Chemistry - 3 Structure and Bonding - 3.9 Bonding in Metals & 3.10 Giant Metallic Structures & 3.11 Nanoparticles
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Metals form ...
crystals
Galvanised steel
applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron to prevent rusting
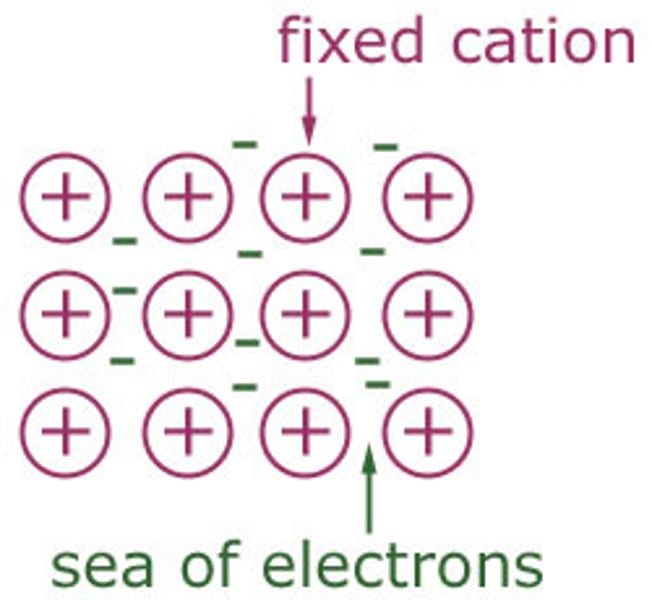
Metallic bonding [4]
- metal ions are arranged in fixed layers
- their electrons are free to move between them
- these electrons are delocalised and flow freely among the ions
- the strong electrostatic attraction between the positive ions and negative electrons hold the metal together
Properties of metals
- ductile
- malleable
- good thermal and electrical conductors
Alloy
a mixture of two or more metals
Why are alloys harder than pure metals? [3]
- different sized atoms of metals distort layers
- the layers cannot slide over one another as easily
- it is more difficult to change their shape
Why are metals malleable?
the layers of ions can slide over one another without breaking up the structure, as they are held together by delocalised electrons
Why are metals ductile?
layers of atoms can slide over each other
Why do metals have high melting and boiling points? [3]
- the electrostatic forces of attraction extend in all directions
- because electrons move freely
- it takes a lot of energy to overcome these forces
Why are metals good thermal and electrical conductors?
their delocalised electrons can flow and carry charges through the metallic lattice
Nano-
one billionth
Nanoscience
the study of molecules and nanostructures whose size ranges from 1 to 100 nanometers (one billionth of a meter).
What is the range of sizes a structure can be to be within nanoscience?
1-100 nm
For larger particles in the air, the unit used is
micrometres (μm)
Micro-
one millionth
These larger airborne particles are called
particulate matter (PM)
Coarse particles
particles with a diameter of 2.5-10 μm (PM₂.₅-PM₁₀)
Fine particles
particles with a diameter of 0.1-2.5 μm (PM₀.₁-PM₂.₅)
0.1 μm in nm
100 nm
1 nm in μm
0.001 μm
Nanoparticles have a high...
SA:V ratio, meaning a large proportion of their atoms are exposed at the surface
As the side of a cube decreases in size by a factor of 10,
its surface area to volume ratio increases by 10
The exposure of a large percentage of atoms at the surface of nanoparticles makes them
highly reactive
Why could nanoparticles be more sustainable? [2]
- they are more reactive
- less material is needed