Product Design
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Total Stress
S = normal + shear
Stress
F/A
Strain
change in length / original length
units of stress
N/m²
Units for strain
dimensionless
Area of cylinder
pi r²
elastic modulus
A measure of a material's stiffness, defined as the ratio of stress to strain.
Gigapascals
10^9
Pascal
N/m²
elastic modulus for rubber
0.01 to 0.1 Gpa
elastic modulus for plastic
0.7 to 14 GPa
elastic modulus for steel
200 GPa
delta strain (e prime)
change in b over b (lateral strain —> perpendicular to applied force
poissons ratio
v = - lateral/longitudinal strain = -e’/eIt quantifies the ratio of transverse strain to axial strain in a material under load.
ductile
bends before break. goes back to original shape. deform significantly under stress before fracturing
brittle
does not bend before it breaks. chalk. broke without bending at all
elastic deformation
reversible; object will return to original shape
plastic deformation
irreversible; after large deformation, which is initially elastic
stress strain curve
graph showing relationship between stress and strain in materials
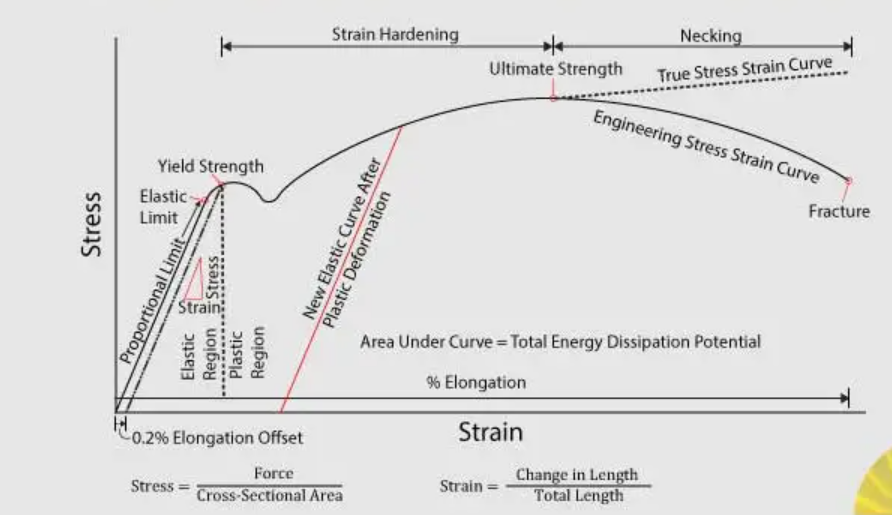
failure
for most ductile materials, failure occurs if we have reached yield strengthand the material cannot withstand further loading.
factor of safety
allowed stress = yield strength / n
polymers
long chains of repeating molecules that exhibit unique mechanical and thermal properties, making them suitable for various applications in product design.
is wood a polymer
yes
is skin a polymer
yes
the raw material to make most plastics is oil
True
thermosets (heat + permanent)
epoxy resin is an example
thermoplastics
most common with toys; heated and harden again to original state when cooled. molded to complex shapes. easy to reshape
common thermoplastics
ABS, PVC, PolyPropylene (PP), PolyEthylene (PE), PolyStyrene (PS), Acrylic, PolyCarbonate (PC), POlyEsters (PET), PolyAmide (Nylon)
ABS
hard with high impact resistance; takes color well with excellent surface finish. Consumer product cases. Most expensive out of PVC, PP, PE. Examples: Legos, suitcases
PVC
Cheap, heavy, rigid, durable. Vinyl toys. Examples: CDs, rubber duck, inflatable boat
PolyEthylene PE
most common plastic. cheap, flexible, easy to mold. Examples: crates, shampoo bottles, milk container, plastic bags
PolyPropylene PP
similar to PE but more rigid, doesn’t fatigue hinge/snap. examples: straws, markers, pill bottles
polystyrene PS
clear, hard, cheap. makes styrofoam.
crazing
network of small voids or cracks
PolyMethyl MethAcrylate (PMMA)
acrylic, plexiglass, transparent like glass, hard, brittle. Examples: lamps, fish bowl
polycarbonate
the “engineering” plastic. expensive, tough, rigid, clear. Safety glasses, laptops, hard hats
Polyethylene terepththalate (PET,
cheap, transparent, food products, barrier to moisture, easy to recycle: plastic soda bottles, ketchup bottles, t shirt, peanut butter jar
which is commonly used to manufacture groccery bags?
low density Polyethylene
which is the following is used to make CDs?
polycarbonate is very tough and optically transparent
what type of plastic used to make styrofoam?
polystyrene
compression molding
for complex parts with various thickness. thermosets and some advanced thermoplastics
extrusion
like pasta extruder. constant profile extrusion (pipers0. high volume bc dies are expensive
injection molding
for thin, constant parts. mass production because molds are expensive. think forks, legos
thermoforming (vacuum forming)
for thin sheets, simples one sided forms. glass transition, relaxing the chain
blow molding
for open thin walled hollow parts. Milk jugs, most bottles
rotational molding
for simple closed hollow shapes. good for inexpensive large parts
what process is used to make plastic pipers
extrusion molding
which process best for making plastic die?
The most appropriate process for making a plastic die is A. Injection molding.
Here's why:
Injection molding: involves injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies, forming the desired shape. This method is well-suited for creating complex shapes and intricate details, making it ideal for producing the precise geometry of a die.
Blow molding: is used for creating hollow plastic parts, not solid dies.
Plastic forming: refers to shaping plastic materials, but it doesn't involve the same level of precision and repeatability as injection molding for creating a die.
Extrusion molding: is used to make long, continuous shapes, not solid dies.
which process would be most appropriate for making a plastic drinks bottle
The most appropriate process for making a plastic drinks bottle is B. Blow molding.
Explanation: Blow molding is specifically designed to create hollow, thin-walled plastic objects like bottles, making it the ideal choice for this application.
Why other options are incorrect:
A. Injection molding:
While injection molding can create solid plastic parts, it's not as efficient for hollow objects like bottles. It's better suited for solid components like bottle caps.
C. Plastic forming:
This is a general term encompassing various plastic manufacturing techniques, including blow molding, injection molding, and others. It doesn't describe a specific process.
D. Extrusion molding:
Extrusion molding creates a continuous plastic tube, which is then used in other processes like extrusion blow molding, but it's not the primary method for making bottles on its own.
which process is most appropriate for making a thin plastic bowl
The most appropriate process for making a thin plastic bowl is B. Blow molding.
Explanation: Blow molding is specifically designed to create hollow, thin-walled plastic parts by inflating a heated plastic tube within a mold, making it ideal for producing items like bottles and bowls.
Why other options are not as suitable:
A. Injection molding:
While injection molding can produce thin parts, it's better suited for more complex shapes and solid parts. It may not be as efficient for thin-walled hollow items like a bowl.
C. Thermoforming:
Thermoforming involves heating a plastic sheet and forming it into a mold. While it can create thin parts, blow molding is generally more efficient and cost-effective for hollow shapes.
D. Extrusion molding:
Extrusion is used to create continuous profiles like pipes or rods. It's not designed for hollow, thin-walled shapes like a bow