Biochem Lecture 32: Collagen
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
collage n
This is the most abundant protein in the body
connective tissues
component of ECM, tendons, cartilage, bones, cornea, gumns
collagen is an important constituent of _______ ______
fibroblasts
collagen is secreted by _______
fibrous proteins (scleroproteins)
proteins that form fibrous structures and provide strength and integrity to a tissue
strain
high tensile strength
elasticity
fibrous proteins are highly resistant to applied ____
gingival connective
collagen fibers are the main constituent of _______ ______ tissue
highly regulated
deposition and degredation of collagen fibers are _____ ______ to maintain a healthy periodontium
alternative splicing
most collagen genes have multiple isoners through ______ _____
COL1A1
_______ gene encodes for a Type I collagen subunit
gums
collagen type I forms the ___
left handed helix (spins counterclockwise)
is collagen a left handed or right handed helix
right
a triple helix of collagen is ____ handed
glycine, proline
each collagen strain is a long ___ and ____ rich sequence
hydroxylated
prolines and lysines are _______ post-translationally
2,1
Three collagen chains, ___ a1 and __ a2 intertwine into the right-handed superhelical triple helix
endo and exo
in proline hydroxylation, the ___ proline and ____ hydroxyproline forms of proline are in equilibrium
exo hydroxyproline
which form must proline be in for the triple helix formation
stability
Loss of hydroxylation leads to dramatic decrease in _____
hydroxy-proline
the formation of _______ _____ is very important
dioxygenase
hydroxylation of prolines is catalyzed by an akg dependent ______
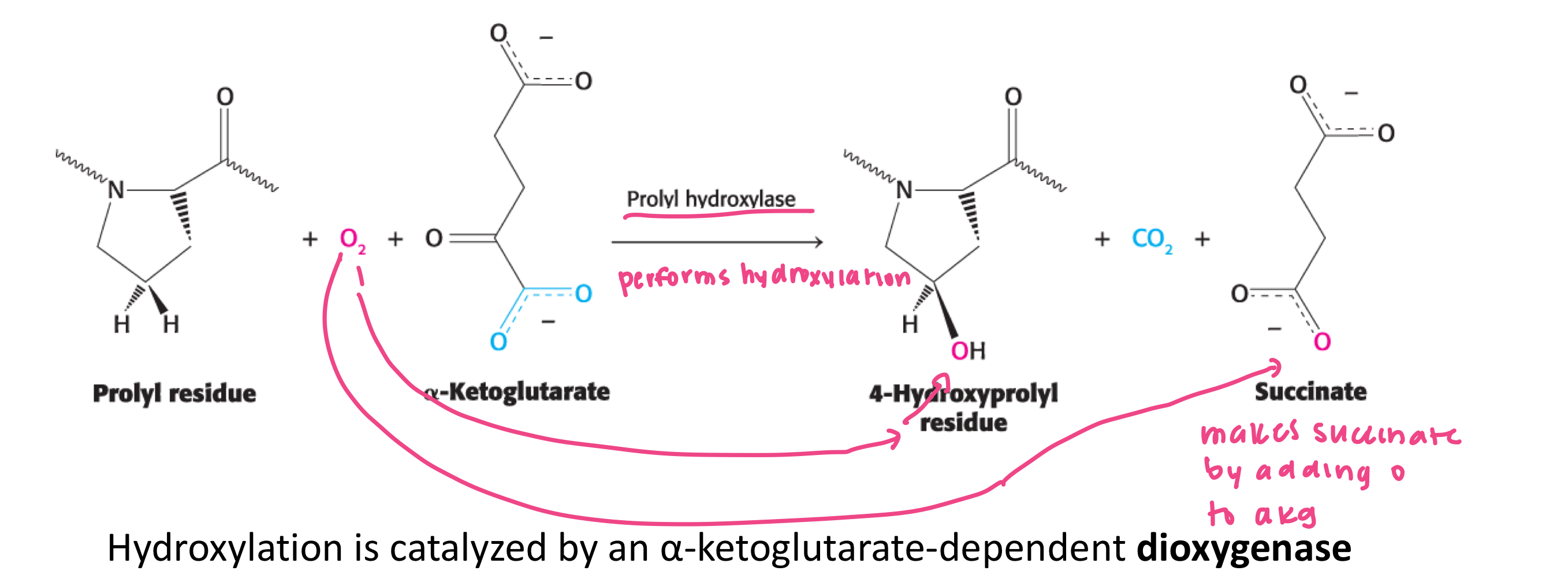
one atom of oxygen is attached to proline and one to the product succinate
what happens in the akg dependent dioxygenase reaction
no
is any external energy source required for the hydroxylation of collagen prolines?
True
True or false: Humans cannot biosynthesize ascorbic acid (Vitamin C)
another reaction takes place, resulting in a heme iron of the enzyme becoming oxidized and inactivated
Vitamin C gives an electron to the iron, regenerating the active form of the enzyme
How does Vitamin C contribute to collagen processing?
Scurvy
A disease associated with Vitamin C deficiency
collagen
causes gums to receed
scurvy leads to shortage of _____
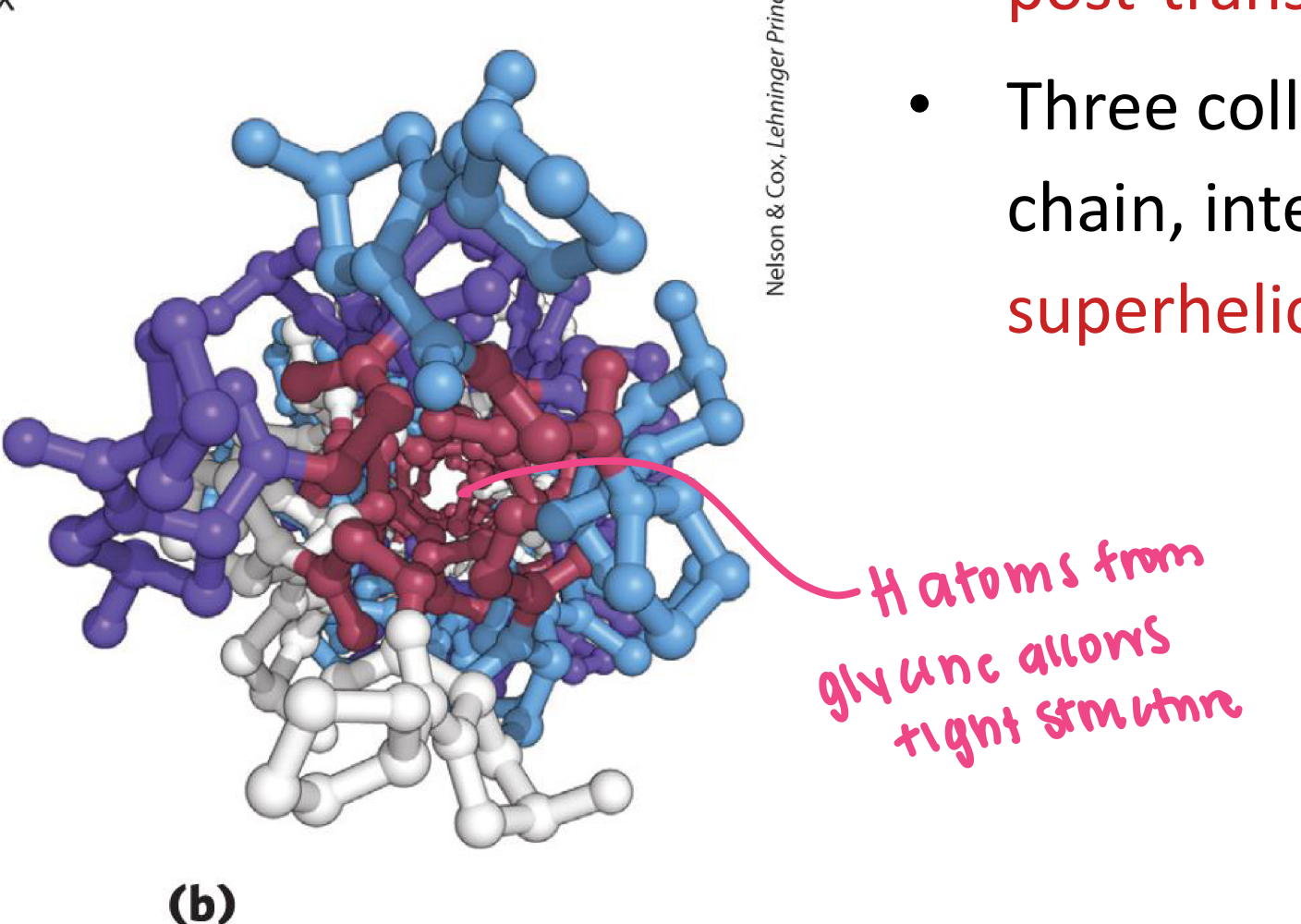
Hydrogen
_____ atoms from glycine allows for very tight packing in the triple helix structure of collagen
intracellulary, secreted
Collagen is synthesized _______, and eventually _____ out of the cell
in and outside
post-transcriptional modifications of collagen occur ___ and _____ the cell
amplifies strength
processing and crosslinking ____ ____ of the collagen fibers
fibrils
triple helices crosslink in a regular pattern to make _____
lysine residues
triple helices are crosslinked together via modified ______ _____
strength
degree of crosslinking affects ______
disease
_____ can arise from anything that interferes with the crosslinked collagen structure
structure
genetic mutations can disrupt the ____ of collagen
replaces glycine center with a bulkier amino acid preventing tight packing
disrupts the inter strand hydrogen bonding - no longer close enough
example of how genetic mutations disrupt the structure of collagen
osteogenesis imperfecta
_______ _____ is an example of a mutation that causes there to be a bulkier amino acid than glycine
D
What can cause a collagen-deficient phenotype?
A. Mutation in the COL1A1 gene that replaces a glycine with a valine
B. Chronic vitamin DC deficiency
C. mutation in the active site of ADAMTS
D. All of the above