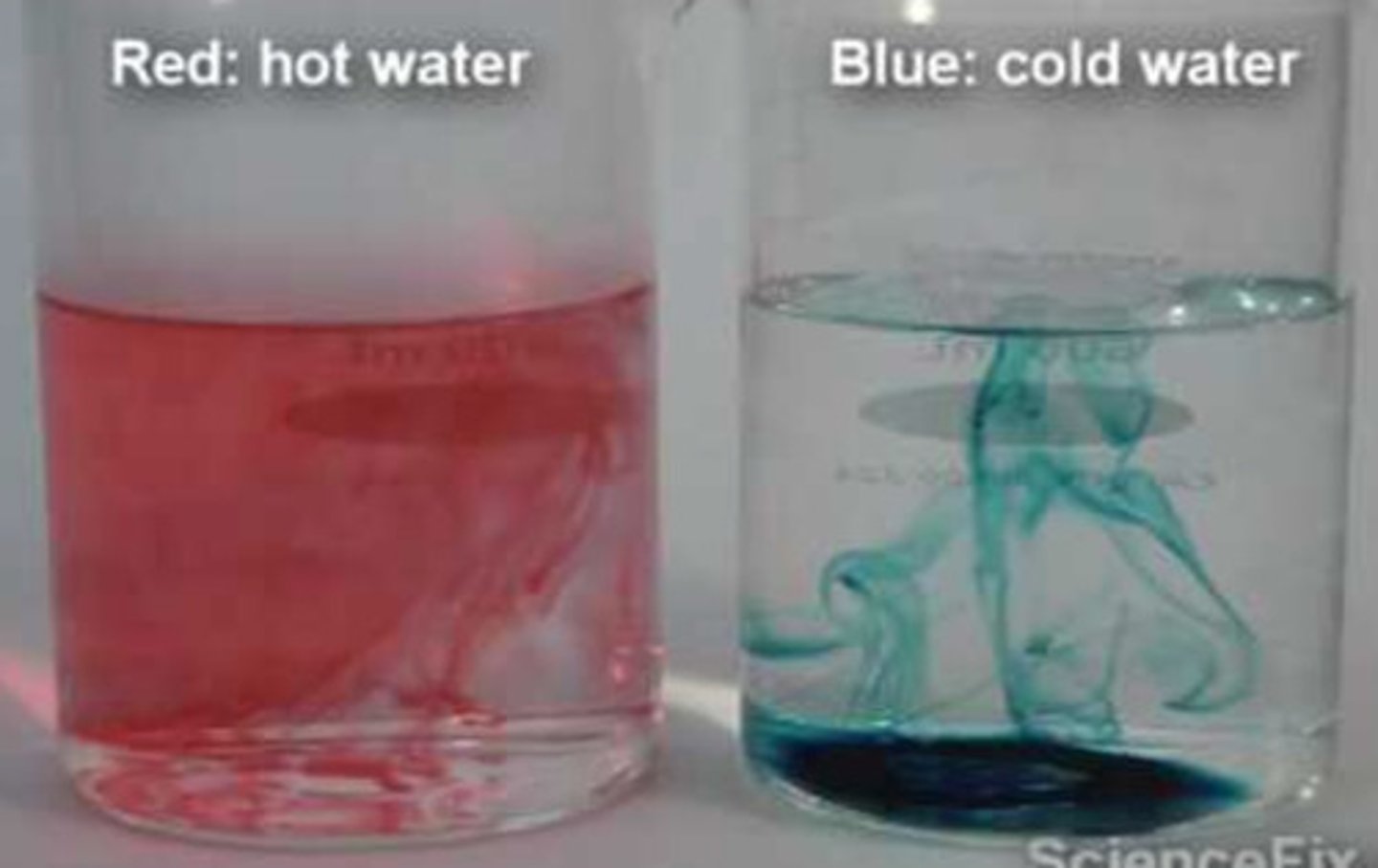
What is the relationship between the factor of temperature and diffusion?
As temperature increases, the rate of diffusion increases (atoms gain more thermal/heat energy, causing atoms to vibrate faster, increasing their kinetic energy)

What is active transport?
the movement of molecules from a region of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration through a partially permeable membrane.
What is different about active transport and why is it this way?
Needs energy from the cell as molecules move against the concentration gradient.