Body Cavities
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Body Cavity
It is a space that holds and protects your organs
Holds the brain
Cranial cavity
Holds the spinal cord
Vertebral cavity
The cavity that contains three smaller cavities
Thoracic cavity
The cavity that contains your heart and lungs
Thoracic cavity
The three smaller cavities within the Thoracic cavity
Plueral cavity
Pericardial cavity
Mediastinum
Pleural cavity
Situated in your thoracic cavity
Covers and protects your lungs
L and R cavities
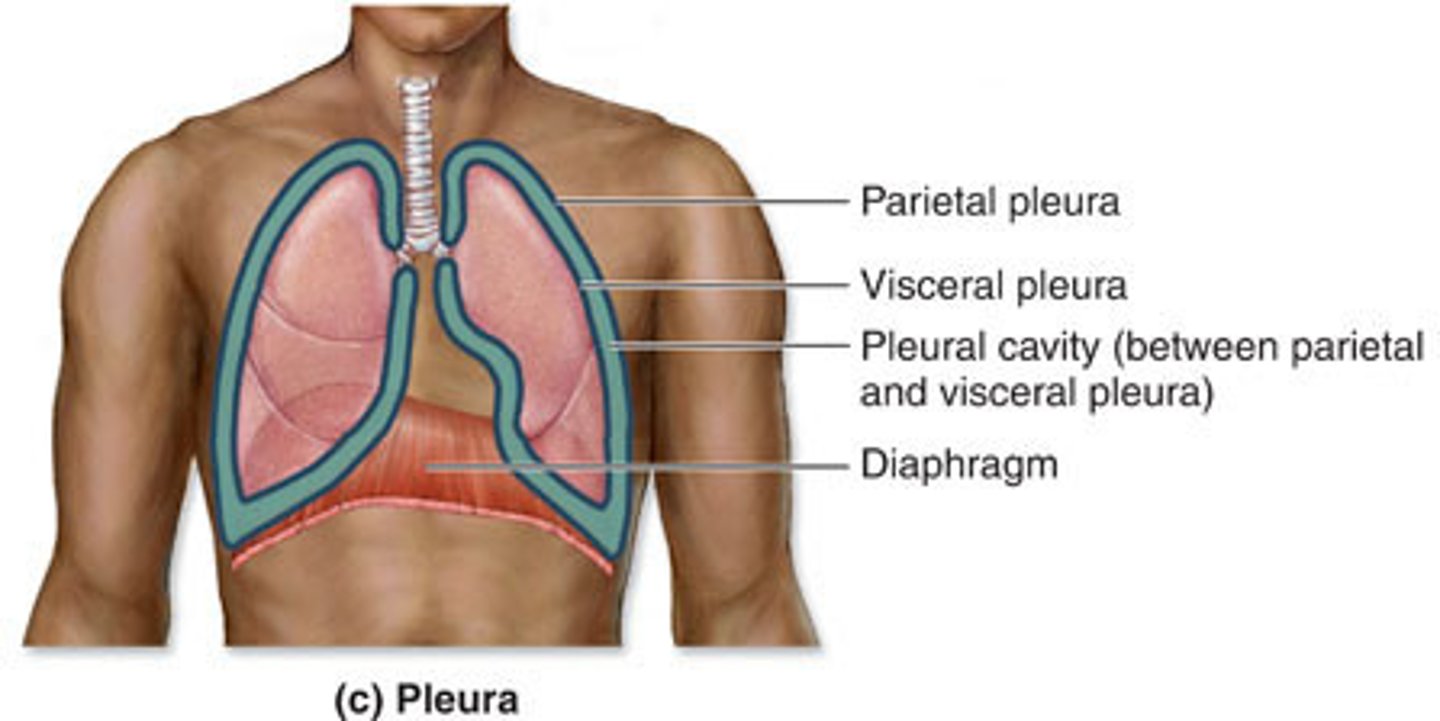
Mediastinum
Medial to lungs and extending from sternum to spinal column and from rib 1 to the diaphragm
Contains all thoracic organs, including the heart (inside of the pericardial cavity), except for the lungs
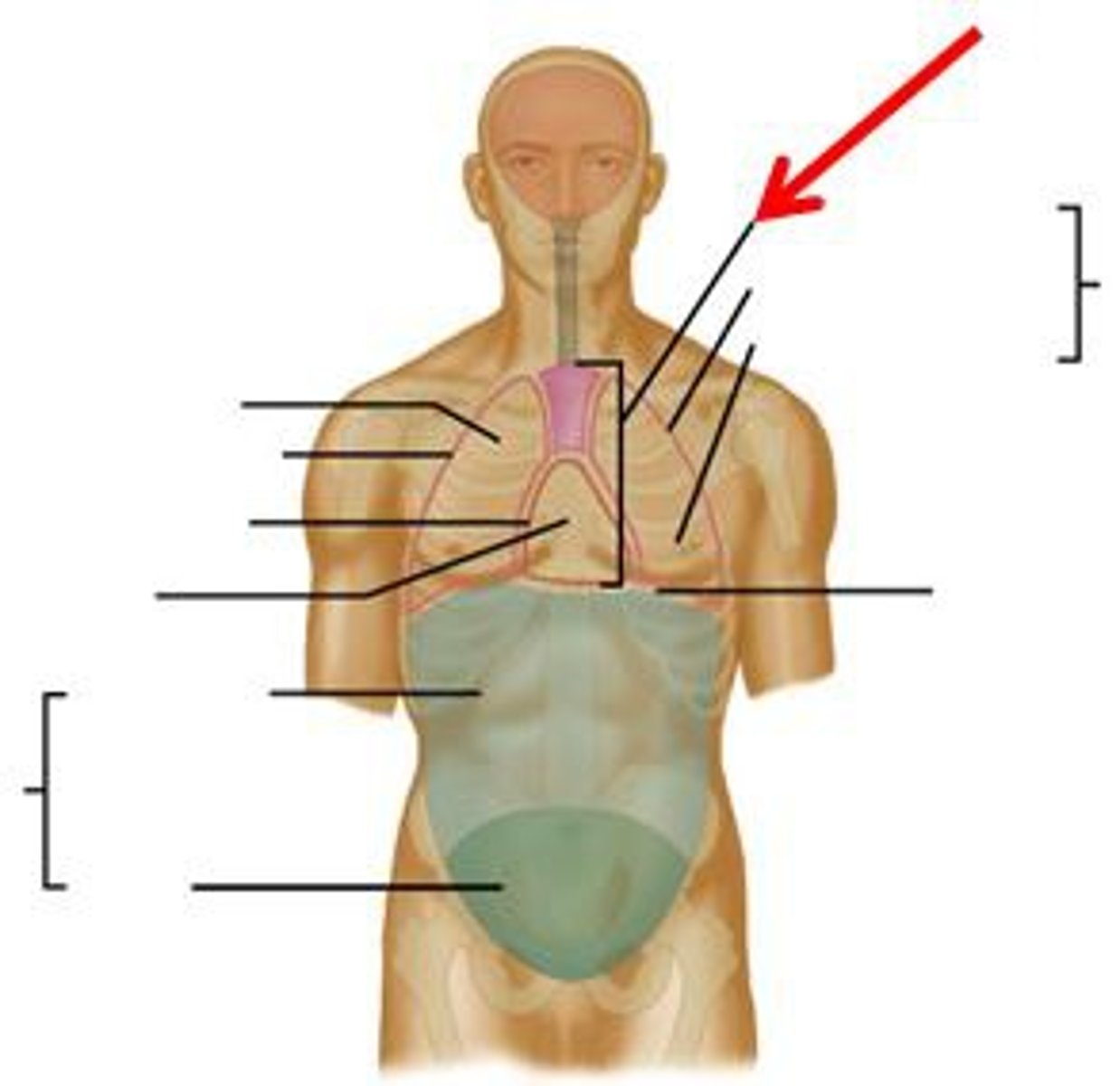
Abdominopelvic cavity
contains both your abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity, which are not separated from one another by any space or wall
separated from the thoracic cavity by the diaphragm
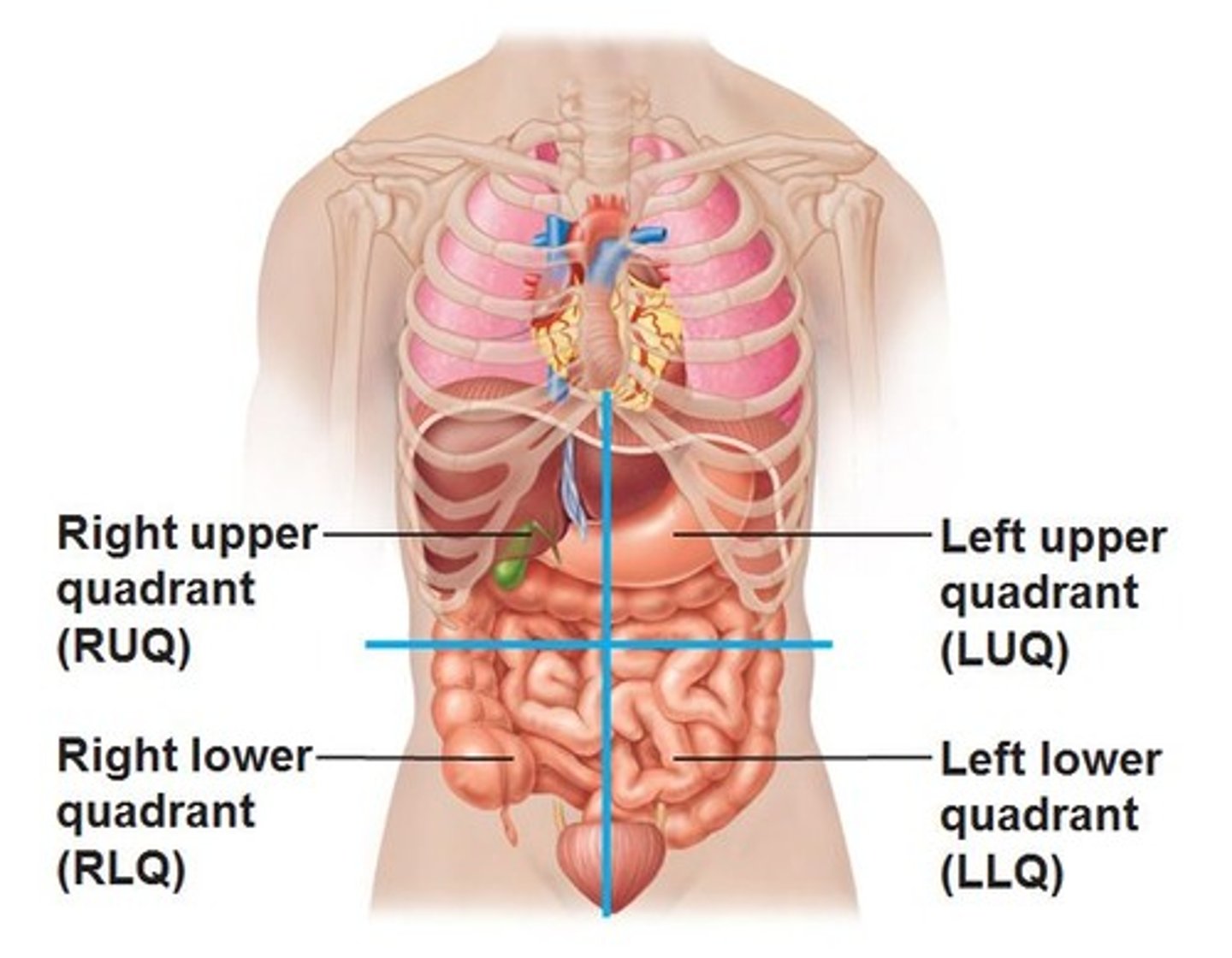
List the Quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity (1-4 in order)
System used by clinicians to distinguish the site of pain, masses, or abnormalities
Separates the region into 4 parts: Upper Right Quadrant (URQ), Upper Left Quadrant (ULQ), Lower Left Quadrant (LLQ), Lower Right Quadrant (LRQ),
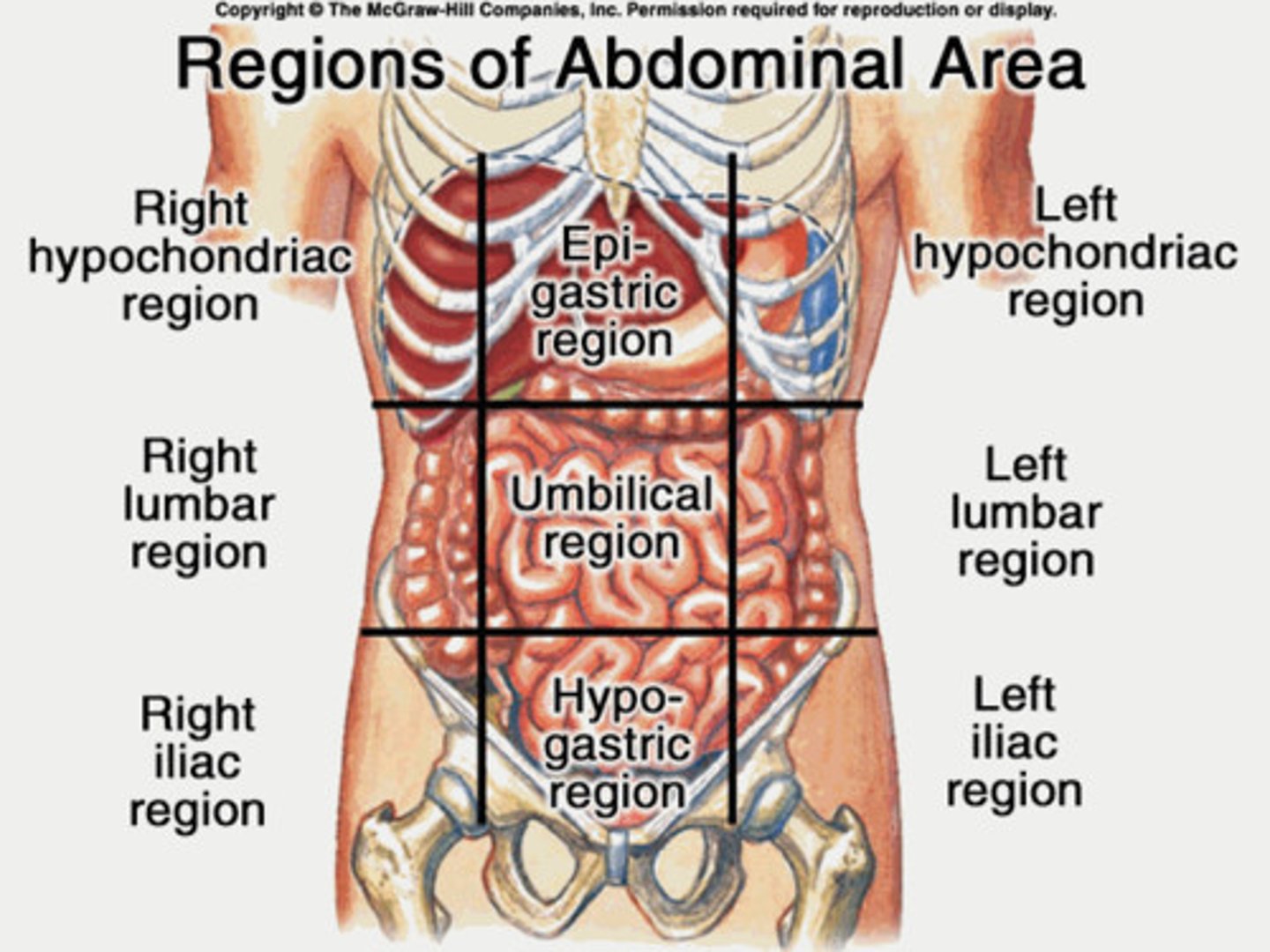
Regions of the abdominopelvic cavity
(LIST 1-9)
Used by anatomists
Separates the cavity into 9 regions:
1. Right Hypochondriac region
2. Epigastric region
3. Left Hypochondriac region
4. Right Lumbar region
5. Umbilical region
6. Left Lumbar region
7. Right Illiac region
8. Hypogastric (pubic) region
9. Left Illiac region
Remember that L and R correspond to the individual's body being studied (not your L and R if you're looking at the person)
Name the two parts of the Thoracic Cavity
Mediastinum—midportion of thoracic cavity; heart and trachea are located in mediastinum
Pleural cavities—right lung is located in right pleural cavity, and left lung is in left pleural cavity
Which cavity is located midportion of thoracic cavity which contains the heart and trachea
Mediastinum
Which cavity houses the lungs
Plural Cavities: right lung is located in right pleural cavity, and left lung is in left pleural cavity
The body portion that consists of the upper and lower extremities is the ________ portion.
Appendicular
The two major cavities of the body are the:
a. thoracic and abdominal
b. abdominal and pelvic
c. dorsal and ventral
d. anterior and posterior
c. dorsal and ventral
The structure that divides the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity is the:
a. mediastinum
b. diaphragm
c. lungs
d. stomach
b. diaphragm
The epigastric region of the abdominopelvic cavity:
a. is inferior to the umbilical region
b. is lateral to the umbilical region
c. is medial to the umbilical region
d. none of the above
d. none of the above
The hypogastric region of the abdominopelvic cavity is:
a. inferior to the umbilical region
b. lateral to the left iliac region
c. medial to the right iliac region
d. both a and c
d. both a and c
Which of the following is an example of a positive feedback loop?
a. maintaining a constant body temperature
b. contractions of the uterus during childbirth
c. maintaining a constant volume of water in the body
d. both a and c
b. contractions of the uterus during childbirth
The excretion of larger than usual volumes of urine when the volume of fluid in the body is greater than normal is an example of:
a. positive feedback
b. negative feedback
c. normal fluctuation
d. both b and c
d. both b and c
Match each of the directional terms in Column B with its opposite term in Column A.
19. ________ superior
20. ________ distal
21. ________ anterior
22. ________ lateral
23. ________ deep
a. posterior
b. superficial
c. medial
d. proximal
e. inferior