PPhysics
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms

What is the centre of mass?
Point through which the weight of an object acts
How is weight measured?
A newtonmeter
When is one joule of work done?
When one joule causes a displacement of one metre
What does work done against friction cause?
Rise in temperature of object
What is elastic deformation?
Returns to original shape
What is inelastic deformation?
Stays deformed
explain why, to change the shape of an object (by stretching, bending or compressing), more than one force has to be applied – this is limited to stationary objects only
a single force would simply cause the object to move in the direction in which the force were to be applied
Describe the energy transfer involved when a force stretches or compresses a spring. (4)
force does work on spring
Energy transferred mechanically to Ep store of spring
Work done on spring = Ep stored if it is not inelastic

describe the difference between a linear and non-linear relationship between force and extension
linear - gradient = spring constant, directly proportional
Non linear - gradient not equal, not directly proportional, extension increases more for each unit increase in force
How do levers transmit the rotational effect of forces?
increasing the perpendicular distance from the pivot at which a force is applied relative to that of the load
causing larger force to act upon pivot than it is applied at the lever
What happens when a gear is connected to a smaller gear?
second gear will turn faster
But with less force
In opposite direction to first gear
What happens when gear is connected to bigger gear
Turns slower
More force
In opposite direction
Why take multiple readings
- to identify any anomalous results
- to reduce the effect of random error
explain why, in a liquid, pressure at a point increases with the height of the column of liquid above that point and with the density of the liquid.
increasing depth increases the height of the water column above the swimmer
- increasing the weight of water acting on the swimmer
Why does atmospheric pressure decrease with an increase in height?
number of air molecules above a surface decreases as the height of the surface above ground level increases, smaller weight
So there is always less air above a surface than there is at a lower height
Terminal velocity
Initially no air resistance
As velocity incrases, air resistance increases
So resultant force decreases so acceleration decreases
Eventually air resistance = weight
So resultant force = 0, terminal velocity
Parachute
Fluid increases so at that velocity air resistance greatly increases
So resultant force is upwards, you accelerate, ie. decelerate downwards
Eventually AR = weight
So 0 resultant force and 0 acceleration and new slower terminal velocity
What is inertial mass?
How difficult it is to change the velocity of an object, f/a
What is stopping distance?
Thinking distance + braking distance
What happens when force is applied to the brakes of a vehicle?
Work done by brakes (by friction) onto the wheel
So vehicle KE reduces
And brake temperature increases
Greater the speed = greater braking force needed to stop the car
So greater force = greater acceleration
may lead to brakes overheating and a loss of control, dangerous
Seatbelts
Without these, when hard braking you will keep moving and not decelerate, causing to fly through the windshield
These strap you in, but also stretch under large forces
Stretching increases the distance moved slightly, but extends the time taken more for passengers to stop
This decreases the rate of change of momentum and therefore reduces the average force

Crumple zones
Without these, the car would be a solid metal block, which would immediately stop during a crash instead of “softening” the blow slightly
“softer” areas at the front of the car, which crumple upon a crash
It absorbs energy to deform and compact
It increases the time taken for the car to stop
This reduces acceleration and force on passengers
Airbags
Without these your head will whip forward during a crash, hitting the steering wheel or whipping back to hit the back of the head, which would cause serious neck injury
These inflate instantaneously upon a crash
Your head hits this and slows down
Increases the time taken for the head to stop moving
So reduces the force on the neck
What are the differences in density between solids, liquids and gases?
Solids and liquids - similar
Gases - spacing between atoms increases x10, as particles have lots of energy to move, so volume increases greatly therefore density decreases greatly
Describe solids
- Particles are arranged in rows (in a regular arrangement).
- Particles vibrate about fixed point.
- There are forces of attraction between particles but don't have enough energy to overcome the forces of attraction.
Describe liquids
- Particles are randomly arranged.
- Particles can move around each other.
- Particles have more energy than solids and can therefore overcome the forces of attraction.
- Do not have enough energy to sufficiently overcome attractive forces completely.
- No fixed shape but take the shape of the container.
Describe gases
- Particles arranged randomly and far apart.
- Sufficient energy to overcome forces of attraction completely.
- Particles are moving quickly in all directions.
What is internal energy?
energy stored by particles within a system, kinetic and potential energy
How does heating change the internal energy?
increasing the energy of the particles that make up the system
What affects the increase in temperature of a system?
mass of the substance heated, the type of material and the energy input to the system.
What is specific latent heat?
The amount of energy needed to change the state of 1kg of a substance without a change in temperature
Fusion - solid to liquid
Vaporisation - liquid to vapour
explain how the motion of the molecules in a gas is related to both its
temperature and its pressure
Temperature - measure of average kinetic energy of particles
· pressure - result of collisions of gas molecules with container walls.
· Pressure dependent on number of collisions in second and particle speed
· When molecule collides with container walls, exerts a force on wall.
· The greater the average speed of the particles the greater the force on the wall
explain qualitatively the relation between the temperature of a gas and its
pressure at constant volume
If volume of the gas is kept constant and the temperature increased the pressure will increase.
increase in temperature means molecules have greater average Kinetic energy and speed
· So when they collide they will exert larger force on walls
· Because volume is constant, number of collisions in a second will increase hence the pressure increases.
· Pressure and Temperature are directly proportional providing the Volume is constant
use the particle model to explain how
increasing the volume in which a gas is contained, at constant
temperature can lead to a decrease in pressure
· If temperature is constant the average speed of the molecules is constant
· If the volume is increased there will be greater time between collisions and so there will be less collisions per second
· pressure will decrease.
· Pressure and Volume are inversely proportional providing the Temperature is constant.
What is work done in a gas?(increases internal energy and temperature)
pressure x volume

Describe adding more particles to a fixed volume
more particles are present, so more collisions occur per unit time with the walls, so pressure increases.
Energy transferred to the particles when more gas is added into the fixed volume, so this heats the gas
Describe a fixed number of particles for a smaller volume
o The particles collide with wall which is moving inward
o So particles gain momentum, as the rebound velocity is greater than the approaching velocity
。 So as the particle has a greater velocity, the pressure increases as the particles collide with the walls more frequently (time between collisions decreases)
And the temperature also increases, as the kinetic energy of each particle increases.

What is the radius of an atom?
1×10^-10m
What is the radius of the nucleus compared to the radius of the atom?
1/10,000
How do elecron arragnements change with electromagnetic radiation?
Absorption - move further from nucleus, higher energy level
Opposite for emission
What did the results of the alpha particle scattering experiment lead to?
MAss of atom concentrated at charged nucleus
What did niels bohr discover?
Electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances
Who discovered the neutron?
James chadwick
Compare the nuclear and plum pudding models
nuclear model mass concentrated at the centre
plum pudding model mass evenly distributed
nuclear model positive charge occupies only small part of the atom
plum pudding model positive charge spread throughout the atom
• nuclear model electrons orbit some distance from the centre
plum pudding electrons embedded in the (mass) of positive (charge)
• nuclear model the atom mainly empty space
plum pudding model is a ‘solid’ mass
What is activity measured in?
Becquerel
What is count rate?
Number of decays each second by detector
Describe an alpha particle
2 protons 2 neutrons
(a helium nucleus)
Highest ionising
sheet of paper
5cm range
Describe a beta particle
fast moving electron
Medium ionising
1m of air
thin aluminium
Describe gamma particle
Energy transferred away from nucleus
Low ionising
several centimetres of thick lead, metres of concrete
unlimited range in air
What is the half life of a radioactive isotope?
Time it takes for the number of nuclei in a sample / count rate
to halve
What is net decline?
initial number - number after half lifes / inital number
What is radioactive contamination?
The unwanted presence of materials containing radioactive atoms on other materials
Hazard is due to decay and type of radiation
What is irradiation?
Process of exposing an object to nuclear radiation
Irradiated object does not become radioactive
Where does background radiation come from?
Natural sources eg. rocks and cosmic rays from space
man made sources eg. fallout from nuclear weapon testing and nuclear accidents
What is radiation dose?
Measures health risk of exposure to radiation
Why do the hazards associated with radioactive material differ according to the half life involved?
short half-life:
source presents less of a risk, as it does not remain strongly radioactive
initially very radioactive, but quickly dies down
So presents less of a long-term risk
Long half-life:
source remains weakly radioactive for a long period of time
What are the uses of nuclear radiation?
Exploration of internal organs
Control or destruction of unwanted tissue
Describe nuclear radiation for exploration of internal organs
Gamma emitting tracers injected or swallowed
Gamma cameras create an image showing where it is gone
Half life of tracer must be short enough so most nuclei will decay shortly after the image is taken to limit the patient’s radiation dose
Describe nucleaer radiation for control or destruction of unwanted tissue
Narrow beams of gamma radiation focused on tumour cells to destroy them, gamme because it can penetrate tumours from outside the body
Beta or gamma emitting implants placed next to tumours
Half lives must be long enough to be effecive, but short enough that it does not irradiate the patient after treatment
What is nuclear fission?
Splitting of a large and unstable nucleus
Spontaneous fission rare so nucleus absorbs neutron
Splits into 2 smaller eqal nuclei, 2-3 neutrons and gamma rays
energy released
all products have kinetic energy, neutrons start chain reaction

How is the fission chain reaction controlled in a nuclear reactor?
To control energy released
Nuclear weapon - uncontrolled chain reaction
What is nuclear fusion?
Joining of 2 light nuclei to form a heavier nucleus
Some of the mass may be converted into the energy of radiation
Describe images formed by concave lens
always virtual
What is magnification?
Image height / object height
What is specular reflection?
Reflection from a smooth surface in a single direction
What is diffuse reflection?
Reflection from a rough surface, causes scattering
What is a perfect black body?
An object that absorbs all the radiation incident on it
Does not rflect or transmit radiation
Also the best emitter
What absorbs and emits infrared radiation?
All objects, the hotter the body, the more radiation it radiates
When does the temperature of a body increase?
When the body absorbs radiation faster than it emits radiation
What does the temperature of the earth depend on?
Rates of absorption and emmission of radiation, reflection of radiation into space
How is the earth heated?
Sun emits radiation onto earth
some emitted back into space
Greenhouse gases absorb longer wavelength radiation
re emit radiation, increasing temperature of the earthq
Circuit diagrams
.
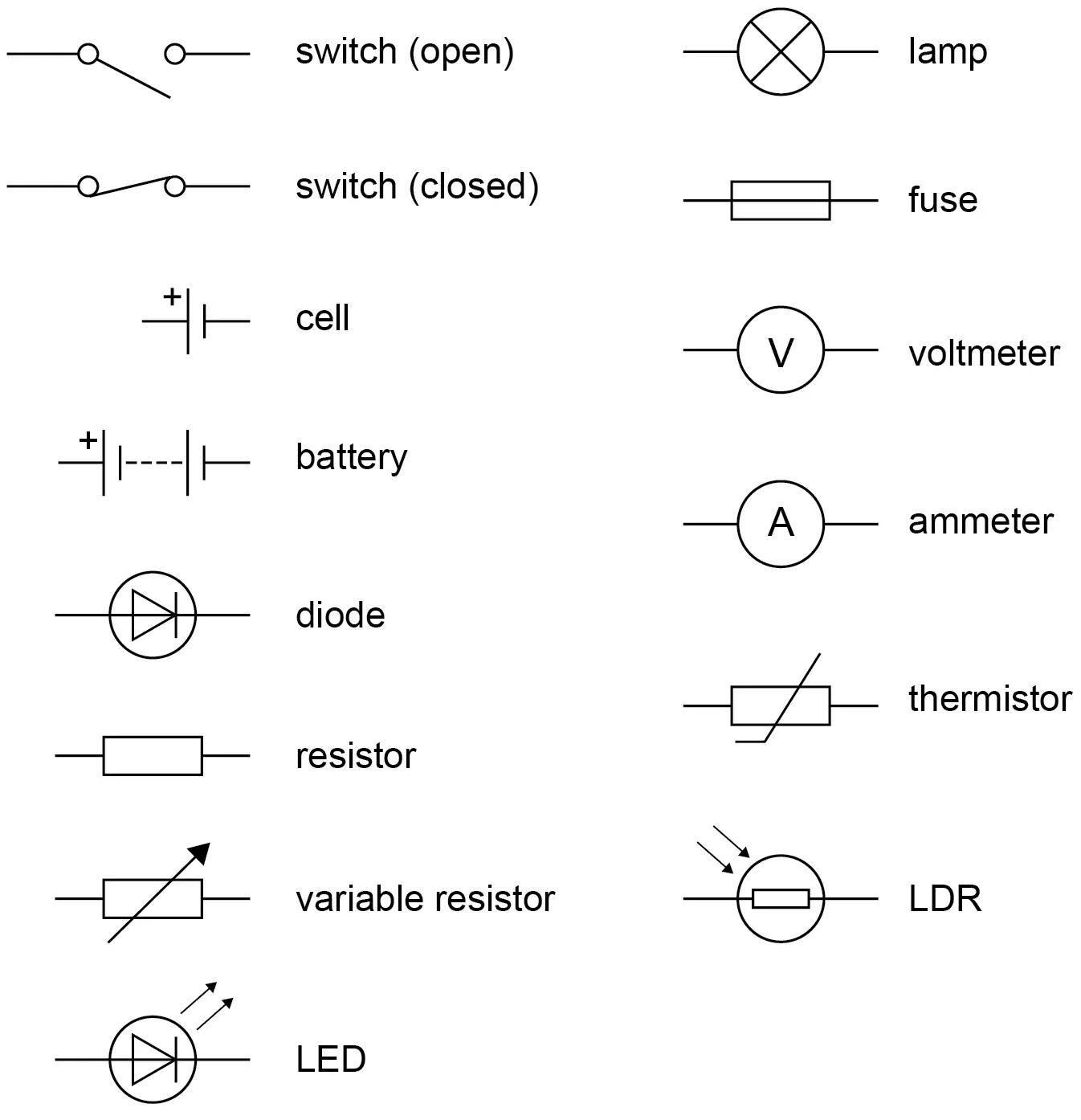
What is the size of electric current?
Rate of flow of electrical charge
Q = it
What is the current in a series circuit?
Same everywhere
What is the relationship between resistance and current at a given voltage?
V = ir
What is the current trhough an ohmic conductor at a constant tempreature?
Directly proportional, resistance remains constant
What is the relationship between the resistance of a filament lamp and temperature?
Directly proportional
Explain the diode graph
Current flows in one direction and has a very high resistance in reverse direction
What is the resistance of a thermistor?
Decreases as temperature increases
used in thermostatsW
What is the resistance of an LDR?
Decreases as light intensity increases, used in lights

Deascribe series circuits
Same current
Total pd is shared between components
total resistance of 2 components is the sum
Describe parallel circuits
Pd across each component is the same
Total current is the sum of currents through separate components
total resistance of 2 resistors is less than the resistance of the smallest individual resistor
- Explain qualitatively why adding resistors in series increases the total resistance whilst adding resistors in parallel decreases the total resistance
current has to pass through each component in turn so it cannot bypass any resistor.
parallel - there are more pathways that current can take so it flows more easily.
How does resistance change with current?
As current increases, electrons have more energy
When electrons flow through a resistor, they collide with the atoms in the resistor
transfers energy to atoms, causing them to vibrate more
makes it more difficult for electrons to flow through the resistor
So resistance increases, and current decreases
How does resistance change with temperature?
Normal wires - See above, the same process occurs as atoms vibrate when hot
Thermistor
In hotter temperatures the resistance is lower
These are often used in temperature detectors/thermostats
How does resistance change with length?
The greater the length, the more resistance and the lower the current
Electrons have to make their way through more resistor atoms, so it is harder than using a shorter wire
How does resistance change with light?(LDR)
The greater the intensity of light, the lower the resistance
■So the resistance is greatest when it is dark
How does resistance change with voltage?
Diodes:
allows current to flow freely in one direction
•In the opposite direction, it has a very high resistance so no current can flow
Describe the electricity supply of the UK
AC, 50hz, 230v

What is the difference between AC and DC?
DC - movement of charge in one direction only
AC - current continously changes direction from positive to negative
What does the live wire do?
Carries the alternating pd from supply
may be dangerous even if mains is off, because current is flowing through it
Describe the neutral wire
0v, completes circuit
Describes earth wire
Only carries current if there is fault
safety wire to stop the appliance from becoming live
connected to earth and casing
if live wire touches metal casing, it will become live
Describe energy transfers in everyday appliances
kinetic energy for motor, thermal for kettle
work done = energy transferred = charge flow in a circuit
Greating power rating means it uses more energy
What are step up transformers?
increase pd from power station to national grid, decrease current
so less energy is lost
What are step down transformers?
decrease pd from national grid to consumers for consumer safety
What happens when insulators are rubbed against each other?
Material that gains electrons becomes negatively charged, material that loses electrons is left with positive charge
So they attract, non contact force
Describe the production of static electricity and sparking by rubbing surfaces
Sparking occurs when enough charge builds up, and the objects are close but not touching
The "spark" is when the charge jumps through the air from the highly negative object to the highly positive object, to balance out the charges
Describe evidence that charged objects exert forces of attraction or repulsion on one another when not in contact
Greater charge = greater force
Closer together = greater force
Explain electric fields
point in direction a positive charge would go
point to charges at right angles to the surface
stronger the charge, the most field lide present and the stronger the force felt