Bacteria physiology, Fermentation, Respiration, and ATP synthesis
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what is fermentation
oxidation of an organic compound to yield energy where the electrons generated are accepted by an internal electron acceptor
what is substrate-level phosphorylation
ATP is directly synthesized from an energy-rich intermediate
what is oxidated phosphorylation
the dissipation of proton motive force coupled to ATP synthesis
the stages of fermentation
stage 1. preparatory reactions
stage 2. oxidation (production of NADH, ATP, Pyruvate)
stage 3. reduction (redox balance and produce fermentation product)
What is stage 1
glycolysis
ATP is used
Starts with glucose
what is stage 2
glycolysis (continued)
ATP is formed
ends with pyruvate
what is stage 3
reduction
NADH dumps e- to become NAD+
different type of fermentation
Ethanol
Lactic acid
Mixed acid
Propionic acid
what is respiration
oxidation of an organic or inorganic energy source in which electrons pass down an electron transport chain and are accepted by an external electron acceptor
what is Aerobic respiration
when the electron acceptor is Oxygen
complete oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide
what are the steps in Aerobic respiriation
Glycolysis
Pyruvate to acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
ETC in aerobic respiration
ETC is fueled by the reduced NADH and FADH2 from the citric acid cycle and glycolysis
What does ATPase do
it converts proton motive force (PMF) to ATP
Aerobic respiration with an organic compound as the starting material
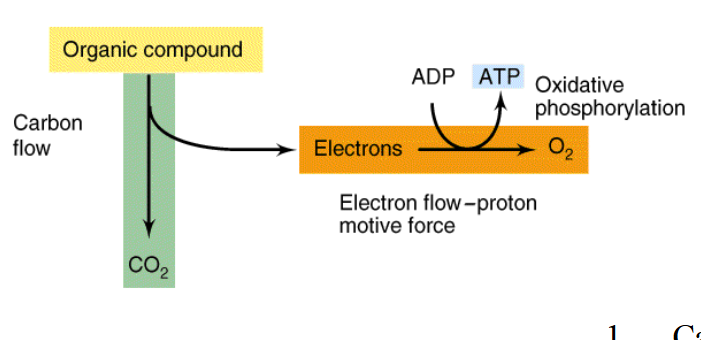
Lactic acid fermentation
Glucose → 2 pyruvate → 2 lactate
Process of Aerobic respiration
Glucose → 2 pyruvate → 6 CO2
Anaerobic respiration
when the external electron acceptor is either Nitrate or Sulfate