AP art history ID notes
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
188 Terms

Jade cong. Liangzhu, China. 3300–2200 B.C.E. Carved jade.

Running horned woman. Tassili n’Ajjer, Algeria. 6000–4000 B.C.E. Pigment on rock.

Anthropomorphic stele. Arabian Peninsula. Fourth millennium B.C.E. Sandstone.
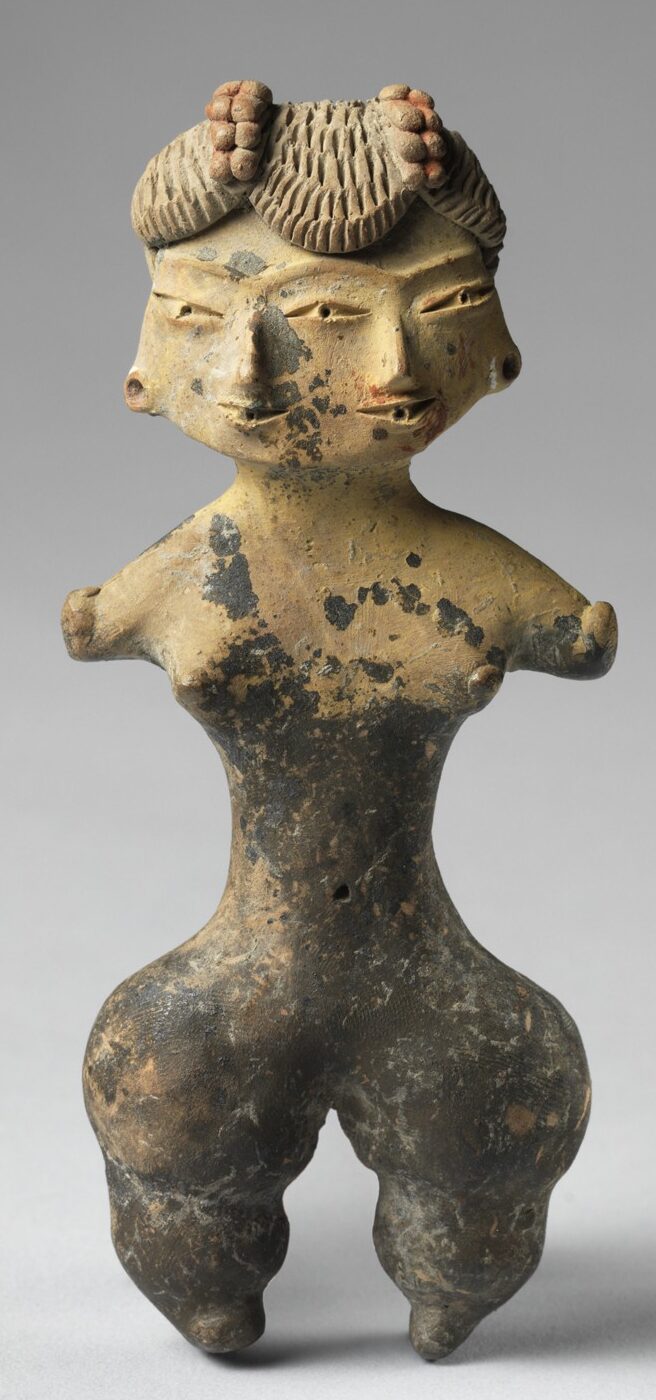

Tlatilco female figurine. Central Mexico, site of Tlatilco. 1200–900 B.C.E. Ceramic.

Terra cotta fragment. Lapita. Solomon Islands, Reef Islands. 1000 B.C.E. Terra cotta (incised).
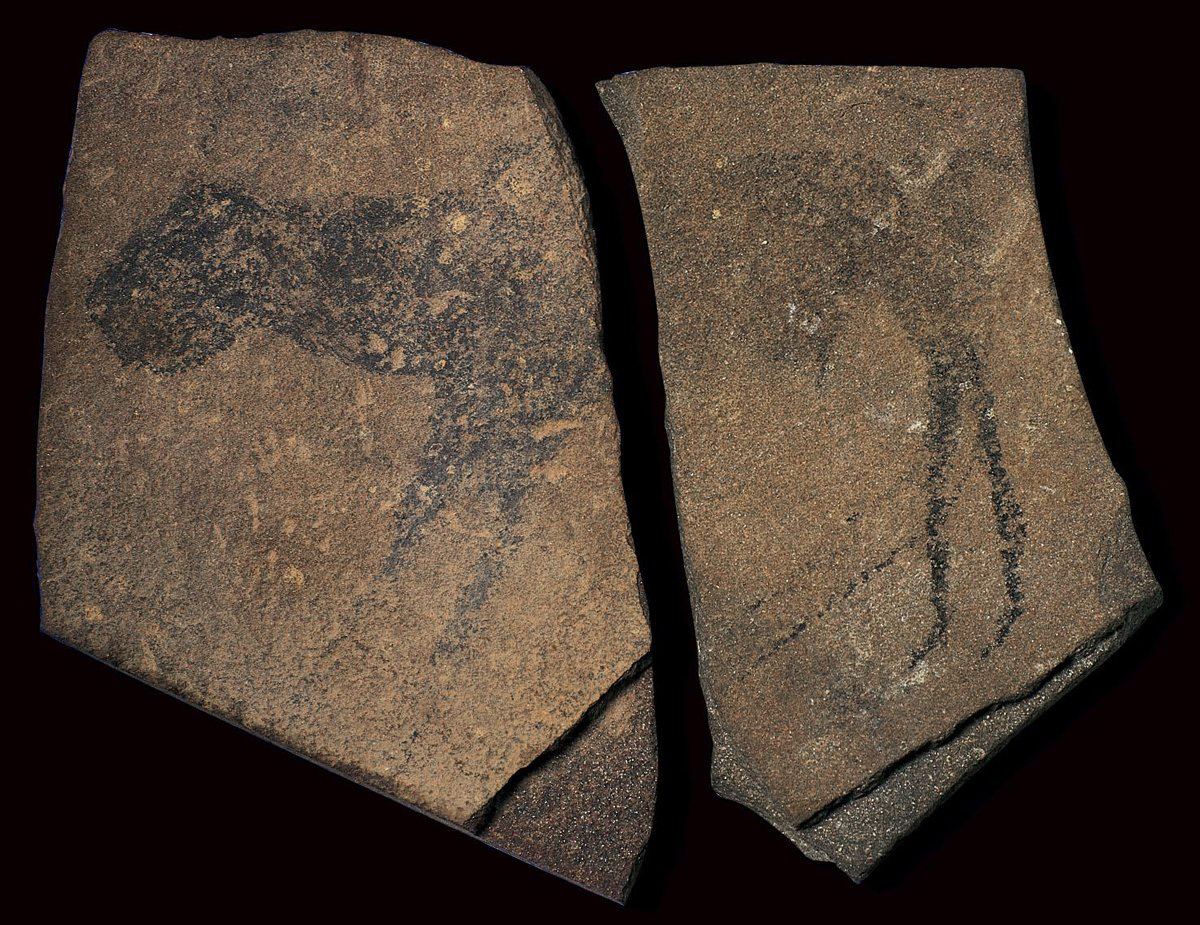

Apollo 11 stones. Nambia, c. 25,500-23,300 B.C.E. Charcoal on stone

Great Hall of the Bulls. Lascaux, France. Paleolithic Europe. 15,000-13,000 B.C.E. Rock painting.

Beaker with ibex motifs. Susa, Iran. 4200–3500 B.C.E. Painted terra cotta.

Camelid sacrum in the shape of a canine. Tequixquiac, central Mexico. 14,000-7,000 B.C.E. Bone.
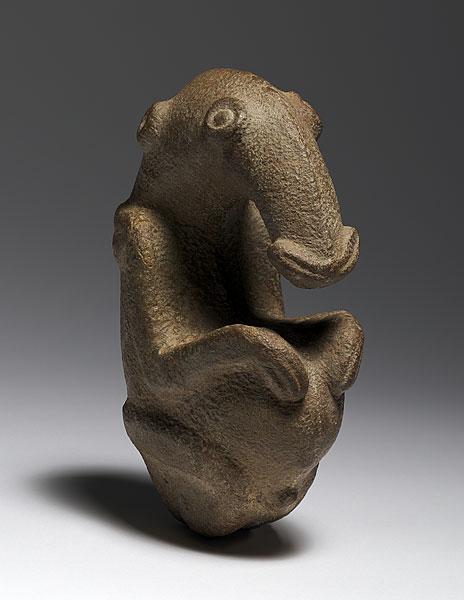

The Ambum Stone. Ambum Valley, Enga Province, Papua New Guinea. c. 1500 B.C.E. Greywacke.
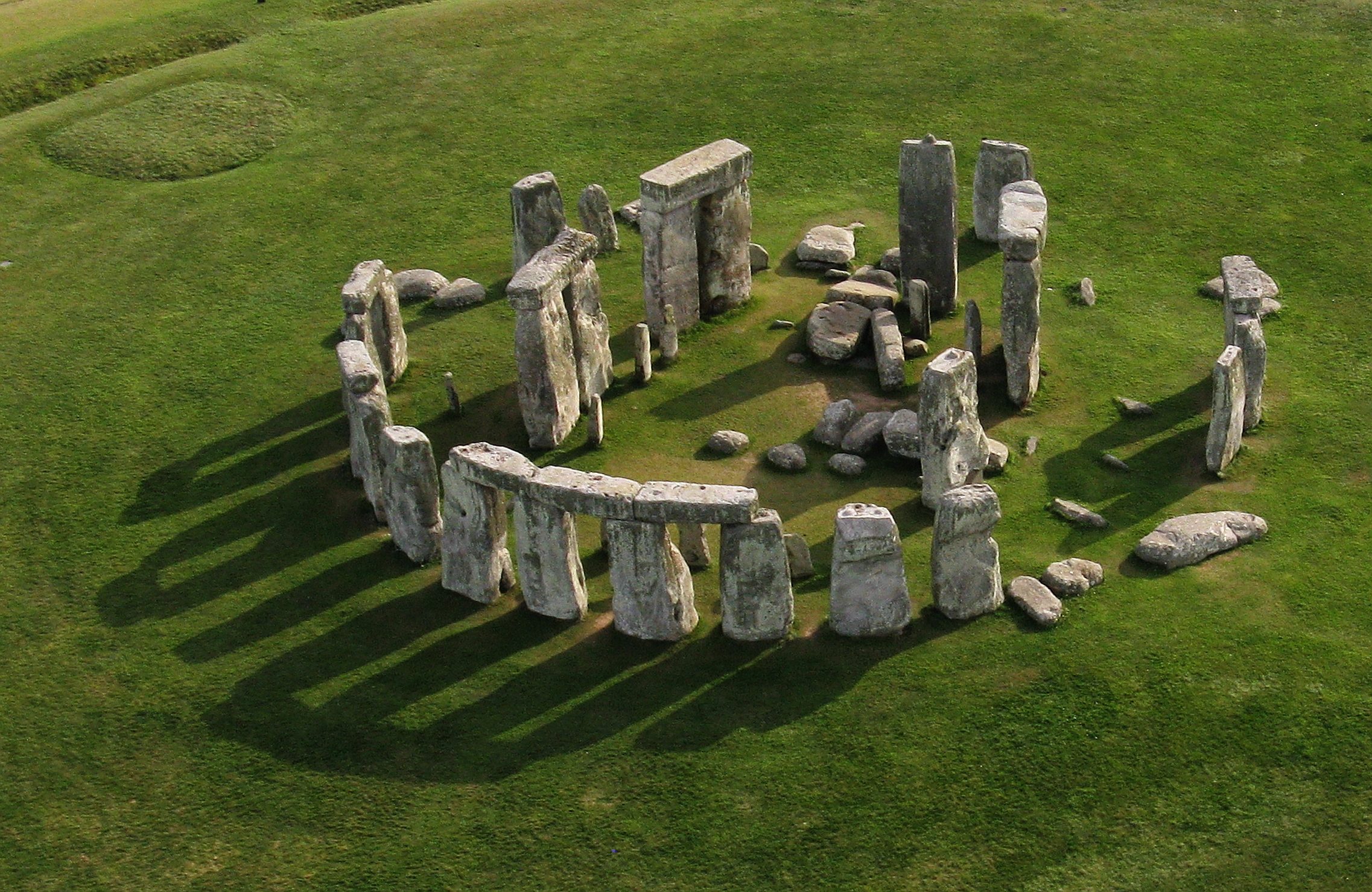

Stonehenge. Wiltshire, UK. Neolithic Europe. c. 2500–1600 B.C.E. Sandstone.
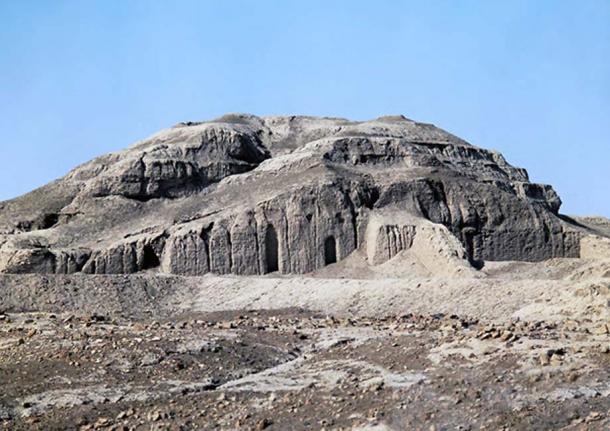

White Temple and its ziggurat. Uruk (modern Warka, Iraq).
Sumerian. c. 3500–3000 B.C.E. Mud brick.

Statues of votive figures, from the Square Temple at Eshnunna (modern Tell Asmar, Iraq). Sumerian. c. 2700 B.C.E. Gypsum inlaid with shell and black limestone.

Lamassu from the citadel of Sargon II,
Dur Sharrukin (modern Khorsabad, Iraq). Neo-Assyrian. c. 720–705 B.C.E. Alabaster.

Audience Hall (apadana) of Darius and Xerxes. Persepolis, Iran. c. 520-465 B.C.E. Limestone.
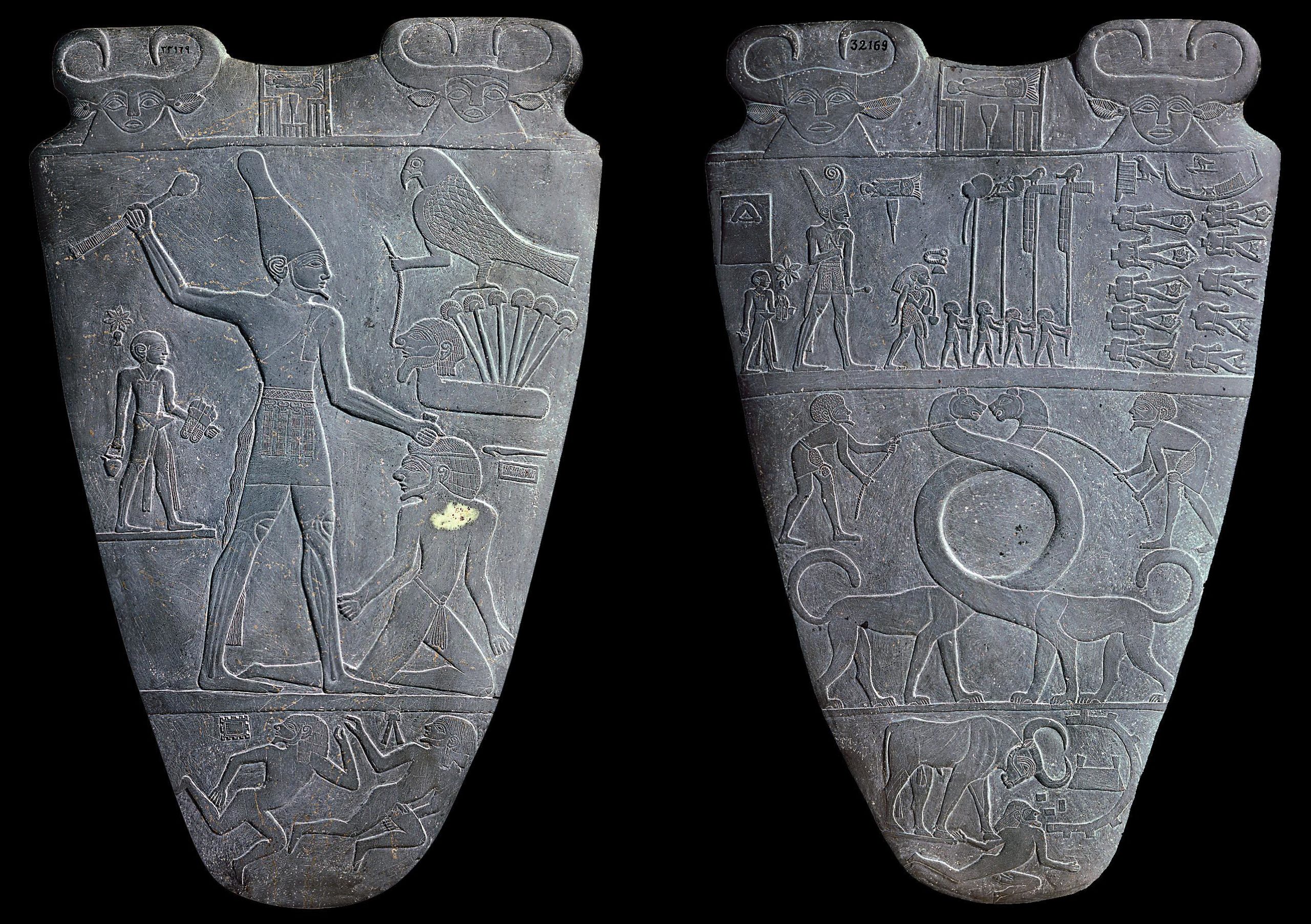

Palette of King Narmer, from Hierakonpolis, Egypt, Predynastic, c. 3000–2920 B.C.E., slate

Seated Scribe, c. 2500 B.C.E., c. 4th Dynasty, Old Kingdom, painted limestone with rock crystal, magnesite, and copper/arsenic inlay for the eyes and wood for the nipples, found in Saqqara
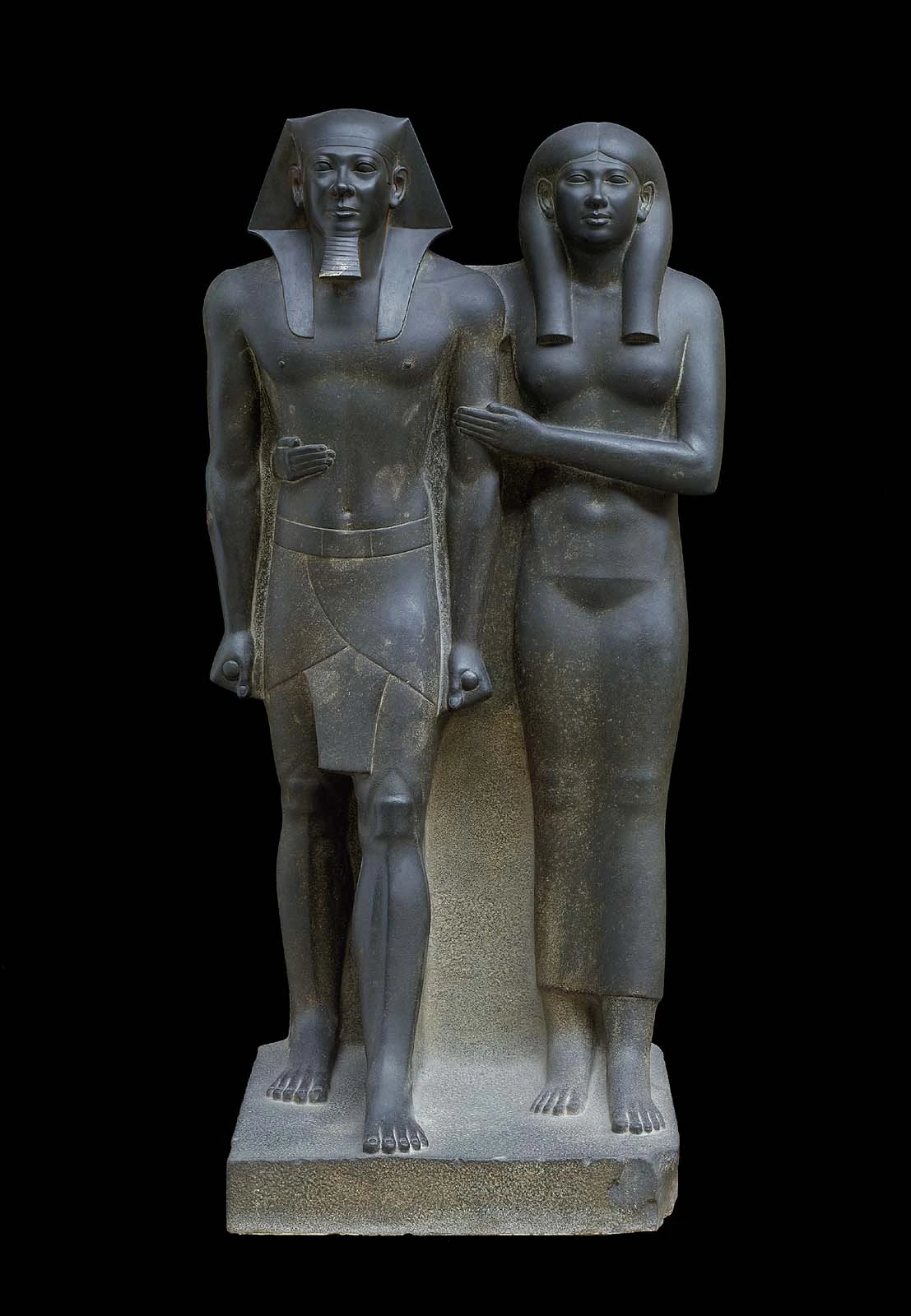

King Menkaure (Mycerinus) and queen, 2490–2472 B.C.E., greywacke

Mortuary Temple and Large Kneeling Statue of Hatshepsut, Near Luxor, Egypt. New Kingdom, 18th Dynasty. c. 1473–1458 BCE. Sandstone, partially carved into a rock cliff, and red granite.

House Altar depicting Akhenaten, Nefertiti and Three of their Daughters, c. 1350 B.C.E. (New Kingdom, Amarna period, 18th dynasty), limestone

Law Code Stele of King Hammurabi, basalt, Babylonian, 1792–1750 B.C.E.
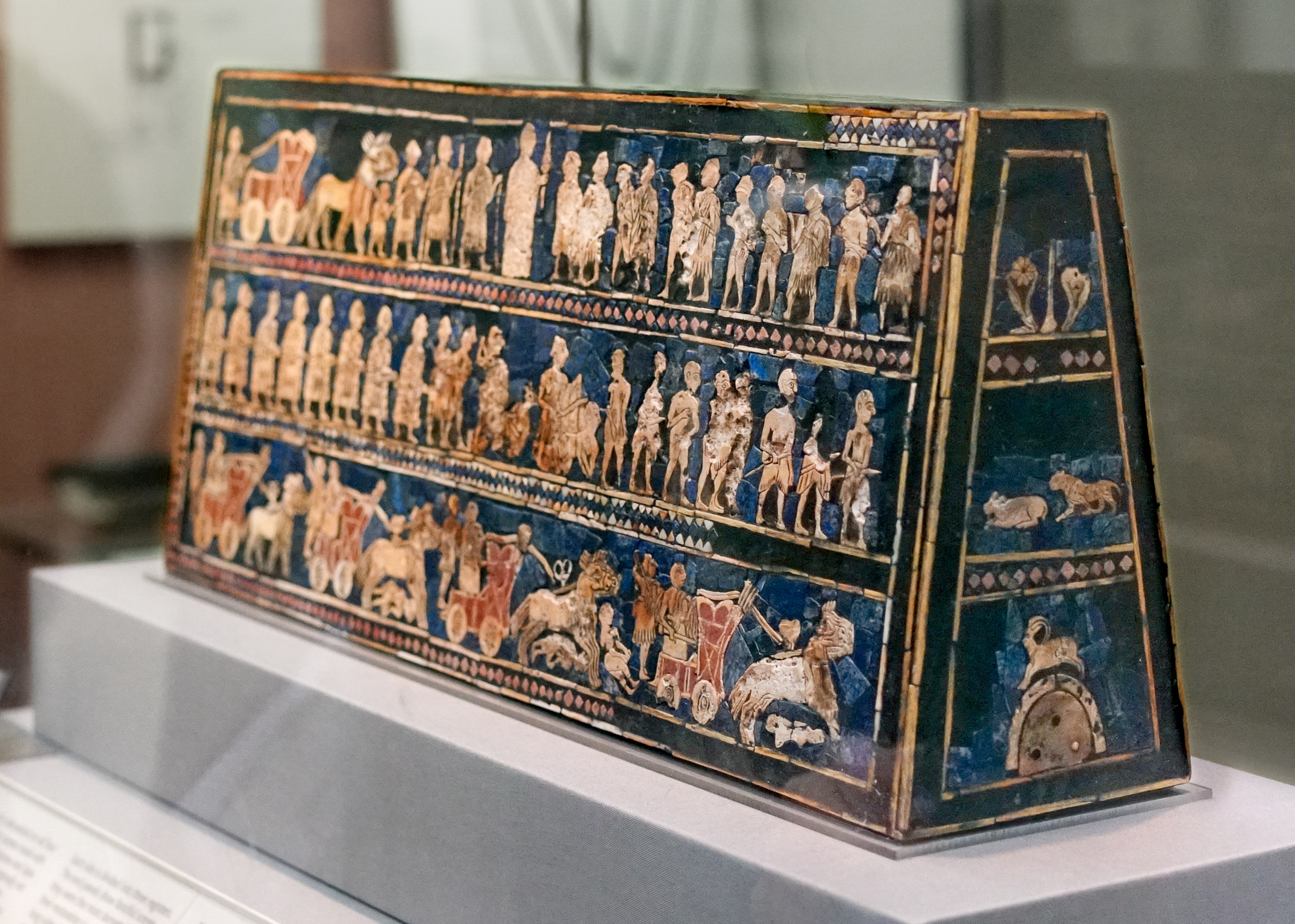

Standard of Ur from the Royal Tombs at Ur (modern Tell el-Muqayyar, Iraq). Sumerian. c. 2600–2400 B.C.E. Wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli, and red limestone.
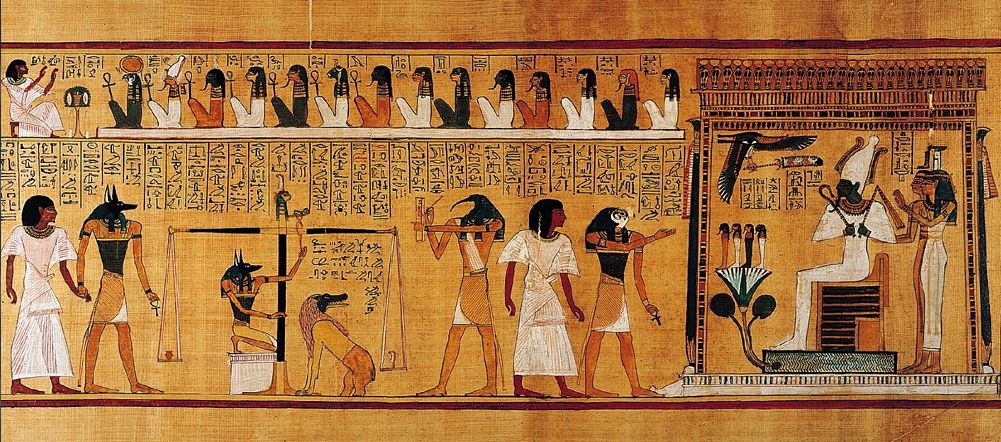

Last Judgement of Hunefer, from his tomb (page from the Book of the Dead)/ Hunefer’s Judgement in the presence of Osiris, Book of the Dead of Hunefer, c. 1275 B.C.E. (19th Dynasty, New Kingdom, Thebes, Egypt), papyrus

Tutankhamun’s tomb, innermost coffin, New Kingdom, 18th Dynasty, c. 1323 B.C.E., gold with inlay of enamel and semiprecious stones
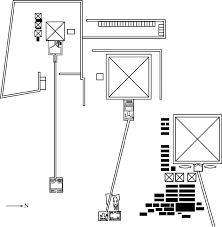
Great Pyramids (Menkaura, Khafre, Khufu) and Great Sphinx. Giza, Egypt. Old Kingdom, Fourth Dynasty. c. 2550–2490 BCE. Cut limestone.
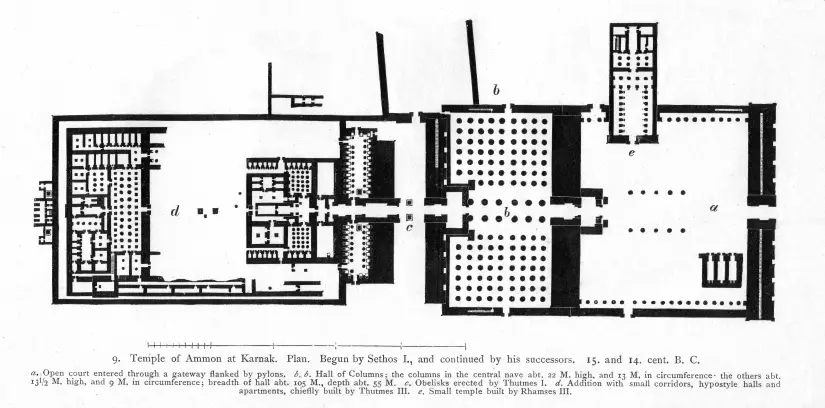
Temple of Amun-Re and Hypostyle Hall. Karnak, near Luxor, Egypt. New Kingdom, 18th and 19th Dynasties. Temple: c. 1550 BCE; hall: c. 1250 BCE. Cut sandstone and mud brick.
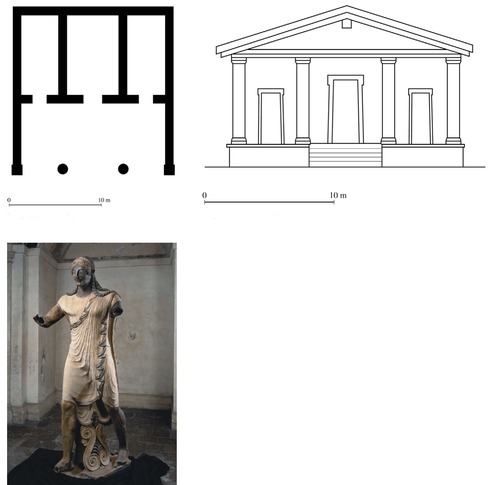


Temple of Minerva and sculpture of apollo. (Veii, near Rome, Italy.) Master sculptor Vulca. c. 510-500 BCE. Original temple of wood, mudbrick, or tufa (volcanic rock)
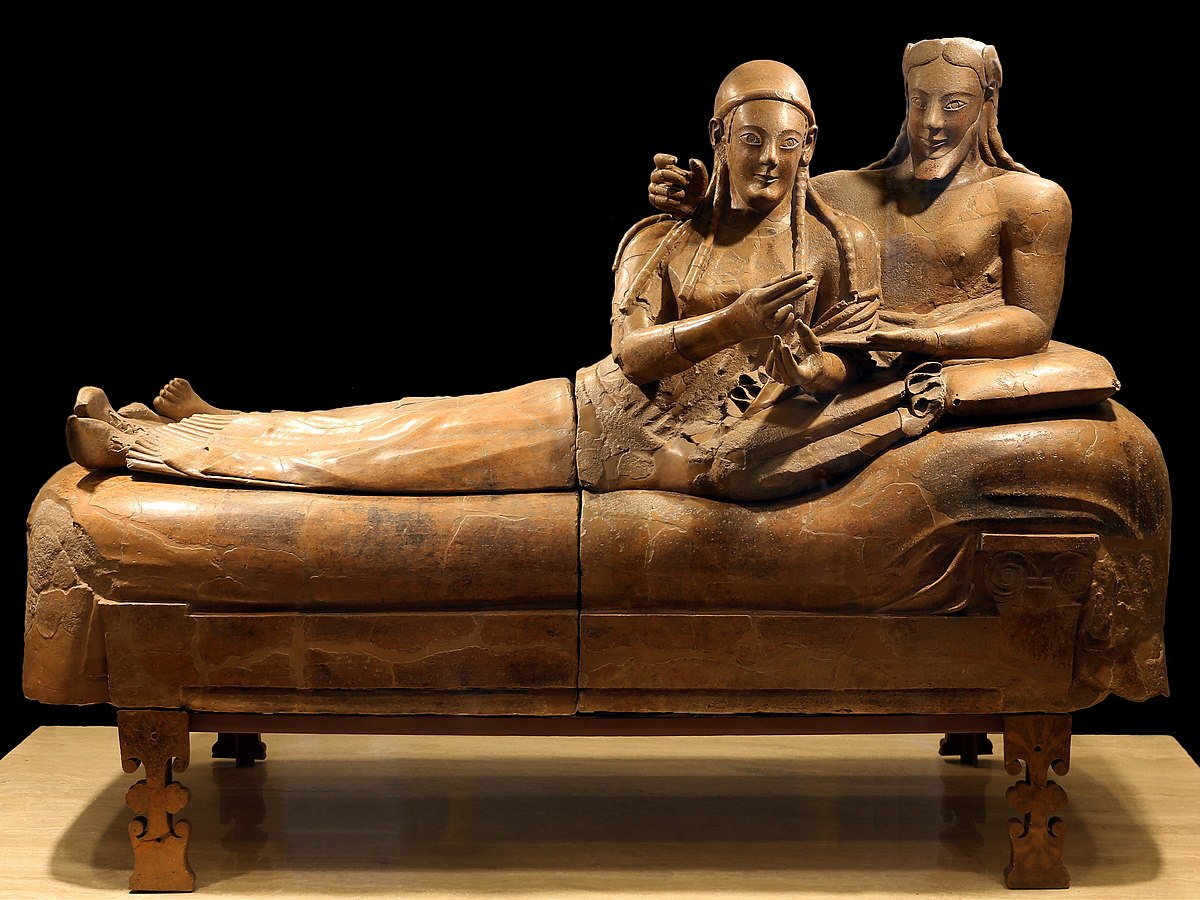

Sarcophagus of the Spouses. Etruscan. c. 520 BCE. Terra cotta.
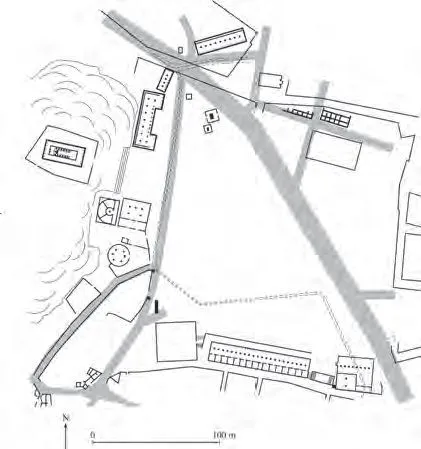
Athenian Agora, Reconstructed. Archaic - Hellenistic Greek. 600 B.C.E. – 150 C.E.

Tomb of the Triclinium Tarquinia, Italy. Etruscan. c. 480–470 BCE. Tufa and fresco
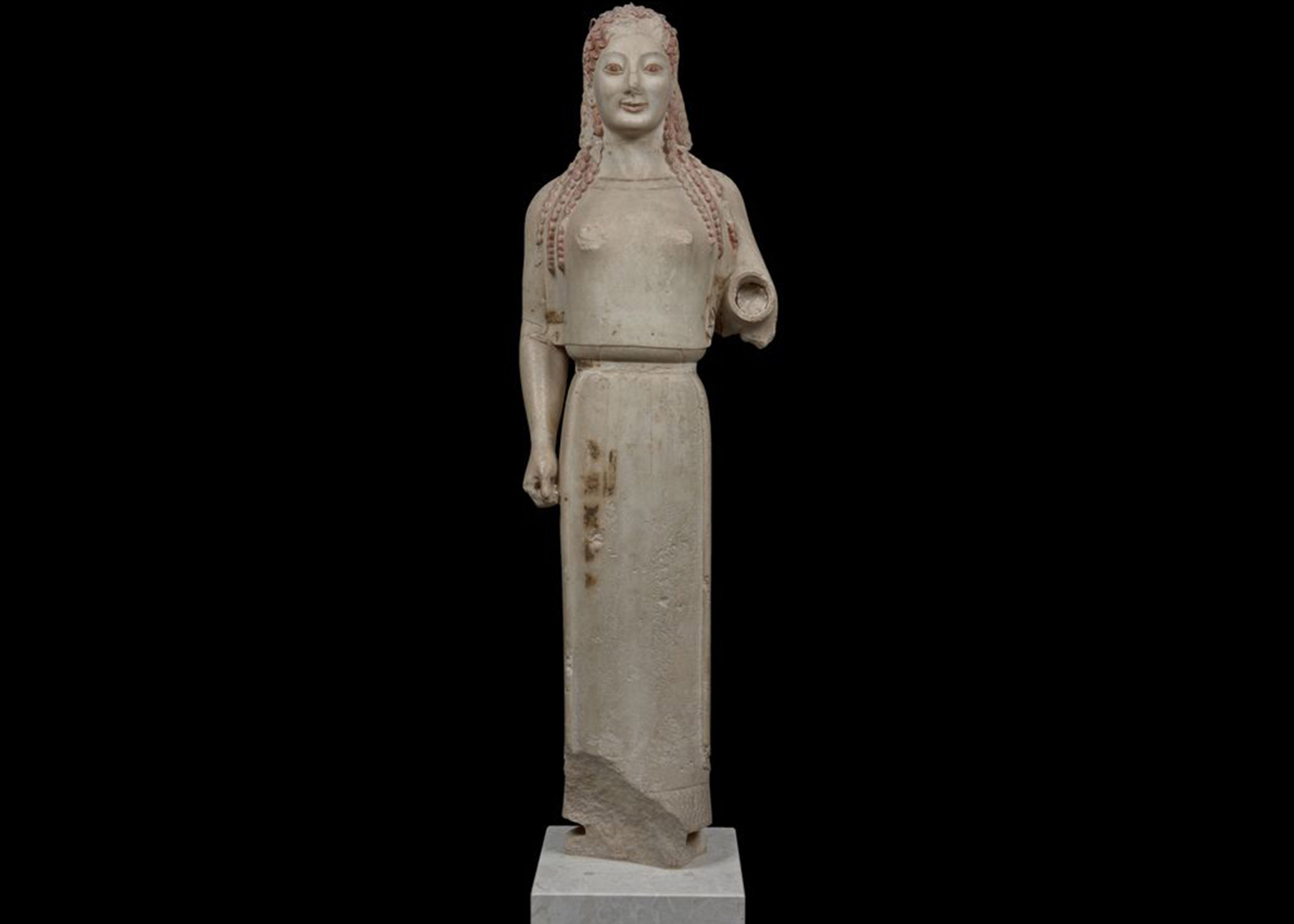

Peplos Kore from the Acropolis. Archaic Greek. c. 530 BCE. Marble, painted details.
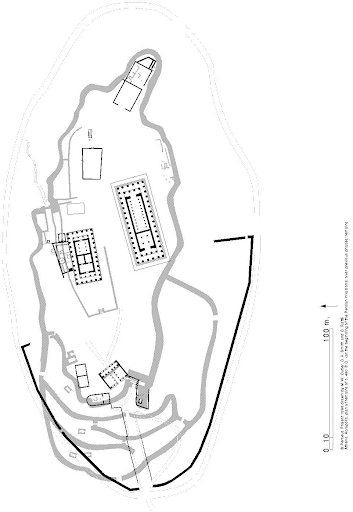
Acropolis Plan. Athens, Greece. Iktinos and Kallikrates. c. 447-410 BCE. Marble. (Parthenon, temple of Athena Parthenos, Temple of Athena Nike, etc…)

Plaque of the Ergastines, Parthenon. Acropolis. Athens, Greece. Iktinos and Kallikrates. c. 447-410 BCE. Marble.

Helios, horses, and Dionysus (Heracles?), Parthenon. Acropolis. Athens, Greece. Iktinos and Kallikrates. c. 447-410 BCE. Marble.
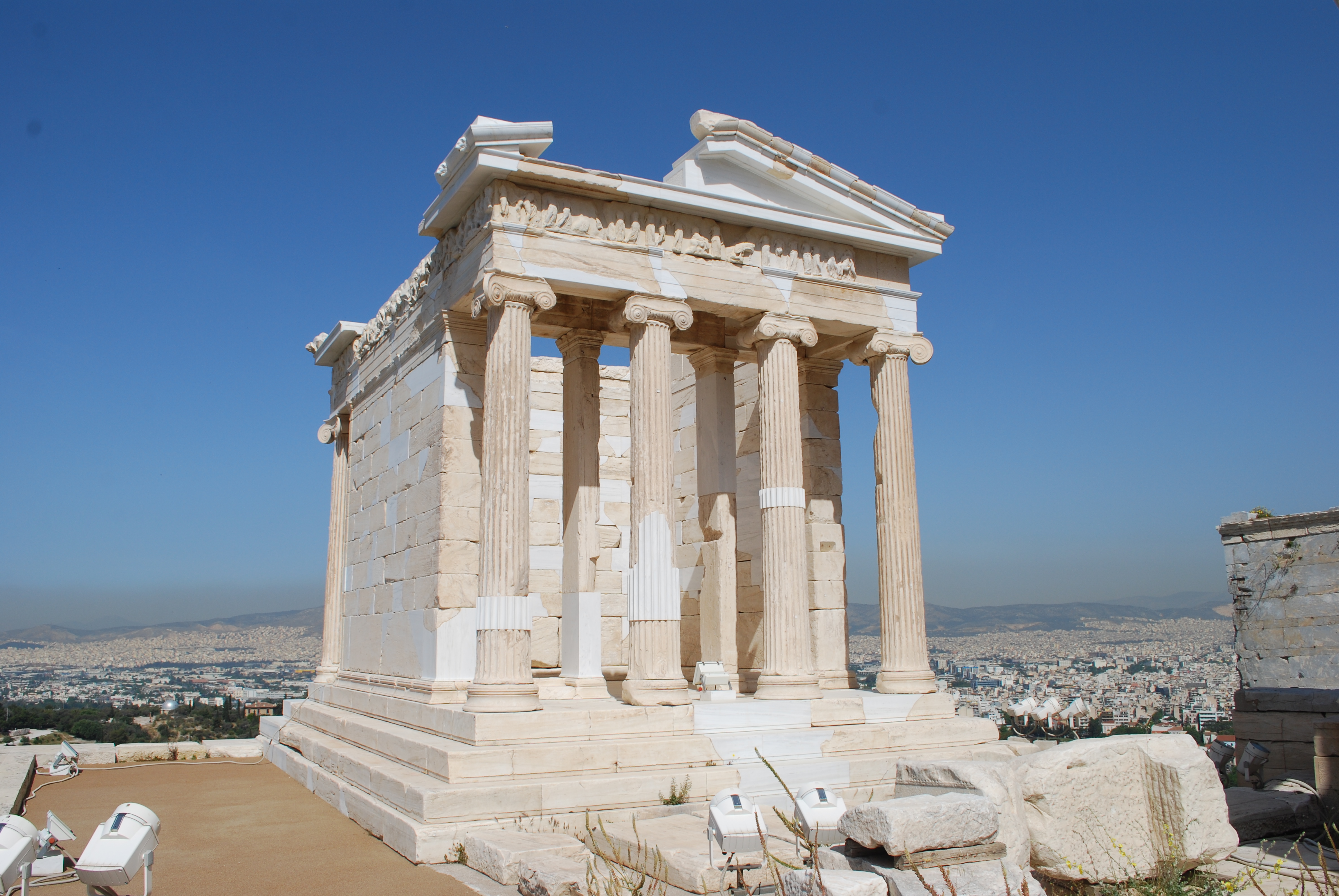

Temple of Athena Nike. Acropolis. Athens, Greece. Iktinos and Kallikrates. c. 447-410 BCE. Marble. (plus photo of Nike adjusting her sandal)


Parthenon (Acropolis), Artist/Culture: lktinos and Kallikrates (architects of the Parthenon, the Temple of Athena Parthenos), Kallikrates (architect of Temple of Athena Nike), Phidias (sculptor)
Medium: Architecture (marble) and sculpture (marble) Date: 447 - 438 B.C.E. Creator's Origin/Location: Athens, Classical Greece.

Grave stele of Hegeso. Attributed to Kallimachos. c. 410 BCE. Marble and paint.

Anavysos Kouros. Archaic Greek. c. 530 BCE. Marble with remnants of paint
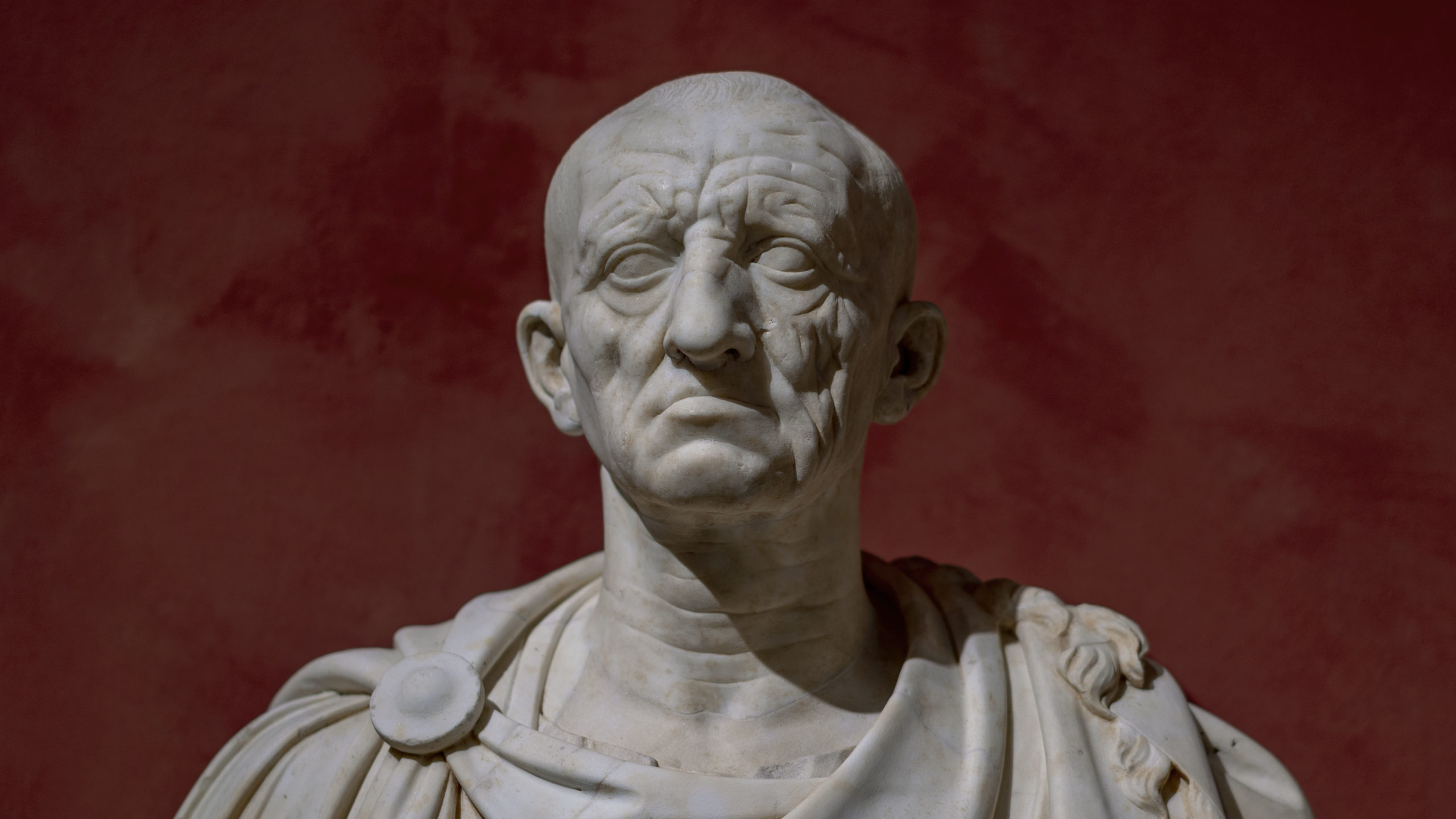

Head of a Roman patrician. Republican Roman. c. 75–50 BCE. Marble.
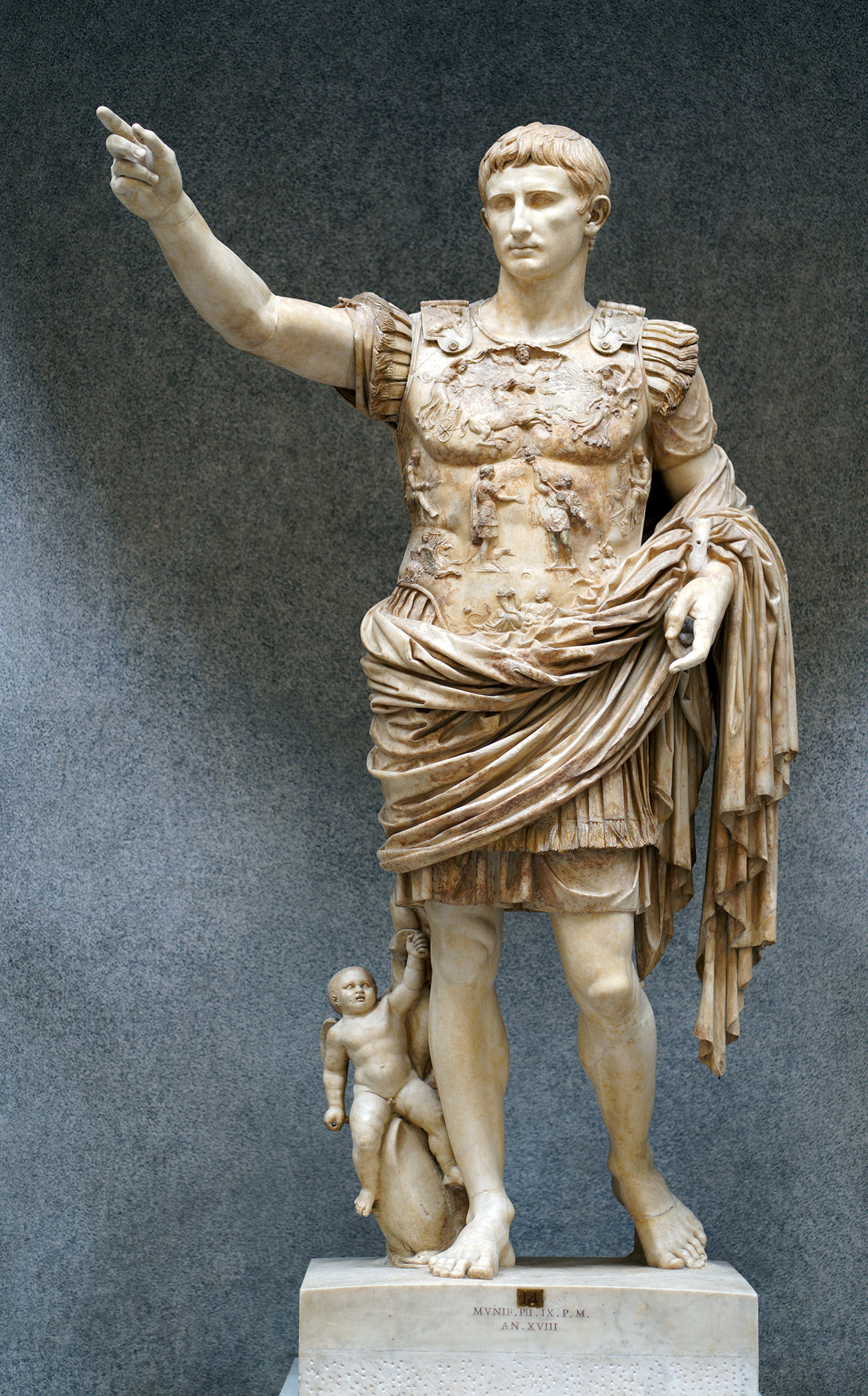

Imperial Roman.Early 1st Century C.E. , Vatican Museum, Marble - 6'8"
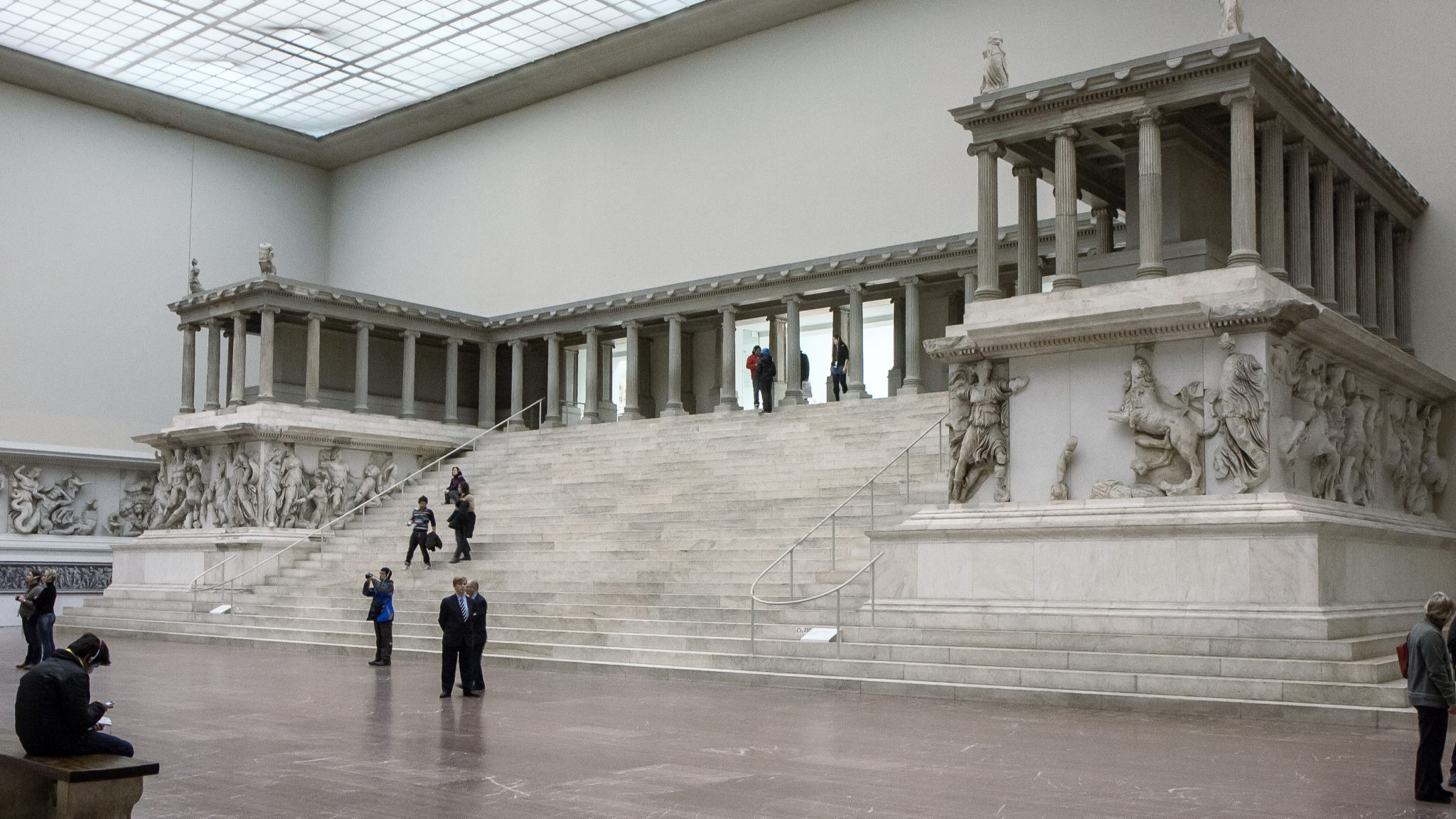

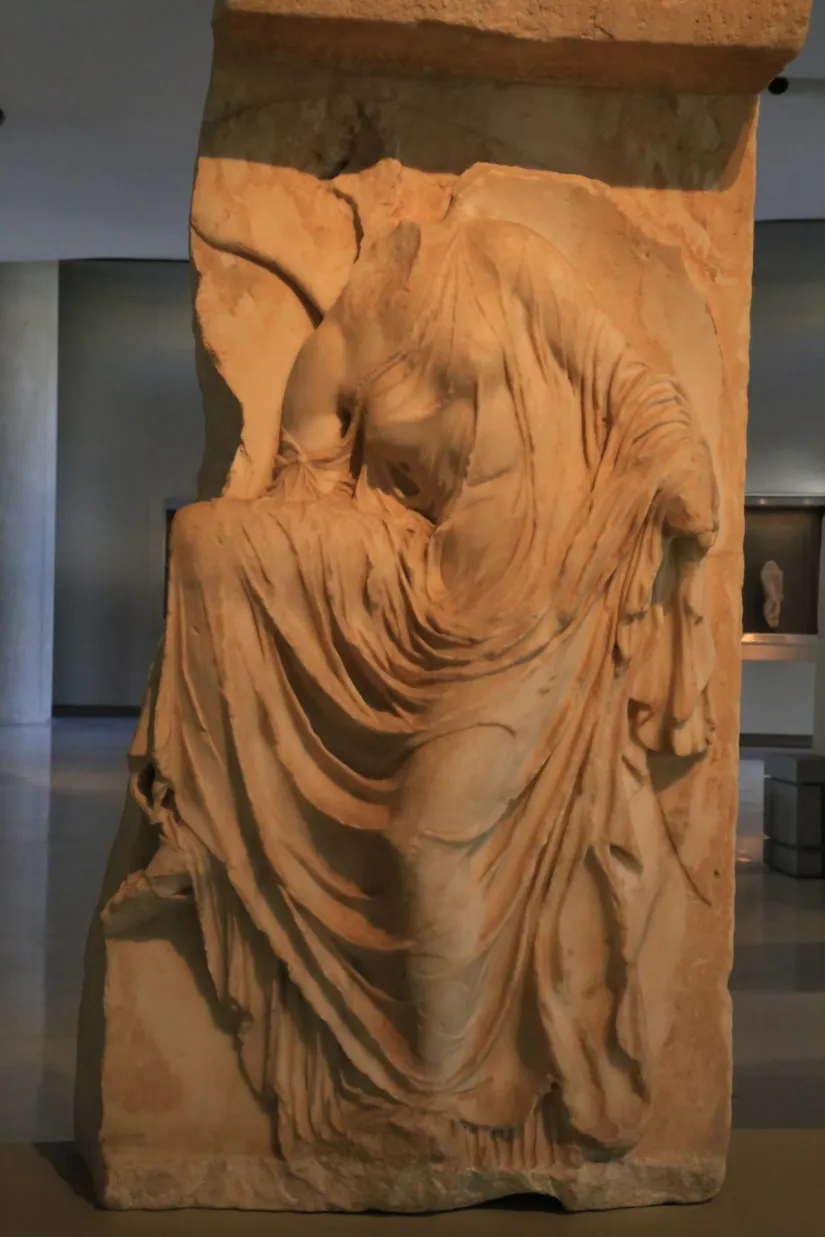
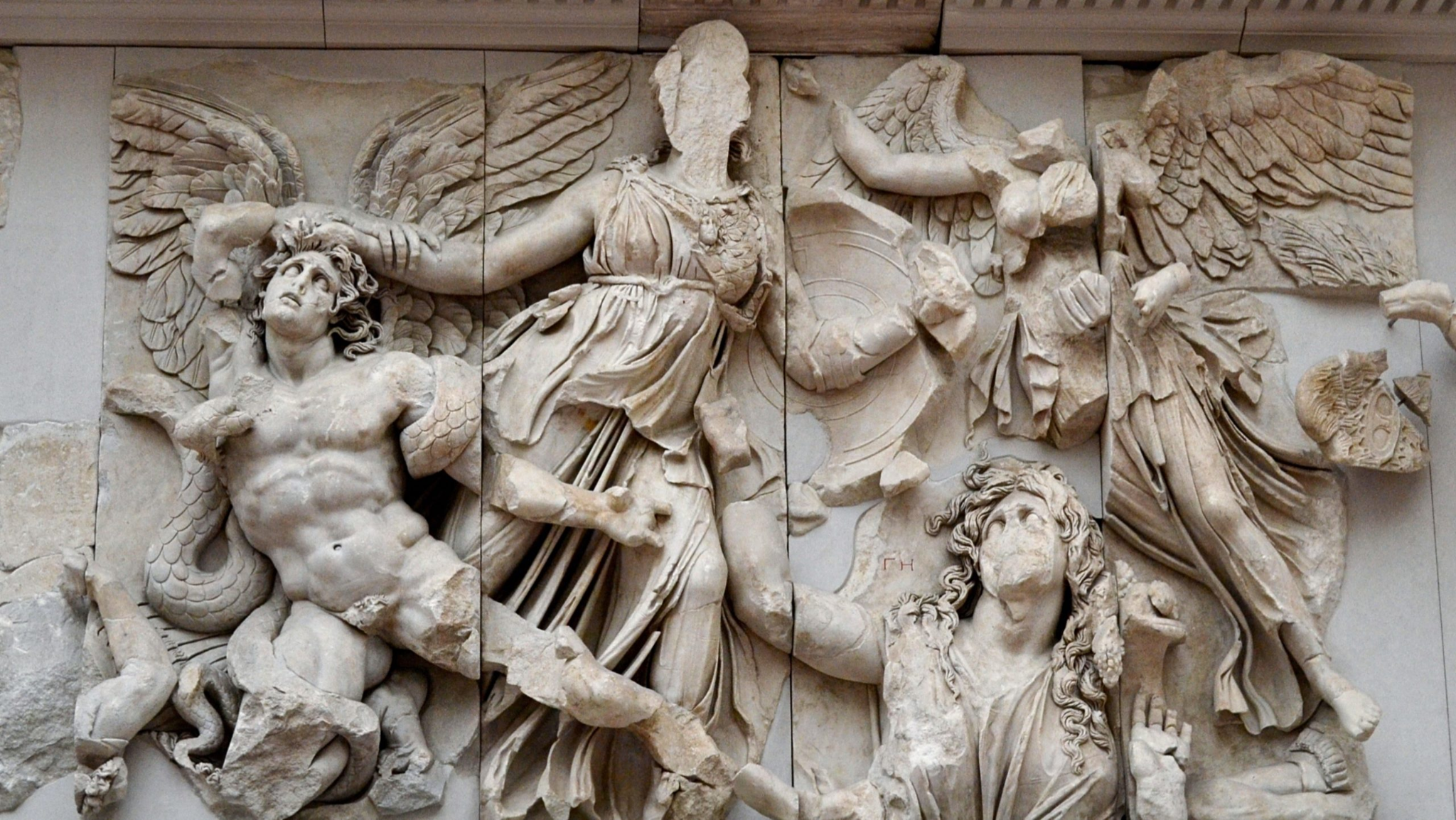
Great Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon. Asia Minor (present-day Turkey). Hellenistic Greek. c. 175 BCE. Marble (architecture and sculpture).
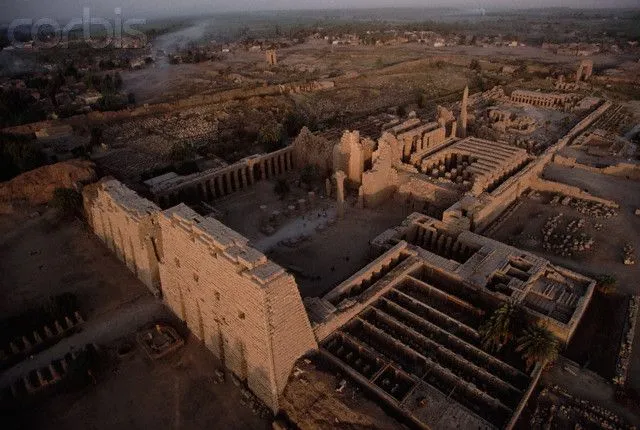


Amun-Re and hypostyle hall (3 images total)
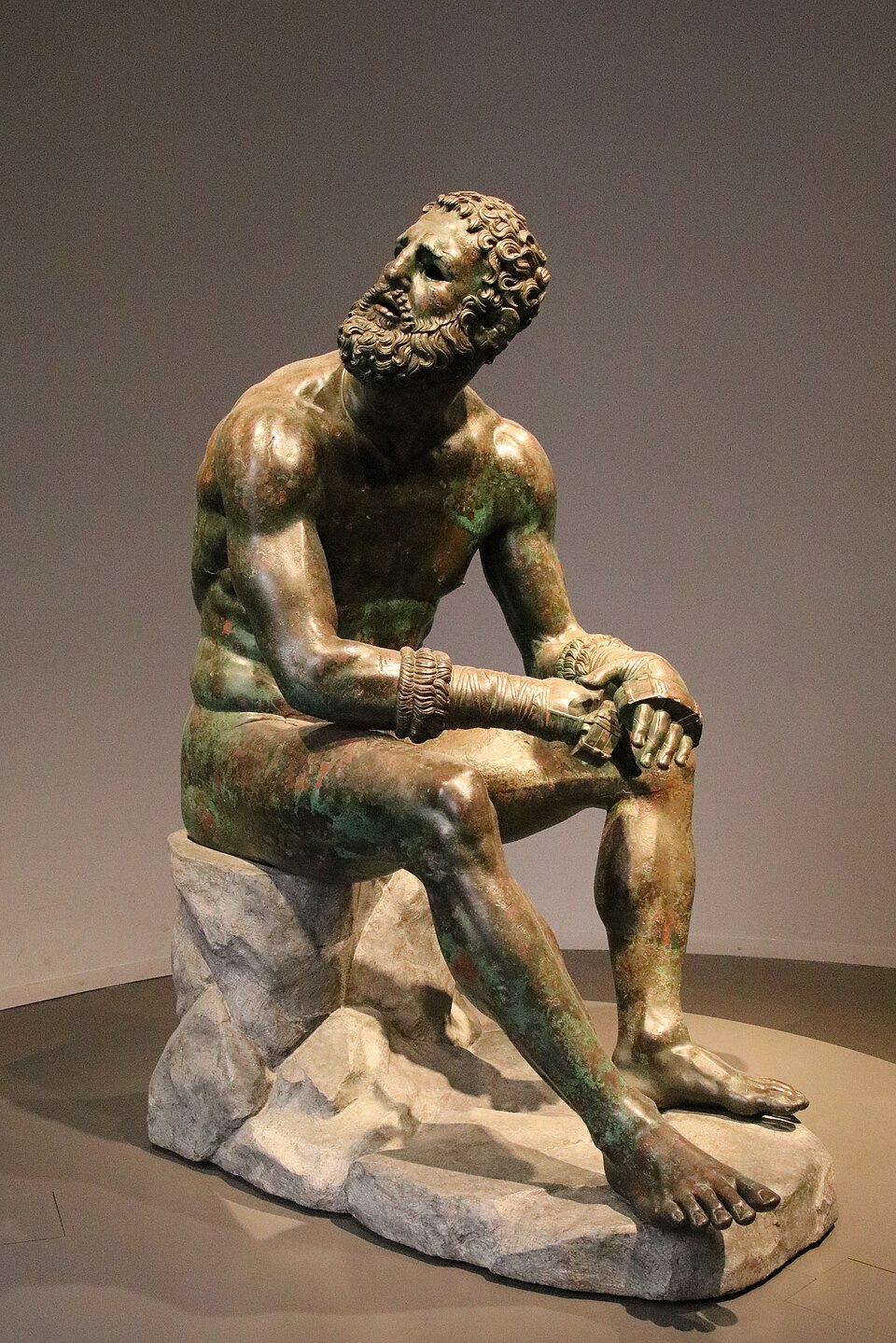

Seated boxer. Hellenistic Greek. c. 100 BCE. Bronze.
Great altar of Zeus architecture plan (three images total in this ID)
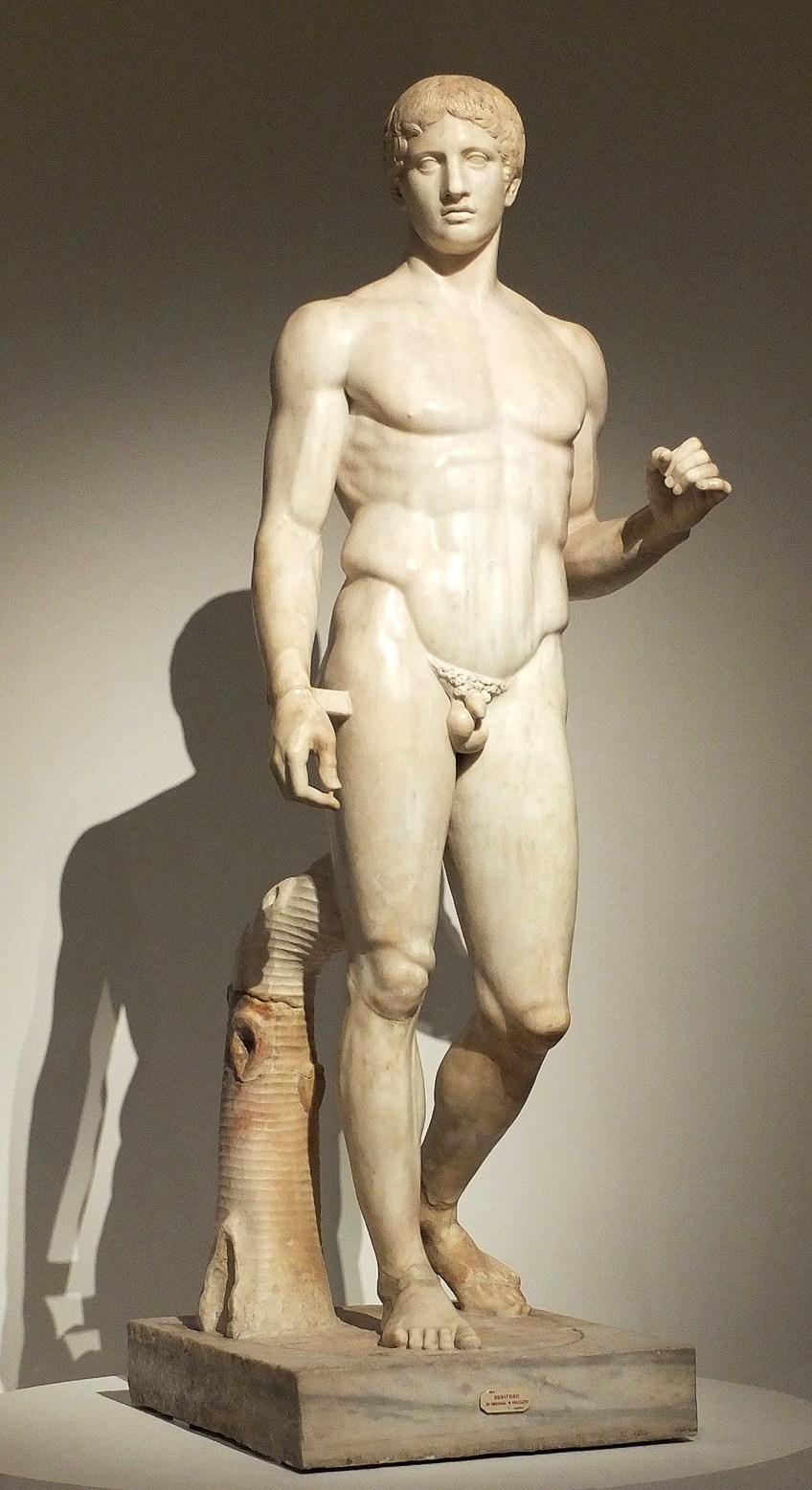

Doryphoros (Spear Bearer). Polykleitos. Original 450-440 BCE. Roman copy (marble) of a Greek original (bronze)
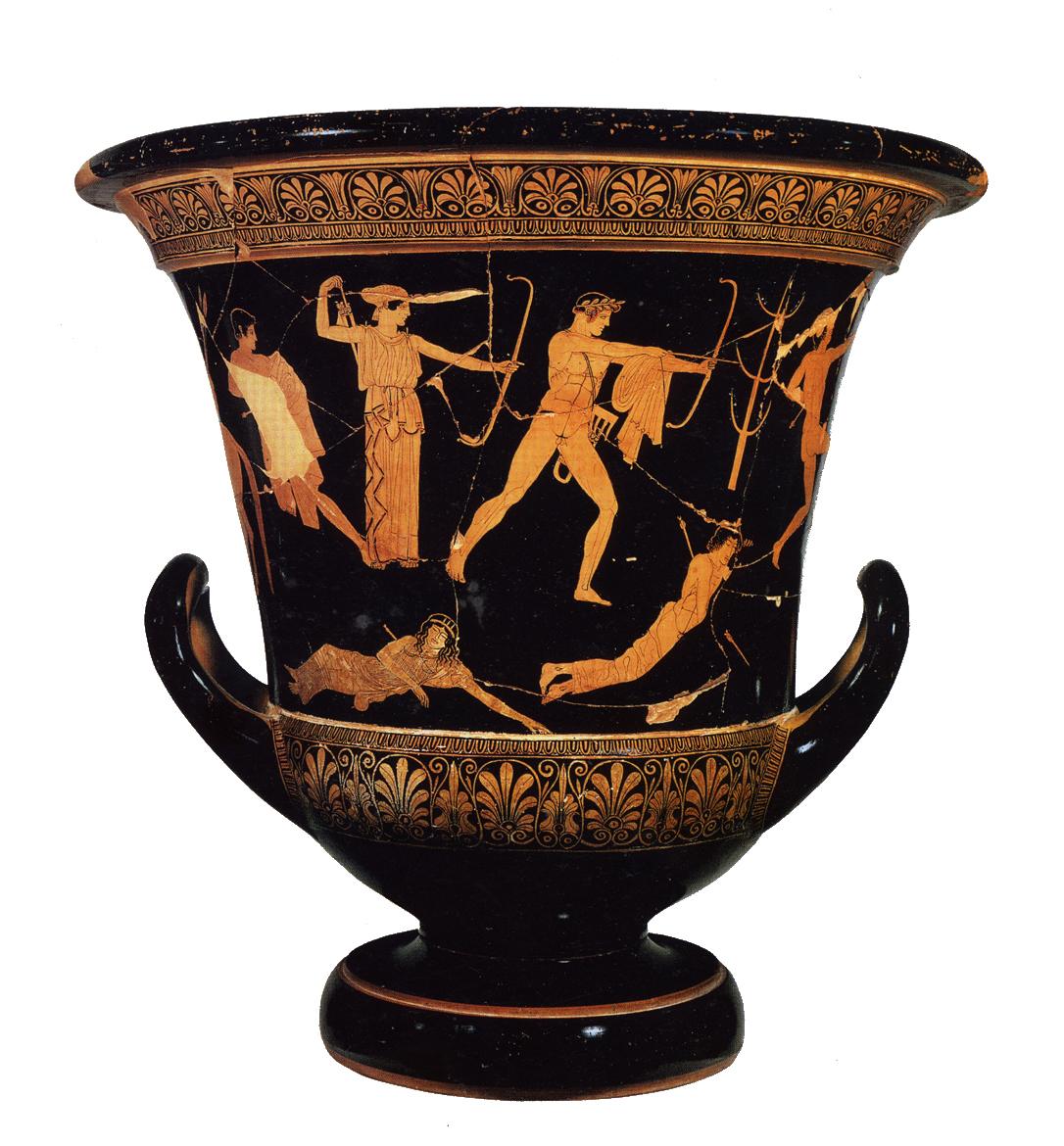

Niobides Krater, Anonymous vase painter of Classical Greece known as the Niobid Painter. c. 460-450 BCE. Clay, red-figure technique (white highlights).
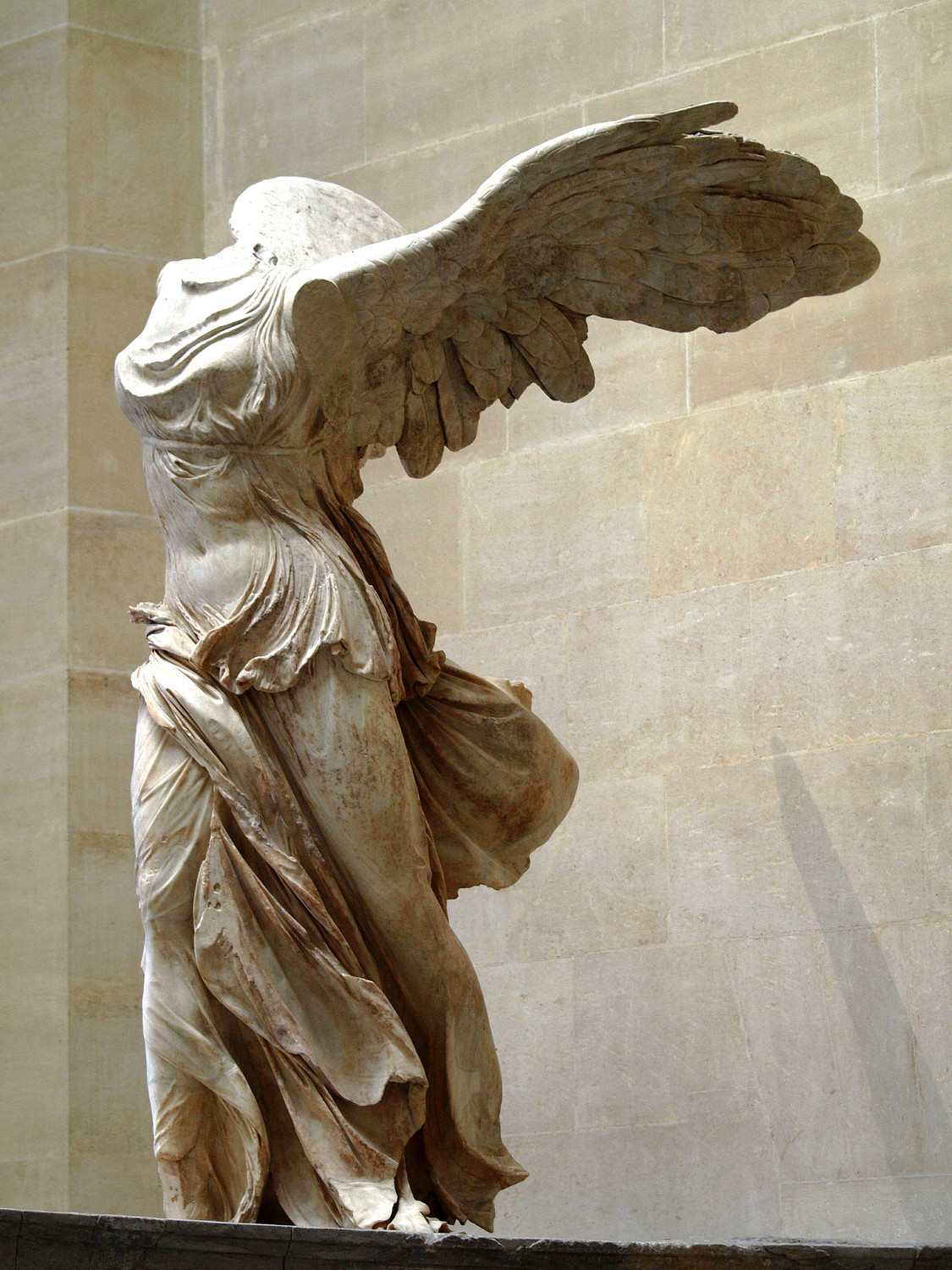

Nike of Samothrace (winged Victory), Lartos marble (ship), Parian marble (figure), c. 190 B.C.E., 3.28 meters high

Alexander Mosaic from the House of Faun, Pompeii Republican Roman. c. 100 BCE. Mosaic.
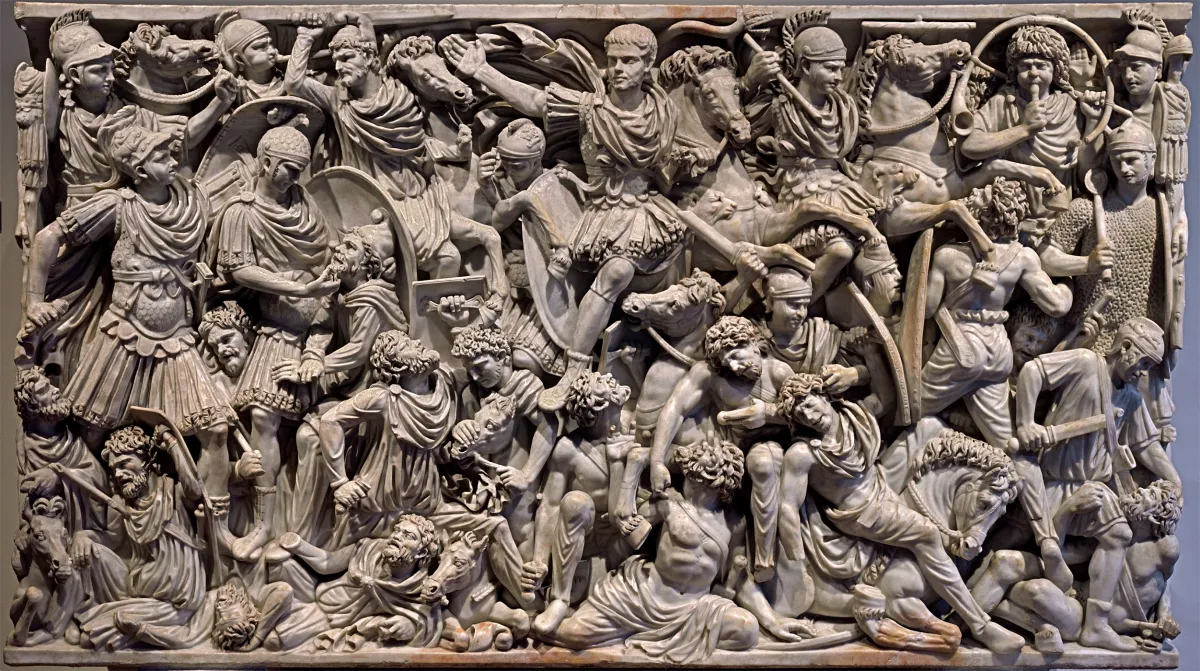

Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus. Late Imperial Roman. c. 250 CE. Marble.

Forum of Trajan. Rome, Italy. Apollodorus of Damascus. Forum and markets: 106–112 C.E.; column completed 113 C.E. Brick and concrete (architecture); marble (column).
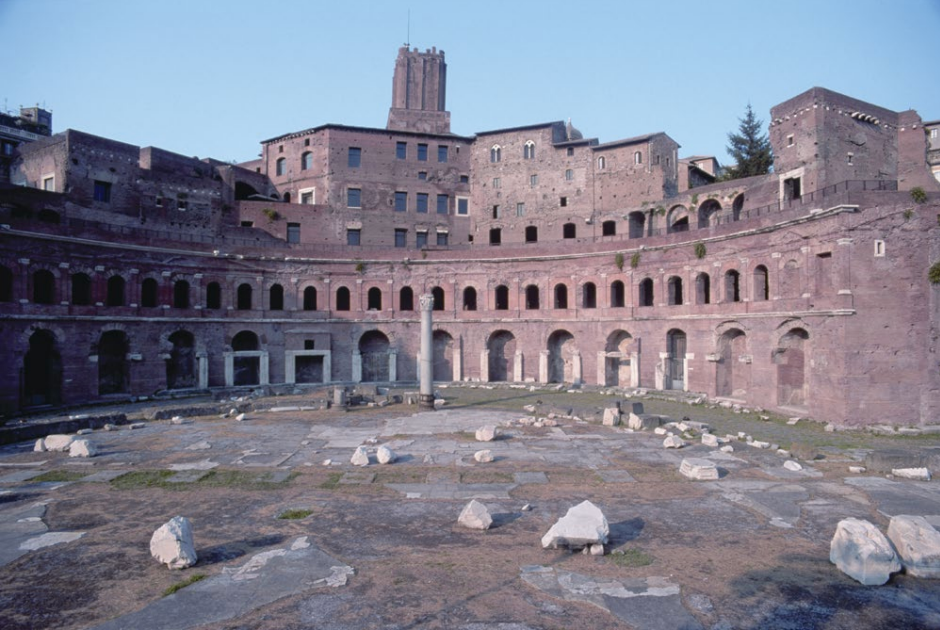


Forum of Trajan continuation

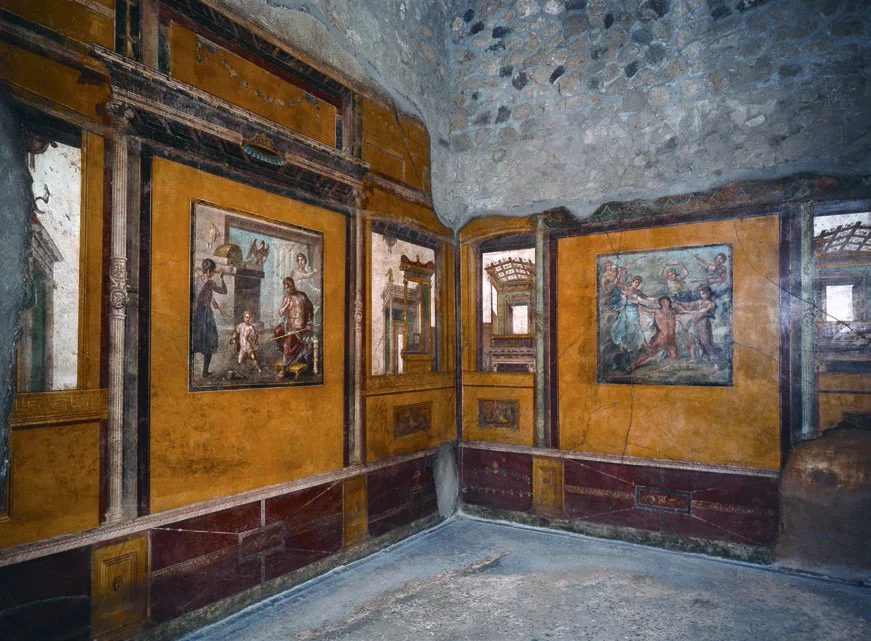
House of the Vettii. Pompeii, Italy. Imperial Roman. c. second century BCE; rebuilt c. 62–79 CE. Cut stone and fresco.
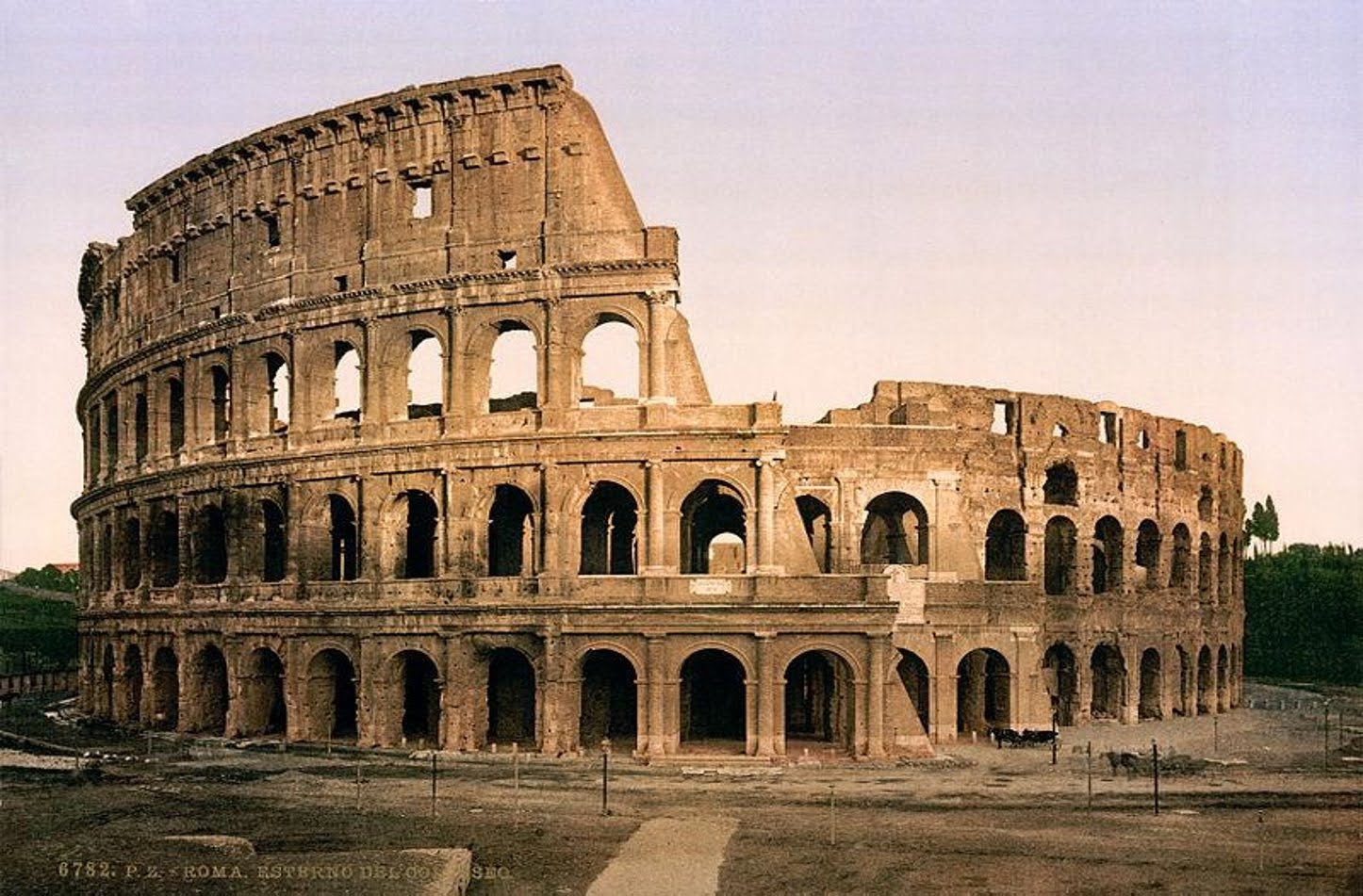


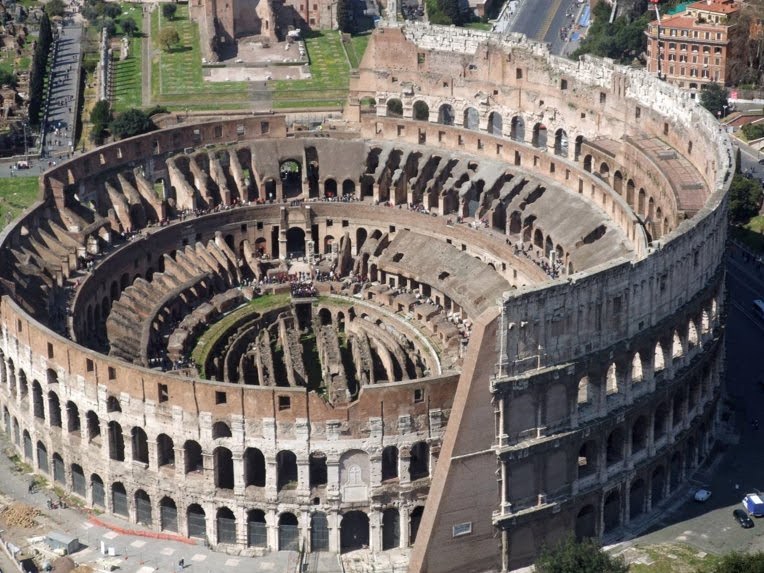
Colosseum (Flavian Amphitheater). Rome, Italy. Imperial Roman. 70–80 CE. Stone and concrete.
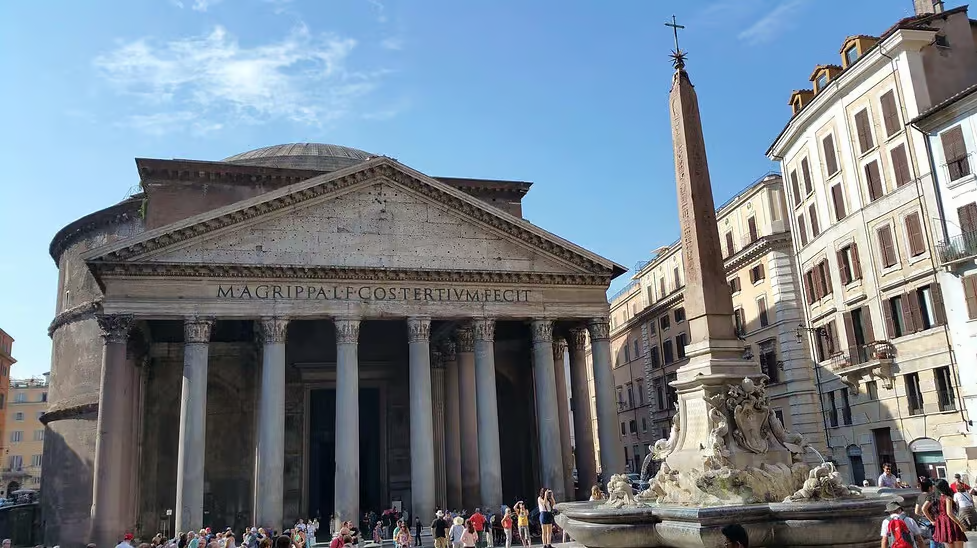


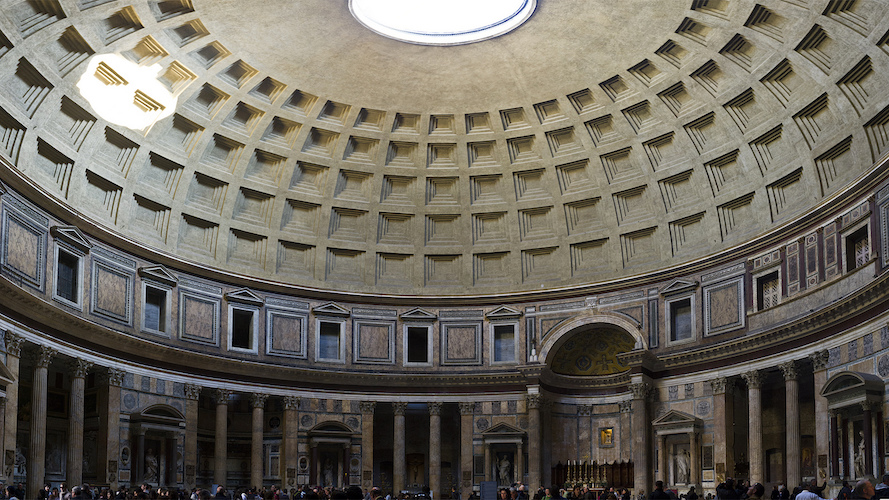
Pantheon,Built during the reign of Emperor Hadrian. Imperial Roman. 118–125 C.E. Concrete with stone facing. Dome=140 ft. in diameter
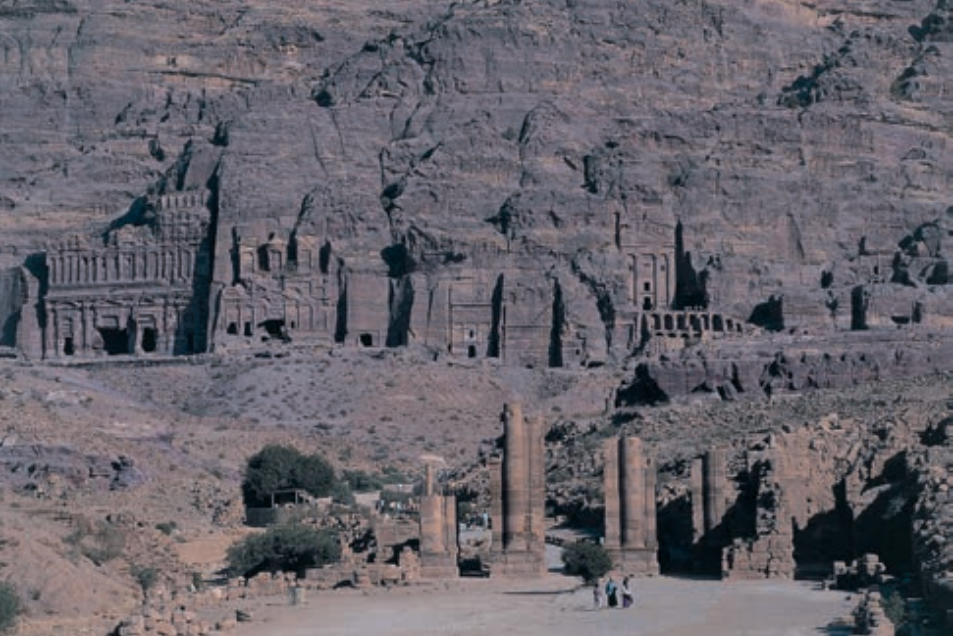


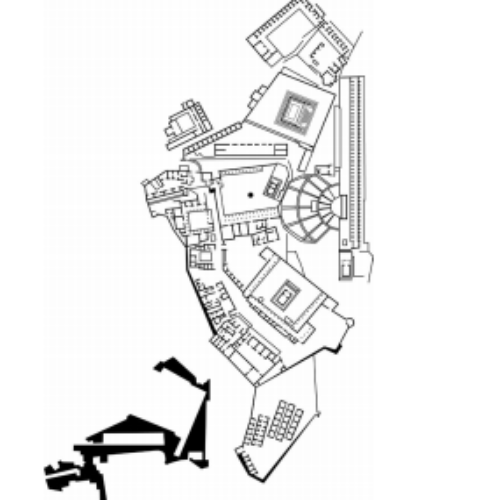
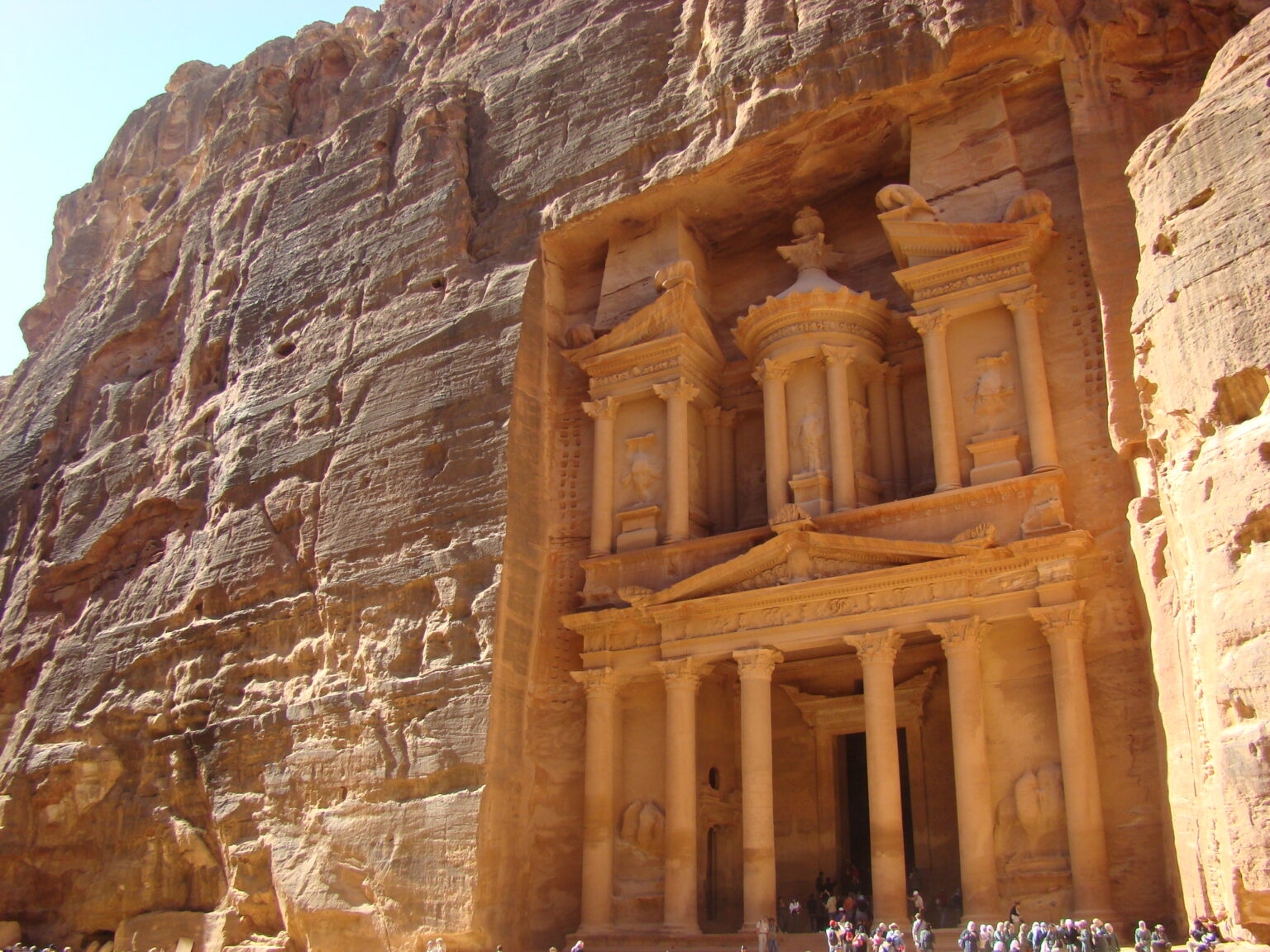
Petra, Jordan: Treasury ad Great Temple. Nabataean Ptolemaic and Roman. c. 400 B.C.E.–100 C.E. Cut rock.

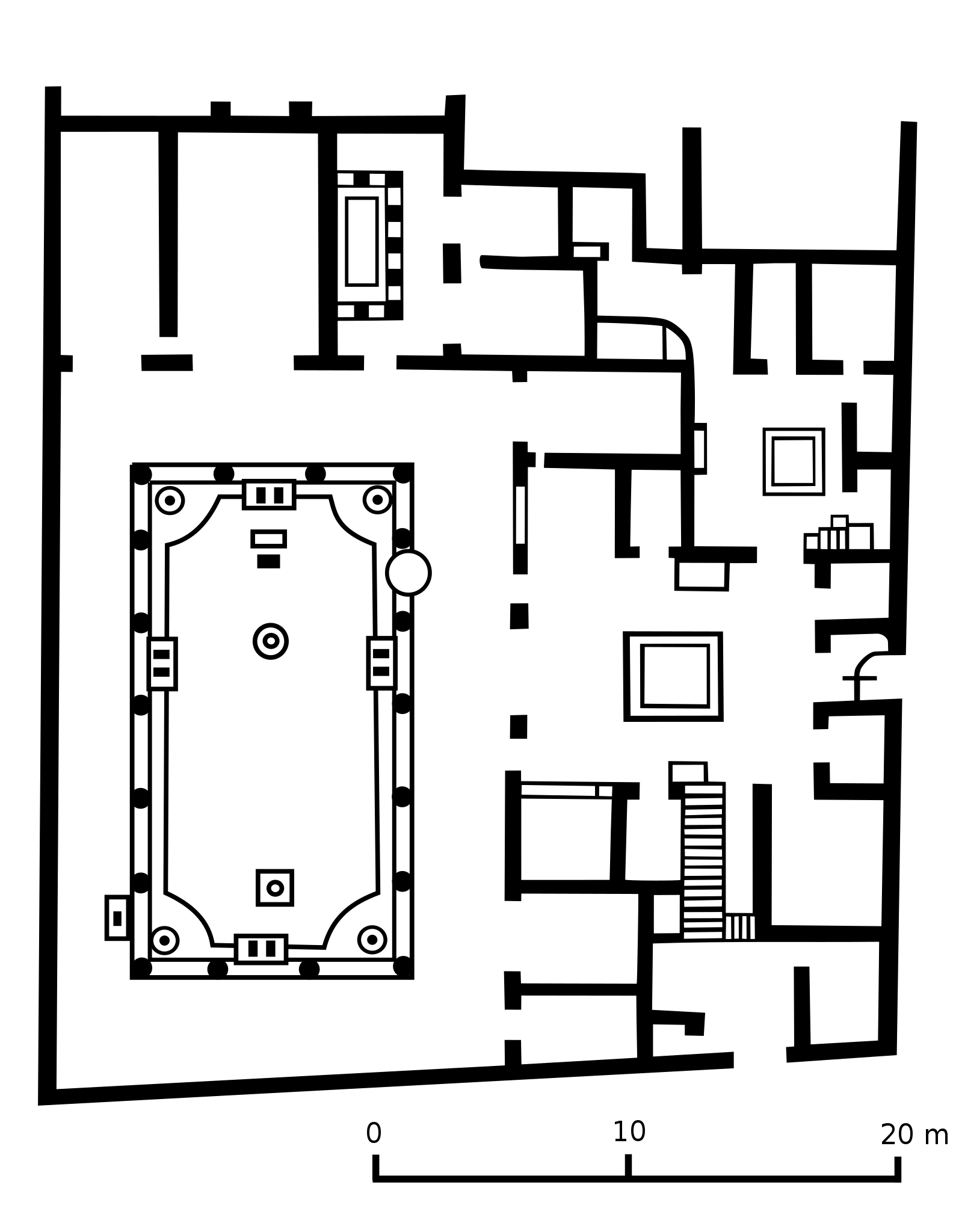
architecture plan for House of Veti
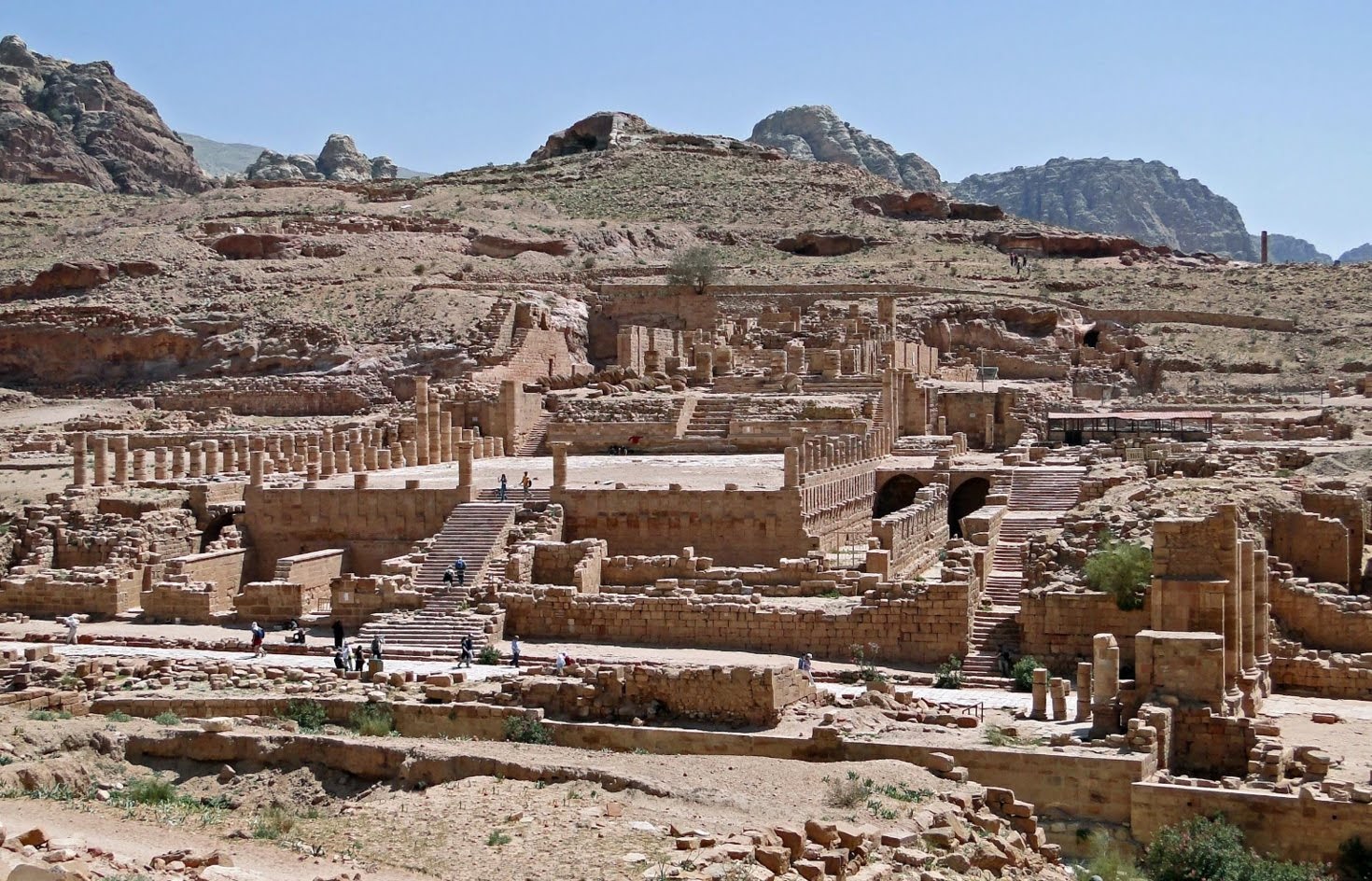

Petra, Jordan image #3

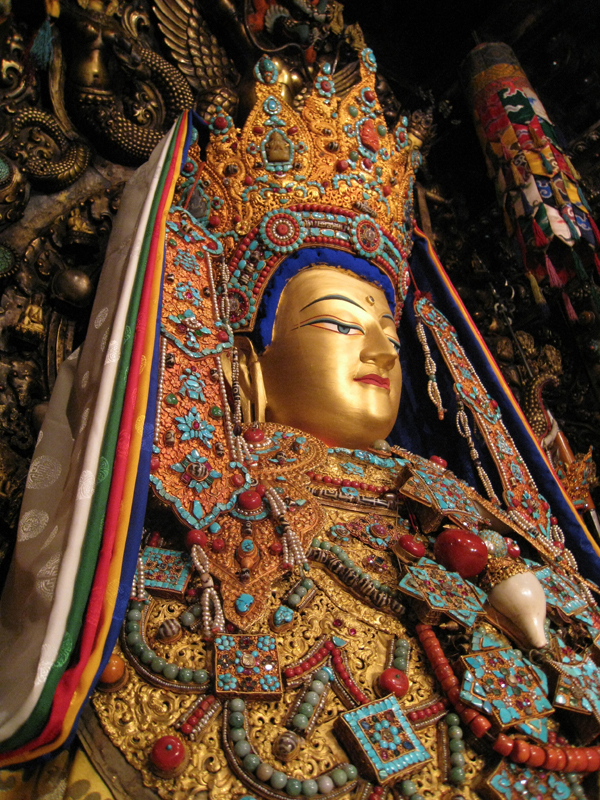
Jowo Rinpoche, enshrined in the Jokhang Temple. Lhasa, Tibet. Yarlung Dynasty. Believed to have been brought to Tibet in 641 C.E. Gilt metals with semiprecious stones, pearls, and paint; various offerings.
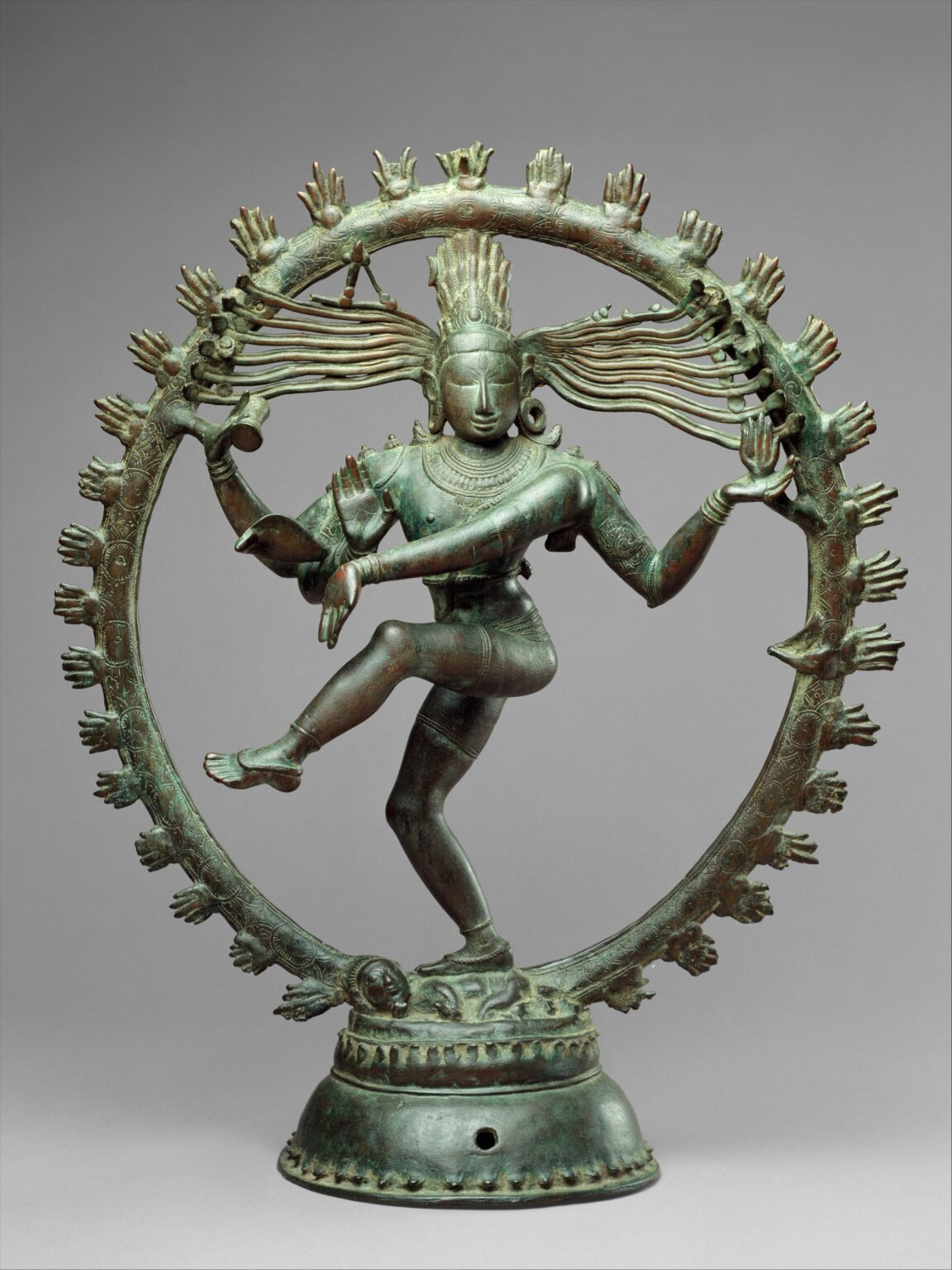


Shiva as Lord of Dance (Nataraja). Hindu; India (Tamil Nadu), Chola Dynasty. c. 11th century C.E. Cast bronze.

Buddha. Bamiyan, Afghanistan. Gandharan. c. 400–800 CE (destroyed in 2001). Cut rock with plaster and polychrome paint.


Longmen caves. Luoyang, China. Tang Dynasty. 493–1127 C.E. Limestone.
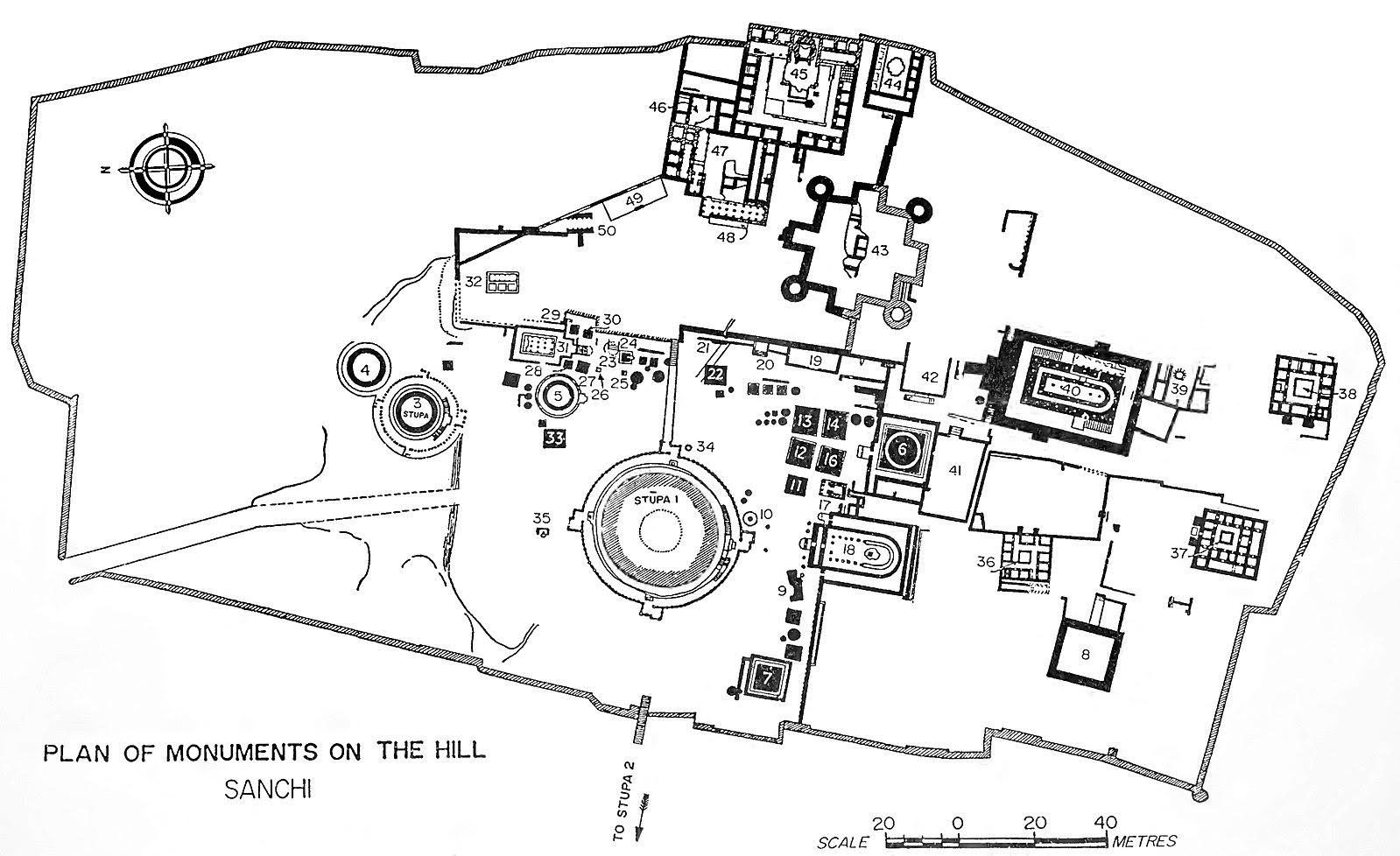
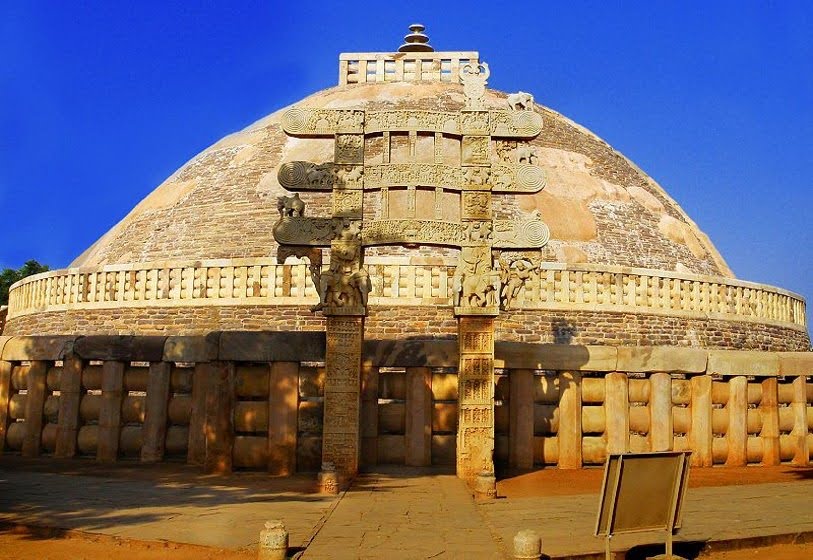
# 192. Great Stupa at Sanchi. Madhya Pradesh, India. Buddhist; Maurya, late Sunga Dynasty. c. 300 B.C.E.–100 C.E. Stone masonry, sandstone on dome.
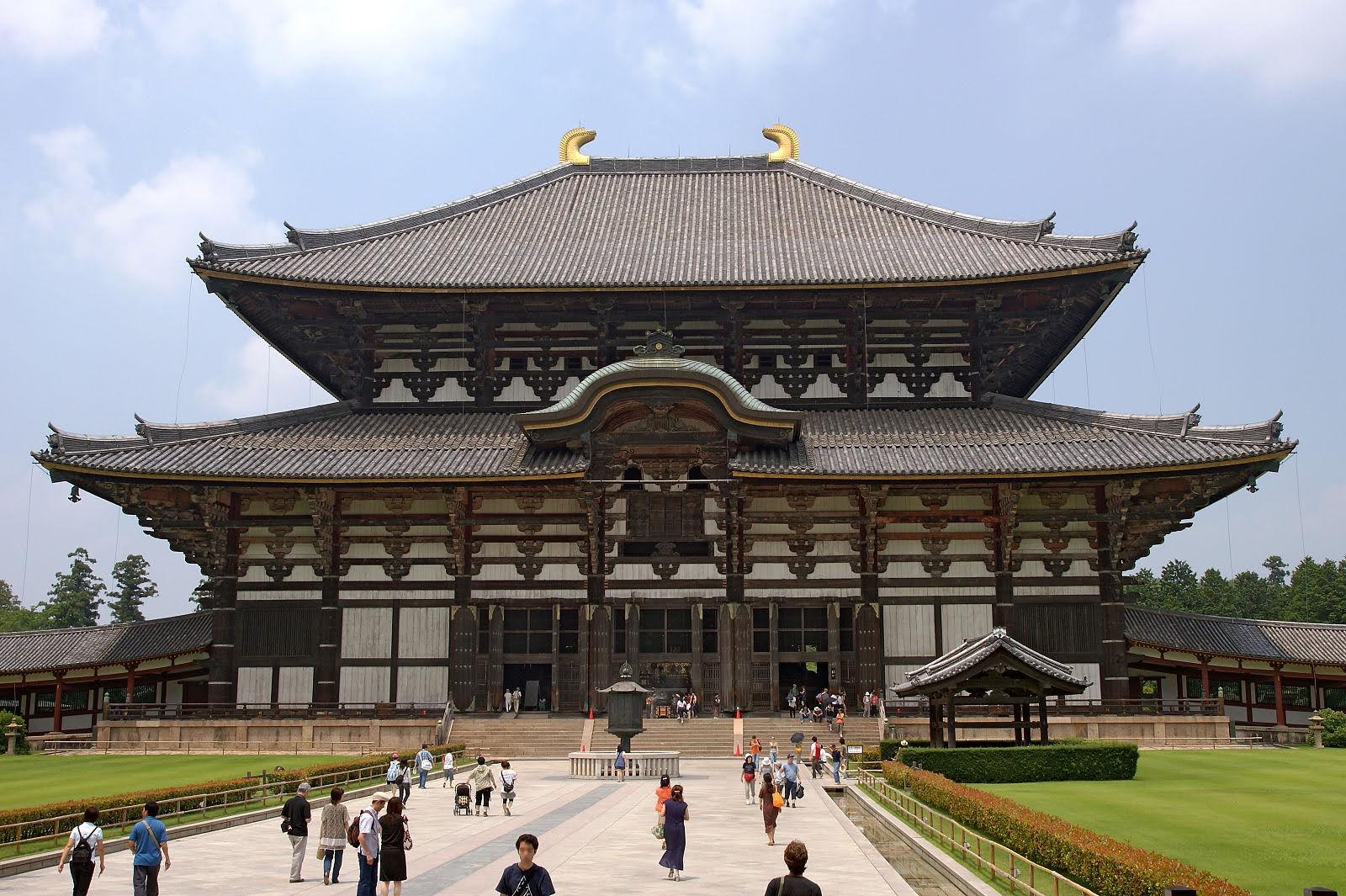


# 197. Todai-ji. Nara, Japan. Various artists, including sculptors Unkei and Keikei, as well as the Kei School. 743 C.E.; rebuilt c. 1700. Bronze and wood (sculpture); wood with ceramic-tile roofing (architecture).


# 197. Todai-ji. Guardian Figures Ungyo and Agyo

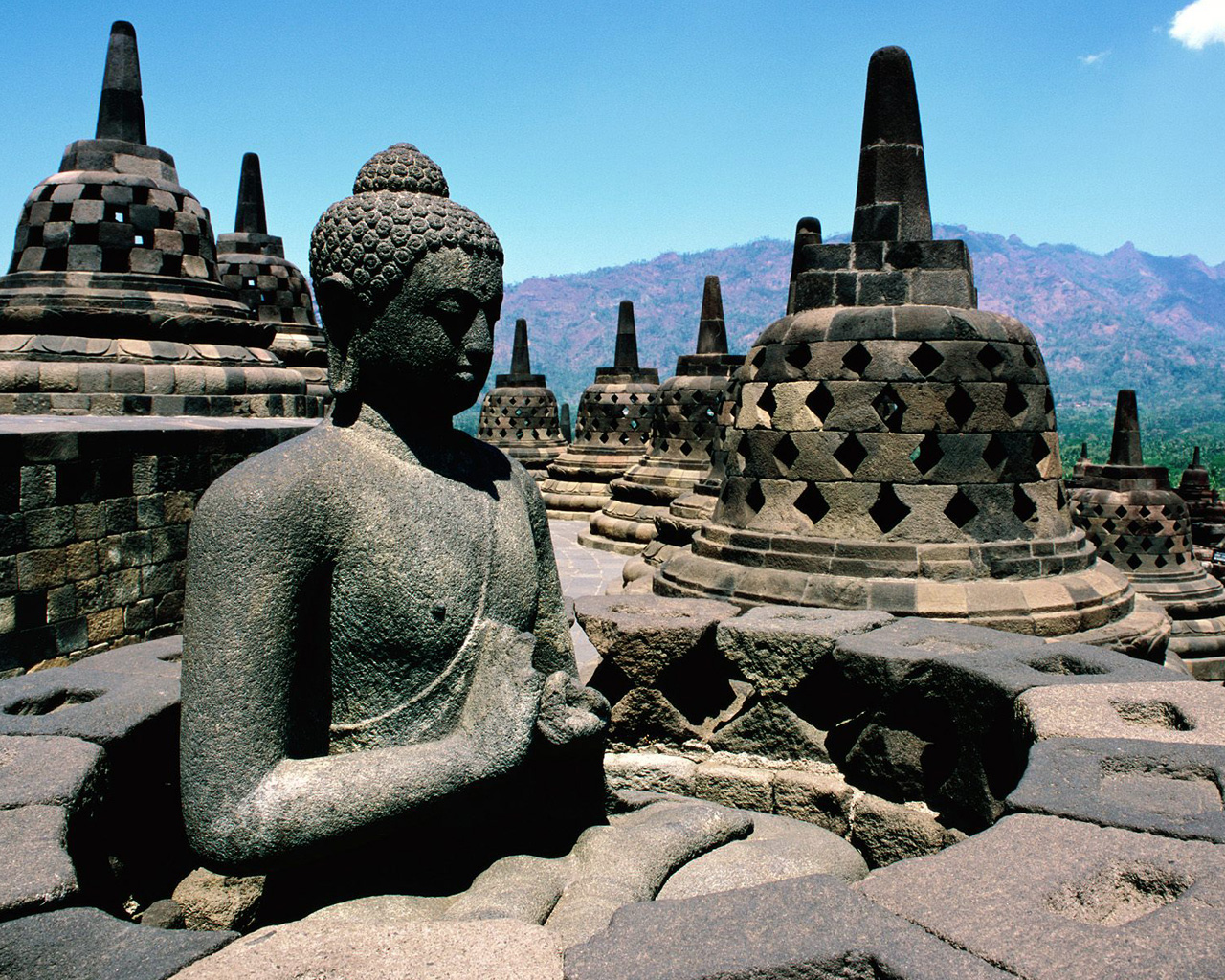
# 198. Borobudur Temple. Central Java, Indonesia. Sailendra Dynasty. c. 750–842 C.E. Volcanic-stone masonry.

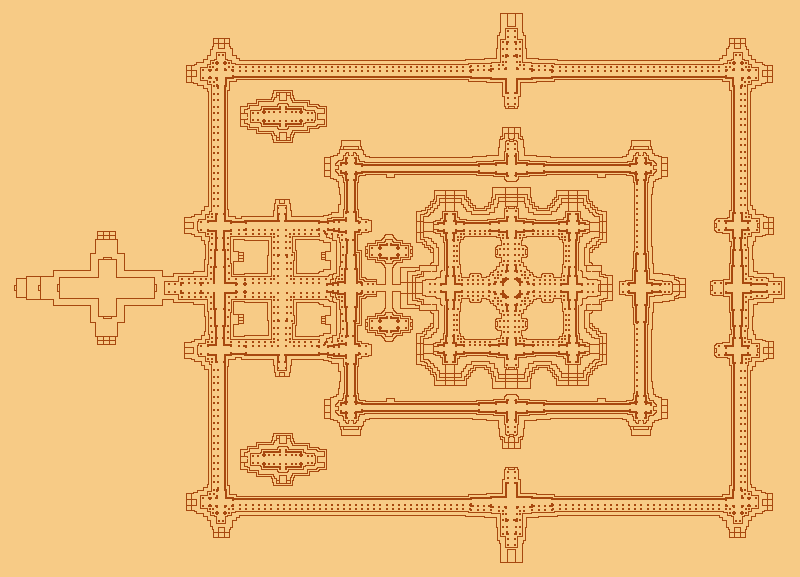
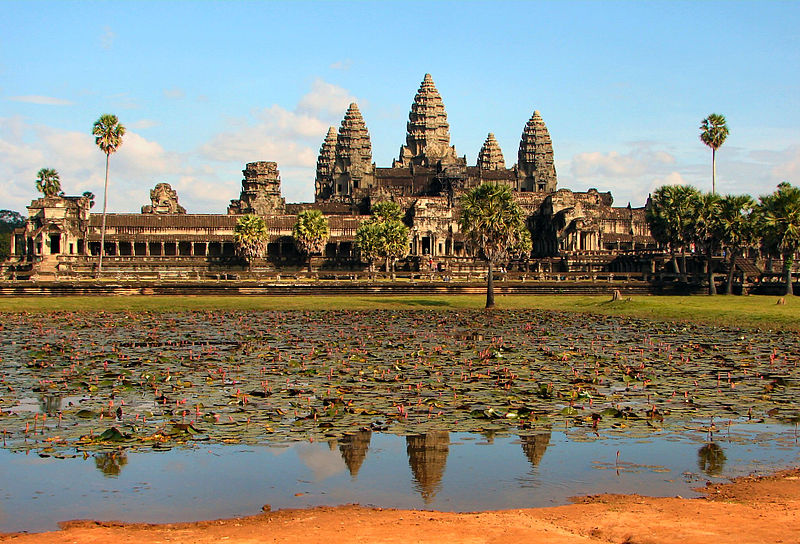
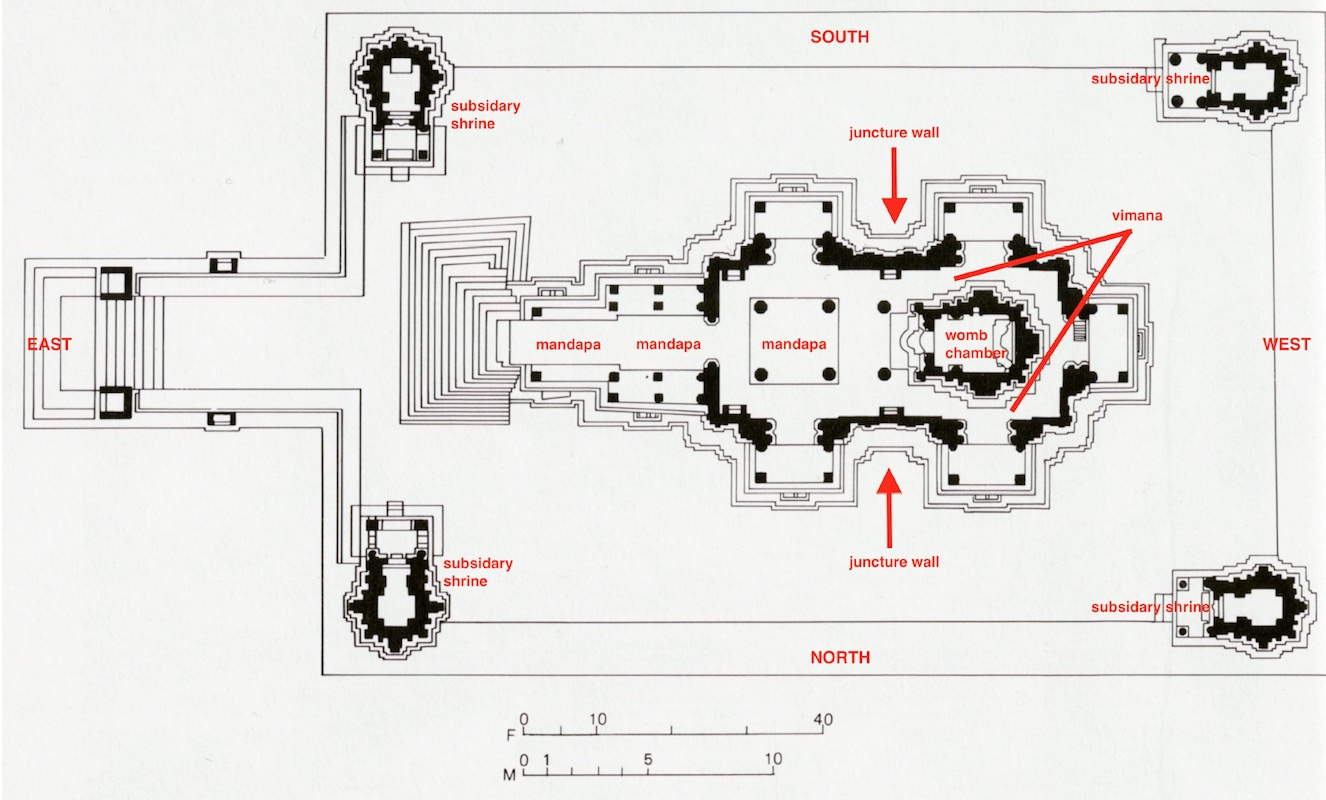
199. Angkor, the temple of Angkor Wat, and the city of Angkor Thom, Cambodia. Hindu, Angkor Dynasty. c. 800–1400 C.E. Stone masonry, sandstone.

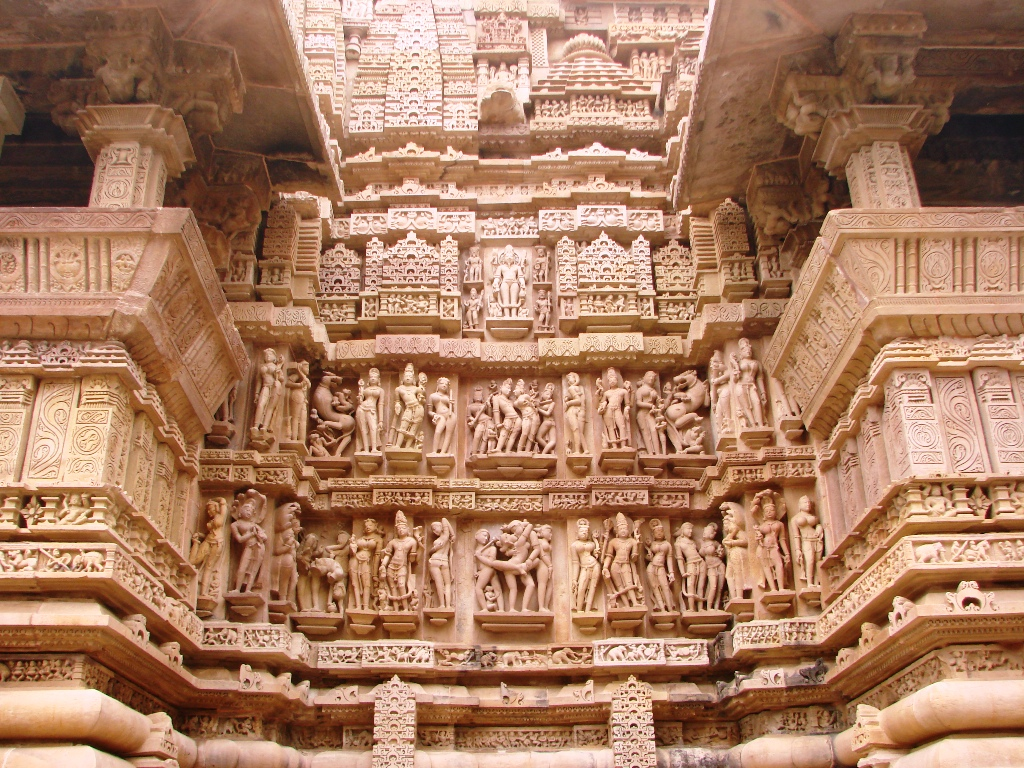
#200. Lakshmana Temple. Khajuraho, India. Hindu, Chandella Dynasty. c. 930–950 CE. Sandstone.
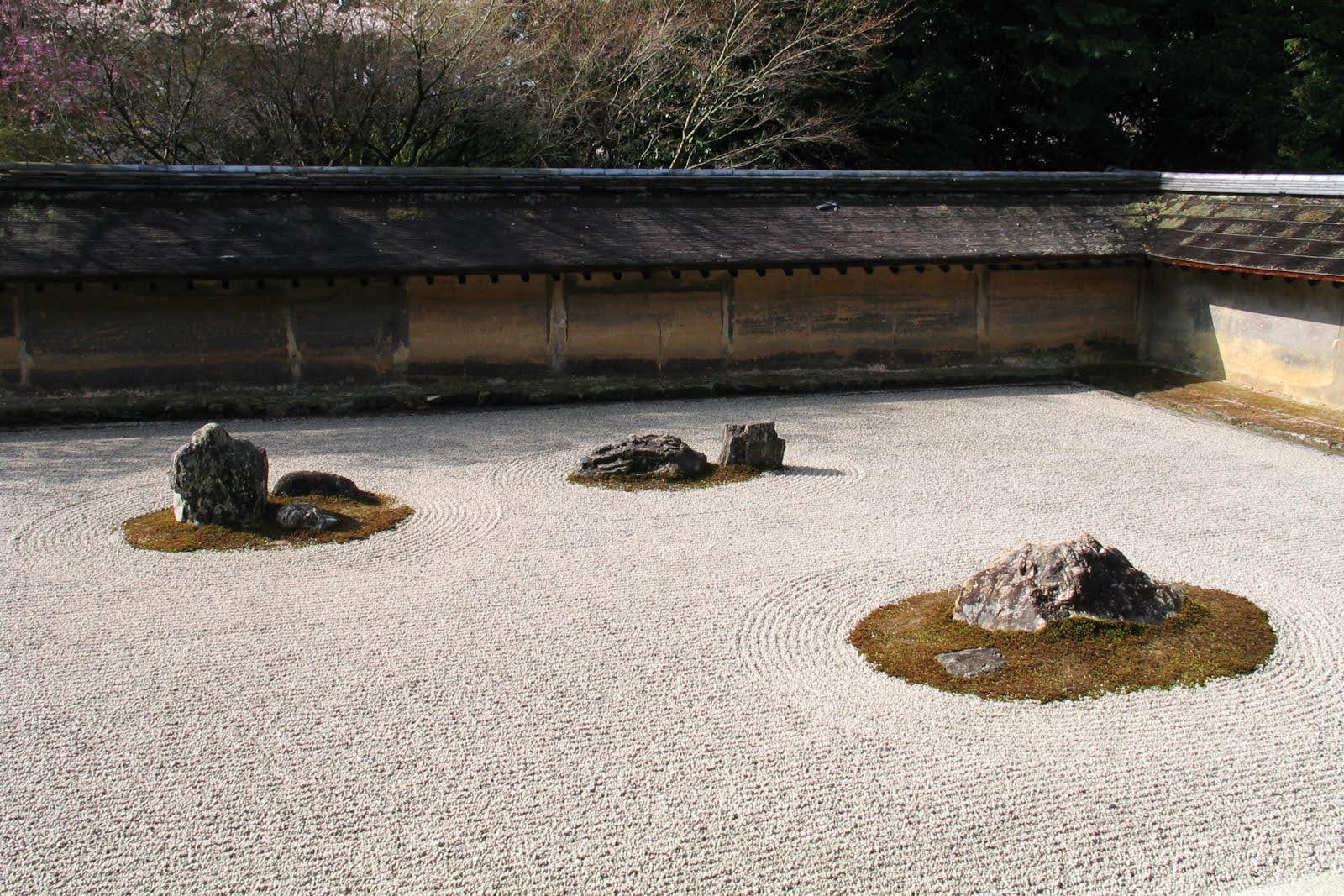


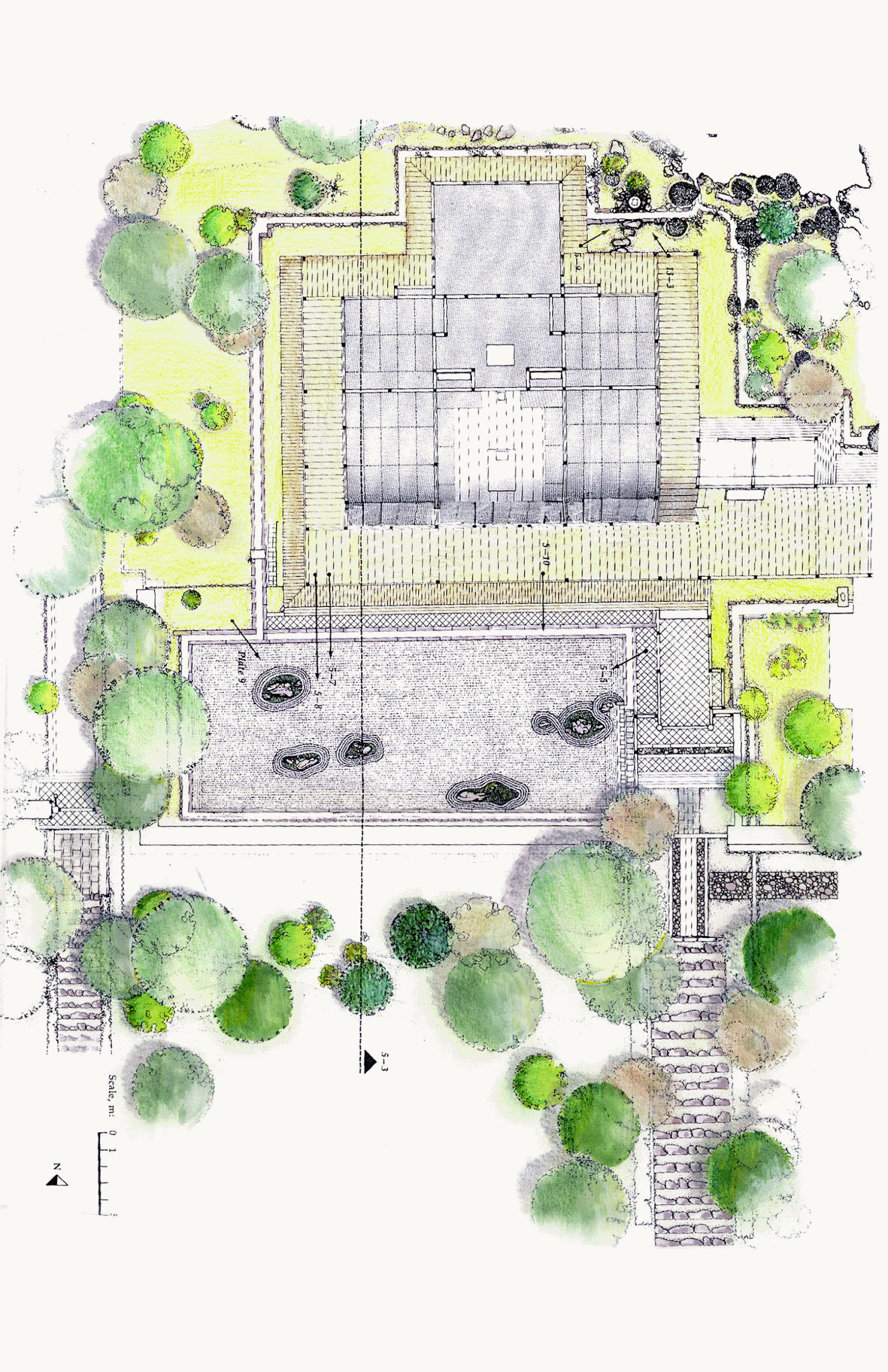
# 207. Ryoan-ji. Kyoto, Japan. Muromachi Period, Japan. c. 1480 C.E.; current design most likely dates to the 18th century. Rock garden.
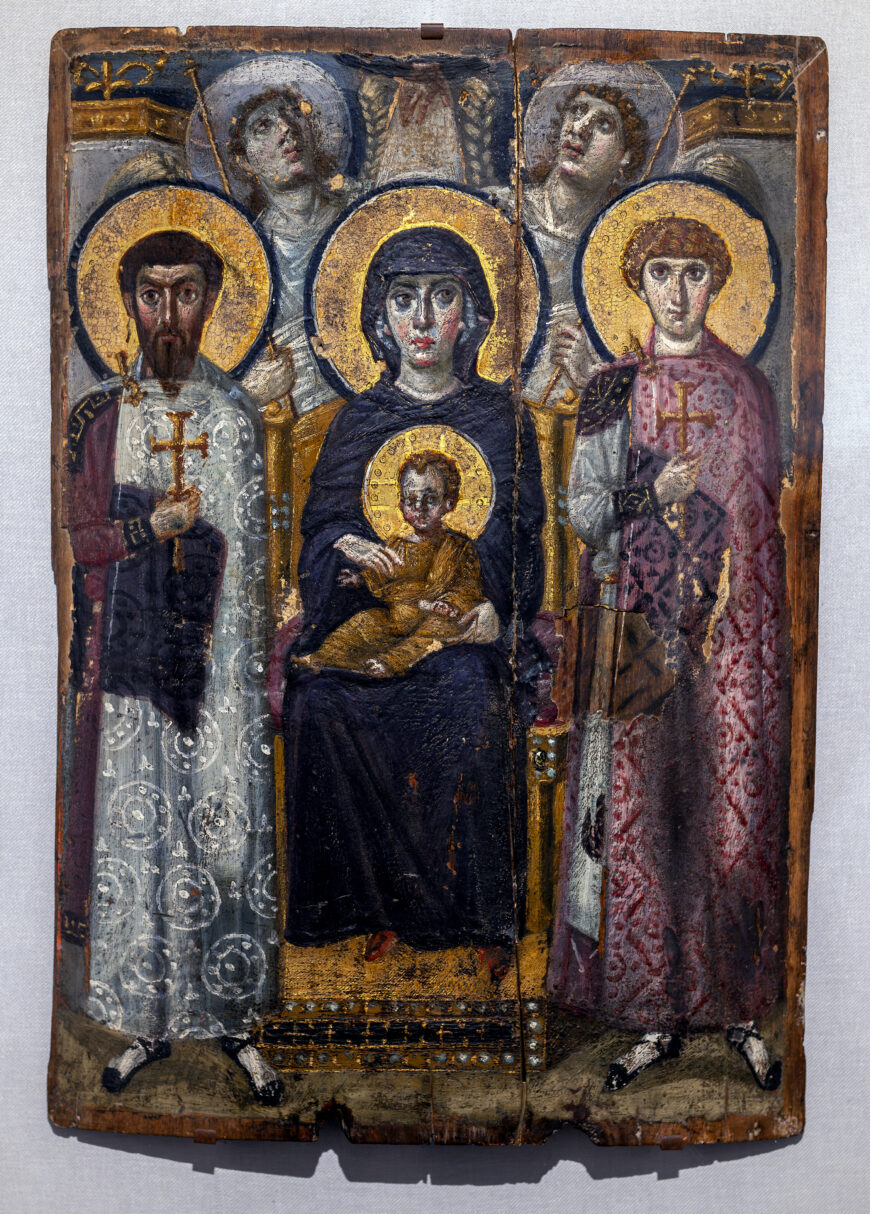

# 54. Virgin (Theotokos) and Child between Saints Theodore and George. Early Byzantine Europe. Sixth or early seventh century C.E. Encaustic on wood.

# 187. Folio from a Qur’an. Arab, North Africa, or Near East. Abbasid. c. eighth to ninth century C.E. Ink, color, and gold on parchment.
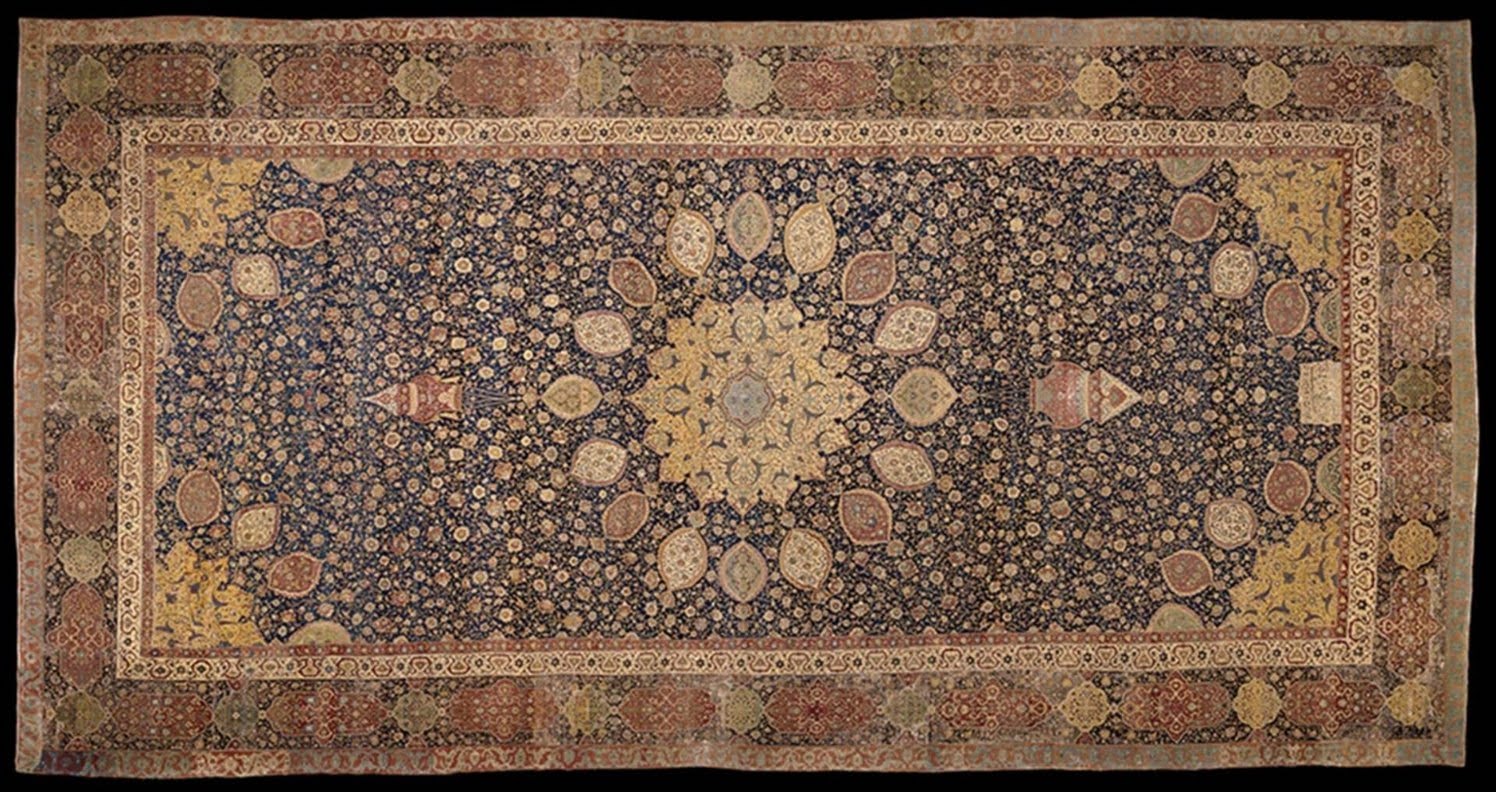

# 191. The Ardabil Carpet. Maqsud of Kashan. 1539–1540 C.E. Silk and wool.
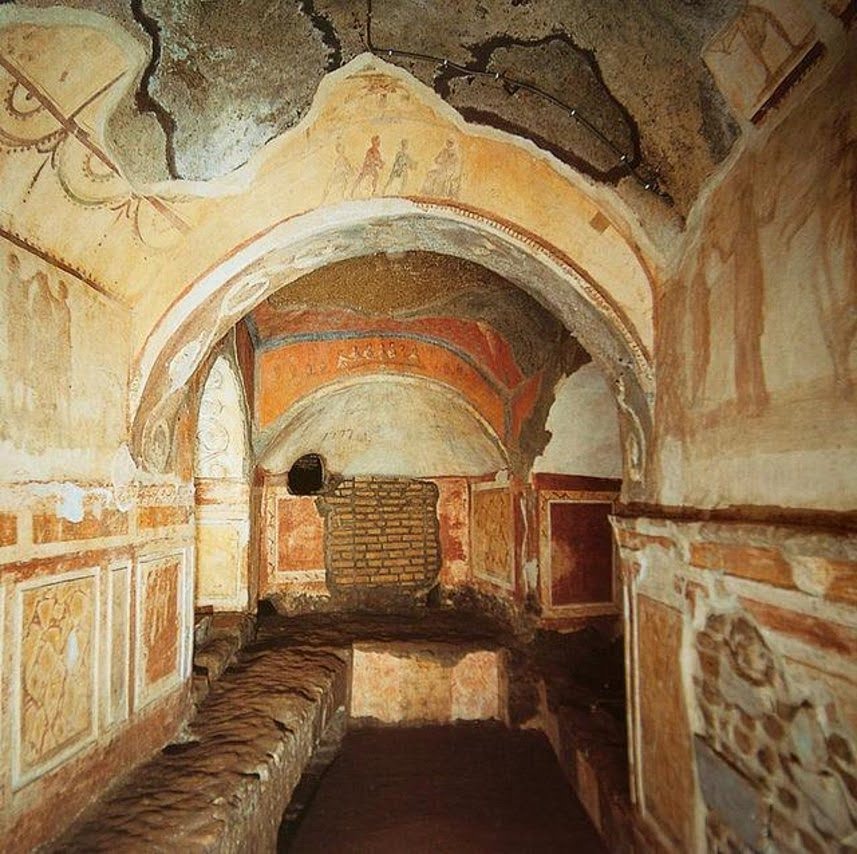

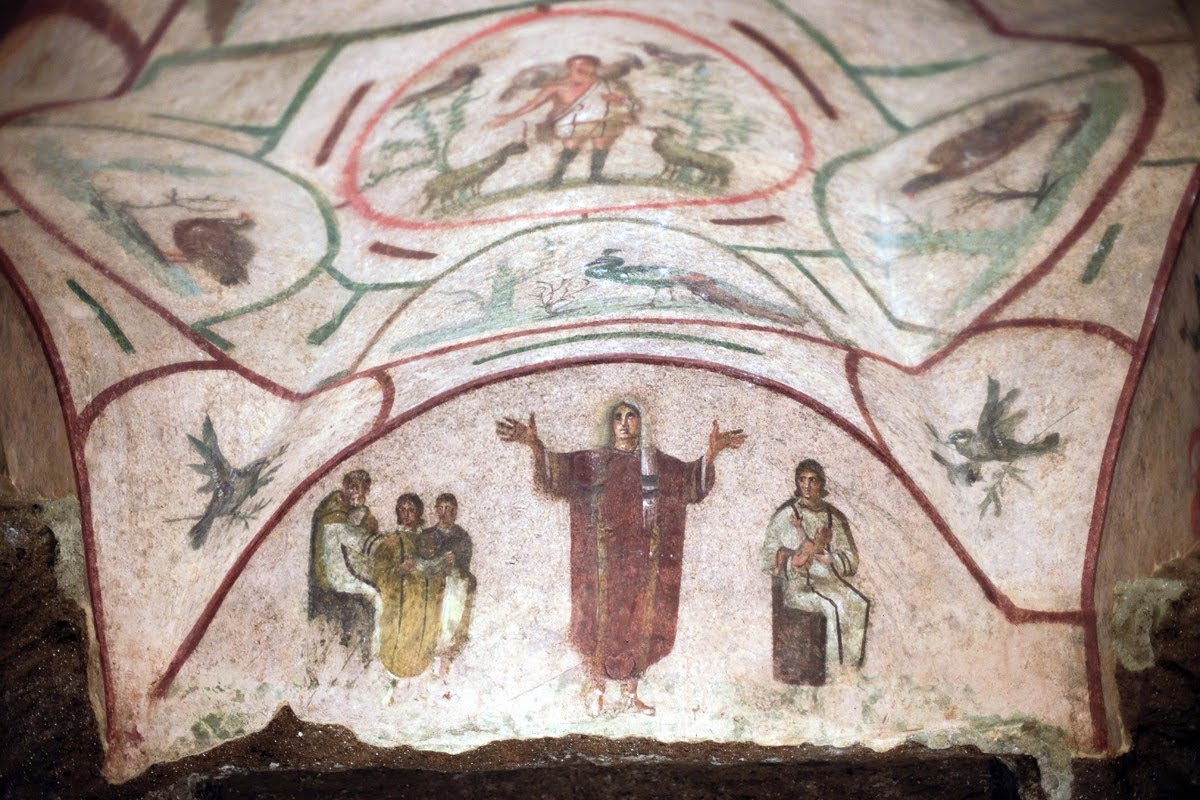
# 48. Catacomb of Priscilla. Rome, Italy. Late Antique Europe. c. 200–400 C.E. Excavated tufa and fresco.
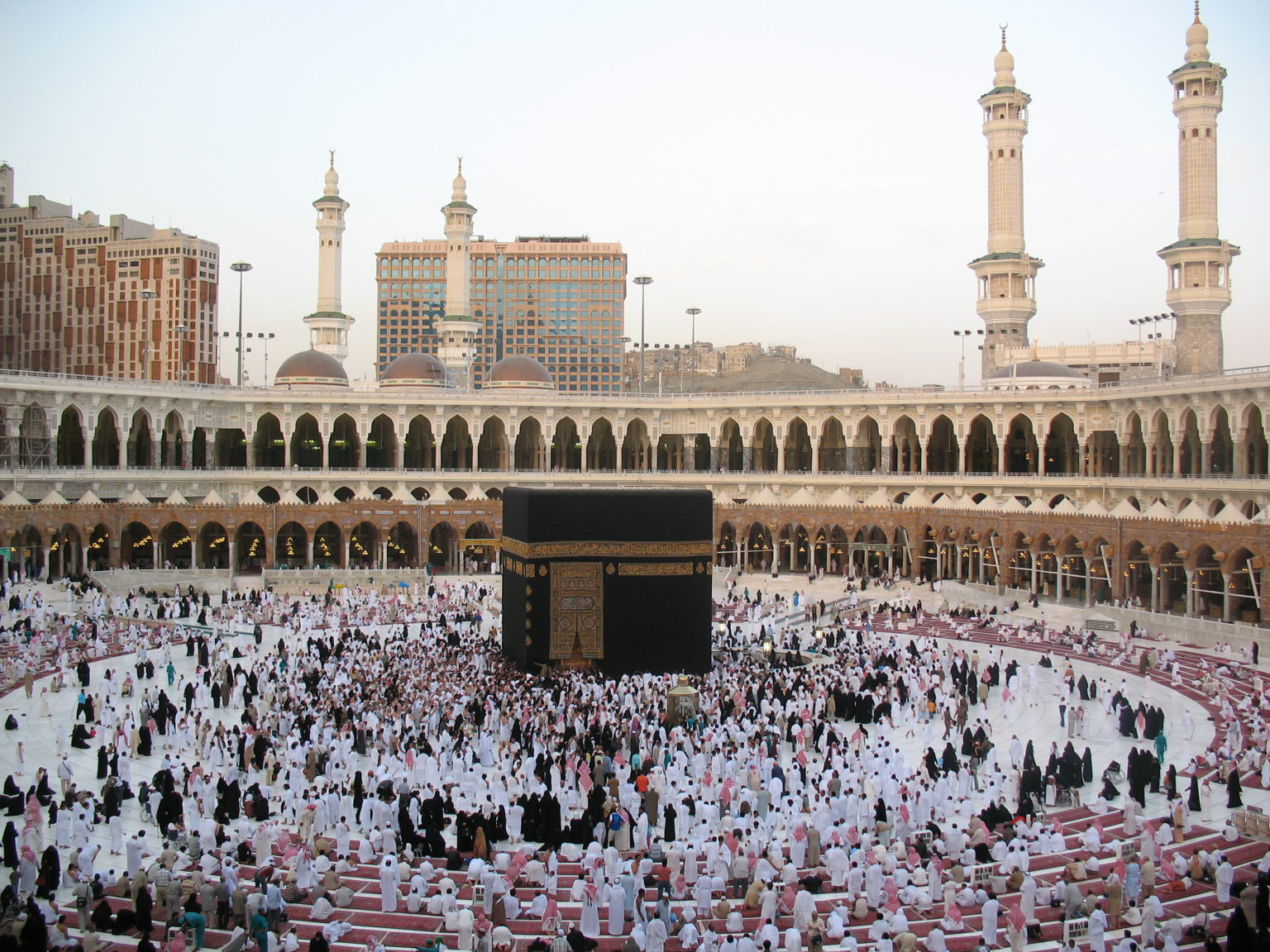


# 183. The Kaaba. Mecca, Saudi Arabia. Islamic. Pre-Islamic monument; rededicated by Muhammad in 631–632 C.E.; multiple renovations. Granite masonry, covered with silk curtain and calligraphy in gold and silver-wrapped thread.

# 185. Dome of the Rock. Jerusalem. Islamic, Umayyad. 691–692 C.E., with multiple renovations. Stone masonry and wooden roof decorated with glazed ceramic tile, mosaics, and gilt aluminum and bronze dome.

# 56. Great Mosque. Córdoba, Spain. Umayyad. c. 785–786 CE. Stone masonry.

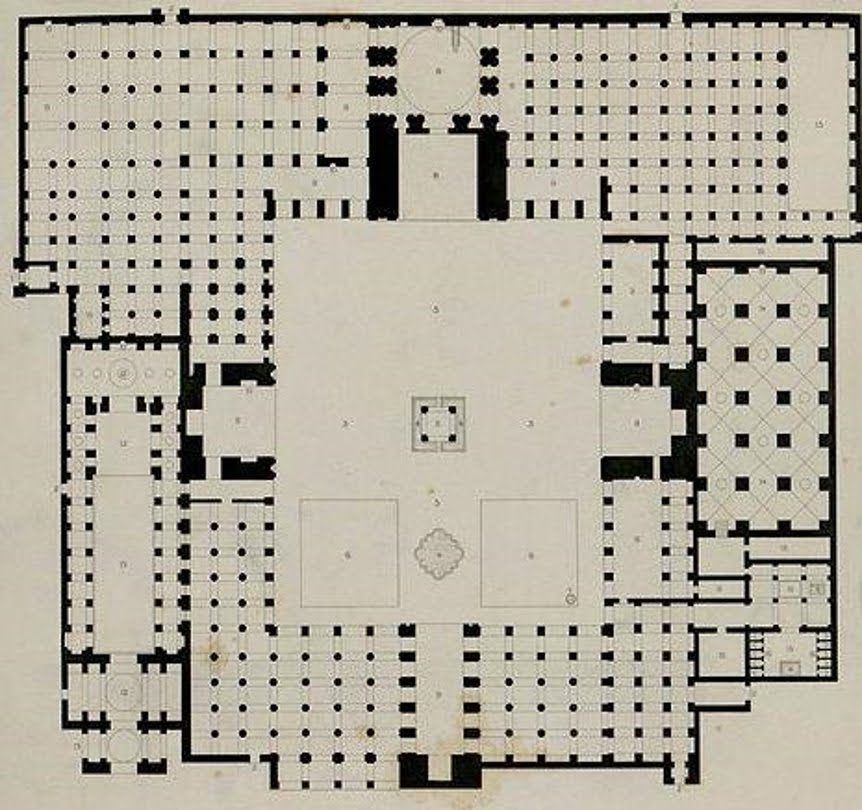
# 186. Great Mosque (Masjid-e Jameh). Isfahan, Iran. Islamic, Persian: Seljuk, Il-Khanid, Timurid and Safavid Dynasties. c. 700 CE; additions and restorations in the 14th, 18th, and 20th centuries CE. Stone, brick, wood, plaster, and glazed ceramic tile.

# 168. Great Mosque of Djenné. Mali. Founded c. 1200 CE; rebuilt 1906–1907 CE. Adobe.
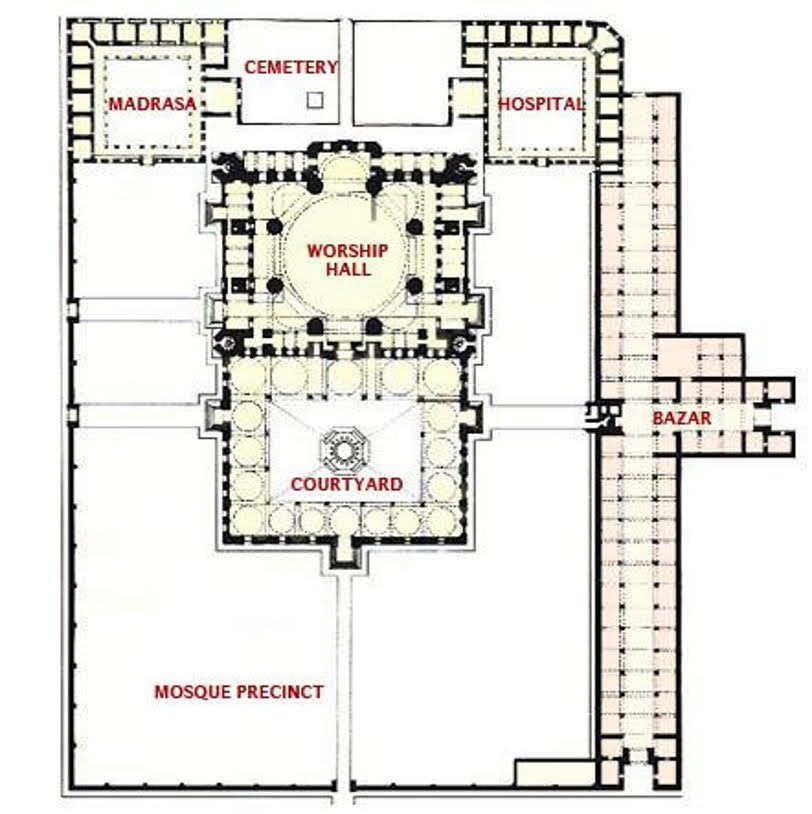
# 84. Mosque of Selim II. Edirne, Turkey. Sinan (architect). 1568–1575 CE. Brick and stone.

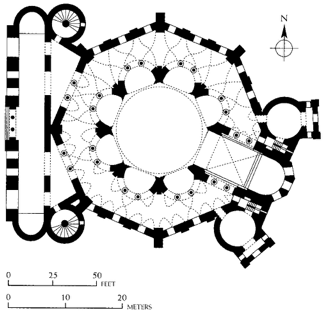
San Vitale. Ravenna, Italy. Early Byzantine Europe. c. 526–547 CE. Brick, marble, and stone veneer; mosaic.

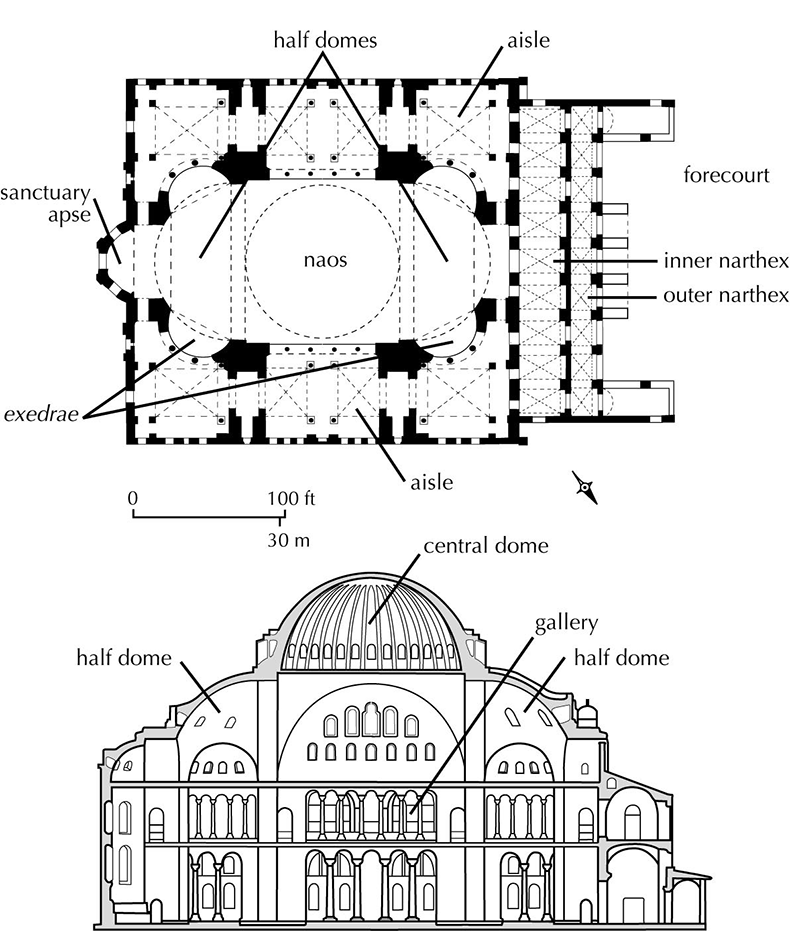
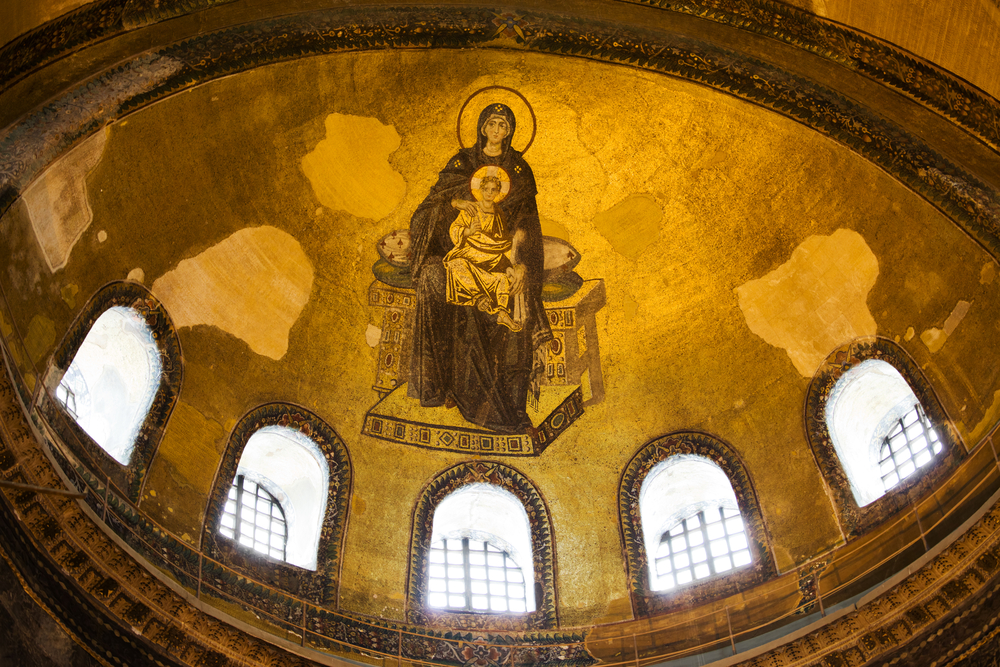
Hagia Sophia. Constantinople (Istanbul). anthemius of Tralles and Isidorus of Miletus. 532-537 CE. Brick and ceramic elements with stone and mosaic veneer.


Vienna Genesis: Rebecca and Eliezer at the Well and Jacob Wrestling the Angel, from the Vienna Genesis. Early Byzantine Europe. Early sixth century CE. Illuminated manuscript (tempera, gold, and silver on purple vellum).

Rebecca and Eliezer at the Well and Jacob Wrestling the Angel, from the Vienna Genesis. Early Byzantine Europe. Early sixth century CE. Illuminated manuscript (tempera, gold, and silver on purple vellum).
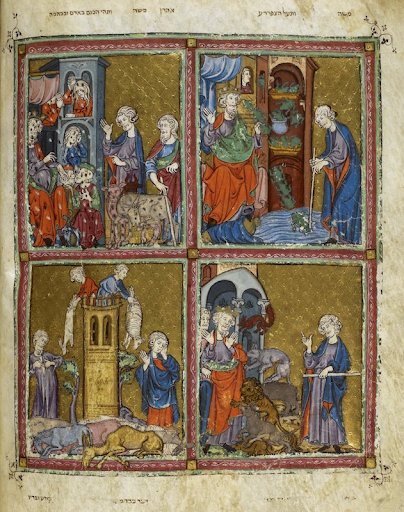

Golden Haggadah (The Plagues of Egypt, Scenes of Liberation, and Preparation for Passover). Late medieval Spain. c. 1320 CE. Illuminated manuscript (pigments and gold leaf on vellum).
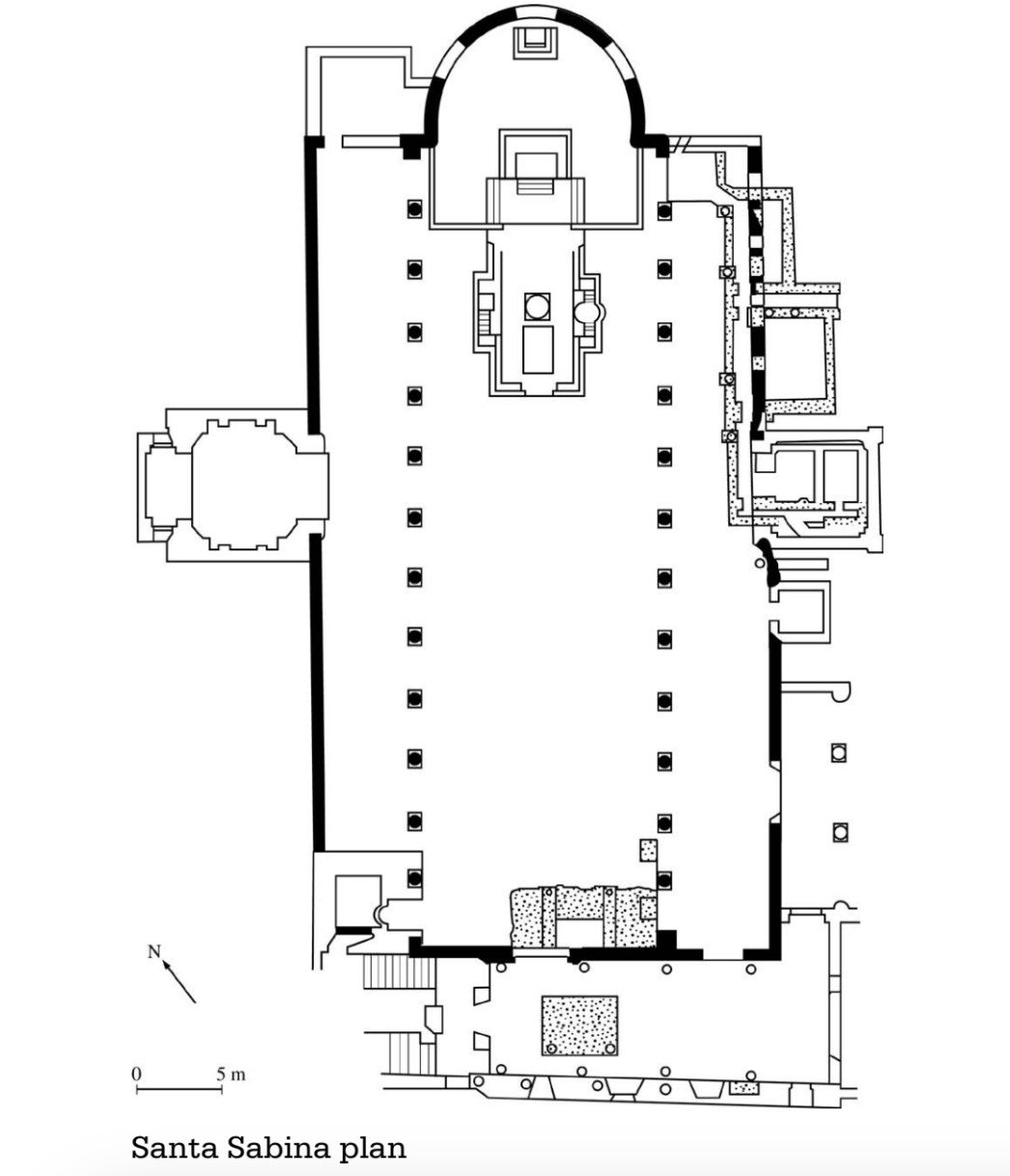
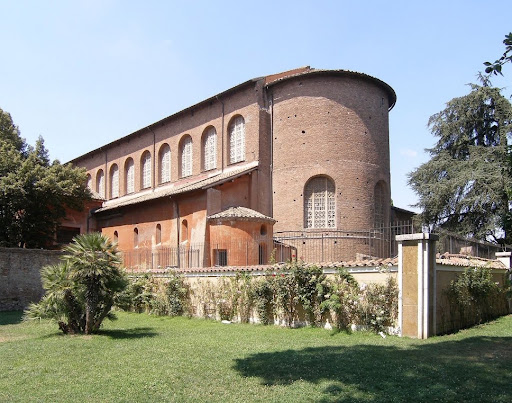
Santa Sabina. Rome, Italy. Late Antique Europe. C. 422–432 C.E. Brick and stone, wooden roof.


san vitale

Lindisfarne Gospels: St. Matthew, cross-carpet page; St. Luke portrait page; St. Luke incipit page Early medieval (Hiberno Saxon) Europe. c. 700 CE. Illuminated manuscript (ink, pigments, and gold on vellum).


Pyxis of al-Mughira. Umayyad. c. 968 CE. Ivory.
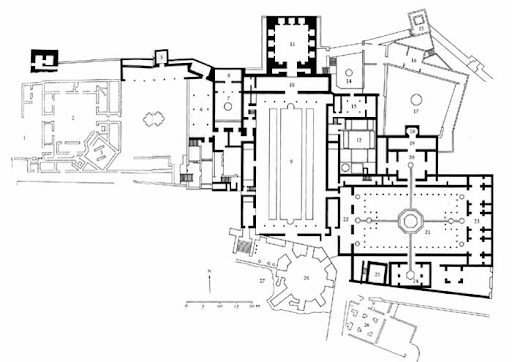
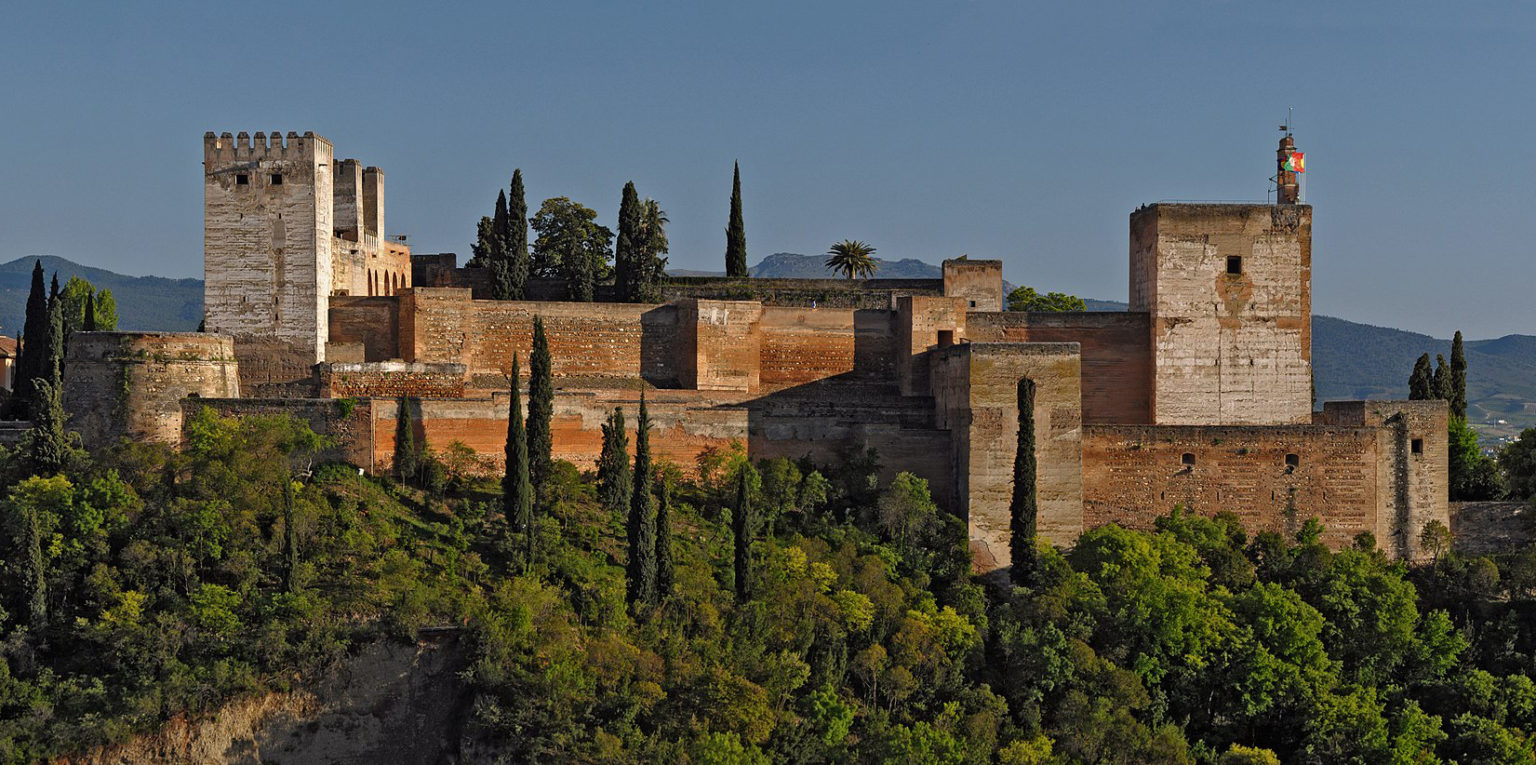
Alhambra. Granada, Spain. Nasrid Dynasty. 1354–1391 CE. Whitewashed adobe stucco, wood, tile, paint, and gilding.
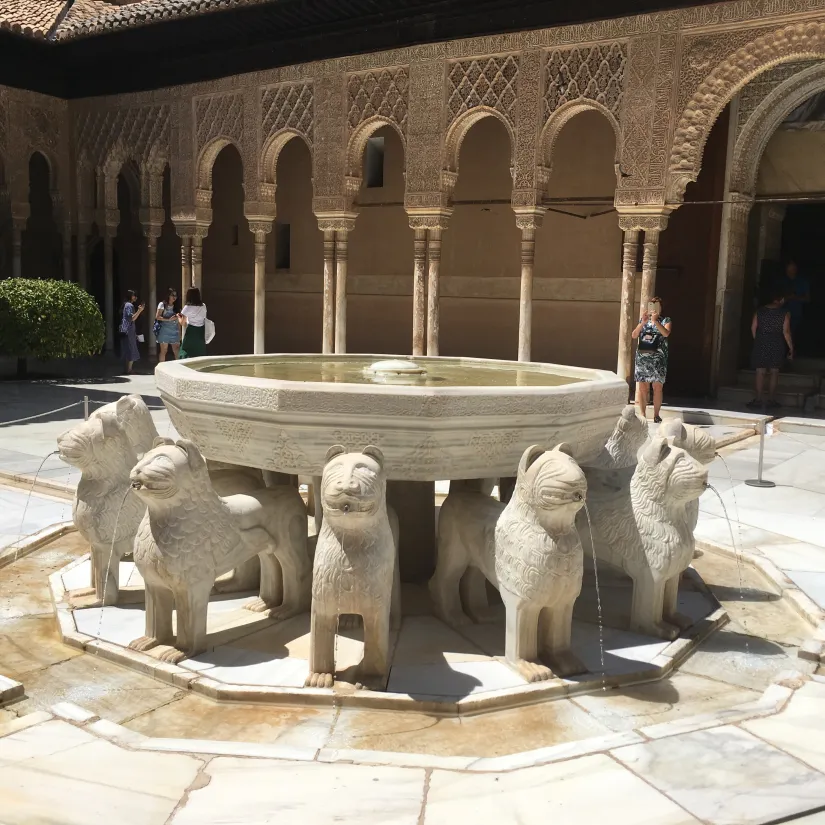


Alhambra, Court of Lions
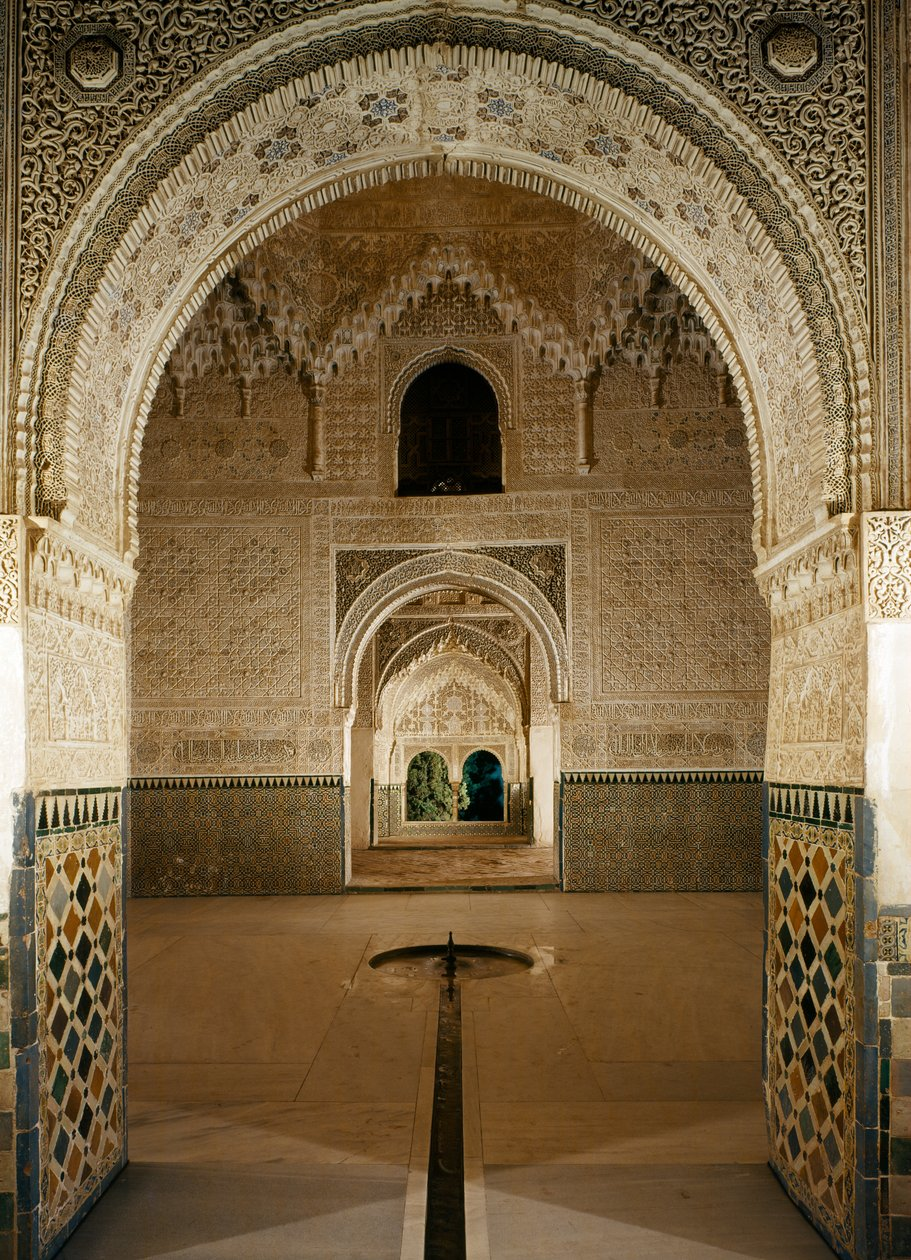

Alhambra, Hall of sisters
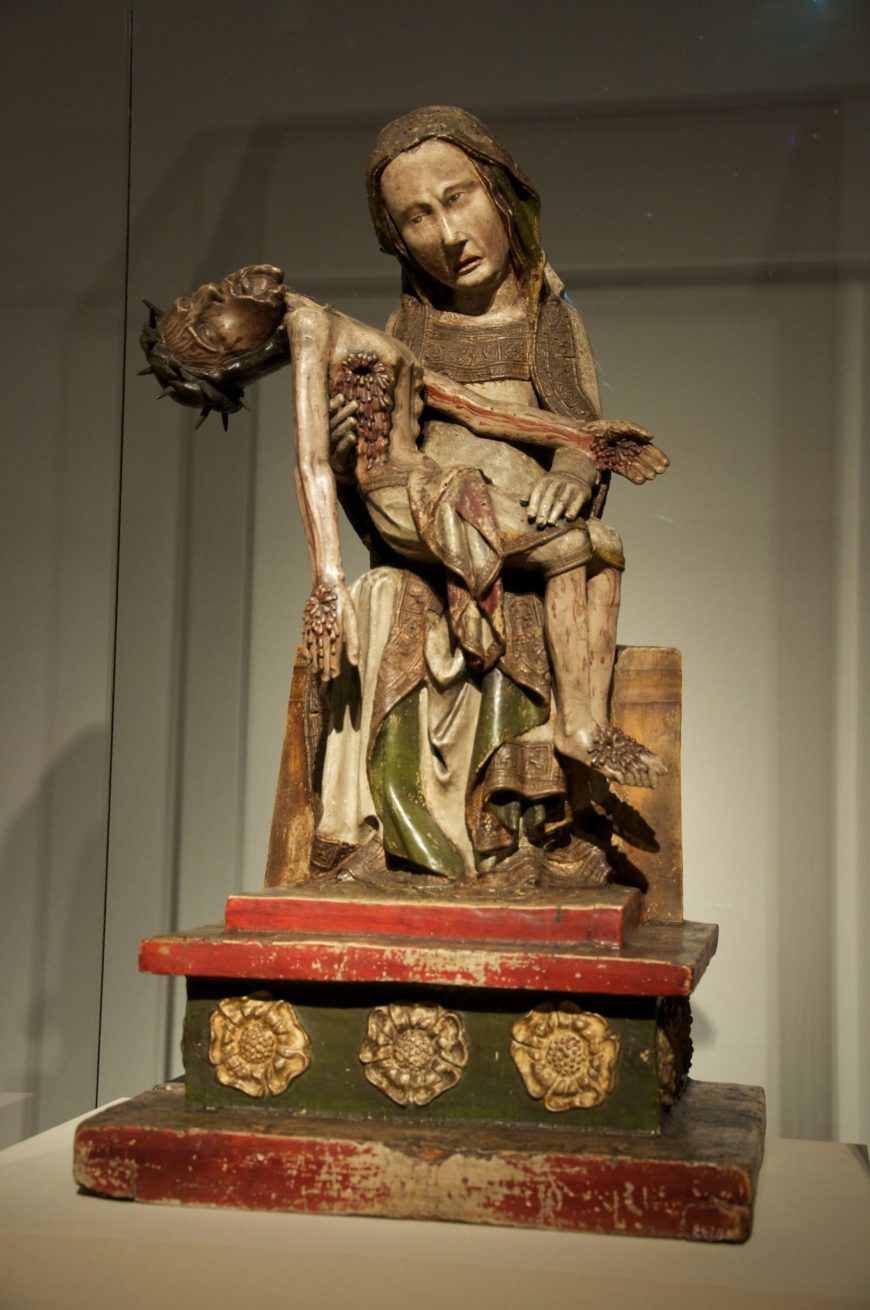

Röttgen Pietà.Late medieval Europe. c. 1300–1325 CE. Painted wood.
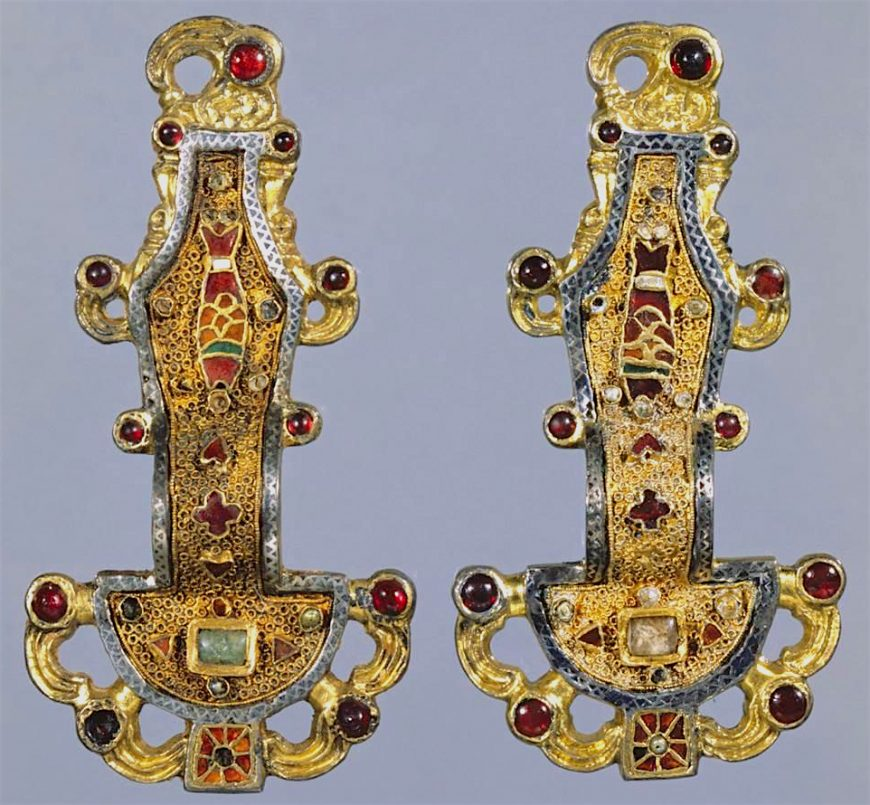

Merovingian looped fibulae. Early medieval Europe. Mid-sixth century C.E. Silver gilt worked in filigree, with inlays of garnets and other stones.
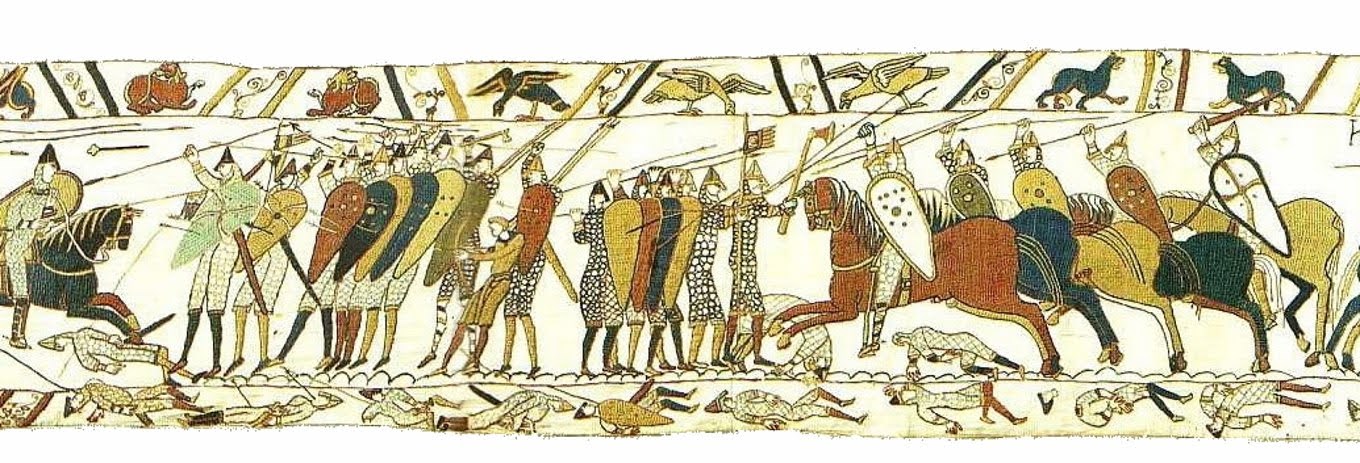


Bayeux Tapestry: Romanesque Europe (English or Norman). c. 1066–1080 C.E. Embroidery on linen.
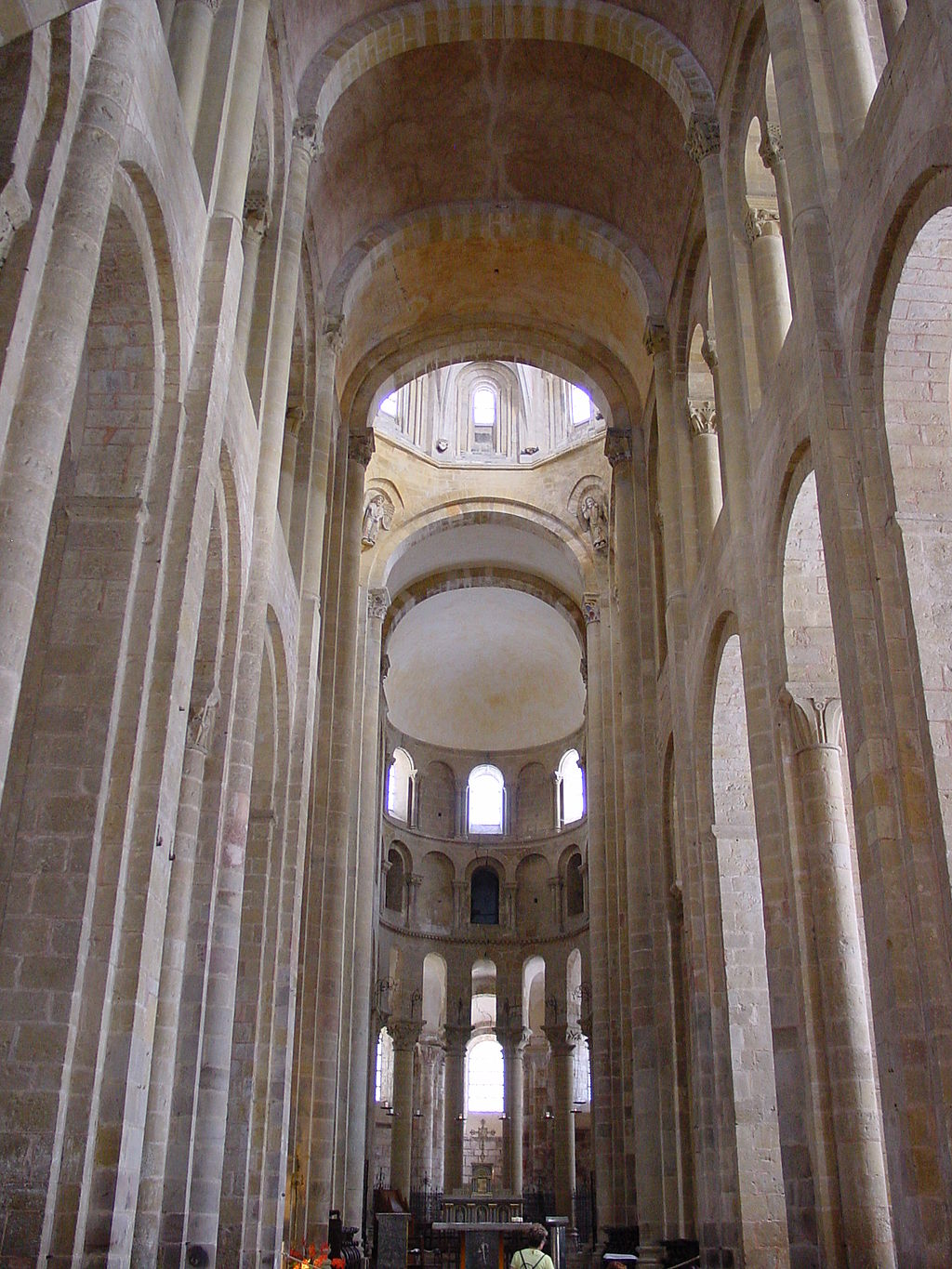

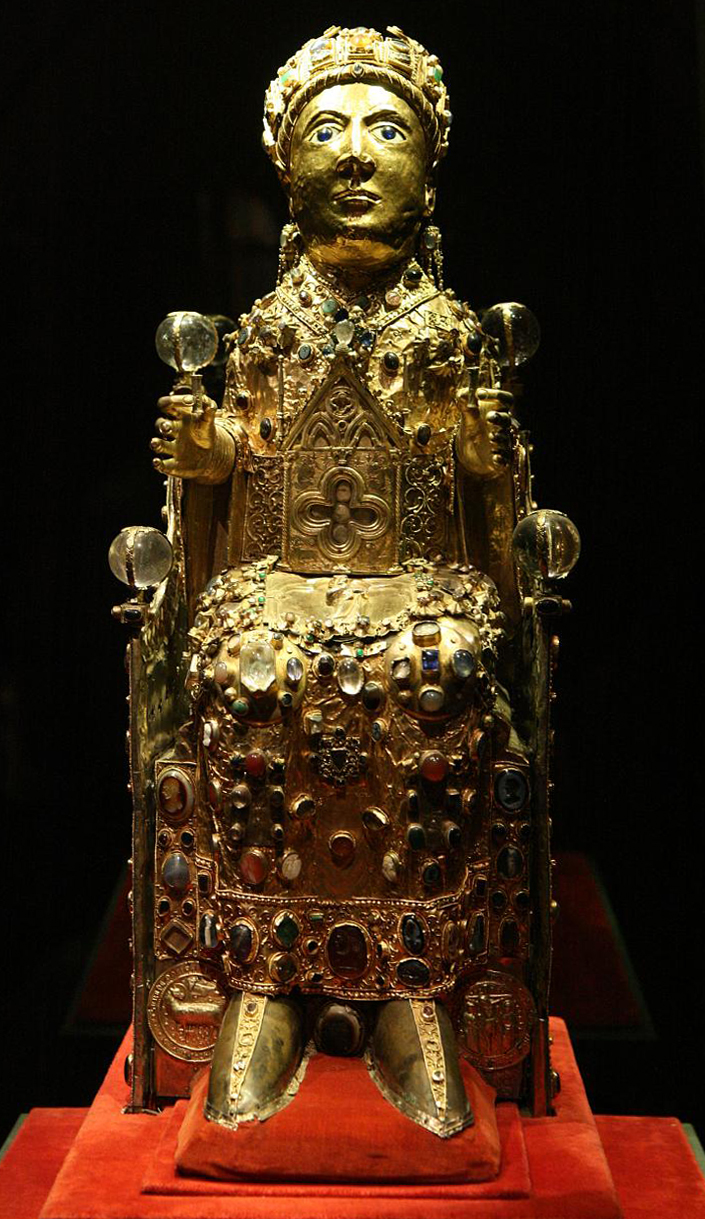
Church of Sainte-Foy: Conques, France. Romanesque Europe. Church: c. 1050–1130 C.E.; Reliquary of Saint Foy: ninth century C.E., with later additions. Stone (architecture); stone and paint (tympanum); gold, silver, gemstones, and enamel over wood (reliquary).
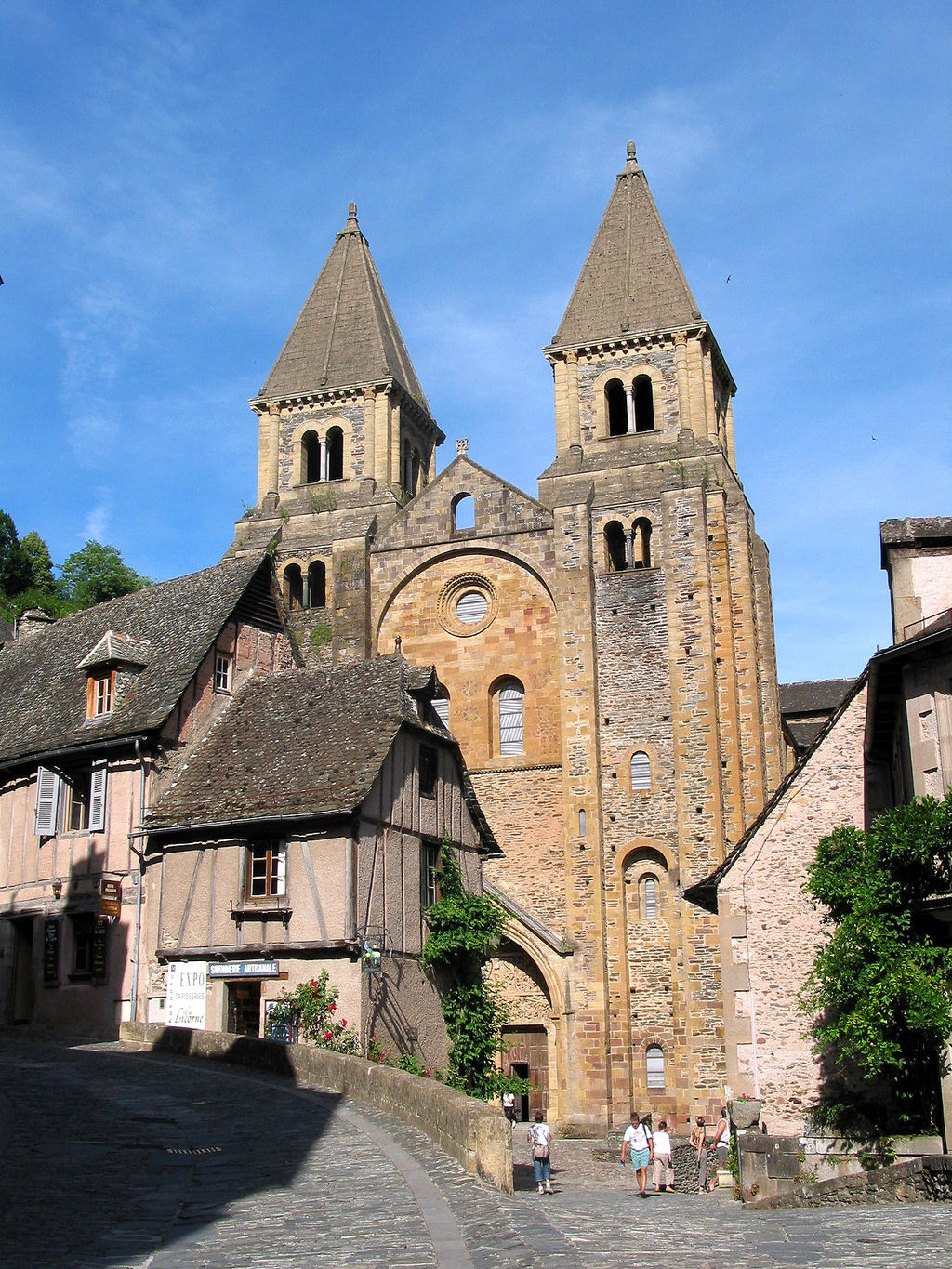


Church of Sainte-Foy: Conques, France. Romanesque Europe. Church: c. 1050–1130 C.E.; Reliquary of Saint Foy: ninth century C.E., with later additions. Stone (architecture); stone and paint (tympanum); gold, silver, gemstones, and enamel over wood (reliquary).
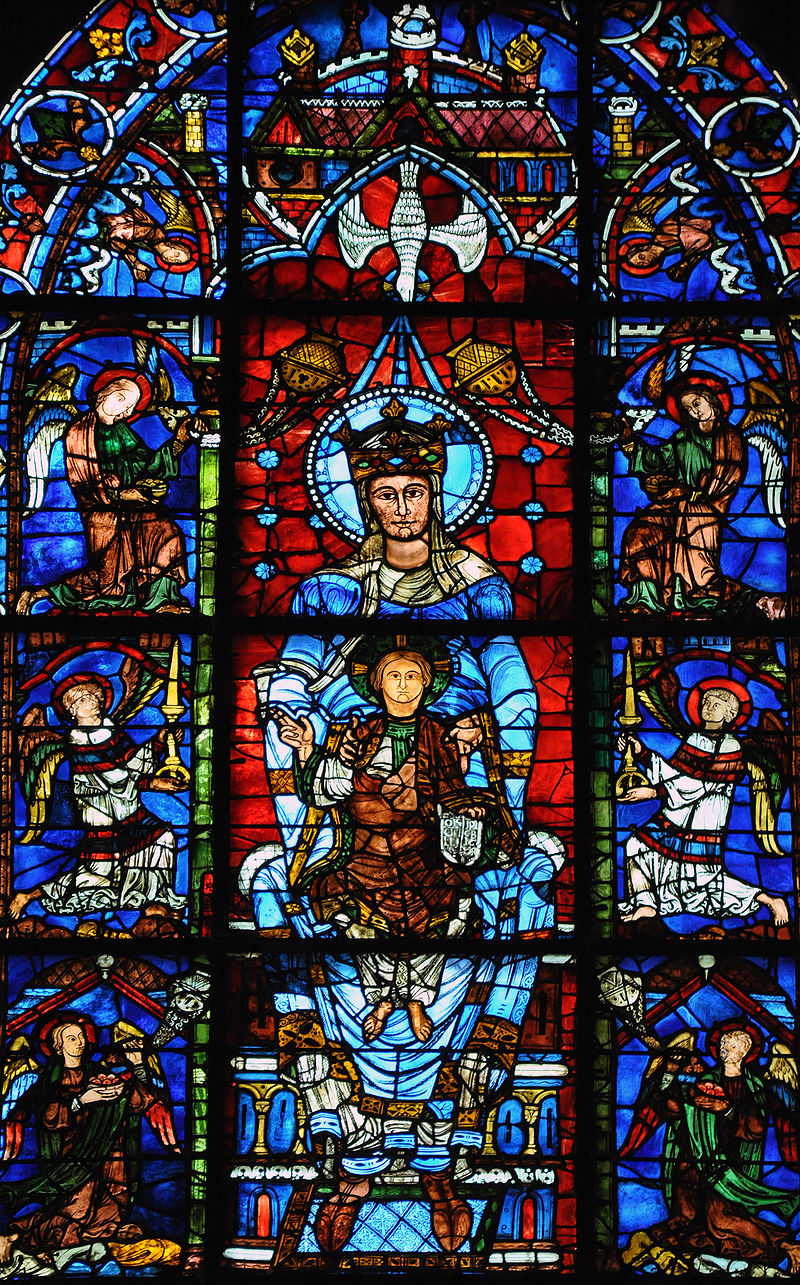


Notre Dame de la Belle Verriere
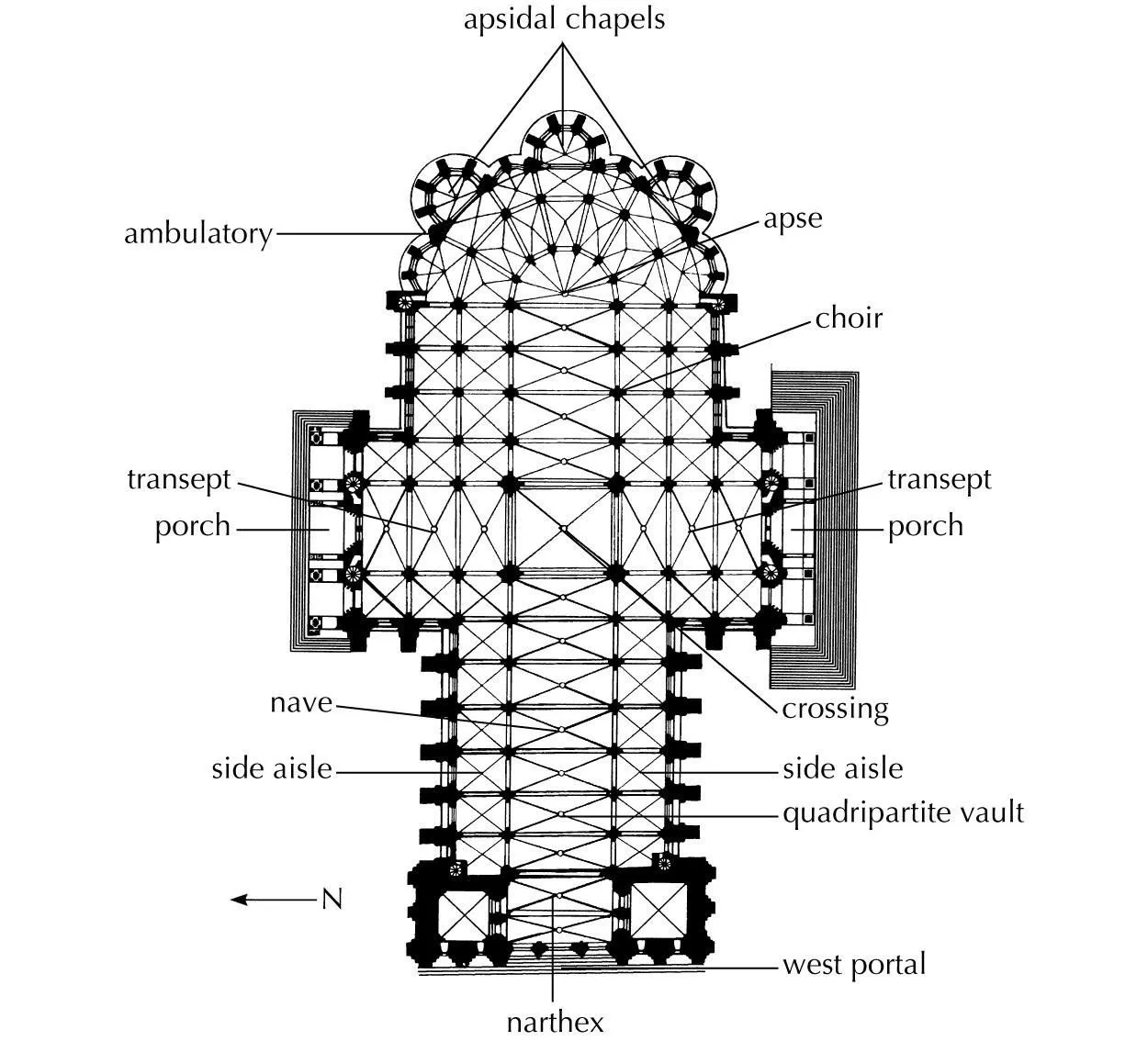
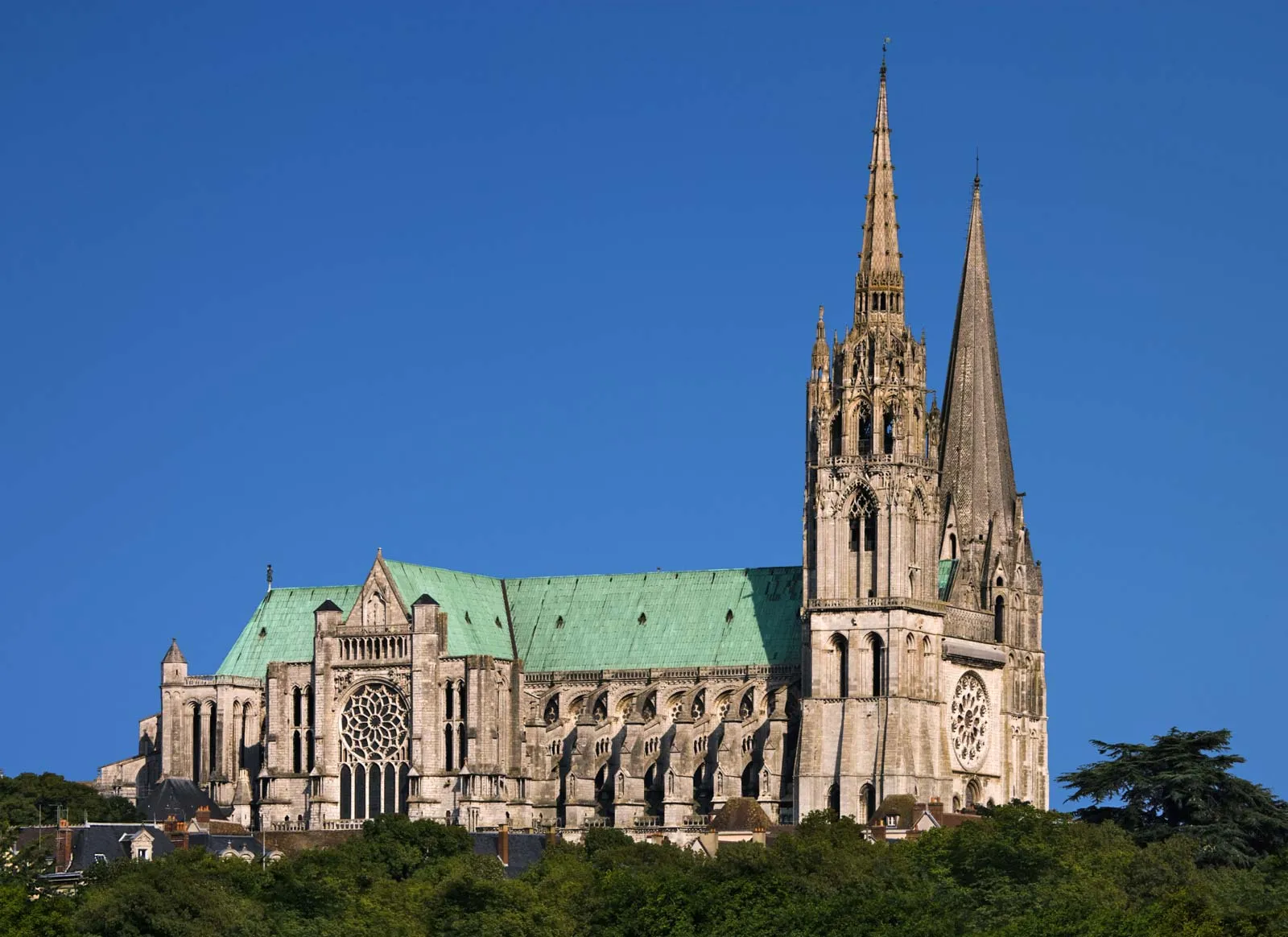
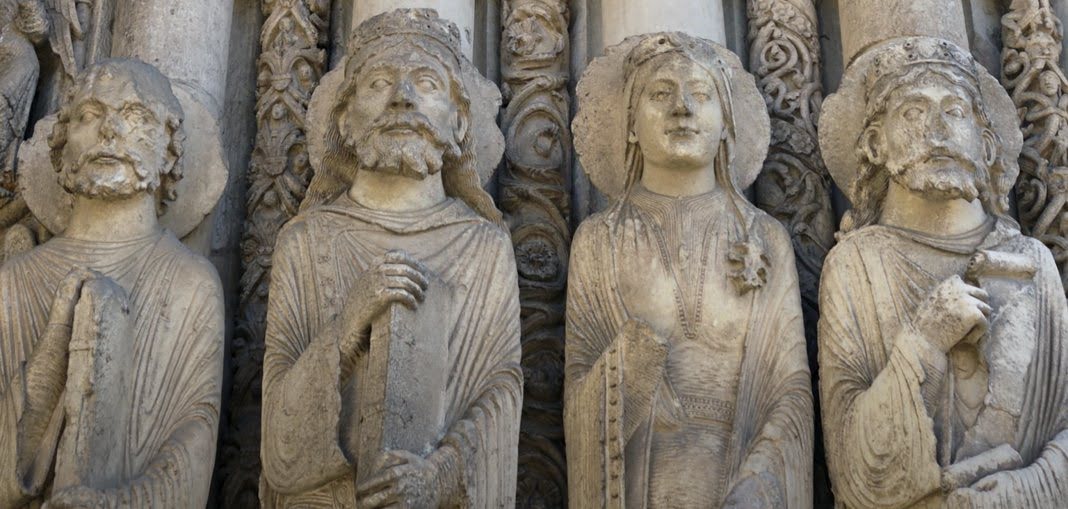
Chartres Cathedral: Chartres, France. Gothic Europe. Original construction c. 1145-1155 CE; reconstructed c. 1194-1220 CE. Limestone, stained glass.
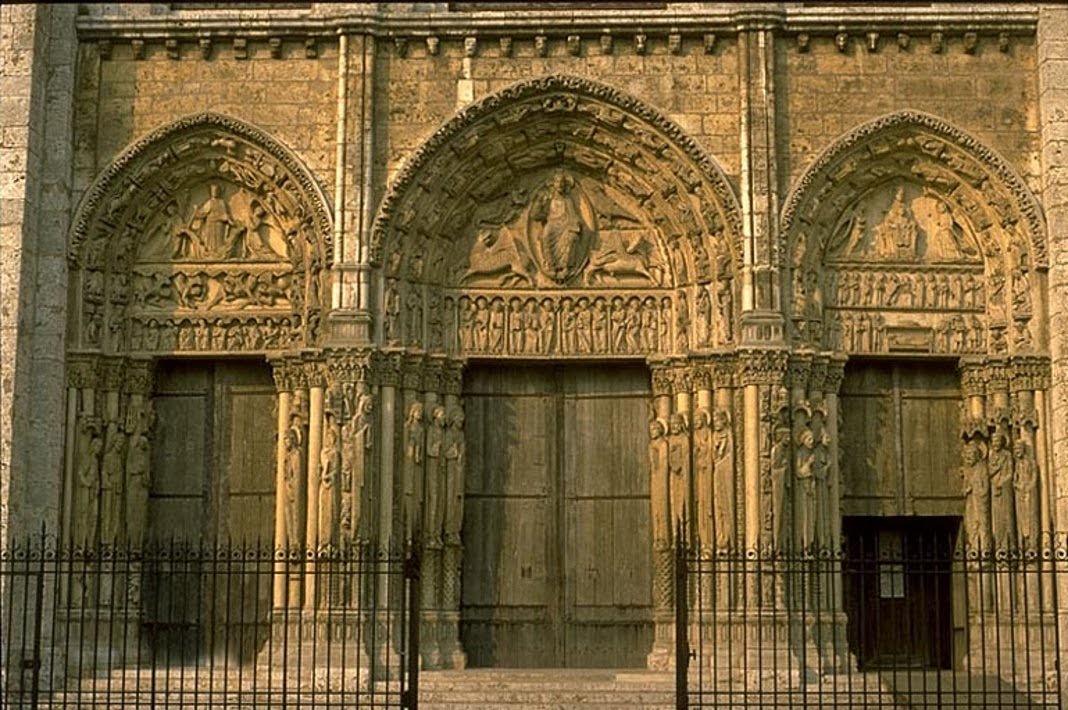


Great Portal
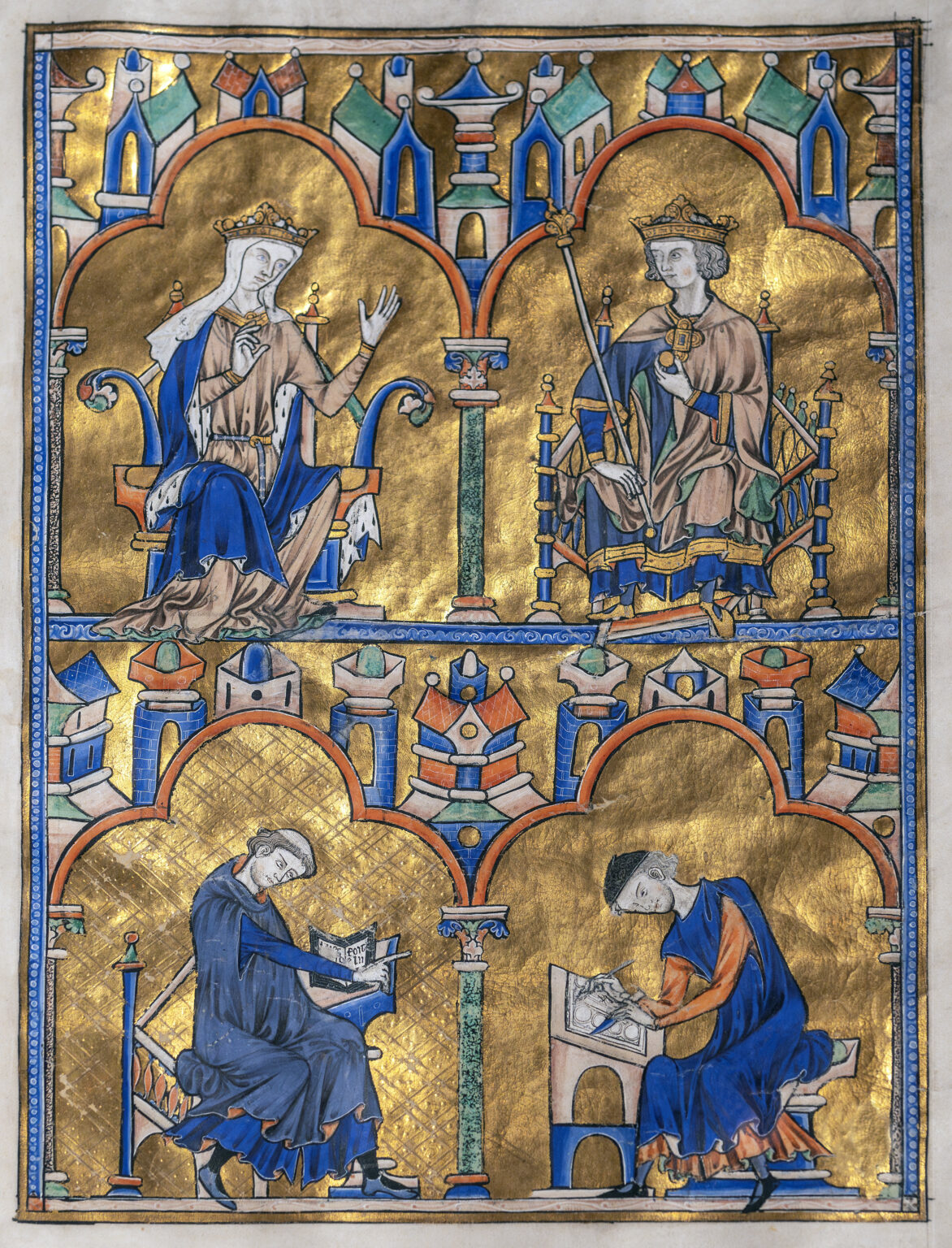


Dedication Page with Blanche of Castile and King Louis IX of France, Scenes from the Apocalypse from Bibles moralisées .Gothic Europe. c. 1225–1245 CE. Illuminated manuscript (ink, tempera, and gold leaf on vellum).


# 66 Annunciation Triptych (Merode Altarpiece). Workshop of Robert Campin. 1427– 1432 C.E. Oil on wood.