personality + individual differences
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what is the dark triad (Paulhus + Williams, 2002) + what does the theory refer to
collection of 3 traits that are maladaptive, but still within the normal range of functioning (so are sub-clinical). includes:
narcissism
Machiavellianism
psychopathy
though NPD + APD are established clinical disorders, these traits can also be found in the normal population
how did Ames et al. (2006) define narcissism + what are 3 key features
a grandiose yet fragile sense of self, as well as preoccupation with success + demands for admiration. features:
an excessively self-centered perspective, strong sense of entitlement + preoccupation with success
require excessive admiration + believes they are special, so as such only associate with high-status people
feelings of inferiority usually at the root of inflated ego, so can be envious of others + diminish others’ success/accomplishments
what are the two main aspects to the narcissistic personality
grandiosity + vulnerability
where did the term ‘Machiavellian’ come from
derived from Machiavelli → Italian diplomat who lived during the Renaissance + famously discussed tactics rulers should employ to maintain power + achieve political goals
argued it was sometimes necessary for leaders to use any means, including deception, to achieve authority
how does Wilson et al. (1996) define Machiavellianism + what are 3 key traits
personality traits referring to a strategy of social conduct that involves manipulating others for personal gain, often against the other’s self-interest. traits include:
use of a range of deliberate manipulation techniques, e.g. flattery/intimidation, for personal gain
engagement in unethical + counterproductive behaviours e.g. lying, theft + sabotage
possessing a cynical view of human nature + demonstrating little concern for the welfare of others above own wellbeing
how does Ames et al. (2006) define psychopathy + what are 3 key features
a drive to engage in impulsive or antisocial behaviour without empathy, anxiety or remorse. traits include:
impulsivity + thrill-seeking —> may engage in risky behaviour without regard for consequences
callousness + consistent lack of empathy
lack of emotional bonds + does not experience remorse for their behaviour
what is Jon Ronson’s ‘psychopath test’ and what 3 traits does he include as criteria
explores the proportion of psychopathic traits in the general population + outlines 3 ways to ‘spot’ a psychopath in day-to-day life:
glibness/superficial charm
cunning/manipulative behaviour
grandiose sense of self worth
what are two questionnaires commonly used to measure dark triad traits in the general population
the Dirty Dozen (Jonason + Webster, 2020) —> 12 item questionnaire
the Short Dark Triad (Jones + Paulhus, 2014) —> 27 item questionnaire
what are 3 criticisms of measures quantifying dark triad traits
social desirability bias associated with self-report measures → people high in these traits are more likely to lie, manipulate or ‘fake good’, so asking to rate themselves may not be reliable (especially considering some items = blatant)
short measures loose nuance —> convenient, but do not capture the complexity of each trait; much too general
e.g. many scales don’t capture narcissism’s fragile ego, which motivates seeking external validation
cultural assumptions —> many scales were developed on Western samples, so items may not capture how traits e.g. manipulation/narcissism are expressed in other cultures
how did Muris et al. (2017) investigate how gender affects propensity for dark triad traits
conducted meta analysis comprised of 65 samples —> dummy coded gender + computed effect sizes for the relationship between gender in each dark triad trait
found men generally display higher levels of dark triad traits relative to women
found medium-sized effect for psychopathy (.29), and small effect for narcissism (.15) + Machiavellianism (.16)
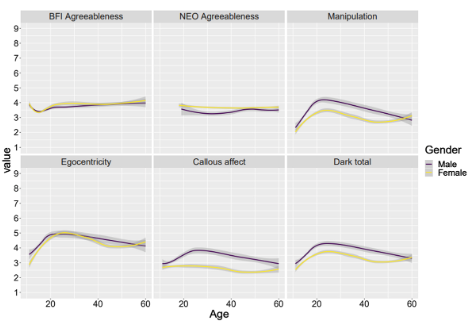
how did Klimstra et al. (2020) investigate how age affects propensity for dark triad traits + what do these findings imply
performed meta-analysis on multiple datasets on participants of various ages completing the Dirty Dozen scale + measures of agreeableness
found all 3 dark triad traits show a rise during adolescence
after early 20s, these traits seem to decrease, suggesting adult aging = associated with lower levels of these dark tendencies
suggests evidence for the maturity principle —> as people age, traits that are socially useful + acceptable on average tend to increase
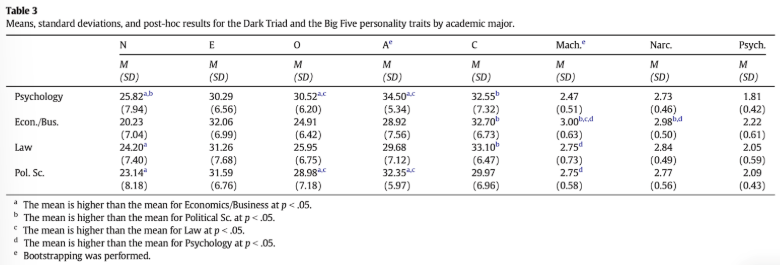
how did Vedel + Thomsen (2017) investigate influence of degree choice on propensity for dark triad traits
Big 5 + Dark Triad traits were measured in a sample of students from 4 different academic majors:
psychology
economics/business
law
political science
mean scores on the dark triad traits were compared across academic courses by a 2×4 ANOVA
what were the results of Vedel + Thomsen (2017)’s study
there were no differences in psychopathy scores according to course
psychology students scored significantly lower on Machiavellianism than students on any other course assessed
psychology students scores significantly lower on narcissism than students studying economics/business
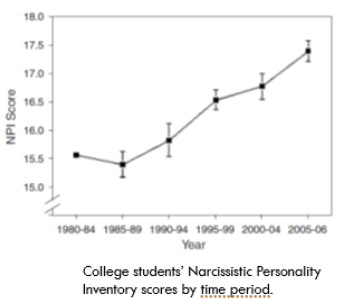
how did Twenge et al. (2008) examine whether narcissism is increasing
investigated how narcissism scores have changed over time in university students through use of 85 samples between 1979-2006
found since 1982, narcissism scores have increased significantly
NPI scores were 30% higher in the most recent cohort compared to the first cohort → increase found more prominently among women
what are 2 possible reasons as to why we are observing a rise in narcissism
social media use
changes in parenting styles
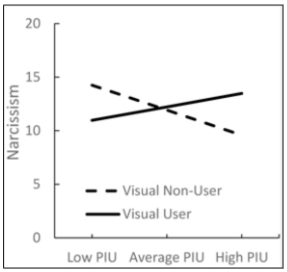
how did Reed et al. (2018) investigate the relationship between social media and narcissism + what were the findings
measured levels of narcissism + quantity of problematic internet use in participants aged 18-34
found higher amounts of time, frequency of posts (25% increase in particular) + number of followers on visual social media was significantly associated with higher levels of narcissism
relationship was only found with high proportion of visual social media
how did Brummelman et al. (2015) investigate how changes in parenting style was associated with narcissism
conducted longitudinal study monitoring ~550 children aged 7-12 + their parents over a 2-year period + measured 4 variables:
child self-esteem
child narcissism
parental warmth
parental overvaluation (believing their child is more special + entitled than other children)
found parental overevaluation predicted child narcissism, but not self-esteem, but parental warmth predicted the opposite
what is the unification hypothesis (Joanson et al., 2010)
the dark triad traits show strong, positive intercorrelations with one another, and have been found to load onto the same factor of during factor analysis
believes researchers should instead investigate a general ‘dark tendency’ rather than the separate subscales

what is the uniqueness hypothesis (Buckels et al., 2013)
the three traits have different patterns of associations with other traits + outcome variables —> instead suggests the traits are not enough to capture the dark side of human nature
recently has been proposed that the trait ‘subclinical’ sadism, the proneness to feel pleasant emotions while seeing others in pain, should be included to form a ‘dark tetrad’

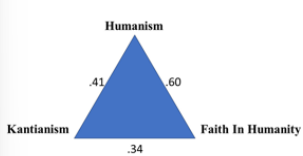
what is Kauffman et al. (2019)’s light triad + what are the 3 traits it contains
encompasses 3 qualities that embody a loving + beneficent orientation towards others —> 3 traits include:
Kantianism —> treating people as ends unto themselves (not just means); includes authenticity, honesty + investment in others
humanism —> valuing the dignity and worth of everyone, having respect for all; includes admiring + applauding the success of others
faith in humanity —> belief in the fundamental goodness of humans; includes being trusting, quick to forgive, looking for the best in others
what is the light triad scale (Kaufman, 2019) + what question are the items in it based on
based on ‘what would a loving + beneficent orientation toward others look like, in direct contrast to the everyday antagonistic orientation of dark traits’
12 item scale consisting of questions conceptually opposite to dark triad ones, but also relating to forgiveness, trust, honesty + caring
the 3 traits emerged from factor analysis —> how the questions grouped together
what is the nomological network
the network of traits, qualities + outcomes you would expect to be associated with a trait to demonstrate that it’s a valid construct
helps to establish that a measure has construct validity —> the extent to which the measure behaves in a way consistent with our hypothesis + represents how well scores on instrument indicate that construct
in what 3 ways can you assess the nomological network (Kauffman et al., 2019)
convergent validity —> correlate the measure with measures you would expect to be highly correlated
discriminate validity —> correlate the measure with measures you would expect to not be correlated
predictive validity —> explore whether the traits correlate/predict outcomes in line with expected hypothesis
how did Kauffman et al. (2019) perform the nomological network of the light + dark triad and what 5 variables were included
aimed to explore correlations between light + dark triad traits —> used cross-sectional online survey with ~1500 participants. variables measured included
the light triad scale
the short dark triad
the big 5 personality factors
measures of wellbeing (life satisfaction, authenticity + self-esteem
measures of moral + social behaviour (empathy, compassion, selfishness + aggression)
what were the results of Kauffman et al. (2019)’s nomological network —> dark vs light triad
calculated light vs dark triad balance score by subtracting each person’s score on dark from light triad
the mean balance score of the entire sample was 1.3, suggesting the average person is tipped more towards the light triad
dark triad traits had a medium-effect negative correlation with light triad traits, suggesting lack of crossover between the two
extreme dark traits = found to be rarer than extreme light traits
what were the results of Kauffman et al. (2019)’s nomological network —> correlations between light triad + big 5
scores with light triad correlated positively with open-mindedness, conscientiousness, extroversion + agreeableness
scores with light triad were negatively associated with neuroticism
agreeableness was most strongly associated with the light triad
what 2 other variables did Kauffman et al. (2019) identify as being positively associated with the dark triad
selfishness
self-enhancement values
what 3 other variables did Kauffman et al. (2019) identify as being negatively associated with the dark triad
life satisfaction
compassion + empathy
belief that others/one’s own self is good
what 5 other variables did Kauffman et al. (2019) identify as being positively associated with the light triad
acceptance of others
compassion + empathy
life satisfaction
positive enthusiasm
belief that others/one’s own self is good