8 Characteristics of Life: Biology Key Concepts for Students
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Cell
The smallest living unit that can carry out life processes.
Unicellular organisms
Single celled organisms that makeup most organisms on Earth and are self-sufficient.
Multicellular organisms
Organisms in which cells specialize to perform specific functions such as bone cells, skin cells, muscle cells, root cells, and leaf cells.
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants convert the energy from the sun into food, specifically glucose.
Stimulus
A change in the environment that living things respond to, which can be immediate or long-term.
Asexual reproduction
Reproduction involving a single parent that produces identical offspring.
Budding
A form of asexual reproduction seen in organisms like Hydra and Sponge.
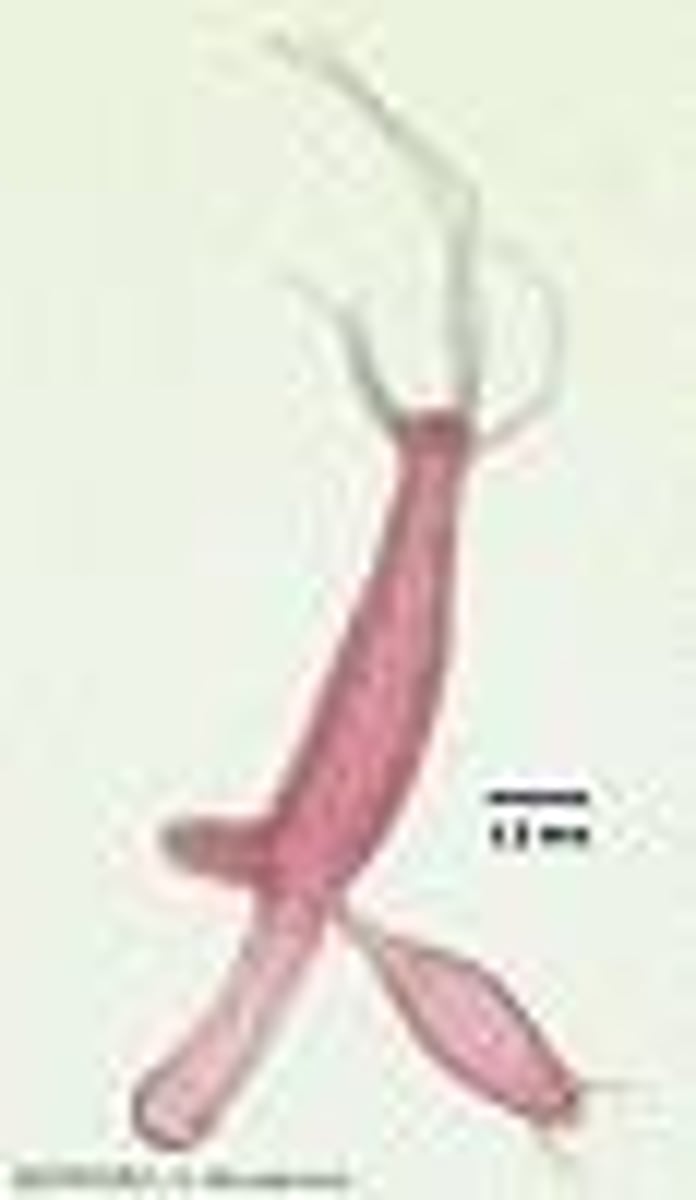
Fragmentation
A form of asexual reproduction where an organism can grow from a fragment, as seen in starfish.
Binary Fission
A form of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms where the cell divides into two identical cells.
Growth
The process of getting bigger, which requires the addition of more cells through cell division.
Development
The process of changing into an adult form or maturing.
Adaptation
The ability of organisms to change to fit their environment over a long period of time, often millions of years.
DNA
A molecule that provides instructions for making proteins and carries genetic material from parent to offspring.
RNA
A molecule that plays a role in the synthesis of proteins from the instructions provided by DNA.
Energy
All living things use energy, primarily sourced from the Sun.
Response to stimulus
Living things respond to stimuli such as shivering when cold or sweating when hot.
Stable internal environment
An organism's ability to maintain a stable internal environment to survive.
Reproduction
The process necessary for a species to survive, which can be sexual or asexual.
Adaptations of organisms
Changes in organisms that allow them to survive in their environment.
Cell division
The process that must occur to increase the number of cells in an organism.
Heredity
The passing of genetic material from parent to offspring.
Biology
The scientific study of life.
Order
An hierarchy of coordinated structures: cells, tissues, organs, organ systems.
Response to Stimuli
Alter growth or behavior based on environmental conditions.
Homeostasis
Stable internal environment inside cells and organisms.
Energy Processing
Gather energy from the environment for metabolic activities.
Growth and Development
Develop in a planned sequence, eventually becoming physically similar to parents.
Evolution
Change in the gene pool of a population over time.
Organization of Life
Biosphere to cells.
Biosphere
Includes all parts of the Earth - surface, atmosphere, and oceans, occupied by life.
Ecosystem
Includes the biological community and surrounding physical environment.
Biological Community
Made of all the populations living and interacting in one area.
Population
Includes all members of a species that live in the same area at the same time.
Organism
An individual life form.
Organ System
Group of organs that work together to perform a task.
Organ
A self-contained structure with a vital function.
Tissue
A group of cells that work together.
Scientific Method
Process of gathering evidence to answer questions about the world.
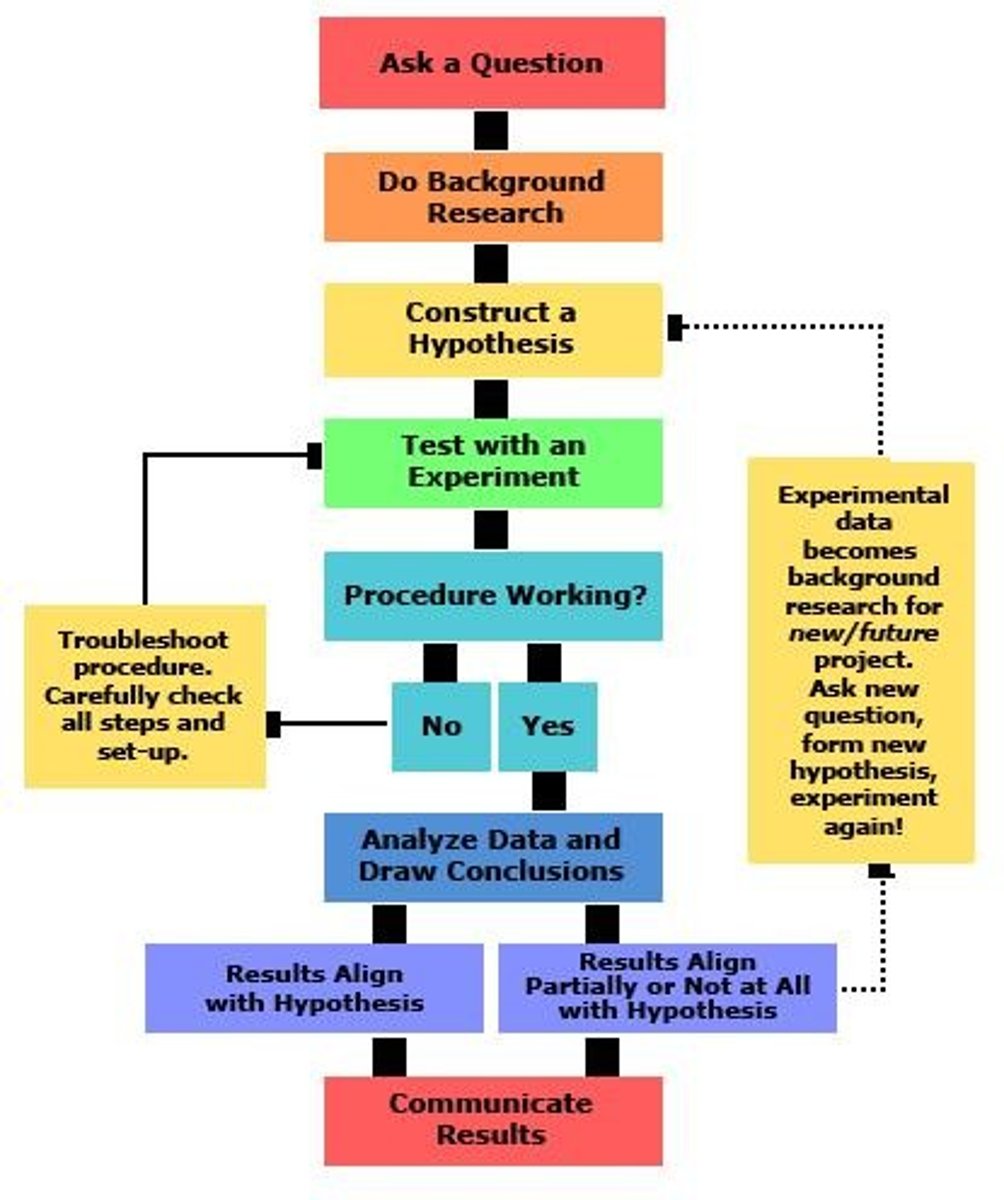
Hypothesis
A testable explanation or prediction based on the observation and the scientist's prior knowledge.
Independent Variable
New factor that is to be introduced and tested.
Dependent Variable
The measured result that is influenced by the independent variable.
Controlled Variables
Kept constant so they do not influence the dependent variable.
Control Group
Does not receive the independent variable.
Experimental Group
Receives the independent variable.
Data
Includes all of the measurements and observations made during the experiment.
Conclusion
States whether the hypothesis is supported by the experiment.
Peer review
Involves publishing the results for other scientists to review and check for error, bias, or uncontrolled variables.
Margin of error
An estimate of how different a result is from the actual value.
Reduction of margin of error
Can be reduced by increasing the sample size, or number of observations used in an experiment or study.
3% margin of error
Correlates with about a 1000-person sample size.
Experimental Design
The plan for how to conduct an experiment.
Controlled Experiment
Takes place in labs or artificial environments.
Natural Experiment
Takes place in the real-world without manipulation.
Bias
The preference for an experiment to turn out in a certain way.
Blind experiments
Reduce bias by ensuring the test subjects do not know whether they are in the experimental or control group.
Double-blind experiments
Prevent both scientists and subjects from knowing which is the experimental group.
Correlation
Observed when there are statistical variables that have a relationship that cannot be expected by chance alone.
Causation
Occurs when one variable directly influences the other.
Positive correlation
As one variable increases or decreases, the other does the same.
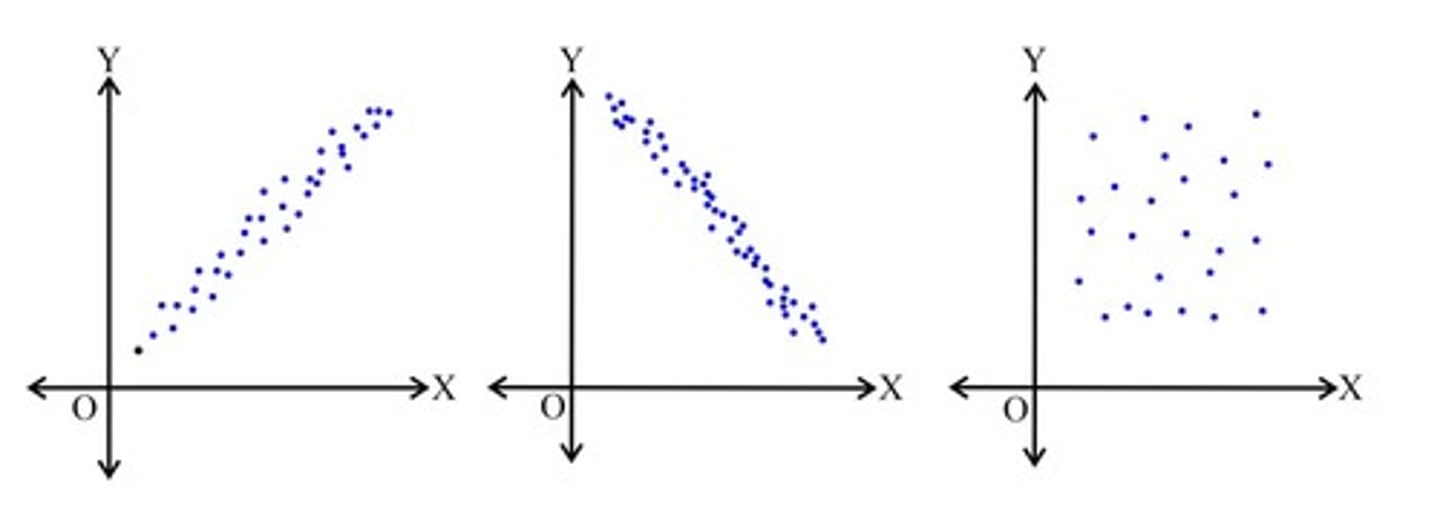
Negative correlation
As one variable increases, the other decreases.
None correlation
There is no observed relationship between the variables.
Pseudoscience
Appears or claims to be scientific, but does not follow scientific practices.
Historical Pseudoscience
Includes theories like spontaneous generation and the Four Elements Theory that lack formal experimental evidence.
Modern Pseudoscience
Includes beliefs such as the anti-vaccination movement and the Flat Earth Society.
Taxonomy
Classification of organisms based on DNA and traits.
Biochemistry
Study of life at the molecular level.
Microbiology
Structure and function of single-celled organisms.
Paleontology
Study of fossils and evolutionary history.
Genetics
Patterns of heredity.