Chapter 19: Epidemiology
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
study of distribution and causes of disease in populations (and its prevention and prediction); determine many daily practices (eg, handwashing); more significant in rate of diesase over case numbers



transmitted host-to-host (eg, influenza); contagious disease
arise from microbiota or environment (eg, Legionellosis); these diseases do not spread from one host to another
A disease constantly present in a population or region; may occur routinely
A sudden increase in disease cases within a specific area or population (local); may be caused by diseases not normally present in a population or by fluctuations in endemic incidences
A localized epidemic limited to a small group or area; group of cases occurring during a brief time interval and affecting a specific population; may indicate the onset of an epidemic.
Attack rate
The number of susceptible persons developing illness in a population who have been exposed to an infectious agent; reflects infectious dose and the general host population health
Secondary cases
Proportion of suseptible people ion contect with an infected individual that contract the disease
Basic reproductive number (R0)
The average number of secondary cases of a communicable disease per case of that disease in a susceptible population; if the number is greater than 1, the amount of new cases will increase over time; if the if the number is less than 1, the amount of new cases will decrease over time
Incidence
The number of new cases of a disease in a population at risk during a specified time period; measures the risk of contraction
Prevalence
The total number of cases of a disease in a given population at a point in time or over a specific time period; measures overall impact of a disease on society (chronic diseases)
Morbidity
Illness after contraction of a disease

Mortality
Death; rate of death or number of people in a population who die during a given period due to disease

Case-fatality rate
The proportion of persons diagnosed with a specific disease who die from that disease; changes over time based on changes of cases (new cases, improved treatments, and changed case definitions); how deadly a disease is among known cases
Infection-fatality ratio
Estimate of the proportion of persons infected with a given pathogen who die as a result of the infection; infections (identified and asymptomatic) estimated using serological data; how deadly a disease is among everyone infected
Qualitative data
Quantitative data
Reservoir of infection
The natural habitat of a pathogen; sum of the potential sources of an infectious agent; may be humans, animals, and the environment; must be identified to determine disease prevention
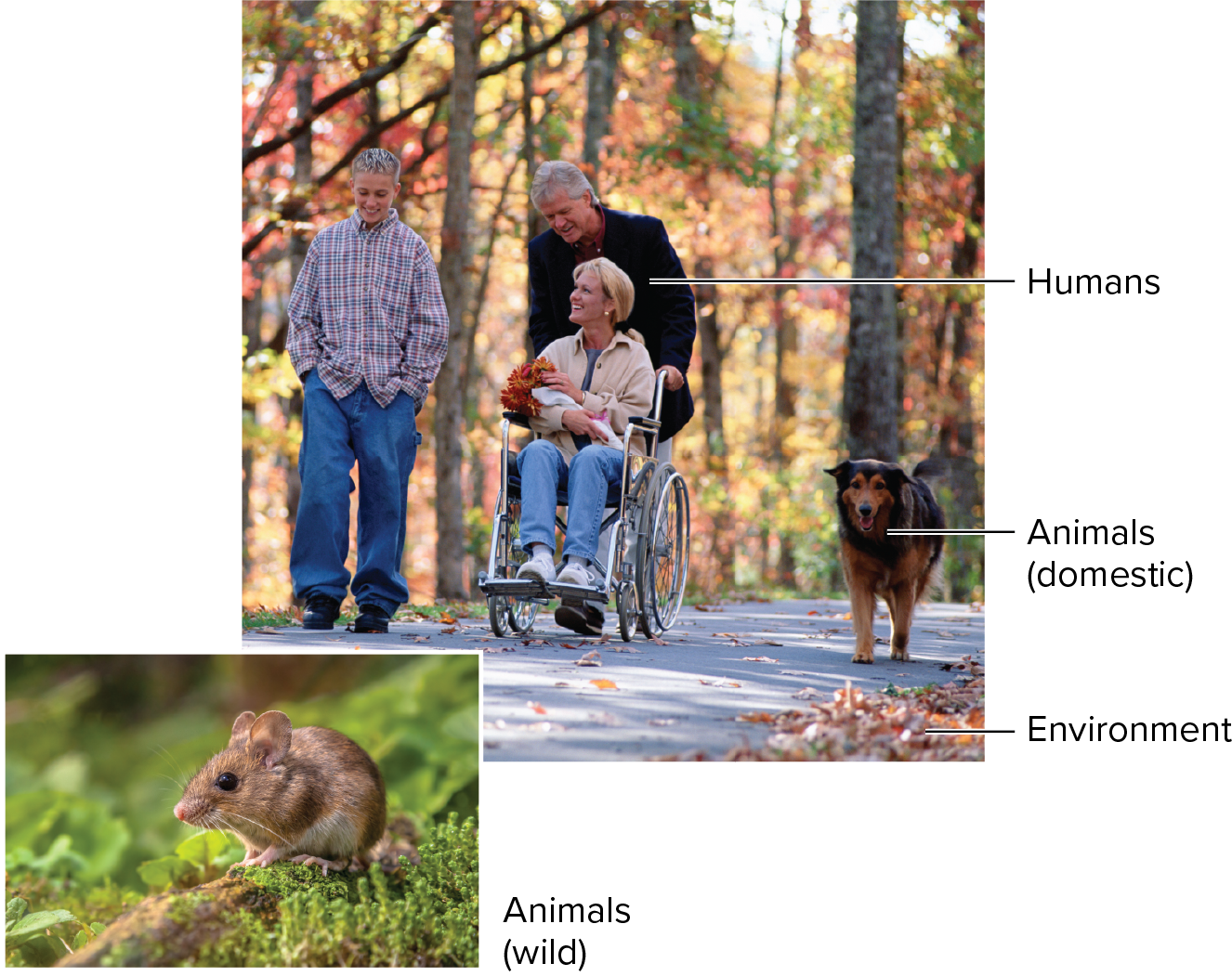

Human reservoirs
Often primary or the only reservoirs but may colonize non-humans and grow in the environment; easier to control as the only reservoir (e.g, smallpox)
Examples of zoonotic diseases
Campylobacter and Salmonella in poultry or the plague and rabies; often difficult to control as infection is often accidental
Examples of environmental diseases
Clostridium botulinum (botulism) and Clostridium tetani (tetanus) in soils; often difficult or impossible to eliminate
Portal of exit
Sites from which an infectious agent leaves the host to find a new host (e.g, Vibrio cholerae in feces or Mycobacterium tuberculosis in saliva)

Vertical transmission
Transfer of a pathogen from a parent to offspring; from a pregnant woman to the fetus, or from a mother to her infant during childbirth or breast feeding
Horizontal transmission
Transfer of a pathogen from one person to another through contact, through ingestion of food or water, or via a living agent such as an insect
Direct transmission
Transfer of a pathogen from one host to another without the use of an intermediate, transmission through touch, direct mucous-to-mucous membrane contact (e.g, Shigella and Neisseria gonorrhoeae)
Indirect transmission
Transfer of a pathogen from a reservoir to a host via airborne particles, vehicles (such as fomites, food, or water), or vectors
Cross-contamination
Transfer of pathogens from one item to another
Mechanical vector
Organism such as a fly that physically moves contaminated material from one location to another
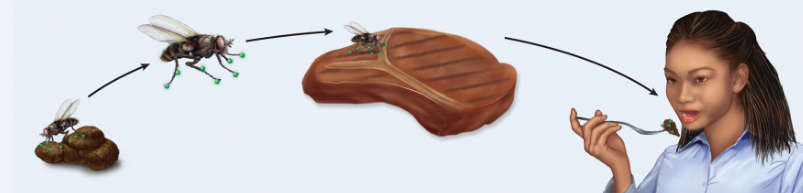
Biological vector
Organism that transmits a pathogen and within which the pathogen can multiply to high numbers; moves contaminated material by feeding on an infected host, multiplying, and feeding on another non-infected host

Fecal-oral transmission
Transmission of organisms that colonize the intestine by ingestion of fecally contaminated material
Disease dosage
Small amounts of germs usually do not cause sickness because the body fights them off; big exposures can make even healthy people sick, so care is needed
Susceptibility factors
Immunity, general health, gender, behavioral practices, genetic background, and age
Herd immunity
Protection of an entire population based upon a critical concentration of immune hosts that prevents the spread of an infectious agent; less people to spread = less incidence
Descriptive study
Study that characterizes a disease outbreak by determining the attributes of the persons affected (susceptibility factors) as well as the place (reservoirs) and time (propagated vs common-source); used to determine risk factors
Epi curve (epidemic curve)
A graph of that illustrates the progression of an outbreak by showing the distribution of cases over time; helps reveal how disease is spread
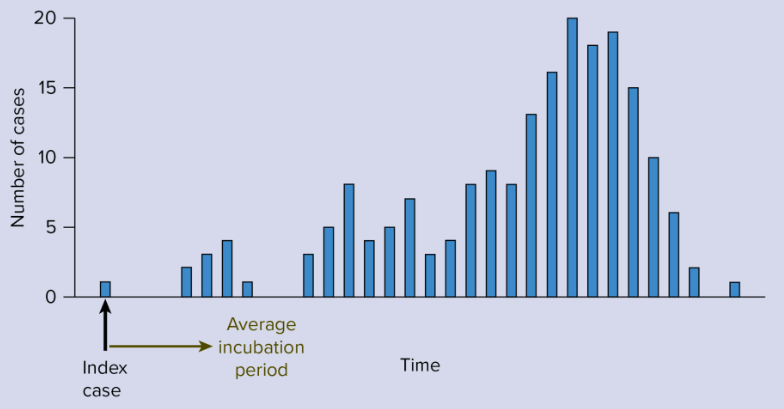
Propagated epidemic
Outbreak of disease in which the infectious agent is transmitted to others, resulting in steadily increasing numbers of people becoming ill

Common-source epidemic
Outbreak of disease due to contaminated food, water, or other single source of infectious agent; contact may be singular, continuous, or intermittent
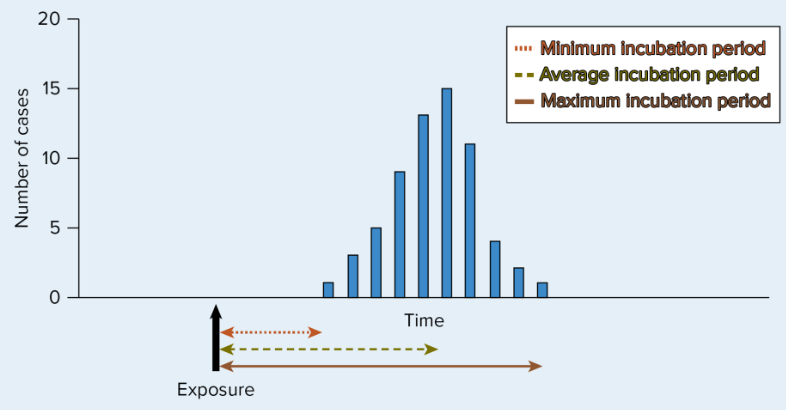
Analytical studies
A study done to identify which risk factors identified by descriptive studies are actually relevant to disease spread; include case-control, cross-sectional, and cohort

Case-control study
An epidemiologic study that compares activities of people who developed a disease (cases) with those of people who did not (controls); controls are compared for similarities to discover patterns

Cross-sectional study
Study that surveys a range of people to determine the prevalence of characteristics including disease, risk factors associated with disease, or previous exposure to a disease-causing agent; studies population traits
Cohort study
An epidemiological study conducted to see if previously identified risk factors actually predict a tendency to develop the disease; observes how different risk factors affect disease development
Experimental case
A study done to assess the effectiveness of measures to prevent or treat disease; often tested with a double-blind method with the use of placebos and real treatments

Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
The U.S. government agency charged with the task of controlling and preventing diseases and injuries; provides support for public health departments, collects data on diseases affecting public health, and distributes health information; researches infectious diseases, offers training, and responds globally to epidemics

National Wastewater Surveillance System (NWSS)
System developed to detect the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater to detect virus spread and detect other pathogens as well (e.g, mpox and polio)
Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR)
Weekly report by the CDC offering insights into disease prevention and significant case reports, like the AIDS epidemic's start; aids professionals and students by providing epidemiological data

World Health Organization (WHO)
International agency devoted to improving the health of all people by helping to fight diseases worldwide; focuses on neglected tropical diseases, collects health data globally, and shares updates on global health issues (Weekly Epidemiological Record).
Emerging infectious disease (EID)
An infectious disease that has become more common or more widespread in the last several decades
Disease emergence factors
Microbial evolution, complacency, misinformation, widespread use of antibiotics, societal changes, technological advances, population growth, development, mass food production/distribution/importation, war/civil unrest, and climate change
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs)
Infections acquired while receiving treatment in a hospital (nosocomial infections) or other healthcare facility
HAI factors
Patient microbiota, healthcare environment, other patients, visitors, and healthcare workers
HAI prevention
Hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE) use, respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette, patient placement, patient-care equipment/device sanitation, textiles/laundry handling, safe injection practices, and worker safety/proper sharps handling
Transmission-Based Precautions
A set of measures used in addition to Standard Precautions when caring for a patient who is, or might be, infected with a highly transmissible or epidemiologically important pathogen