Post-Lab 4: Saponification
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Saponification
The process by which soaps, carboxylate salts with very long hydrocarbon chains, are made from the base hydrolysis of a fat or an oil
Animal fat and lye (NaOH)
Traditionally, soaps were made from _____
Esters
They are converted into carboxylate salts when treated with sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
Carboxylic acids
Neutralization of carboxylate salts yield _____
deprotonated
If a base (usually NaOH, sometimes KOH) is used for hydrolysis, the fatty acids produced are _____ and are present as its corresponding carboxylate salt
soluble
Charged carboxylate salts are _____ in water than the uncharged fatty acids
Nonpolar
Carboxylate salts have a long (polar/nonpolar) tail
Sodium palmitate
Common soap ingredient
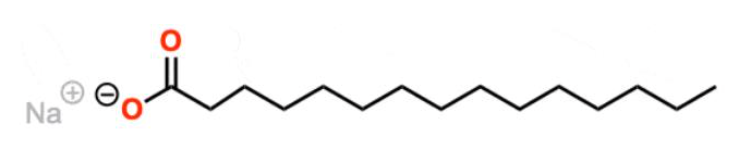
Irreversible
Saponification under basic conditions is _____
Micelles
Soaps are able to emulsify fats and oils by forming _____ around oil droplets
Dispersion
Enough soap molecules surrounding the oil droplets facilitate the _____ of the oil droplets in water where they can be easily washed away
Using lots of soap
Method of breaking down fat/oil
→ To accommodate more fat molecules
Using hot water
Method of breaking down fat/oil
→ To melt solid fats
Agitation
Method of breaking down fat/oil
→ To break down fats and oils into smaller droplets
Glycerol and three fatty acids
Fats and oils are triesters of _____
Insoluble; hydrophobic
Fats, oils, and fatty acids are generally _____ in water because of the presence of long _____ tails
Vacuum filtration
Formation of negative pressure at the outlet of the filtrate and using it as the driving force of filtration → accelerates the filtration process
Use: to obtain a filter residue with low moisture content
Solid soap sample
End product of the experiment
White, solid clumps with little to no moisture
Expected result of soap solution after being subjected to vacuum filtration
50ml of 30% NaCl
Some soap samples hardened or formed solid clumps as soon as _____ solution was added, but some soap samples remained liquid even after the ice bath
Too much coconut oil
Portion of NaOH solution not dispensed properly
Inadequate mixing
Possible sources of error in the soap samples
4 weeks
Curing time for soaps lasts for around _____ where the soap lose more water and become milder
7 to 10
Homemade or laboratory made soap should have a pH level that ranges from ph _____
greater than 10
Soaps that have a pH level _____ are considered lye-heavy and can irritate or burn the skin
24 hours
Saponification reaction takes around _____ and continues to become milder with time
Colloidal
When shaking the soap mixed with water, the soap solution becomes _____ in nature
foaming
Agitation (by mixing) concentrates the solution on the surface which causes _____
Height
Foaming capacity of the soap samples is usually based on the ____ of the foam created after agitation
Surfactant
Substances that reduce the surface tension in the liquid
Surface tension
Soap reduces the _____ of the water, making its molecules less likely to stick together and more likely to interact with oil or grease
Hydrophilic
The (hydrophobic/hydrophilic) part of soap molecules interact with the water molecules in solution, forming the outer surface of the micelle
Hydrophobic
The (hydrophobic/hydrophilic) part of the soap interacts with the oil, trapping the oil in the center
Hard water
Water that contains a significant concentration of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions
Soap scum
Precipitates with soap molecules formed by Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions
Less emulsification capacity and less foam formed
Result of soap forming precipitates with Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions
Hard
Soaps are less effective in _____ water
Soft water
Water that contains very few or no ions that precipitate with soap
Soft
Soaps are more effective in ____ water
Detergents
Similar to soap (also have a charged head group and long hydrophobic tail)
However, they are not prepared from natural fats or oils
Detergents
Work effectively both in soft and hard water (they don’t form precipitates)
Sodium lauryl sulfate
Typical ingredient found in commercial shampoos and other cleaning products
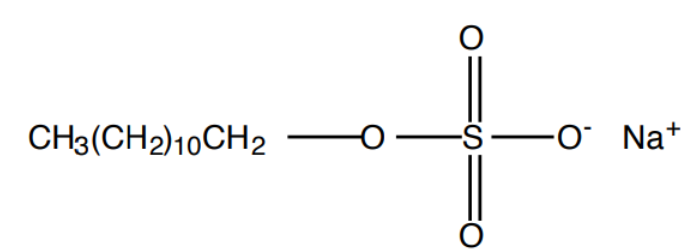
Sodium lauryl sulfate
Nonbiodegradable detergent
Sodium laurylbenzenesulfonate
Biodegradable detergents were developed substituting sodium lauryl sulfate with biodegradable compounds like _____
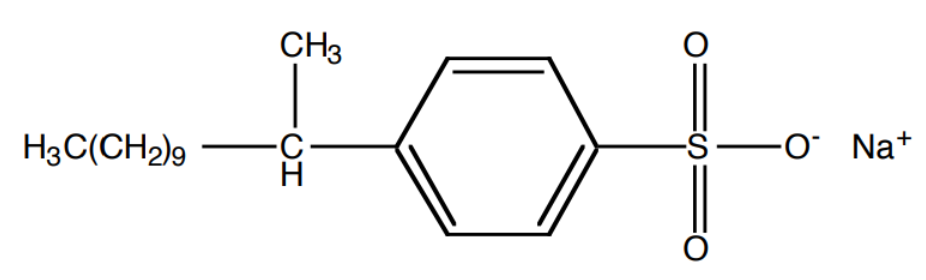
Phosphate
Excessive amounts of _____ in bodies of water accelerate the growth of algae which consumes too much of the dissolved O2 in water
Bile salts
Lipid emulsification in the body is primarily facilitated by _____
Amphipathic nature
The _____ of bile salts aid in the digestion of fat droplets in the body, preventing their reaggregation
Galbladder
Bile salts are stored in the _____, which is stimulated to contract and secrete the bile when food passes from the stomach into the duodenum
Steroidal
Bile salts are _____ detergents
→ Form mixed micelles with lipids, dats, and/or cholesterol, and thus enable the digestion and absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins in the intestine