N470: Oncology
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
The formation and development blood cells
hematopoiesis
Where does hematopoiesis occur in adults?
bone marrow and lymphatic tissues
hematopoiesis process (may not be important)
1) Pluripotent stem cell
2) lymphoid progenitor cell
3) b and t stem cells
4) b and t lymphocytes
5) b lymphocytes further to plasma cells
6) myeloid progenitor cell-3 further types
- granulocytes and monocytes line
- erythroid- RBCs
- megakaryocytic line- platelets
2 types of bone marrow and their purpose
1) yellow (adipose): Produces fat, cartilage, and bone
2) Red (hematopoietic): Stem cell produces all three types of cell
- found in flat/irregular bones
Group of malignant disorders affecting the blood and blood forming tissues
leukemia
where do Myeloid leukemias start?
in immature forms of myeloid cells
where do Lymphocytic leukemias start?
in immature forms of lymphocytes
Etiologies of leukemia (5)
1) Smoking
2) genetic
3) radiation & chemical exposures
4) drugs
5) viruses
Patho of leukemia
lack of normal regulatory mechanisms of bone marrow cell proliferation and maturation
General symptoms of leukemia
1) fever
2) fatigue
3) night sweats
4) SOB
5) bruising
6) petechiae
7) bone/joint pain
Secondary (physiological) symptoms of leukemia (5)
1) anemia
2) leukopenia
3) thrombocytopenia
4) swollen lymph nodes
5) enlarged liver or spleen
Acute leukemia patho
- bone marrow cells cannot mature properly
- Immature leukemia cells continue to reproduce and build up
- Without treatment, live only a few months.
Chronic leukemia patho
- cells can mature partly but not completely
- cells live longer, build up, and crowd out normal cells
- most can live for many years.
Abbreviations for types of leukemia
- Acute (A)
- Chronic (C)
- Myeloid cell type (M)
- Lymphoid cell type (L)
Leukemia diagnostic tests (3)
1) Bone Marrow Biopsy: increased # of immature cells (blasts)
2) WBC range: <1000/mm3 to >100,000/mm3 (*differential to identify type)
3) Platelets & Hemoglobin – low
Malignant disorders which arise from lymphatic structures
Lymphoma
Describe Hodgkin Lymphoma (4)
•Presence of Reed Sternberg cells
•Spreads contiguously
•Altered B cells
•80% survival
Describe Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (2)
•B, T, or NK cells
•Spreads non contiguously
Lymphoma diagnostics (3)
•Biopsy of lymph node(s)
•Lumbar puncture: leukemic cells in CNS
•MRI/CT/PET: infiltrates and/or sites of infection
Treatment for heme cancers (5)
1) Chemotherapy
•Induction
•Consolidation
2) Radiation therapy
•Targeted
•Total Body Irradiation
3) Targeted Therapy
•Specific gene mutation
•Biotherapy
4) Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant
•Autologous
•Allogeneic
5) CAR T cell Therapy
Supportive care for leukemia (7)
•Anti-infectives
•Antipyretics
•Transfusions
•Fluids and electrolytes
•Symptom Management
•Psychological
•Spiritual
carcinogenesis stages (3)
1. Initiation
2. Promotion
3. Progression
carcinogenesis stages:
Mutation of cellular DNA, cellular differentiation
Initiation
carcinogenesis stages:
Growth of altered cells; Can still potentially stop cancer growth (Promoting factors)
Promotion
carcinogenesis stages:
Tumor growth rate increases, metastasis occurs through lymph and vascular routes
Progression
Three types of carcinogens
1) viral
2) chem
3) radiation
patho of cancer cells
stem cells --> differentiation --> dedifferentiation
general mutations that promote cancer development
- mutation of proto-oncogenes into oncogenes
- mutations that inactivate tumor suppressor genes
What do cancer cells lack?
- contact inhibition
- apoptosis
how does metastasis occur?
- lymphatic and vascular routes
- angiogenesis
time it takes for tumor to double in size
doubling time
Proliferation time does not increase in CA cells, but instead is ______________
Proliferation time does not increase in CA cells, but instead is continuous
How is the growth rate of cancer determined?
mitotic rate of cells of origin
Why is the geriatric population more likely to die from cancer? (2)
- Symptoms may be attributed to old age leading to later stage at diagnosis
- Comorbidities
Primary prevention of cancer (5)
-Decrease/eliminate exposure to carcinogens
-Healthy diet
-Exercise
-Alcohol in moderation
-Limit UV exposure (Sun/tanning beds)
Secondary prevention of cancer (3)
-Inspection
-Palpation
-Screening
Cancer warning signs (CAUTION) *
C: change in bowel or bladder habits
A: a sore that does not heal
U: unusual bleeding or discharge
T: thickening of a lump
I: indigestion or trouble swallowing
O: obvious change in mole
N: nagging cough or hoarseness
How is extent of cancer (with solid tumors) determined? (4)
- anatomic site
- clinical staging (0-IV)
- histological grading (I-X)
- classification (T, N, M)
classification of cancers
- Tumor: T1-T4
- Node: N1-N3
- Metastasis: M0-M1
4 treatment modalities for cancer
Surgery, Radiation therapy, Chemotherapy, Immunotherapy
What does cancer grade X mean?
cannot tell origin
What does M1 mean in the TNM system?
metastasis present
Most common cancers that cause death (4)*
•Lung
•Prostate OR breast
•Colon/Rectum
•Pancreas
Leading cause of cancer related death in the United States
lung cancer
Risk factors for lung cancer (6)
-Smoking (#1)
-Pollution
-Radiation Exposure
-Asbestos Exposure
-Exposure to Industrial Agents (nickel, coal dust, formaldahyde)
-EGFR gene
Early symptoms of lung cancer (5)
- persistent cough
- blood tinged sputum
- dyspnea
- wheezing
- chest pain
Late symptoms of lung cancer (6)
- anorexia
- fatigue
- weight loss
Metastasis
- SVC syndrome
- pericardial effusion
- dysphagia
Diagnostic tests for lung cancer (4)
-CXR: identifies masses
-CT scan: can i.d. location, mediastinal involvement, lymph node enlargement
-Biopsy (sputum cytology, pleural fluid)
-MRI, PET, Bone scan, CBC, CMP to assist with staging
treatment for lung cancer (4)
- Surgical resection (non small cell; *stage I-IIIA only)
- radiation
- chemotherapy
- targeted therapy
Risk factors for colorectal cancer (4)
-Diet (red/processed meat)
-Lifestyle
-History of IBD
-Heredity
colorectal cancer is most commonly _________________ arising from __________
colorectal cancer is most commonly adenocarcinoma arising from polyps
Symptoms of colorectal cancer (5)
-Anemia
-Rectal bleeding
-Abdominal pain
-Change in bowel habits
-Tenesmus (heavy feeling in bum)
Diagnostic studies for colorectal cancer (5)
-Flexible sigmoidoscopy
-Colonoscopy
-CEA
-FOBT
-Know family history
treatment for colorectal cancer
1) Surgery
•Resection of tumor with clear margins
•Excision of regional lymph nodes
•Colectomy
3) Targeted Therapy
•Avastin, Erbitux
4) Radiation
Risk factors for breast cancer (10)
–Age – most important
–Ethnicity – highest risk for African-American women
–Long hormonal cycle exposure (early menarche & late menopause)
–Pregnancy history: nulliparity & first child after 30yo
–HRT (estrogen + progesterone)
–Benign breast disease combined with family history
–Family history: 15-20% (genetic + environmental)
–Genetics: BRCA1, BRCA2, & p53 tumor suppressor gene (5-10%)
–Hx of mantle radiation @ < 20yo for Hodgkin’s lymphoma
–Dietary: alcohol (2-5 drinks/ day); increased dietary fat
Symptoms of breast cancer (6)
-Skin changes- dimpling, thickening
-Lump
-Nipple discharge
Metastatic Disease
-Dyspnea
-Back pain
-Confusion/altered LOC
Diagnostic Tests for breast cancer (4)
- Mammography
- U/S
- Biopsy
- HER2/hormone receptor status
Treatment for breast cancer (4)
1) Surgery
-Lumpectomy
-Mastectomy
2) Radiation
-External Beam (5x/week 5-7 weeks)
-Brachytherapy (5 days)
-Palliative (bone pain, brain)
3) Chemotherapy
-Treat known or suspected metastatic disease
4) Hormonal Therapy
-Used to treat hormone receptor positive breast cancer
what is triple negative breast cancer?
Negative for estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 receptor. Difficult to treat w/ conventional therapy.
Most common gynecological cancers
1 - Endometrial
2 - ovarian
3 - cervical
Risk factors for endometrial cancer (6)
- Estrogen (unopposed)
- Age
- Nulliparity
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Diabetes
Risk factors for ovarian cancer (7)
- BRCA gene mutation
- Nulliparity
- Early menarche
- Late menopause
- Obesity
- Family history
- Age
Risk factors for cervical cancer
- Exposure to HPV
- Multiple sexual partners or partner with multiple sex partners
- Early age of first intercourse
- Smoking tobacco
- Untreated chronic cervical infections
- STDs
GYN cancers are often __________________ until later stages
GYN cancers are often asymptomatic until later stages
Symptoms of endometrial cancer (2)
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
- Pain
Diagnostic tests for endometrial cancer (2)
- Biopsy
- Hormone Receptor status
Symptoms of ovarian cancer (6)
- Vague symptoms
- Abdominal pain or bloating
- Changes to bowel or bladder
- Early satiety
- Weight loss or weight gain
- Menstrual changes
Diagnostic tests of ovarian cancer (3)
- No specific screening test
- U/S
- Pelvic exam
Symptoms of cervical cancer (6)
- Dysplastic changes are asymptomatic
- Leukorrhea & bleeding
- Pain
- Bowel or bladder changes
- Weight loss
- Anemia
Diagnostic tests of cervical cancer (3)
- Pap smear
- Colposcopy
- Biopsy
treatment for GYN cancers (4)
1) Radiation
- External Beam
- Brachytherapy
2) Surgery
- Vaginal vs Abdominal hysterectomy
3) Chemotherapy
4) Hormone Therapy
Risk factors for prostate cancer (5)
-Age
-Ethnicity
-Family History
-Diet high in red meat and high fat dairy, low intake vegetables
-Occupational (fertilizer, textile, & rubber industries)
Symptoms of prostate cancer (3)
-Asymptomatic in early stages
-Urinary changes
-Pain in lumbosacral area (metastases)
Diagnostic tests for prostate cancer (4)
-PSA testing (risk vs benefit)
-DRE
-Transrectal resection of prostate (biopsy)
-MRI/CT (metastases)
Prostate cancer treatment (5)
1) Active surveillance
2) Radiation
-External beam
-Brachytherapy
3) Hormone Therapy
4) Chemotherapy (palliative)
5) Surgery
-Radical Prostatectomy (retropubic, perineal, laparoscopic, robotic assisted)
-Nerve sparing procedure- cancer limited to prostate only
Post-prostate surgery care (2)
-Catheter 3 way foley
-Perineal care
complications of prostate surgery (3)
-Hemorrhage, DVT, PE, infection
-ED
-Urinary incontinence
general cancer/treatment side effects (7)
1) BMS
2) fatigue
3) GI symptoms
4) integumentary effects- alopecia
5) reproductive loss
6) pain
7) respiratory, hepatic, and renal toxicities
Bone marrow suppression causes _____________ which can increase risk for ____________ and ___________
Bone marrow suppression causes pancytopenia which can increase risk for bleeding and infection
What are specific GI symptoms associated with cancer treatment? (4)
•Nausea/ Vomiting
•Diarrhea
•Mucositis
•Anorexia
Types of oncologic emergencies
1) Infiltrative
2) Obstructive
3) Metabolic
Cancer infiltrates organ or caused by treatment of cancer
Infiltrative onc emergency
Types of infiltrative onc emergencies (2)
1) cardiac tamponade
2) carotid artery rupture
emergency radiation may be indicated for... (2)
1) cardiac tamponade
2) carotid artery rupture
Why might cardiac tamponade occur in an onc patient?
tumor compresses the heart
Why might carotid artery rupture occur in an onc patient?
infiltrated tumor can erode blood vessels
Types of obstructive onc emergencies (3)
1) Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
2) Spinal Cord Compression
3) Intestinal Obstruction
In which cancers is Superior Vena Cava Syndrome most common? (3)*
1) Non-Hodgkin's (NHL)
2) breast
3) lung
Symptoms of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome (3) *think chest-up fluid overload*
1) HA
2) facial/periorbital edema
3) vein distention head/neck/chest
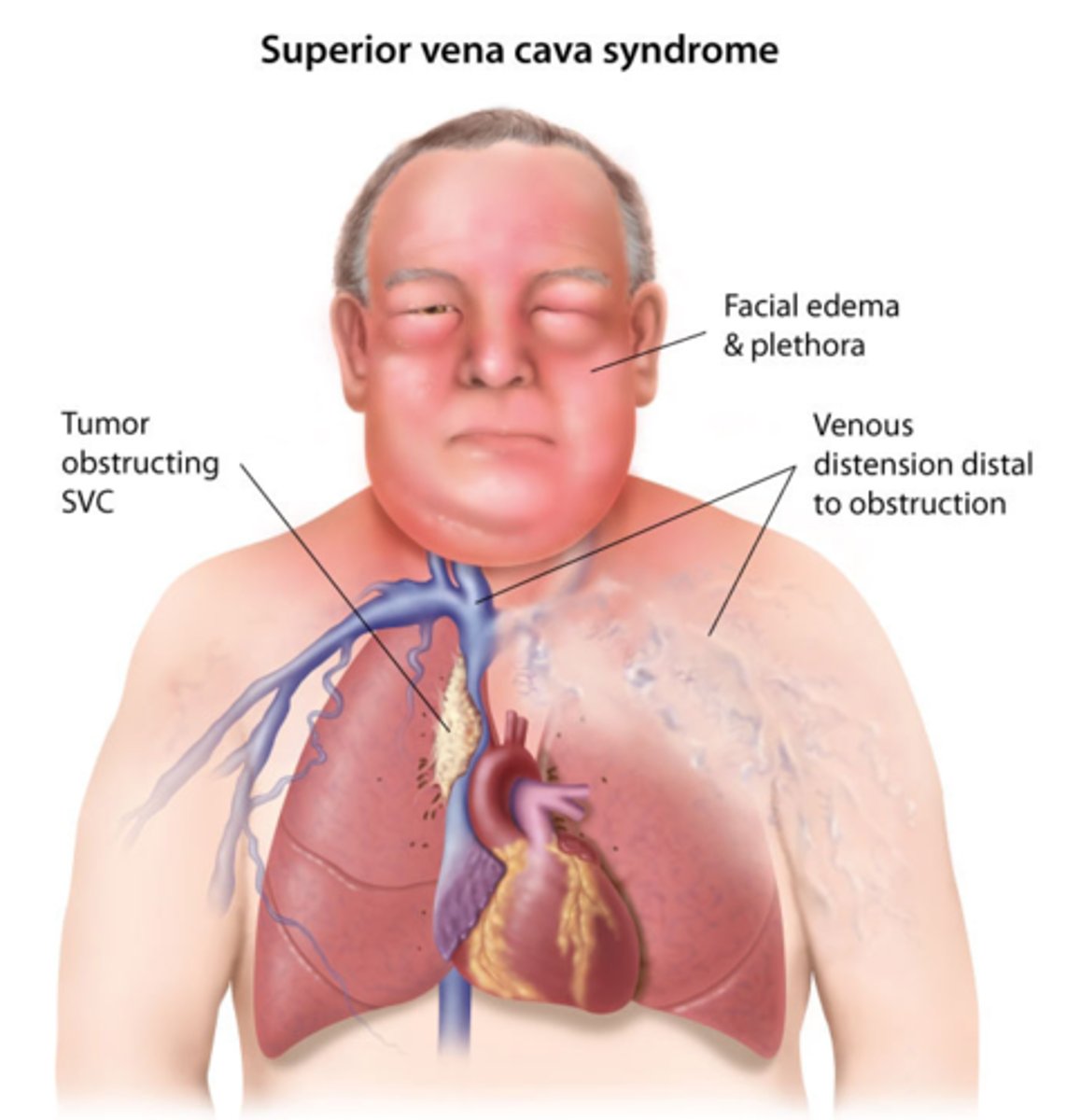
Treatments for Superior Vena Cava Syndrome (3)*
1) radiation to reduce tumor size
2) thrombolytic
3) steroids
Nursing management for Superior Vena Cava Syndrome (3)*
1) elevate HOB
2) O2
3) weights
4) ADLs
In which cancers is Spinal Cord Compression most common? (6)*
1) breast
2) lung
3) prostate
4) GI
5) renal
6) melanoma
Symptoms of Spinal Cord Compression (3)*
1) change in bowel/bladder
2) intense pain in the back
3) motor dysfunction/weakness (change in sensation)
Treatment for Spinal Cord Compression (4)*
1) MRI/CT
2) steroids
3) radiation
4) chemotherapy
Nursing management for Spinal Cord Compression (2)*
1) spinal precautions
2) pain management
Types of metabolic onc emergencies (5)*
1) Hypercalcemia
2) SIADH
3) Tumor Lysis Syndrome
4) DIC
5) Sepsis
In which cancers is Hypercalcemia most common? (2)*
1) MM
2) advanced metastatic cancers (lung, breast, kidney, colon, ovarian, thyroid)
Symptoms of Hypercalcemia (8)*
1) apathy
2) confusion
3) depression
4) fatigue
5) ECG changes
6) muscle weakness
7) anorexia
8) n/v
Treatments for Hypercalcemia >12 (3)*
1) IV fluids
2) bisphosphonate therapy
3) diuretics
Nursing management for Hypercalcemia (3)*
1) Safety precautions
2) monitor labs
3) increase mobility