Eating Disorders
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What are eating disorders?
Disturbances in eating habits or behaviors stemming from an intense fear of being overweight and a preoccupation with one's weight and shape.
What are the prevalent diagnoses of eating disorders?
- Anorexia nervosa
- bulimia nervosa
- binge eating disorder
- avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID)
eating disorders
serious and complex mental illnesses associated with significant physical, psychological, and social impairments
What is anorexia nervosa (AN)?
Extreme restriction of food intake, excessive calorie burning, and an inability to accurately appraise body weight (distorted belief of body image)
DSM-5 criteria scale of AN
mild, moderate, severe, extreme
3 multiple choice options
what is the BMI limit to be considered a life-threatening disorder?
< 13 kg/m2
3 multiple choice options
according to the DSM5 what are the characteristics of anorexia nervosa?
- intense fear of being fat
- disturbance of body image
- obsession with food, thinness, and controlling food
- refusal to maintain the expected BMI
- severe food restriction
- extreme weight control behaviors (counting calories, over-exercising)
What are the subtypes of anorexia nervosa?
- Restricting type
- binge eating/purging type
- combination of restricting and binge eating
anorexia nervosa - restricting type
decrease in food intake dramatically and continuously, leading to a striking weight loss
anorexia nervosa - binge eating/purging type
cycles of eating excessively and compulsively but then negate this by self-induced vomiting, misuse of laxatives, or other means, which lead to a striking weight loss
What are common physical conditions associated with anorexia nervosa?
- Bradycardia and cardiac failure risk
- amenorrhea
- loss of muscle tone
- osteoporosis
- hormonal problems
- skin issues
- brittle nails and hair, hair loss, and lanugo
- metabolic, biochemical, renal, and GI problems
- generalized weakness
What are common psychosocial comorbidities of anorexia nervosa?
- Depression
- anxiety
- obsessive-compulsive disorders
- personality disorders
- mood disorders
what are the predisposing personalities/characteristics of people with AN?
- compulsivity and perfectionism
- desire to conform
- lack of initiative
- introversion and limited emotional expression (feeling of not fitting in)
- need for validation
- excessive self-control
- limited self-gratification
What characterizes bulimia nervosa (BN)?
- Fear of being fat with normal weight, characterized by episodes of binge eating followed by purging with the use of laxatives and diuretics
- rapid weight gain and loss
- shame and guilt
t/f the amount of food eaten during a binge-eating episode can be more than what a typical person would eat, but not always
true
What are the DSM-5 criteria for bulimia nervosa?
Recurrent episodes of binge eating and compensatory behaviors, severity measured by the number of episodes per week.
what is the scale of severity of bulimia nervosa according to the DSM5?
- mild (1-3 episodes/week)
- moderate (4-7 episodes/week)
- severe (8-13 episodes/week)
- extreme (14+ episodes/week)
mild bulimia nervosa
1-3 episodes/week
3 multiple choice options
moderate bulimia nervosa
4-7 episodes/week
3 multiple choice options
severe bulimia nervosa
8-13 episodes/week
3 multiple choice options
extreme bulimia nervosa
14+ episodes/week
3 multiple choice options
what comorbidities may a person with bulimia nervosa have?
- mood disorders
- impulsivity (drug and alcohol abuse, self-harm, sexual disinhibition, shoplifting)
- anxiety
- personality disorders
- electrolyte imbalances
- dental/oral problems
what are the predisposing personalities/characteristics of people with bulimia nervosa?
- impulsivity
- sensory seeking
- extroversion
- limited self-control
- need for validation
- impaired ability to cope with delayed self-gratification
what are the main differences between anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa?
AN: believes food restriction is not causing harm, introverted personality, desires more control
BN: feelings of shame and guilt, extroverted personality, limited self-control
3 multiple choice options
The restricting subtype of anorexia nervosa is characterized by:
dramatic and continuous decrease in food intake
3 multiple choice options
What distinguishes binge eating disorder (BED) from other eating disorders?
- Binge eating without purging
- episodes occurring within a 2-hour timeframe
- amount of food must be clearly larger than typical in the same context
what are specific binging behaviors?
- eating quickly
- uncomfortably full
- eating alone
- guilt/disgust
- feelings of lack of control
what kind of comorbidities can occur with binge eating disorders?
- mood and anxiety disorders
- high health-care utilization
- risk for obesity
what are the predisposing personalities/characteristics of binge eating disorder?
- Low self-esteem
- depressive personality
- harm avoidance (not seeking to harm themselves)
What is avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID)?
A disorder characterized by restricting food intake due to perceptions of food as unappetizing, uninteresting, or fear of adverse consequences.
According to the DSM5, what is the criteria for diagnosis of AFRID?
- sharp decrease in weight
- not meeting expected weight gain for developmental stage
- large deficiency in nutrition
- supplements or feeding tube dependence
- disrupted eating
What are the predisposing factors for eating disorders?
Life events, genetic factors, low self-esteem, adverse life experiences, social and cultural influences.
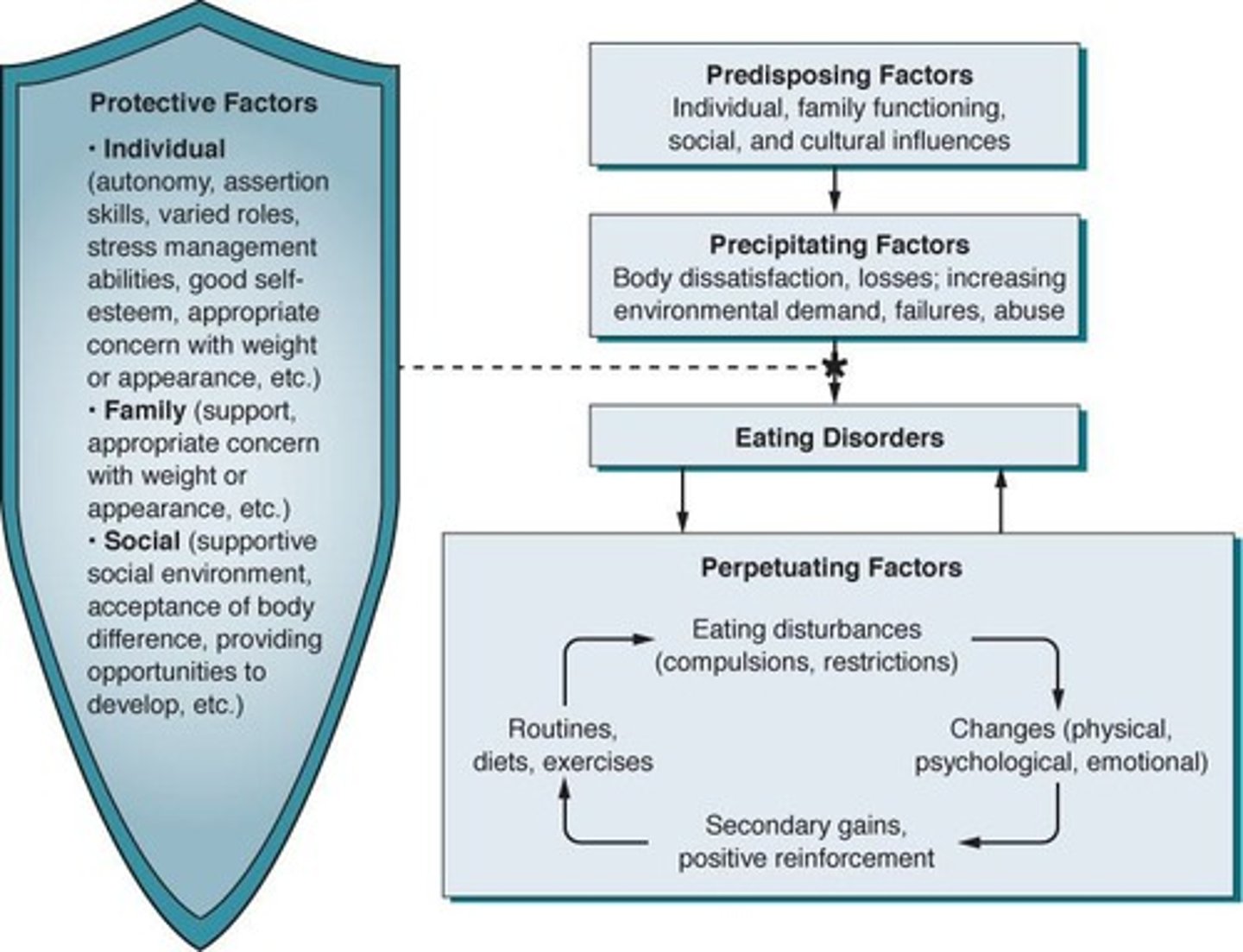
precipitating factors that contribute the development of an eating disorder
negative perceptions about self, self-image, the environment, or the future
what perpetuating factors can lead to developing an eating disorder?
- early changes are reinforced by family members, peers, and strangers
- cognitive disortions to feel "in control"
What impact do eating disorders have on occupational performance?
Impairment in volition, overvaluation of weight and shape, mood intolerance, and interpersonal problems.
what kind of psychological factors can affect an individual's volition for an occupation?
- perfectionism
- cognitive rigidity
- experiential avoidance
how does dissatisfaction with body image affect an individual's participation in social interactions?
may lead the individual to avoid social interactions, social eating, and move toward body-centric activities
how does mood intolerance impact occupational engagement?
individual has difficulty tolerating negative emotions and leads the individual to use maladaptive weight loss activities to avoid negative emotions
how does low self-esteem impact an individual's occupational engagement?
the individual is unable to cope due to distorted beliefs and cognitions about themselves, others, and life
perfectionism impact
What role does occupational therapy play in treating eating disorders?
Interventions include cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness, emotional regulation, and skills training for healthy eating.
What are the characteristics of individuals with anorexia nervosa?
Compulsivity, perfectionism, introversion, excessive self-control, and limited self-gratification.
What are common comorbidities associated with bulimia nervosa?
Mood disorders, anxiety, personality disorders, and multiple physical problems like electrolyte imbalances.
What is the significance of cognitive distortions in eating disorders?
Cognitive distortions reinforce negative perceptions and behaviors related to eating and body image.
How does perfectionism relate to eating disorders?
Perfectionism can lead to feelings of failure and shame, which are alleviated through maladaptive coping mechanisms like weight minimization.