Radiation Biology: Ch. 9
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
science that deals with the incidence, distribution, and control of disease in a population
epidemiology
what does epidemiology compare
incidence of disease within groups of people
ex: radiation induced cancer vs. natural incidence in the human population
the formation of cancer
carcinogenesis “tumorigenesis”
what is cancer defined as
disease in which healthy cells have been transformed into nonstandard cells that divide uncontrollably
graphic representation that maps the observed effects of radiation exposure in relation to the dose of radiation received
radiation dose-response relationship (DR curve)
types of DR curves
linear or non-linear
threshold or non threshold
implies biologic response to radiation is directly proportional to the dose received
linear relationship, straight line
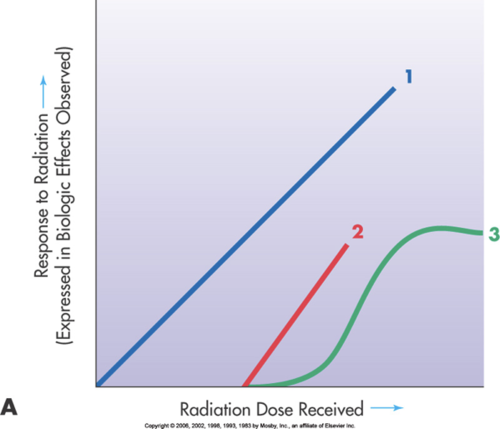
what is each line on this graph
linear non threshold
linear threshold
non linear threshold
curved to some degree, can be threshold or non threshold
non linear
what is a Sigmoid or S-shaped curve generally employed in
radiation therapy to demonstrate high dose, dose cellular response
is the point at which a response or reaction first occurs, below this level nothing occurs
graph begins at some point after 0
threshold
what does a linear non-threshold graph mean
some biological effects are caused in living organisms by even the smallest doses of ionizing radiation
what type of graph are radiation protection standards based on
linear non threshold (LNT)
two types of models- one for high dose exposure and one for low dose exposure
linear and linear-quadratic
fits both high and low dose data, may overestimate the risk of low doses
linear model
shows that no biologic response curve occurs below a specific dose level
linear threshold
what does linear quadratic mean
the data depends on a dose to the 1st power and also on dose squared
what does the BEIR committee recommend the linear quadratic model for
leukemia only
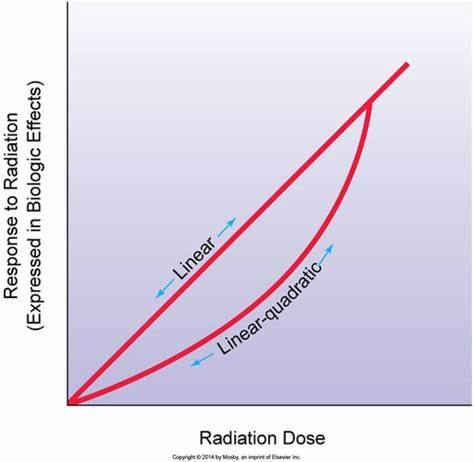
what is this curve representing
linear quadratic
which type of graph does the committee recommend for most types of cancers
linear non threshold
used for leukemia, breast cancer, heritable damage
more conservative dose response outcome for low level radiation
linear quadratic non threshold dose response
what are somatic effects
biological damage to living organism after being exposed to radiation
two classifications of somatic effects
stochastic
tissue reactions
in tissue reactions, what does both probability and severity depend on
the dose received
radiation induced damage at the cellular level may lead to measurable somatic and hereditary damage in the living organism or later on in life
late somatic effects
examples of late tissue reactions
cataract formation
fibrosis
organ atrophy
loss of parenchymal cells
reduced fertility
sterility
examples of stochastic effects
cancer
genetic effects
what has low level radiation dosage been defined as
equivalent dose of 0.1 Sv or less delivered over a short time and larger dose delivered over a long time
3 categories of consequences also require study at low dose levels, concluded by scientific committees
cancer induction
damage to unborn from irradiation in utero
genetic effects
3 major types of late effects
carcinogenesis (late stochastic)
cataractogenous (late tissue)
embryologic effects (late stochastic)
predicts cancer incidence in terms of absolute risk or relative risk
risk models
model that forecasts that a specific number of malignancies will occur as a result of exposure
absolute risk model
model that predicts that the number of excess cancers will increase as the natural incidence of cancer increases with advancing age in a population
relative risk model
types of radiation induced cancers
bone cancer
leukemia
skin cancer
breast cancer
lung cancer
thyroid cancer
how was bone cancer received in the 1920’s and 1930’s
radium watch dial painters-radium incorporated into bone tissue because of being chemically similar to calcium
which bones were most affected by bone cancer
mandible, pelvis, femur
what other malignancies did radium watch dial painters receive
carcinoma of the epithelial cells lining the nasopharynx and sinuses
how much dose were watch dial painters assumed to have received
5Gyt
in the early years of last century, how did many die from lung cancer
European miners worked in uranium mines to extract uranium ore (radon gas is byproduct of uranium decay)
in the 1950’s and 1960’s which group of people were then used to mine uranium
Navajo people of Arizona and New Mexico when the government needed fuel for nuclear weapons
how much dose is assumed each worker received working in the mines
10 Sv or more
received cancerous skin lesions on the hands because of the lack of protection
early radiologists and dentists
why did skin cancer develop in patients
radiation for facials and hair removal treatments
in the 1940’s and early 1950’s doctors diagnosed thymus enlargement in infants, why did this lead to thyroid cancer 10-20 years later
infants were treated with 1.2 Gyt to 60Gyt of radiation to shrink thymus gland
thyroid is so close to the thymus the thyroid gland received substantial dose
what was the average dose to the thyroid across all of the marshal islands
12 Gyt
in the 1950’s to early 1960’s what lead to an increase (almost double) in the number of breast cancer cases
radiation was used to treat for relief of postpartum mastitis
which population of women have a lower natural incidence of breast cancer
Japanese women
atomic bomb survivors in Japan demonstrated higher incidence of breast cancer, what increase did the relative risk ratio have according to studies
4:1 to 10:1
what did studies show in Japanese survivors about leukemia
that there was a significant increase in leukemia in the exposed compared to the non-exposed
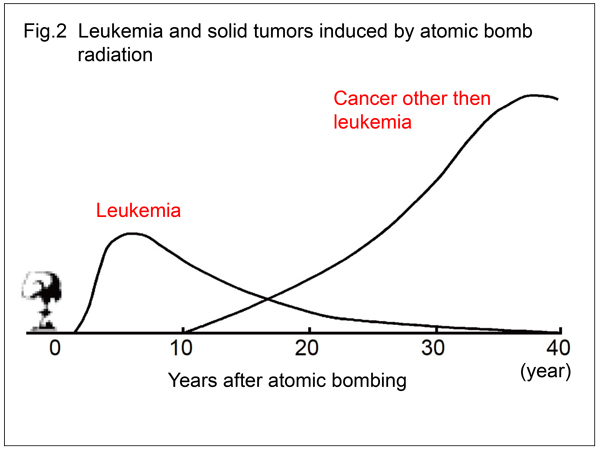
what is this graph indicating
leukemia occurs approx. 2 years after initial exposure and rises to highest level between 7-10 years, then at 30 yrs declines to almost 0
contracting leukemia is directly _______ to magnitude of radiation exposure and follows a ______ dose-response
proportional , linear non threshold
which type of cancer increased dramatically in the first 10 years after Chernobyl
thyroid cancer
in April of 1996, how many cases of thyroid cancer were diagnosed in children
700 cases
how was there an attempt to prevent thyroid cancer in children
potassium iodide administered intended to block uptake of iodine
some things that lab experiments on animals showed with radiation
life span of exposed animals was shorter, died sooner
radiation believed to accelerate all causes of death (nonspecific life span shortening)
accelerated aging process, more susceptible to diseases
what has the study started in 1982, of approx. 146,000 RT’s shown about radiation exposure
techs who began working before 1940 had slightly higher risk of dying from any type of cancer than those who began working before 1950
which population of RT’s have the greatest risk for breast cancer
those who began working before 1940’s
humans can expect reduced life span of 10 days for every ____ received
0.01 Gy
defined as the production of cataracts, formed by an accumulation of dead cells in the lens of the eye
cataractogensis
which type of dose-response does cataractogenesis follow
threshold non linear
what is the threshold for single exposure to the eye for cataract formation
0.5Gy
a gene that is mutated from a gene involved in normal cell growth
may cause growth of cancer cells, can be inherited or caused by being exposed to substances in the environment that cause cancer
oncogene