Forensics arson
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
Arson
The criminal act of deliberately setting a fire
2
New cards
Arson often presents…
Complex and difficult circumstances to investigate
3
New cards
What does arson crimes often leave behind?
Burned or charred evidence and wet conditions (from attempts to eradicate the flames)
4
New cards
The goal of a fire investigator
To detect and identify relevant chemical materials, identify igniters and reconstruct the events that led to the fire
5
New cards
Upon arriving at the scene, the investigator should note:
- Presence, location, and condition of victims
- flame and smoke conditions (direction, height, location)
- status of alarms, sprinklers
- unusual characteristics of scene
- conditions of the structure: Lights, windows, doors
- flame and smoke conditions (direction, height, location)
- status of alarms, sprinklers
- unusual characteristics of scene
- conditions of the structure: Lights, windows, doors
6
New cards
Fire
A product of the process during which oxygen is united with some other substances to produce noticeable quantities of heat and light (a flame)
7
New cards
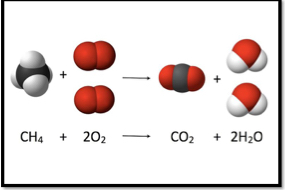
Oxidation
A combination of oxygen with other substances to produce new substances
8
New cards
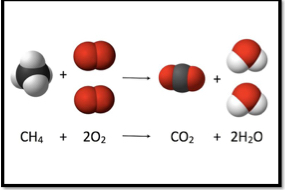
Combustion
When a rapid combination of oxygen and other substances combine accompanied by the generation of heat and light to form a flame
9
New cards
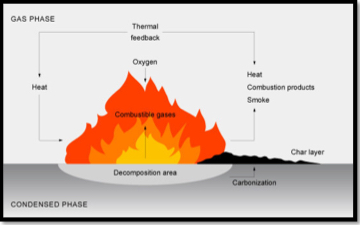
What happens once combustions begins?
Enough heat is liberated to keep the reaction going by itself. A fire becomes a chain reaction, absorbing a portion of its own heat to generate more heat
10
New cards
How things ignite
When fire is held to the paper…
1. Molecules that are bound closely to one another on the surface are…
2. …loosened by the heat. They move further apart from one another becoming a gas
3. The gas molecules combine with oxygen molecules in the air and the paper begins to burn
1. Molecules that are bound closely to one another on the surface are…
2. …loosened by the heat. They move further apart from one another becoming a gas
3. The gas molecules combine with oxygen molecules in the air and the paper begins to burn

11
New cards
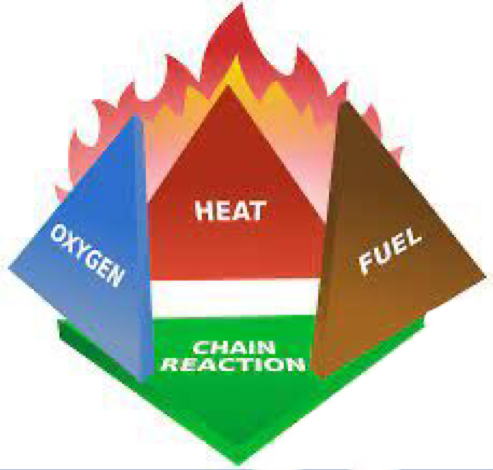
Three requirements must be satisfied to initiate and sustain combustion
1. A fuel must be present
2. Oxygen must be available in sufficient quantity to combine with the fuel
3. Heat must be applied to initiate the combustion, and sufficient heat must be generated to sustain the reaction
2. Oxygen must be available in sufficient quantity to combine with the fuel
3. Heat must be applied to initiate the combustion, and sufficient heat must be generated to sustain the reaction
12
New cards
When arson investigators arrive at the scene…
They begin by searching for the point of origin (where the fire began)
13
New cards
Pattern in which fires burn
“V” pattern of char/soot that leads to origin of fire
14
New cards
Once the point of origin is determined…
Investigators then focus their attention on the search for accelerants or ignition devices
15
New cards
How do investigators detects accelerants?
- Portable hydrocarbon detectors
- accelerant sniffing dogs
- identifiable pour patterns (that are then tested)
- accelerant sniffing dogs
- identifiable pour patterns (that are then tested)
16
New cards
When specimens are collected from a crime scene…
They should be packaged immediately in airtight containers so possible residues are not lost through evaporation
17
New cards
Common reasons for arson crimes
- insurance fraud
- crime concealment
- pyromania
- revenge
- crime concealment
- pyromania
- revenge
18
New cards
Why is arson divided into degrees?
Depending sometimes on the value of the property but more commonly on its use and whether the crime was committed in the day or night
19
New cards
First-degree arson
Burning an occupied structure such as a school or a place where people are normally present
20
New cards
Second-degree arson
Burning an unoccupied building such as an empty barn or an unoccupied house or other structure in order to claim insurance on such property
21
New cards
Third-degree arson
Burning an abandoned building or an abandoned area, such as a field, forest, or woods
22
New cards
How does terrain effect forest fires?
Fire moves faster on steep slopes
23
New cards
John Orr
Was a firefighter; wrote a book called “Point of Origin”; known as the “Pillow Pyro”
24
New cards
If humidity is low, will the fire’s characteristics most likely increase or decrease?
Decrease
25
New cards
How is arson evidence packaged?
Immediately placed in an airtight container