1.9 - Acids, Bases + pH
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What does the pH scale measure?
The number of Hydrogen ions present in a solution to determine its acidity/basic
What is the reaction between an Acid + Base called?
Neutralisaion reaction
What are the general products of:
Metal Hydroxide + Acid
Metal Oxides + Acid
Metal Carbonates + Acid
Metal + Acid
Metal Hydroxides + Acid -→ Metal Salt + Water
Metal Oxides + Acid -→ Metal Salt + Water
Metal Carbonates + Acid -→ Metal Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
Acid + Metal --> Metal Salt + Hydrogen (g)
What is an Alkali?
Base that is soluble in water
What is a Bronsted-Lowry Base?
What is a Bronsted-Lowry Acid?
Base = A substance that accepts protons in a reaction
Acid = A substance that donates a proton in a reaction
What are the general equations for the following with water?
B-L Base
B-L Acid
HA(aq) + H2O(l) -→ H3O+ + A-
Base + H2O -→ BH+ + OH-
Define a Strong acid (+ 3 examples)
Give the Strong acid dissociation equation of HCl
An acid that completely dissociates into its (cat/an)ion when in water:
Examples = HCl, HNO3, H2SO4
HCl -→ H+ + Cl-
Define a Weak acid (+ 3 examples)
Give the Weak acid dissociation equation of Ethanoic acid
An acid that partially dissociates into its (cat/an)ions when in water:
Examples = Carboxylic Acid, Citric acid, Phosphoric acid
CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COO- + H+
Define a Strong Base (+ 3 examples)
Give the dissociation equation of Sodium Hydroxide
A base that completely dissociates into its (cat/an)ions when in water:
Examples = KOH, NaOH, Ca(OH)2
NaOH ⇌ Na+ + OH-
Define a Weak Base (+ 3 examples)
Give the dissociation equation of Ammonia
A base that partially dissociates into its (cat/an)ions when in water:
Examples = NH3, NH4OH, Al(OH)3
NH3 + H2O ⇌ NH4+ + OH-
For Weak Acids or Bases where is equillibrium?
Equilibrium shifts far to the left, since the base/acid partially dissociated (which is on the right)
Is water acidic or basic when reacting water with water?
Equation
Some water molecules acts a proton donor (acid) to make OH, and the others accepts its proton (base) to make H3O:
H2O(l) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq)
What is a Conjugate Acid/Base?
Example with HA (equation)
The base or acid formed from the reversible reaction of the base/acid:
HA ⇌ A- + H+ ----→ where HA is the Acid and A- = Conjugate base
If we reacted 2 acids together or 2 bases together, one strong and the other weak:
2 acids
2 bases
Water with Acid/Base
Acid - The weak acid acts basic and the stronger acid as the acid
Base - The weak base acts and acid and the stronger base acts basic
Water will act as the opposite to the thing it reacts to → with acid water = basic (vice versa)
Define Acidity
The measure of the concentration of H+ ions in a solution
Give the formula for pH → conversely give the equation for Concentration of Hydrogen ions
pH = -log10[H+]
[H+] = 10-pH
What type of scale is the pH scale measured by?
Logarithmic of base 10 meaning, the difference from pH 1-3 is x100
pH changes
pH changes
Explain why Dilution of an acid decreases Concentration?
When diluting the volume increases as the moles of protons are constant, so the overall concentration decreases → decreasing pH
Explain pH change when solid bases react with aq acid
Increasing pH:
When an aqueous acid and solid base react, the volume is constant (since the whole thing is done aqueous the amount of byproduct water is produced is miniscule), and the moles of H+ ions decrease -→ Increasing pH
Explain pH change with aqueous acids + bases
Increased pH:
When an aqueous acid + base react, the volume of the product increases, the number of H+ ions decrease (some water molecules formed) -→ increasing pH
What is the dissociation of water equation?
Comment on enthalpy
H2O ⇌ H+ + OH-
Endothermic → positive enthalpy change
Give the Kw formula (+units)
Kw= [H+][OH-] or Kw= [H+]2
Units = mol2dm-6
Why can Kw = [H+]2 ?
Kc formula is used, but since the concentration of water is so large it’s regearded as constant, so Kw is constant
What is the only factor that affects Kw? (why)
Temperature:
Since the forward reaction of water dissociation is endothermic, increasing T shifts equilibrium to the right - increasing ions concentration (decreasing does the opposite) - resulting in an increased Kw
Why is pure water neutral even if pH isnt 7?
A solution is neutral if [H+]=[OH-], so pure water is always neutral even if pH doesnt equal 7
What is the effect of Concentration of Kw? (why)
What happens if you increase [H+] in water
Changing concentration does nothing to Kw, equilibrium shifts to the side with lower concentration, meaning the other side would balance out:
Increasing [H+] means less OH as equil shifts left, but more water formed so Kw is unchanged
What is the proportionality between [H+] and [OH-]?
[H+] is inversely prop to [OH-]
What is the 3 step method to find the pH of a Strong Base?
How do you find the concentration of [OH-]
Step 1) Find conc of OH- (complete dissoc due to strong base)
Step 2) Find conc of H+ (by rearranging the Kw formula)
Step 3) Plug into pH formula
Reverse the process
What are the 4 factors affecting pH?
Amount of dissociation
Solubility
Concentration of H+ ions
Temperature
Why do Strong Acids have greater dissociations? (talk on an atomic-level)
The bonds between atoms in their molecules are weaker → allowing for easier + greater dissociation
Define strength in terms of acids + bases
The number of molecules to fully dissociated ions
Define Concentration
The number of moles in a substance in a given volume
Give the formula for Ka
When is it used?
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA] or Ka =[H+]2/[HA] --→ (when not told the concentration of A-)
Used only for weak acids
What is the formula for pKa?
pKa = -log10(Ka)
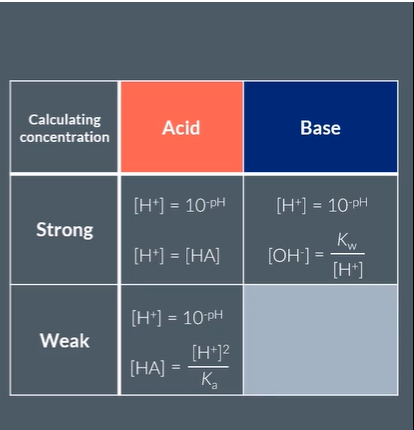
Give the method of Calculating pH of:
Strong Acid
Strong Base
Weak Acid

Give the method of Calculating Concentration of:
Strong Acid
Strong Base
Weak Acid
Acid - Base Titrations
Acid - Base Titrations
Give the 3-step method to find the pH of a neutralisation reaction with a Strong Acid
Determine the moles at start
Determine the moles in use (subtract the smaller moles on both reactants)
Find the moles at the end and plug into the pH formula (keeping in mind how "protic" the acid may be ——> i.e diprotic divide by 2)
Give the 3-step method to find the pH of a neutralisation reaction with a Weak Acid
ICE table method as prior with last Flashcard
Use Ka to find [H+] -→ remember to use total volume of base + acid
Find pH from that
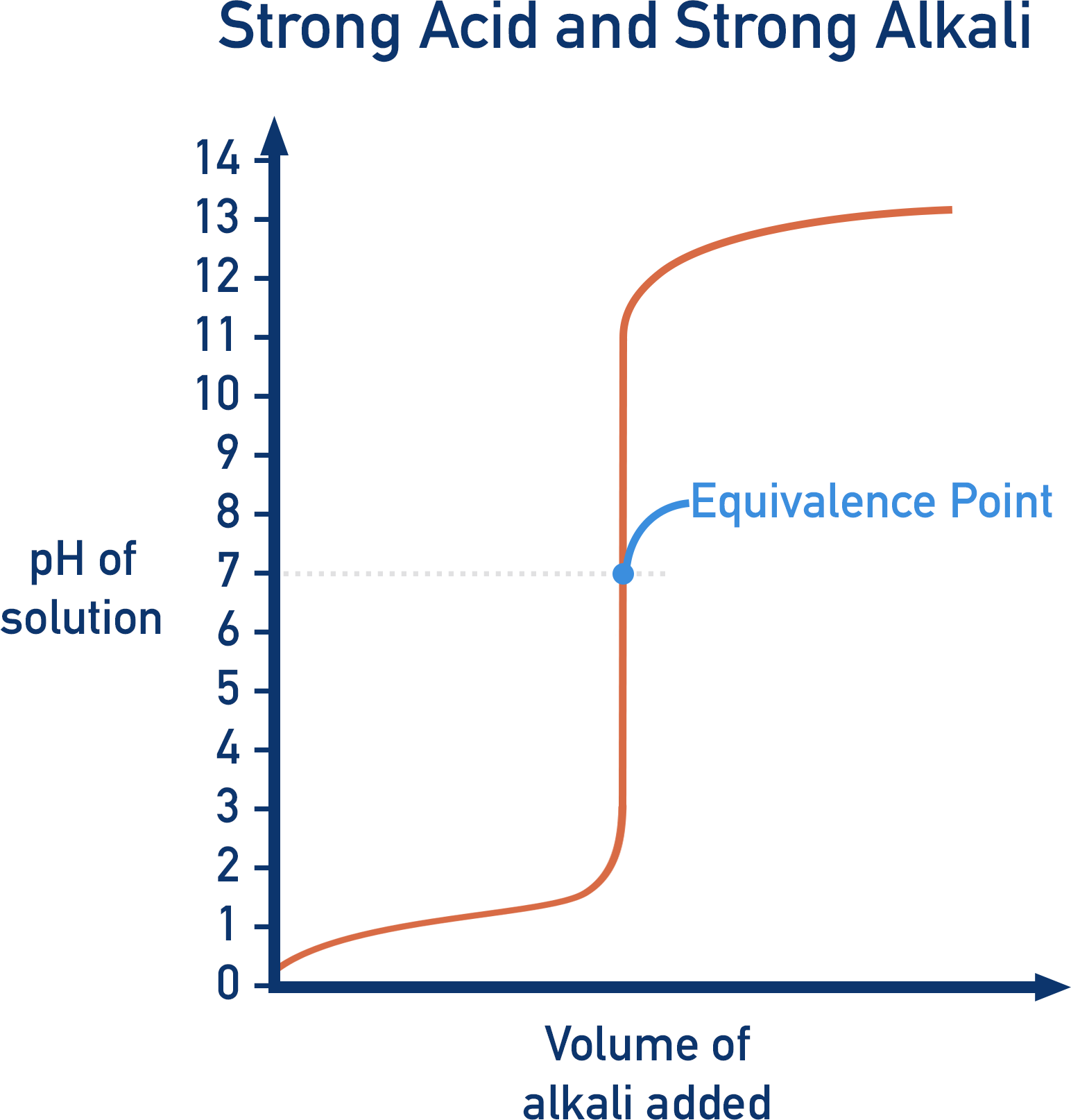
Describe the pH curve of a Strong Acid/Strong Base titration
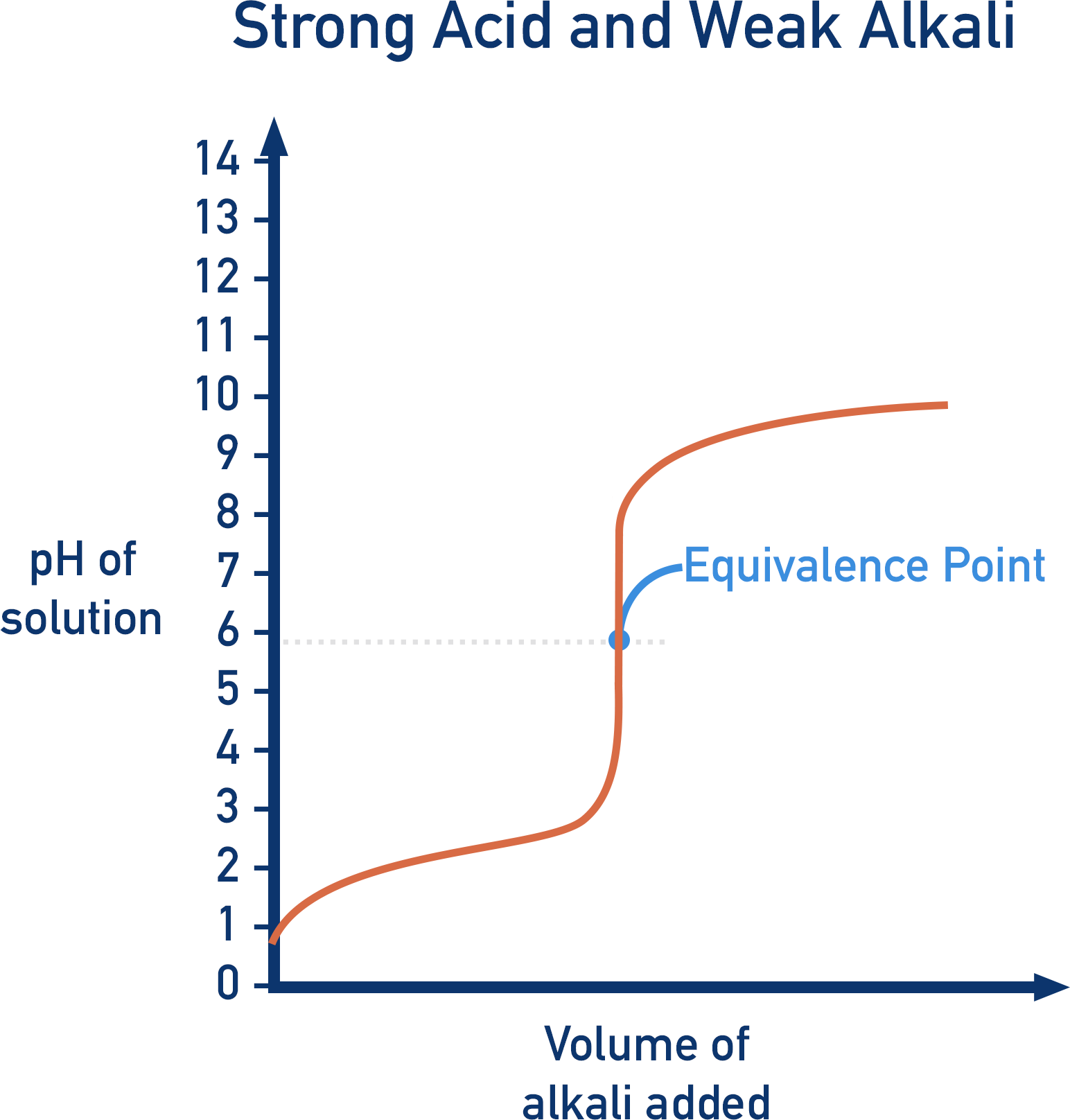
Describe the pH curve of a Strong Acid/WeakBase titration
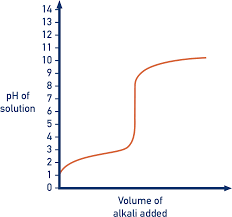
Describe the pH curve of a Weak Acid/Strong Base
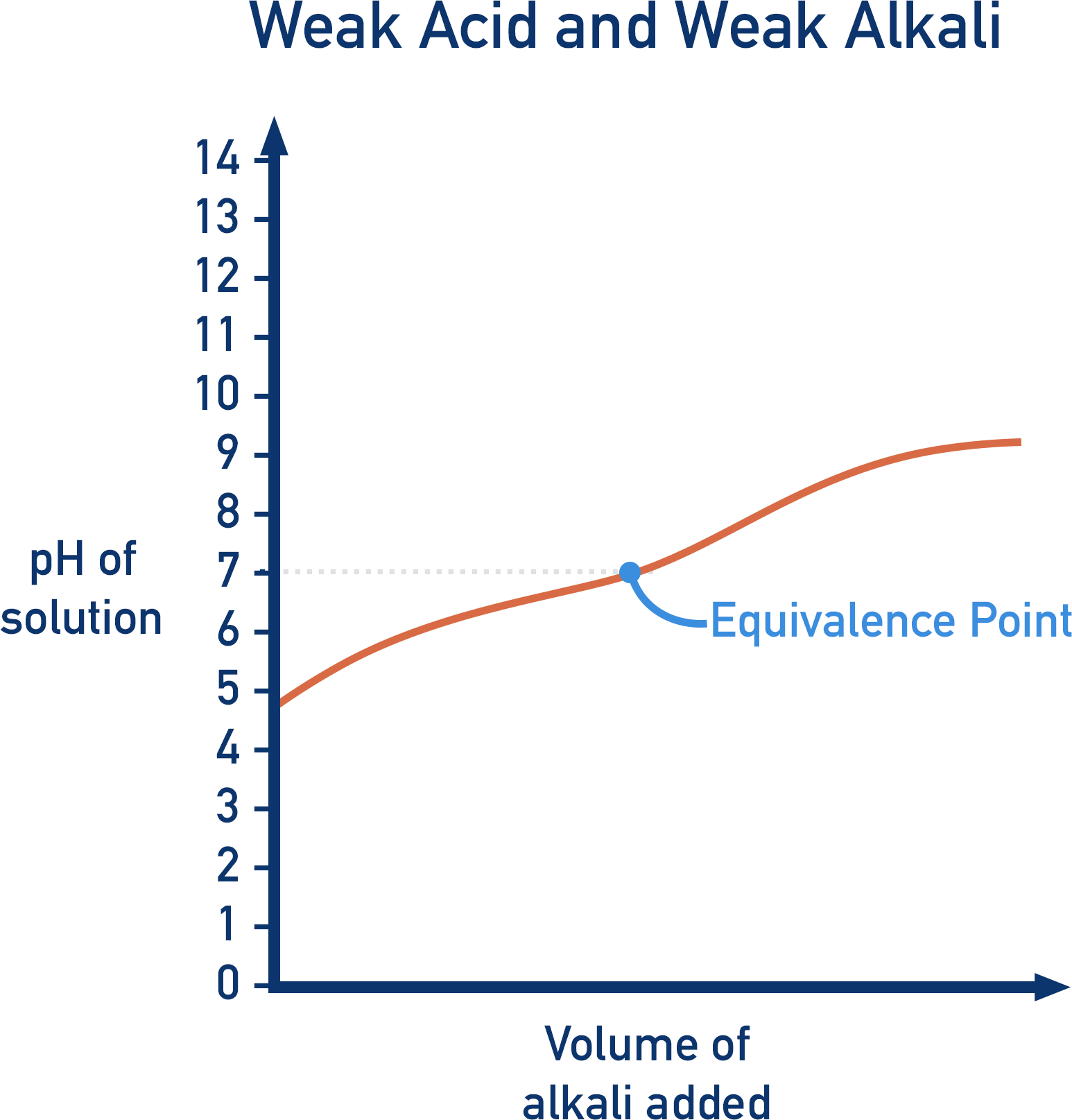
Describe the pH curve of a Weak Acid/Weak Base titration
Name 2 indicators
Include pH ranges
Colour change
Which pH titration can they be used in
Methyl Orange → pH = 3.1-4.4 → Red to yellow - - - (S.Acid with any base)
Phenolphthalein → pH = 8.3-10 → colourless → pink - - - (S.Base with any acid)
Define the Half Equivalence point - aka. H-EP (+ key feature)
H-EP= The point where half of the acid has reacted to form salt and the other half remains in solution (for weak acid/strong base or strong acid/weak base):
@ H-EP: pKa=pH
Buffers
Buffers
What is a Buffer solution?
Solution that resists the change in pH when small amounts of an acid/base are added to it
What must Buffer solutions contain?
Must contain some undissociated acid, with high concentrations of undissociated acid and high concentrations of dissociated ions
Give 3 ways to make a Buffer solution
Weak acid (aq) + Salt (aq or solid), where the salt contains its conjugate base (the non hydrogen ion in the acid)
Weak acid + strong base (the basic salt formed will dissociate into the weak acid ions) -→ adding an amount of base which is half the amount of acid
Weak base (aq) + salt of weak base (aq/s) (i.e NH3 + NH4Cl)
Why is there a Buffer region (Plateu) in the Weak Acid/Strong base pH curve?
Its at the halfway neutralisation point, where half the amount of base is equal to the acid present, acting as a buffer
Explain how a Buffer works:
Adding small amount of Acid
Adding small amount of Base
The buffer has a large amount of acid and its ions so when something is added equillibrium lies far to the opposite side to nullify the effect:
Acid → Adding acid shifts to the left, since your adding a DIFFERENT acid which will dissociate and increase H+, to oppose the acidity
Base → Adding base will make OH- react with H+, decreasing H+ shifting equilibirum right to make more H+ to oppose the base
Why does a Buffer no longer work when large amounts of something is added?
Buffer becomes saturated (when its equilibrium shift has little effect on the change), when large amounts of Acid or Base is added
List 3 uses/cases of Buffer solutions IRL (+ purpose of the buffer)
Blood = Maintains bloods neutral pH
Swimming pools = Prevents skin irritation
Shampoos = Maintains hair/scalp pH, preventing irritation from overly alkaline product
***BUFFER CALC ON WALL***
***BUFFER CALC ON WALL***