Industrial Hygiene
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Industrial Hygiene
science of protecting health and safety through anticipation, recognition, evaluation and control of workplace conditions that may cause workers injury or illnes
Types of health hazards
Chemical
Biological
Physical
Ergonomic
Chemical Hazard Forms
Solids
Liquids
Gases and Vapors
Aerosols- dust, mist, fumes
Effects of chemical exposure
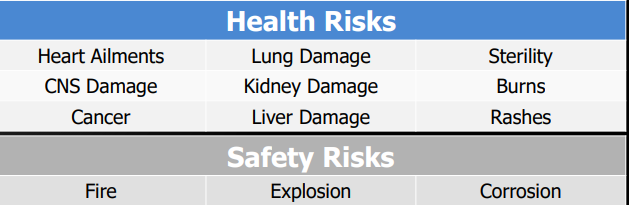
Exposure entry routes
Inhalation
Ingestion
Absorption
Injection
Inhalation
Breathed in (Most common route)
Ingestion
Swallowing via eating or drinking
Absorption
Drawn through skin or eye surface
Injection
Penetration through the skin
Warning Signs of Potential Chemical Exposure:
Dust, mist, smoke in the air
• Accumulation of particulates (dust) on surfaces
• Unusual tastes and/or smells
• Eye, nose, throat, upper respiratory, and/or skin irritation
Examples of chemical exposure symptoms:
• Eye, nose, throat, upper respiratory, skin irritation
• Flu-like symptoms
• Difficulty breathing
• Fatigue
• Loss of coordination
• Memory difficulties
• Sleeplessness
• Mental confusion
Health Effects
Toxicology
The science that studies the poisonous or toxic properties of substances
Local (direct) effects:
• Irritation (dryness, redness, cracking) - fiberglass
• Corrosion (chemical burn) - acid
• Upper Respiratory Track Infection – inhaling particles
Systemic effects:
Hepatotoxins
Nephrotoxins
Neurotoxins
Hepatotoxins
Cause liver damage
• Carbon tetrachloride, nitrosamines
Nephrotoxins
• Cause kidney damage
• Uranium, halogenated hydrocarbons
Neurotoxins
Cause nerve damage
• Mercury, lead, carbon disulfide
Hematotoxins
Cause blood system damage
• Carbon monoxide, cyanides
Anesthetics
Depress nervous system
• Hydrocarbons, propane, isopropyl ethers
Factors affecting exposures:
form and innate chemical activity
• dosage, especially dose-time relationship
• exposure route
• age
• sex
• ability of chemical to be absorbed
• metabolism
• distribution within the body
• excretion
• presence of other chemicals
Chemical Hazards and Control (Elimination and Substitution)
Engage
Inventory and Prioritize
Identify
Assess and Compare
Select
Test
Evaluate
Engineering controls
Ventilation – local (hood) / general (dilution)
• Process and equipment modification
• Isolation/automation
Administrative controls
• Establish written programs & policies
• Training
• Monitor/measure exposure levels
• Inspections and maintenance
• Restricted area signage
• Develop SOPs
PPE
• Respirators
• Gloves
• Safety glasses
• Long clothing
Worksite analysis – assessing exposures:
• Air monitoring – personal and area
• Noise monitoring
• Observation – PPE use and work practices
• Ventilation measurements
• Wipe samples – surfaces and personnel
PELs, or permissible exposure limits:
OSHA’s regulations that establish the acceptable amount or concentration of a substance in the workplace
• Intended to protect workers from adverse health effects related to hazardous chemical exposure
Substance-specific standards
Established by OSHA to identify specific requirements
• Potentially exposed workers must be monitored and protected
Components of substance specific standards: (in general)
• Air monitoring
• Control of exposure
• Engineering controls
• Work practices
• Respiratory protection
• Medical surveillance / removal (lead)
• Recordkeeping
• Worker training
Hexavalent chromium:
Toxic form of chromium;
• Known to cause cancer
• Compounds are man-made and widely used •
Major source of exposure during “hotwork” on stainless steel and other alloy steels containing Cr (VI)
Asbestos:
• Mineral fibers – chrysotile, amosie, crocidolite, tremolite, anthophylite, actinolite, and chemically treated/ altered forms
• Known carcinogen; can cause chronic lung disease, as well as lung and other cancers
• Used in numerous building materials and vehicle products
• Exposure potential during construction and ship repair; as well as manufacturing of products containing asbestos
Silica:
• Important industrial material found abundantly in the earth’s crust; most common form is quartz
• Can cause lung diseases, including silicosis and lung cancer, as well as kidney disease
• Exposure to respirable crystalline silica
• Inhalation of small particles in air
• Common with operations such as cutting, sawing, and drilling
Lead:
Blue-gray, heavy metal occurring naturally in Earth’s crust
• Can harm many of the body’s organ systems; variety of ailments
• Exposure
• Inhalation and/or ingestion of airborne particles containing lead
• Occurs in most industry sectors, including manufacturing, wholesale trade, transportation, construction, remediation, and even recreation
Welding Fumes
Content depends on components of base metal, coatings, and/or filler materials; and welding temperatures
• Potential health effects
• Acute exposure: eye, nose, and throat irritation; dizziness; nausea
• Prolonged exposure: lung damage; various types of cancer, including lung, larynx, and urinary tract
• Certain fumes and gases can lead to additional health issues
Exposure to welding fumes affected by:
Welding process
• Materials used
• Location (outside, enclosed space)
• Work practices
• Air movement
• Use of ventilation
Toxic atmospheres:
Confined spaces and Hazardous atmospheres
Confined spaces
storage tanks, process vessels, bins, boilers, ventilation or exhaust ducts, sewers, underground utility vaults, tunnels, pipelines, opentop spaces more than 4’ in depth (pits, tubs, vaults)
Hazardous atmospheres
Oxygen-deficient
• Hydrogen sulfide
• Carbon monoxide
Biological hazards and control
Insects
Animals
Contaminated Soils
Poisonous Plants
Water/Sewage
Bloodborne Pathogens
Possible effects of exposure to biological hazards:
Mild, allergic reactions
• Serious medical conditions
• Death
• Most virulent and prevalent biological agents
Protection against biological hazards:
• Practice universal precaution with:
• Blood
• Bodily fluids
• Practice personal hygiene
• Provide proper first aid
• Cuts/Scratches
• Vaccinations
• Wear proper PPE/clothing
Types of Physical Hazards
Temperature, Radiation, Vibration, Noise
Effects of exposure to physical hazards:
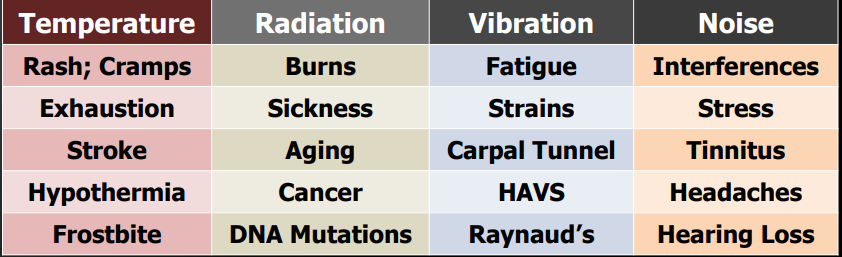
Exposure to heat
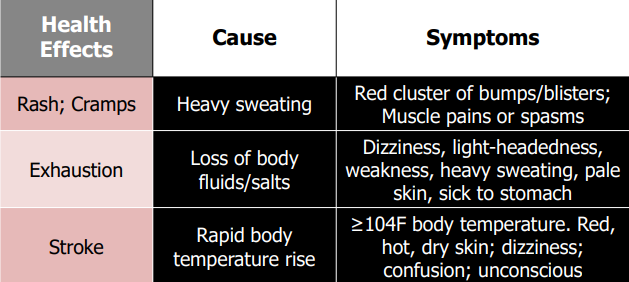
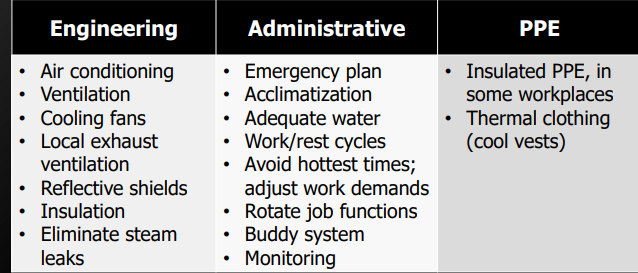
Protection against heat:
Eliminate or substitute hazard, whenever feasible
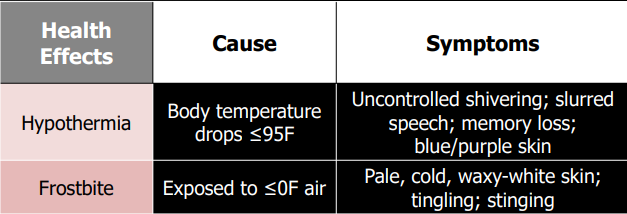
Exposure to cold:
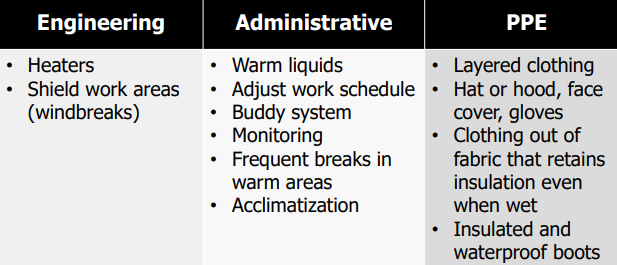
Protection against cold:
Exposure to radiation:
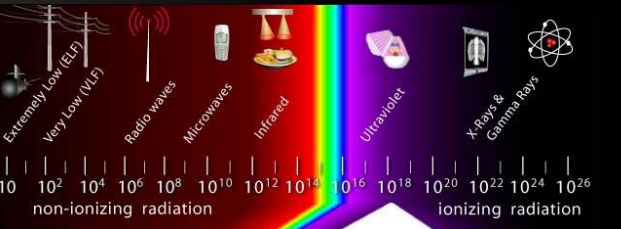
Protection against radiation:
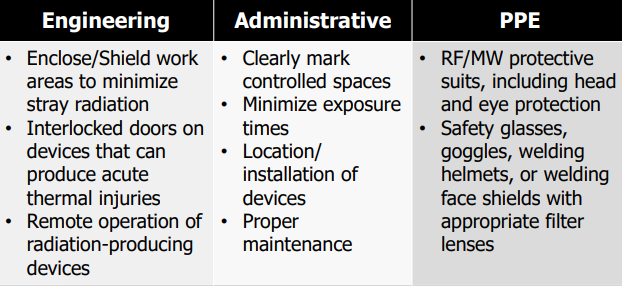
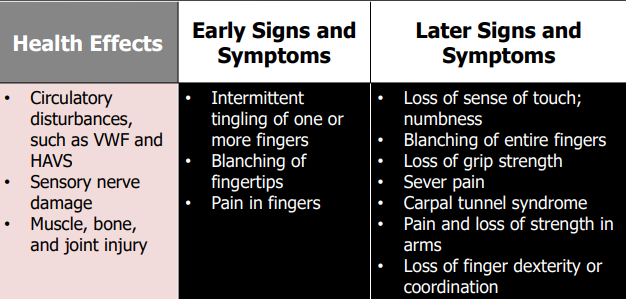
Exposure to vibration:
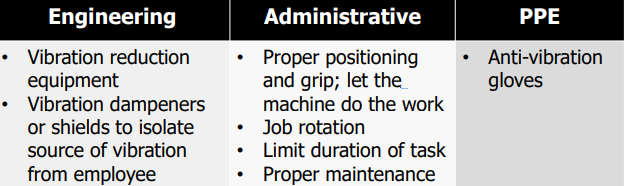
Protection against vibration:
Exposure to noise:

Noise
prolonged exposures to 85 dB can lead to hearing loss
prolonged exposures to 85 dB can lead to hearing loss
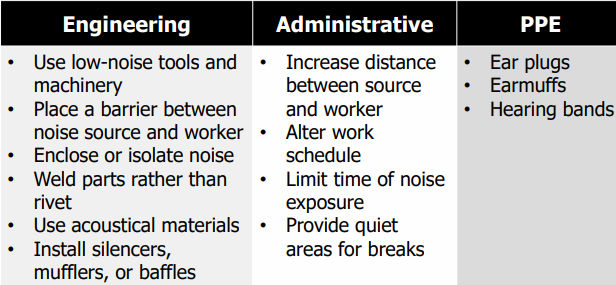
When to wear hearing protection
Noise or sound level exceeds 90 dBA (OSHA) • Recommended when exceeds 85 dBA (NIOSH)
• What to wear as hearing protection
Personal comfort preference
• Long-term/Single use (plugs)
• Short-term/On and off (muffs)
• Consider NRR
Effects of exposure to ergonomic hazards:
• Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)
• Exposure to ergonomic risk factors for MSDs increases a worker's risk of injury
• Repetition
• High force
• Awkward postures
• Work-related MSDs are among the most frequently reported causes of lost or restricted work time.
Risk factors for MSDs:
• Overexertion
• Repetitive tasks
• Awkward posture/positions
• Localized pressure
• Cold temperatures
• Vibration
• Combined exposure
Protection against ergonomic hazards:
• Use ergonomically designed tools
• Use correct work practices
• Proper lifting techniques
• Ask for help when handling:
• Heavy loads
• Bulky/Awkward materials
• Properly fitting PPE