Pregnancy and Prenatal Testing: Key Concepts and Markers
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
How is pregnancy measured?
From the first day of the last menstrual period.
What is the normal term for pregnancy?
40 weeks.
What are the three trimesters of pregnancy?
First trimester: conception to 12 weeks; Second trimester: 13 to 26 weeks; Third trimester: 27 weeks to birth.
What is gestation?
Fetal development from the first day of the last menstrual period until the current date.
What is conception?
The date that the sperm fertilizes the ovum.
What is a zygote?
A fertilized ovum.
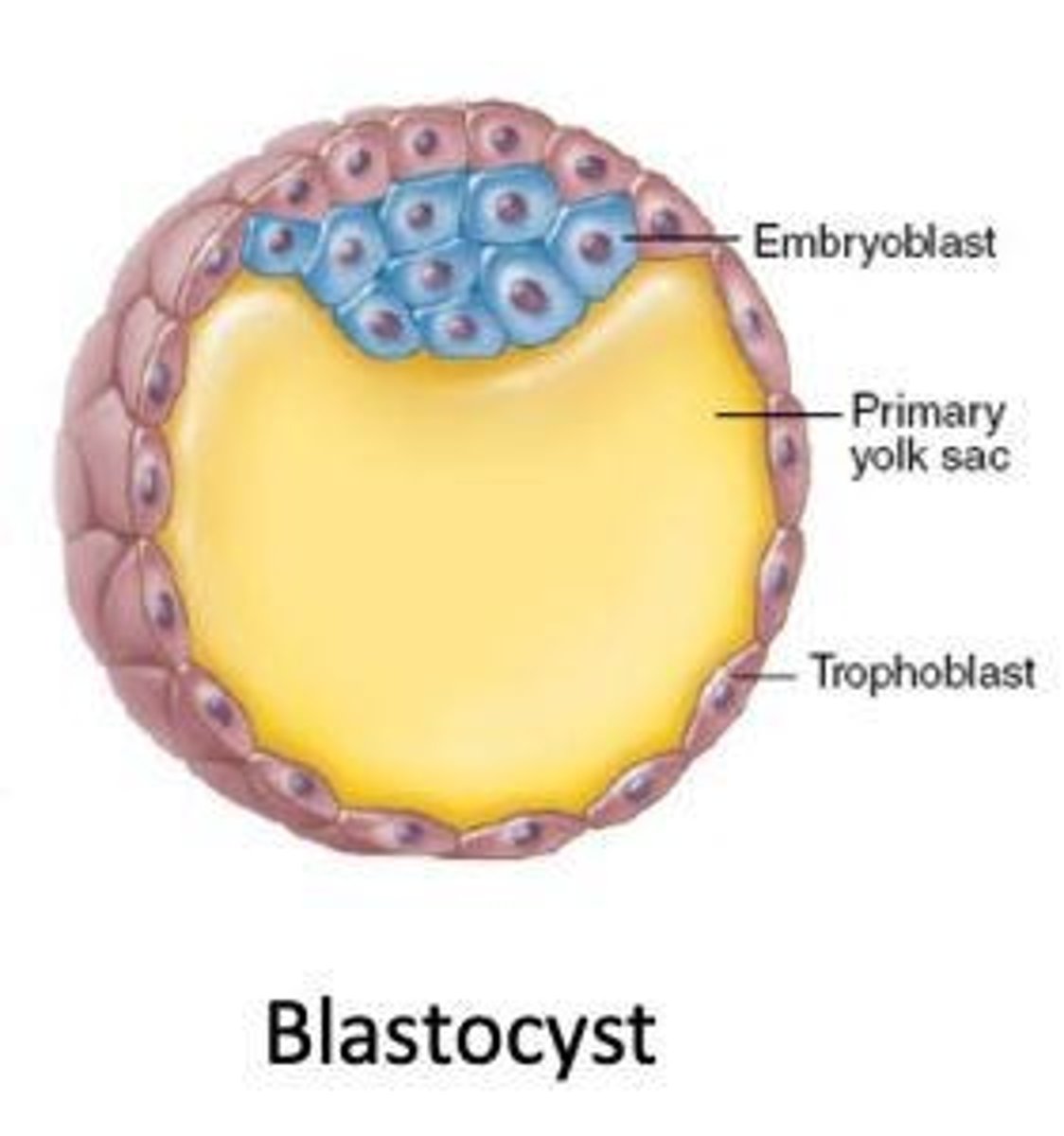
What is a blastocyst?
A stage of development around the 50-60 cell stage that begins implantation into the uterine wall about 5 days post-fertilization.
What role does the placenta play in pregnancy?
It sustains the pregnancy by providing nutrients and oxygen to the developing fetus.
What is an embryo?
The stage where the blastocyst is implanted and nourished by the placenta.
At 10 weeks past conception, what developments occur in the fetus?
All organs are developed, a heartbeat is present, and it can move its arms and legs.
What happens to plasma volume during pregnancy?
It increases.
What is the effect of pregnancy on plasma osmolality?
It falls by around 10 mOsm/kg by the third trimester.
What hormone is released to retain water during pregnancy?
Arginine vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone).
What is the role of aldosterone during pregnancy?
It retains sodium and water, contributing to increased plasma volume.
How does pregnancy affect iron requirements?
Iron requirements increase due to the needs of the fetus and placenta.
What happens to cholesterol levels during pregnancy?
Total cholesterol levels increase by almost 50%, and LDL by 30 to 40%.
What is the primary form of estrogen during pregnancy?
Estriol (E3).
What is the function of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in fetal development?
It is produced by the fetal adrenal glands and converted to estriol in the placenta.
What happens to thyroid hormones during pregnancy?
T3 and T4 increase by over 50% due to estrogen-dependent synthesis of thyroxine binding globulin.
What is the effect of pregnancy on the immune system?
Monocyte levels decrease to prevent an immune response against the fetus.
What is the normal range for a full-term baby delivery?
Between 38 and 42 weeks of gestation.
What role does progesterone play in pregnancy?
It prevents contractions.
What changes occur in glucose levels during pregnancy?
Plasma fasting glucose levels decrease due to the fetus drawing glucose from maternal circulation.
What is the significance of measuring ionized calcium during pregnancy?
Total calcium levels may appear decreased, but ionized calcium levels remain unchanged and are more clinically relevant.
What happens to triglyceride levels during pregnancy?
They increase by two to three-fold as the mother uses circulating triglycerides for energy.
How does pregnancy affect protein metabolism?
There is decreased protein catabolism as proteins are transported to the fetus.
What is the effect of relaxin during pregnancy?
It loosens and relaxes muscles, joints, and ligaments to help the body stretch.
What role does progesterone play during pregnancy?
Progesterone prevents contractions and increases steadily throughout pregnancy, declining rapidly before labor begins.
What hormone triggers uterine contractions during labor?
High concentrations of oxytocin trigger uterine contractions and initiate the birthing process.
What is synthetic oxytocin called and what is its use?
Synthetic oxytocin is called Pitocin, and it is used to induce labor or strengthen contractions.
What is human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) and where is it synthesized?
HCG is synthesized in the placenta and is a dimer consisting of alpha and beta subunits.
Which subunit of HCG is tested for in pregnancy tests?
The beta subunit (β HCG) is an indicator of pregnancy in both serum and urine testing.
When do HCG levels peak during pregnancy?
HCG levels peak around the 8th-10th week of pregnancy at about 100,000 mU/mL.
What can low levels of HCG indicate?
Low levels of HCG are seen in ectopic pregnancies.
What can cause false negatives in HCG testing?
False negatives can occur if urine is tested in a hyperhydrated patient or in high dose hook for extremely high levels.
What can cause false positives in HCG testing?
False positives can occur due to infertility treatments, weight loss, or HCG doping.
What is α Fetoprotein (AFP) used for during pregnancy?
AFP is used to screen for open neural tube defects and Down syndrome.
What do high levels of AFP in maternal serum indicate?
High levels of AFP are seen in open spine defects and multiple fetuses.
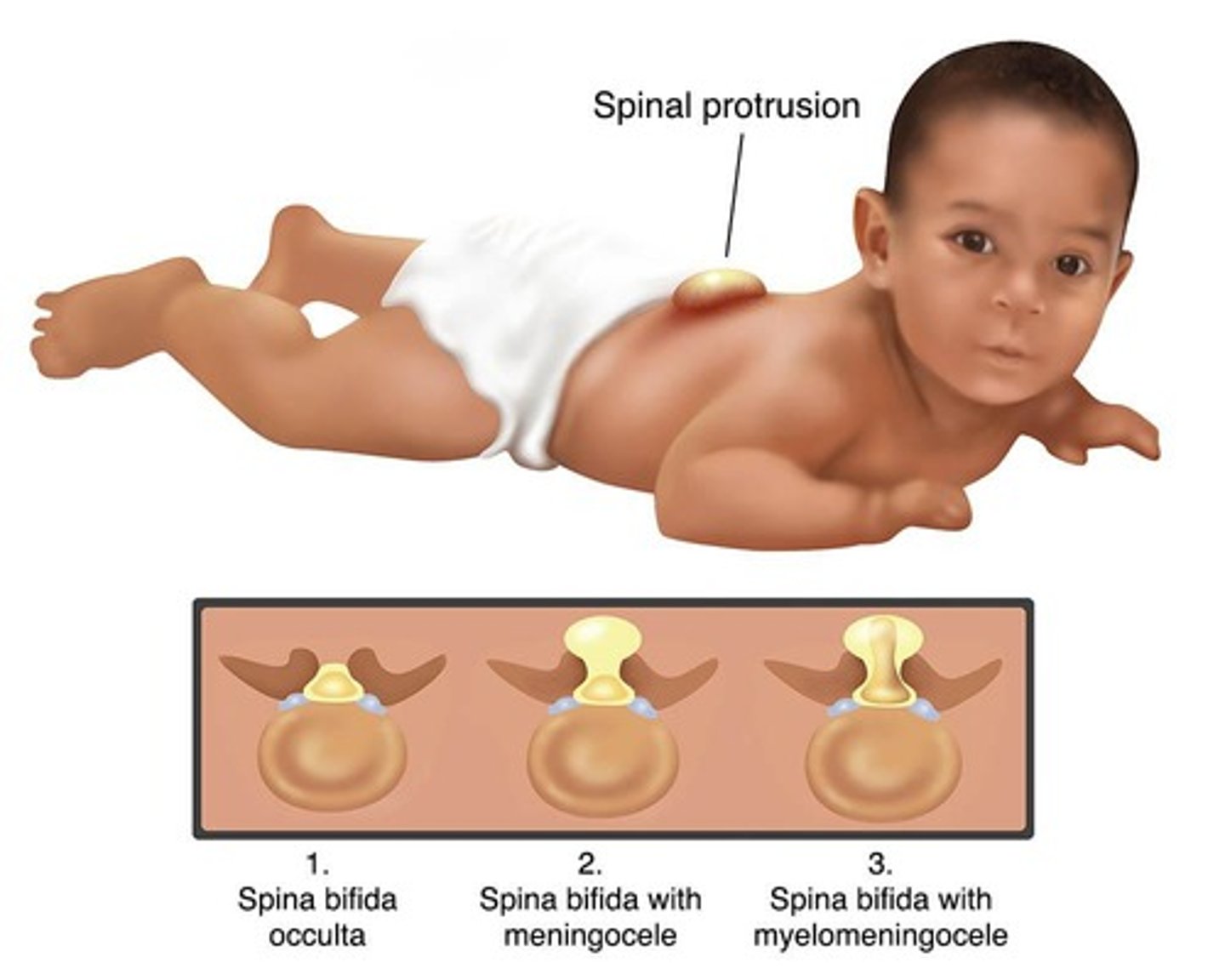
What do low levels of AFP in maternal serum indicate?
Low levels may indicate Down syndrome or trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome).
What is the primary function of Inhibin A?
The primary function of Inhibin A is to suppress FSH.
What conditions are associated with increased levels of Inhibin A?
Increased levels are associated with preeclampsia, fetal malformation, and fetal growth restriction.
What is the triple screen test during pregnancy?
The triple screen measures AFP, HCG, and uE3 during the 16th and 20th week of gestation.
What does a normal quad marker test result indicate?
It means the fetus is NOT at higher risk for trisomy 21, trisomy 18, neural tube defects, or abdominal wall defects.
What does acetylcholinesterase detect?
Acetylcholinesterase detects neural tube defects.
What is fetal fibronectin and when does it appear?
Fetal fibronectin appears 7-14 days before delivery due to the breakdown of the amniotic membranes.
What is Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and its significance?
PAPP-A is made by the placenta in early pregnancy and abnormally low levels could indicate an increased risk for chromosome defects.
What are common conditions associated with pregnancy?
Common conditions include pre-eclampsia, hyperemesis gravidarum, ectopic pregnancy, and HELLP syndrome.
What are the symptoms of pre-eclampsia?
Symptoms include high blood pressure, proteinuria, and swelling edema in the second and third trimesters.
What is hyperemesis gravidarum?
A severe form of morning sickness that causes malnutrition in both the mother and fetus.
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
A condition where trophoblastic cells attach to the lining of the fallopian tube instead of the uterine endometrium.
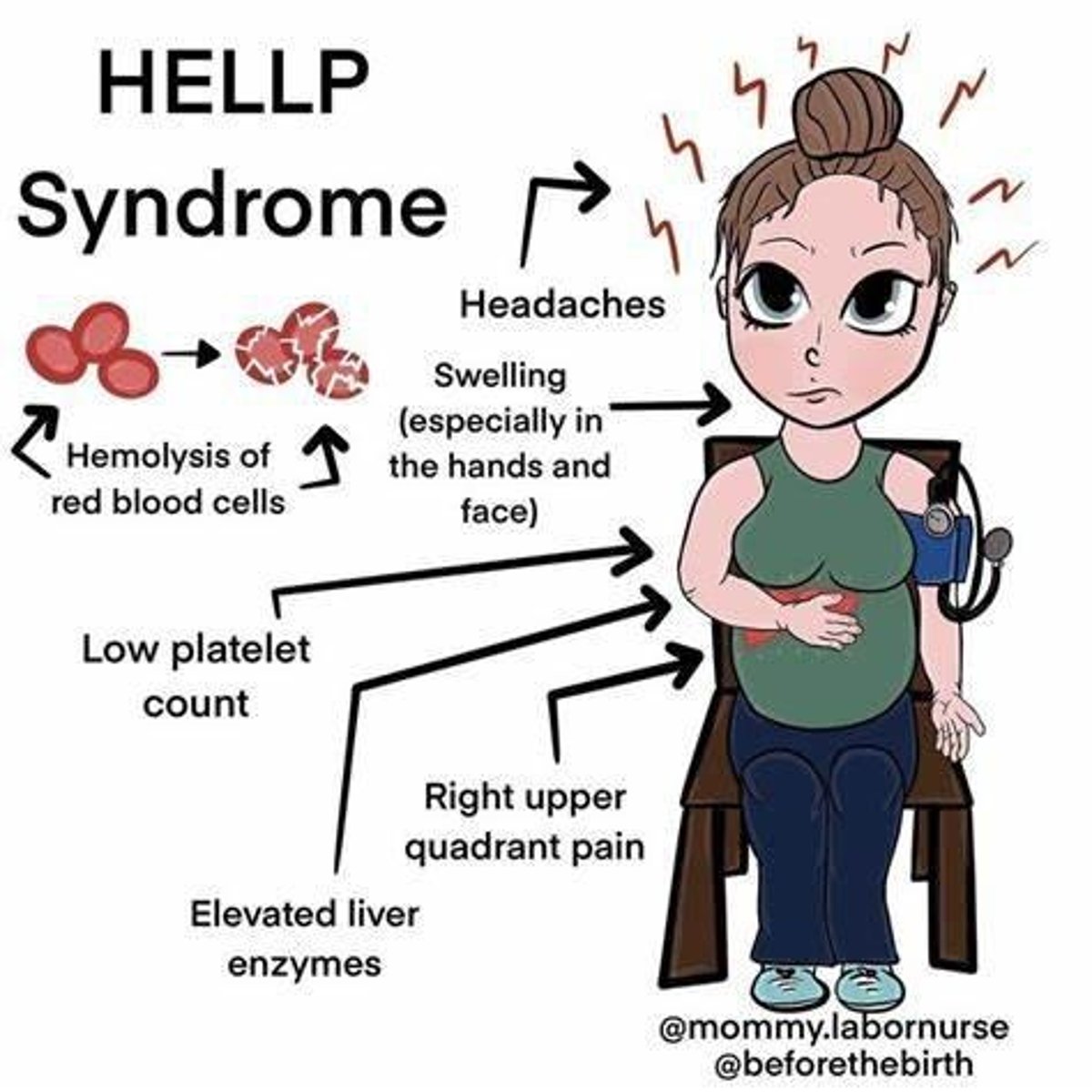
What is HELLP syndrome?
A syndrome characterized by Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, and Low Platelets in pregnant and postpartum patients.