Caribbean and Transatlantic slave trade
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
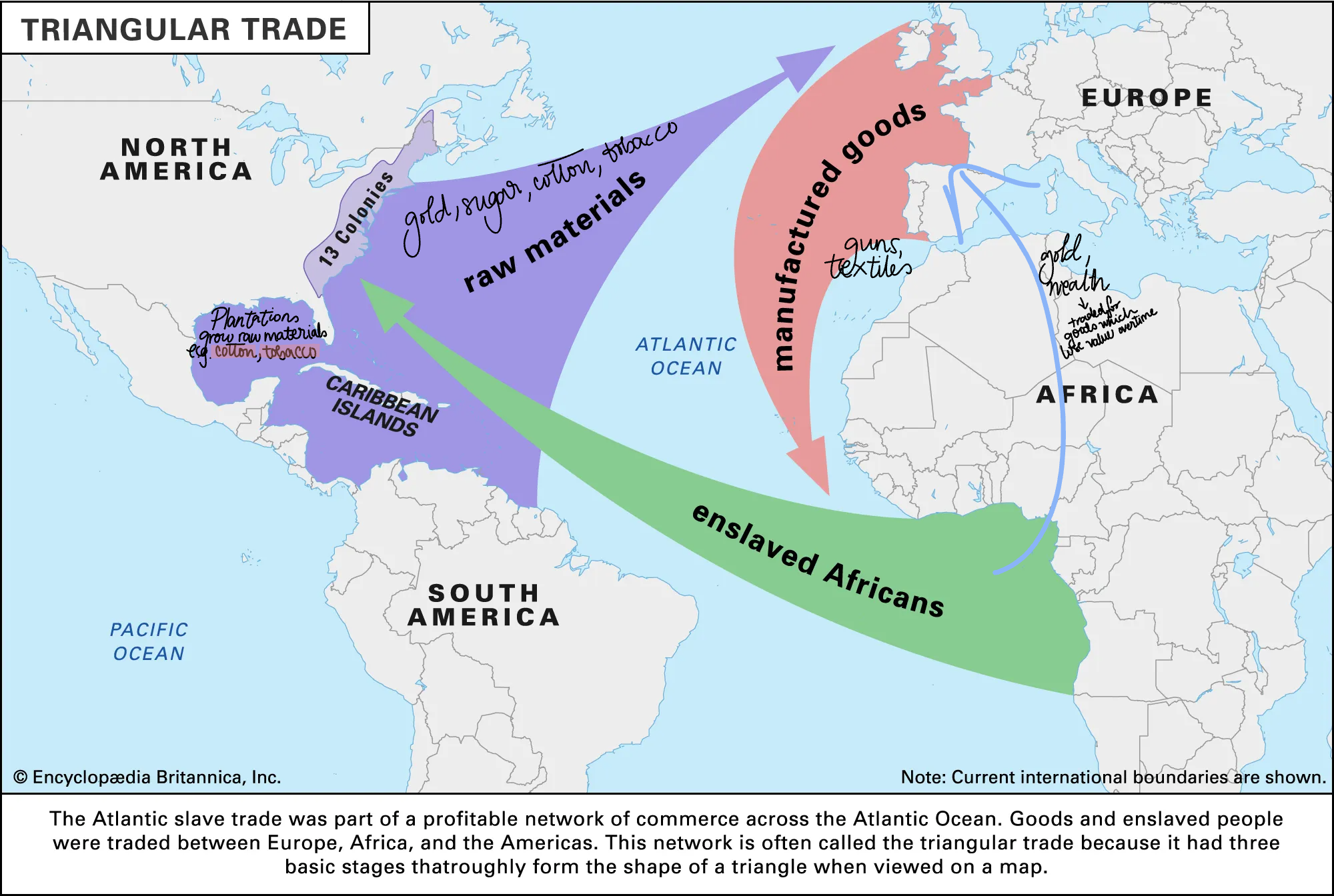
Transatlantic Slave Trade
slave trade from the 16th to the 19th century which transported enslaved Africans to the Carribbean and Europe
Causes for colonisation of Carribean
perfect for growing ‘cash crops’; e.g. sugar
imperialism and social darwinism; british argued they were superior and it was a kindness they would ‘civilise’ them
missionaries ‘save’ settlers by converting them to Christianity
indentured servitude
A form of labour contract where a person agrees to work for a specific period in exchange for passage to a new country or other benefits
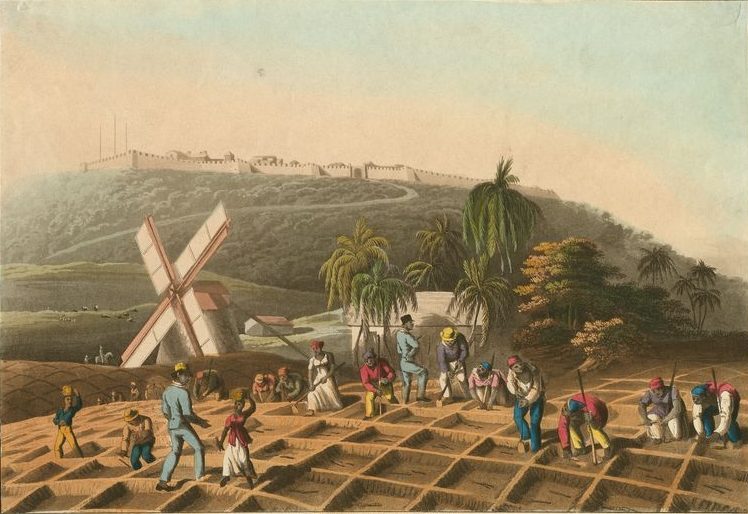

What was the most profitable plantation
Barbados- 1625
sugar
how long was the middle passage form Africa to America
6-8 weeks
Collapse
Caribbean colonies were granted independence after WWII; e.g. Barbados- 1966
Many remained part of Commonwealth; e.g. Jamaica
Impact on enslaved
12m people transported over 400 yrs
subject to torture and dehumanisation due to racist attitudes
developed resistance to strategies; e.g. Maroons in Jamaica hid and lived in forests
short life span; 20 yrs
poor living conditions and poor diets

Impact on Britain
large profits; £60m(1761-1808)
cities(London, Liverpool, Glasgow) expanded due to profits; Liverpool Town hall, National Portrait Gallery
products support industrial revolution- GB ‘workshop of the world’
Growth of coastal towns; e.g. Glasgow, Bristol
Campaigns to abolish
Slave TRADE abolished
1807
SLAVERY abolished
1833