Chapter 16 - Conjugated Pi System / Pericyclic Reactions
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
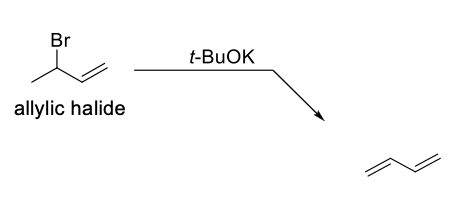
Preparation of Conjugated Dienes Method 1
Large bulky base (ex: t-BuOK) on an allylic halide.
Undergoes an elimination reaction to make another double bond.
Bulky base used to prevent competition with an Sn2 reaction.
Allene won’t be formed since they are too unstable.
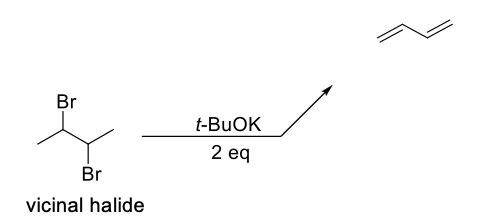
Preparation of Conjugated Dienes Method 2
2 eq of a large bulky base (ex: T-BuOK) on a vicinal halide.
Undergoes two successive elimination reactions to make two double bonds.
Bulky base used to prevent competition with an Sn2 reaction.
Allene won’t be formed since they are too unstable and t-BuOK isn’t strong enough base to undergo the second elimination.
Preparation of Conjugated Dienes Method 3
Concentration H2SO4 with heat on two OH groups.
Undergoes two elimination reactions to make two double bonds.
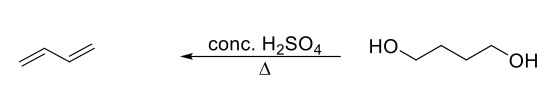
HOMO
Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital
(Goes up one if light is added to the reaction)
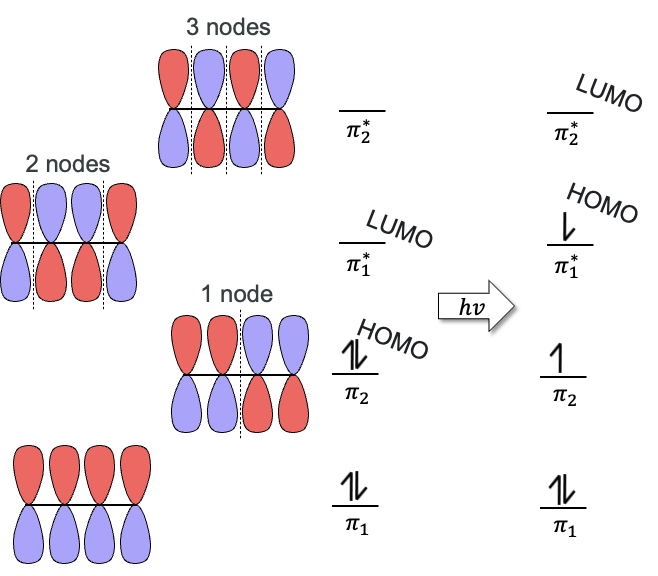
LUMO
Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital
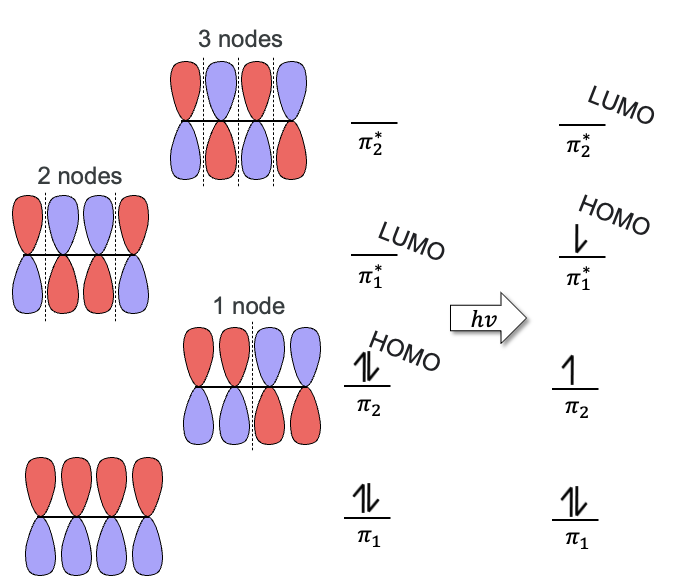
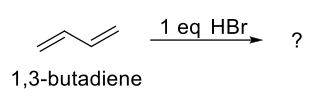
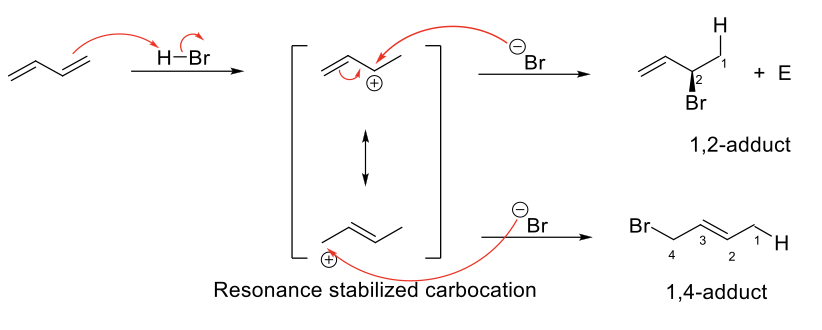
Electrophilic Addition of Conjugated Dienes
Follows Markovnikov Rule (H on less sub C, halogen on more sub C)
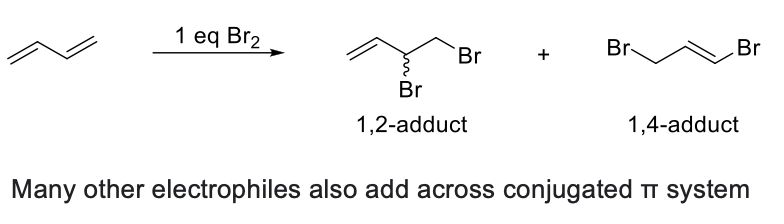
Due to resonance, once H has been added on C1, Br can be added on C2 or C4, giving a 1,2-adduct (addition product) and a 1,4-adduct.
1,2-adduct less stable, forms faster (Kinetic Product)
1,4-product more stable, forms slower (Thermodynamic Product)
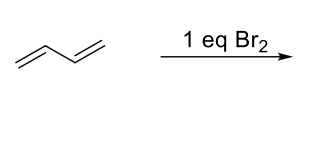
Bromination of Conjugated Dienes
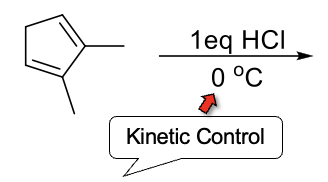
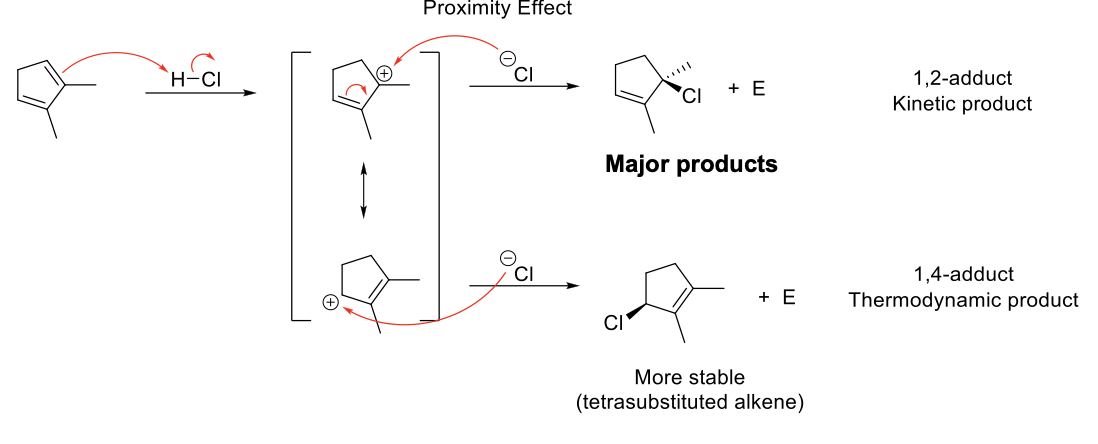
Kinetic and Thermodynamic Control
Kinetic Control - Short reaction time and low temp. Favors 1,2-adduct.
Thermodynamic Control - Long reaction time and high temp. Favors 1,4-adduct.
![<p>[4+2] Cycloaddition (Diels-Alder Reaction)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5a60d4a7-0ecd-474d-8b6e-93b9808ee4c2.png)
[4+2] Cycloaddition (Diels-Alder Reaction)
[4+2] addition - Comes from 4 π electrons and 2 π electrons. Uses three π bonds to form 1 π bond and 2 σ bonds.
Dienophile - Requires electron withdrawing group. Can be an alkyne. Rxn will follow stereochemistry of dienophile)
Diene - Must be in s-cis conformation. S-trans = no rxn.
Stereochemistry:
Endo rule: During a Diels-Alder reaction where the dienophile contains a π bond in its EWG, the π bond interacts with the p orbitals on the diene. These interactions stabilize the TS, lowering Ea of the reaction that leads to the endo product.
Regioselectivity:
If one of products is symmetrical, only 1 product.
If products are assymmetrical, there are 2 products. Product that brings partial positive and partial negative charges of reactants closer together is major.
HOMO of diene and LUMO of dienophile must line up.
![<p>[4+2] addition - Comes from 4 π electrons and 2 π electrons. Uses three π bonds to form 1 π bond and 2 σ bonds.</p><p>Dienophile - Requires electron withdrawing group. Can be an alkyne. Rxn will follow stereochemistry of dienophile)</p><p>Diene - Must be in s-cis conformation. S-trans = no rxn.</p><p></p><p>Stereochemistry:</p><p>Endo rule: <span>During a Diels-Alder reaction where the dienophile contains a π bond in its EWG, the π bond interacts with the <em>p</em> orbitals on the diene. These interactions stabilize the TS, lowering <em>E<sub>a</sub></em> of the reaction that leads to the <em>endo</em> product.</span></p><p></p><p>Regioselectivity:</p><p>If one of products is symmetrical, only 1 product.</p><p>If products are assymmetrical, there are 2 products. Product that brings partial positive and partial negative charges of reactants closer together is major.</p><p></p><p>HOMO of diene and LUMO of dienophile must line up.</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c3e02ab3-d2df-4a90-ac72-e9dfe7c6c0d9.png)
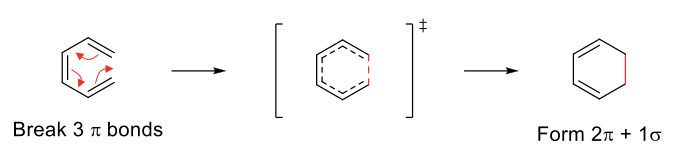
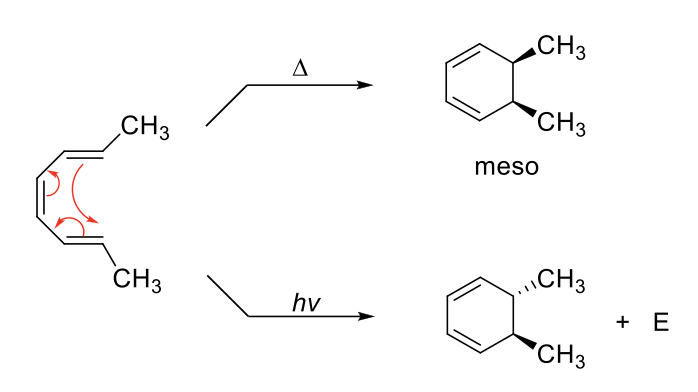
Election Cyclic Addition
Uses three π bonds to form 2 π bond and 1 σ bonds.
Stereochemistry depends on conformation of reactant and whether the reaction is run under heat or light.
1) HOMO reaction centers must line up. Requires rotation which will explain the cis/trans nature of attached groups.
2) Adding light changes the HOMO, which may result in a different product than heat.
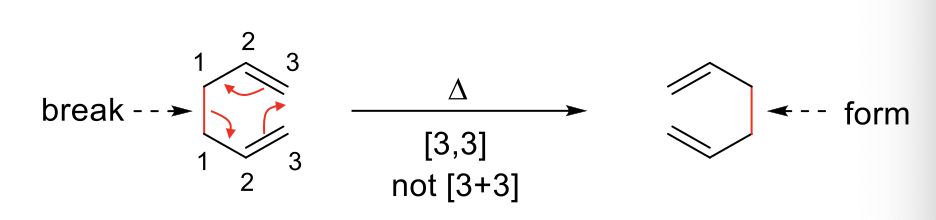
Sigmatropic Rearrangement
Results in a rearrangement of a σ bond. Forms 1 σ bond and breaks another. [X,X] gives the number of atoms between broken bond and formed bond.
COPE Rearrangement - [3,3] rearrangement of a 6-C membered TS.
CLAISEN Rearrangement - Oxygen analog of Cope Rearrangement
Often, Allyl vinyl ethers will undergo claisen rearrangement.
![<p>Results in a rearrangement of a σ bond. Forms 1 σ bond and breaks another. [X,X] gives the number of atoms between broken bond and formed bond.</p><p></p><p>COPE Rearrangement - [3,3] rearrangement of a 6-C membered TS.</p><p>CLAISEN Rearrangement - Oxygen analog of Cope Rearrangement</p><p></p><p>Often, Allyl vinyl ethers will undergo claisen rearrangement.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c573226e-756d-4116-93a4-46925ab0cd37.png)