SQL Calculation
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Calculations
use basic SQL structure:
SELECT column (s) and/or calculations
FROM table
WHERE conditions and/or calculations
ORDER BY column(s) and/or calculations;
add calculations in this SQL structure
write a formula to do calculations & columns are used as variables: column1 + column2
treat the formula as a column
any match operator can be used (+-*/)
complex calculations require functions like cos()
Audit and Data Analytic Mindset
think about the business, problems and issues we need to identify and address, what data we need, and what existing data can tell us
related questions to ask:
how is this related to accounting? there are no numbers here. what can we “crunch”?
relatedly, what kind of data analysis can we do?
from an auditing standpoint, how do we audit the company’s HR practice?
is there anything unusual in the data table?
Audit Question Example
are there any underage employees at the time of their hiring (assuming legal age for formal employment is 18)?
why is this the case?
relevant for internal auditing bc it raises questions such as: how was the company doing in terms of regulatory compliance, were they complying with external laws and regulations?
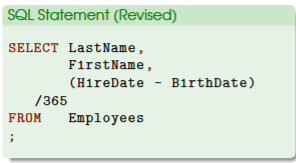
Calculation for Age of Employee
/365 would transform the answers from days to years
years is more relevant when determining one’s age
new formula is: (HireDate - BirthDate)/365
remember to use parenthesis ()
use math operators depending on the specific question we want to answer (+-*/)
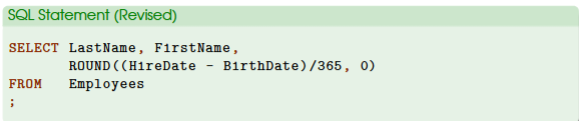
ROUND (n, p)
used to eliminate decimals
an additional step of calculation
n: number to round
p: precision (number of decimals)
example: SELECT LastName, FirstName, ROUND(HireDate - BirthDate)/365, 0)
n: the number we want to round which is (HireDate - BirthDate/365)
p: how many decimal places we want to keep, which in this case is 0
commas are needed in the formula
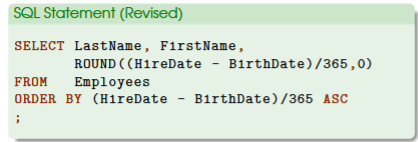
Sort Result
by doing so, we can tell who is the youngest or oldest at the time of hiring
first, add a new block ORDER BY here
calculations can be used with this block
ASC is used to present the youngest employee based on age first
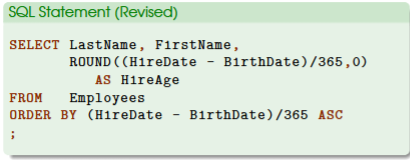
New Column Name
example: SELECT ROUND ((HireDate - BirthDate)/365, 0)) AS HireAge
use AS to change column name
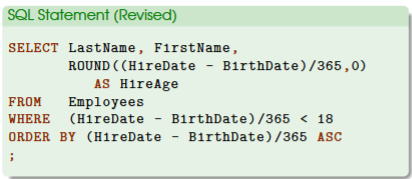
Filtering: Workers who are under 18 at HireDate
WHERE (HireDate - BirthDate)/365 <18
<18 would only show employees under the age of 18
if the result is an empty table, then there are no employees that fit this condition
Record 1-1 would be shown at the bottom which indicates a new, blank row in Access
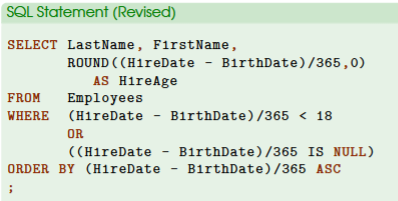
if there are two employees with no age information, we need to use the audit mindset to include these suspicious employees in our data analysis
What to do if employee information is missing and how to include the employee(s)
example: WHERE (HireDate - BirthDate)/365 <18 OR (HireDate - BirthDate)/365 IS NULL)
IS NULL keyword is added and represented in the new condition bc IS NULL checks whether the new column (e.g., calculation) does not have any data and is empty or missing.
NULL = missing or empty value
NULL is not the same as a white space or a zero
OR will be included since the new condition with IS NULL keyword will be considered if the first condition is not satisfied (either condition)
it is wrong to use AND in this case
Steps to Answer Business Questions
maintain an audit and data analytics mindset
how to use data for auditing/business decision making
what data can we use and how to get data
know what questions to ask
understand the business and know existing business problems/issues
understand audit objectives from the auditing standpoint
answer the questions step by step
make tiny improvements at a time
pay attention to missing data
missing data is problematic
determine whether missing data is legitimate
to do so, understand the nature of the business, processes of how people do things (business process integration) and how info systems work (information control & risk and control)
follow up investigation
needed usually to understand the whole picture of the issue