Lesson 4 macromolecules (carbs and nucleic acids )
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are the 4 macromolecules
Proteins, Lipids, Carbohydrates, and Nucleic Acids
What is a dehydration(synthesis) reaction?
when 2 small monomers come together to form a polymer during the reaction water is removed. Ex: used to build proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids and fats.
What is hydrolysis (decomposition) reaction
when a larger polymer is broken down into smaller monomers and water is added to aid the break down. Ex: releases energy and used to break down food and recycle macromolecules.
What is a functional group?
small clusters of atoms that are given to molecules that help identity and behavior. They are responsible for chemical reactivity, interactions with water, bond formation and breakdown, found in all 4 macromolecules
What is the basic structure of a carbohydrate?
carbohydrates are an organic molecule that made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen on a 1:2:1 ratio.
What is the function of carbohydrates?
provide a ready energy source (glucose, sucrose), long term energy source(starch, glycogen), the backbone of nucleic acids(ribose, deoxyribose), converted into amino acids, helps create the cell wall in plants, and peptidoglycan wall in bacteria, used for cell recognition and signaling(glycoproteins and glycolipids)
what are the classifications of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides (glucose), Disaccharides(2 sugars, sucrose and lactose), Polysaccharides (long chains of sugars, starch, cellulose, glycogen)
What do monosaccharides do?
they are the smallest unit of carbohydrates, linear and ring formation, used to build larger carbohydrates. Alpha glucose is what is found in starch, Beta glucose are found in cellulose(plants), N-acetylglucosamine are found on peptidoglycan (bacteria), chitin(fungi)
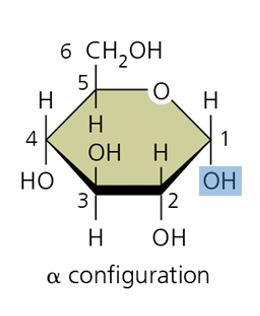
Which way do Alpha bonds point? Example?
down, found in starch
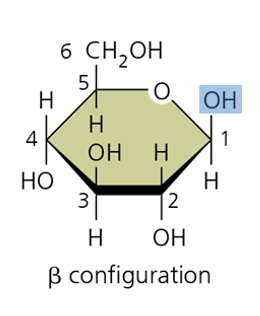
Why way do Beta bonds point? Example?
up, found in cellulose
What are nucleotides?
Nucleotides are the building blocks for nucleic acids.
what type of sugars are found in nucleic acids and what classification are they according to carbohydrates?
ribose and deoxyribose and they are monosaccharides.
What are the 2 major types of nucleic acids
DNA(Deoxyribonucleic Acid), used in long term genetic storage, RNA(ribonucleic acids) helps with gene expression, proteins and can act as an enzyme.
What is the key function of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
inheritance and genome stability
What is the key function of RNA
protein synthesis, regulation, catalysis
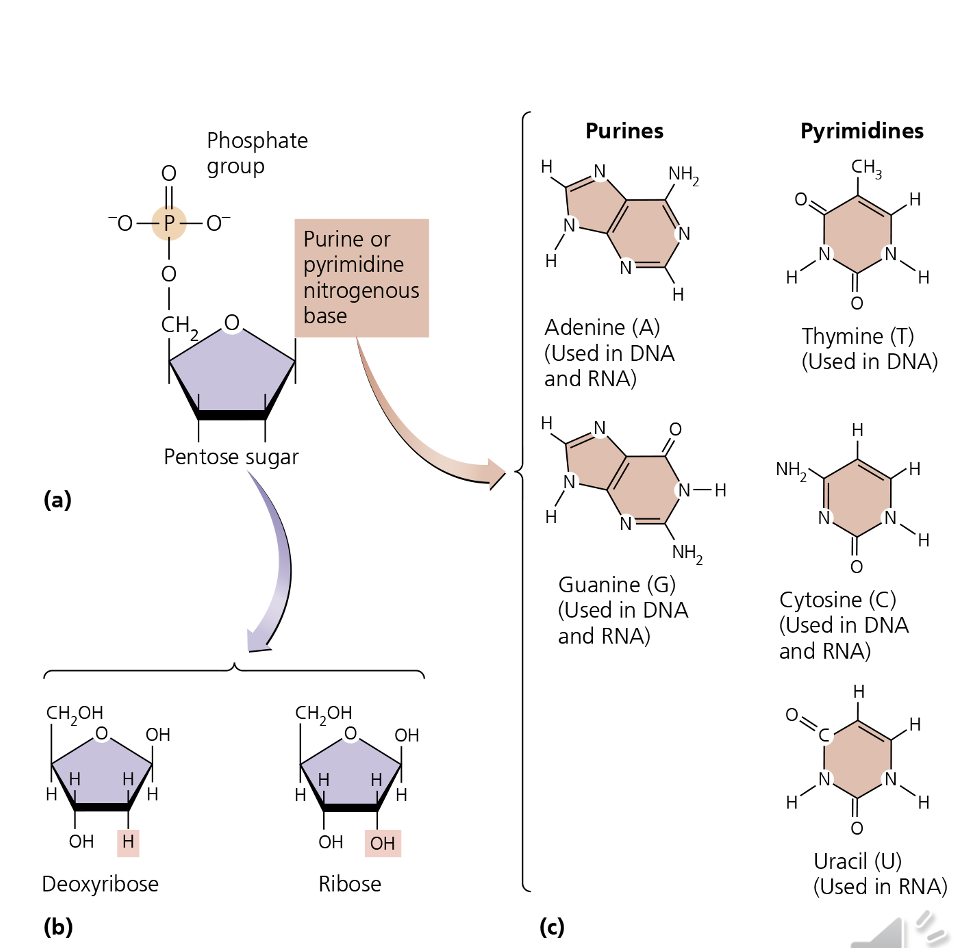
What is the difference between a nucleotide and nucleoside?
Nucleotide has a PHOSPHATE GROUP, PENTOSE SUGAR(ribose or deoxyribose), NITROGENOUS BASE(A,T,G,C,U).
Nucleoside has PENTOSE SUGAR AND NITROGENOUS BASE
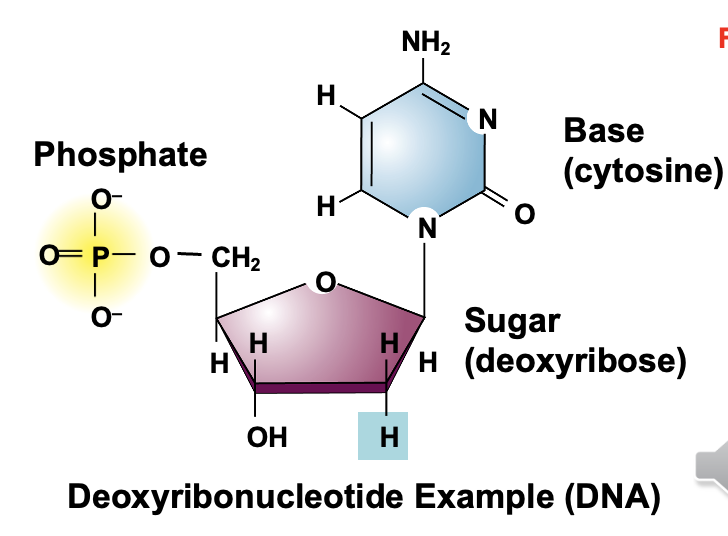
What is DNA and its basic structure?
stands for deoxyribonucleic acid that stores genetic information for the long term, its made of hydrogen bonds that link together across 2 strands(double stranded, antiparallel, and complementary base pairing)
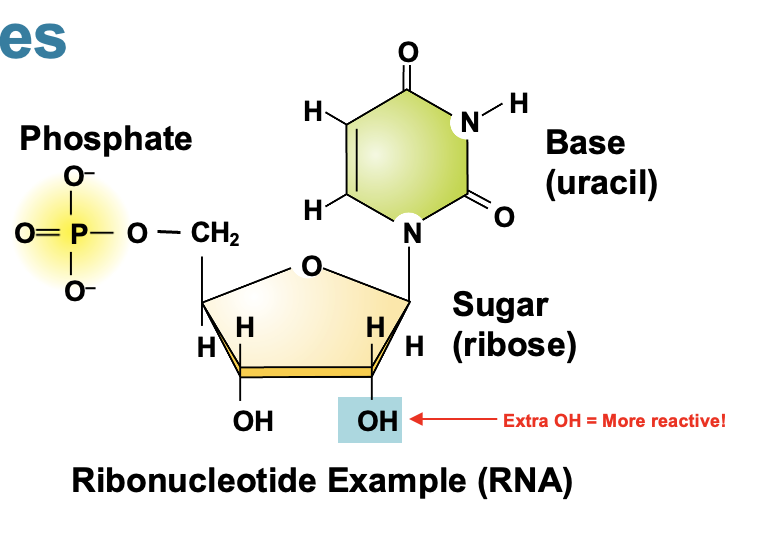
What is RNA its basic structure?
stands for ribonucleic acid that assist with gene expression, protein building, and acts as an enzyme(ribozyme), single stranded carries instructions from DNA to create proteins and regulate cellular function.
What is AMP its basic structure?
stands for Adenosine monophosphate, a adenosine, a ribose and contains 1 phosphate, forms after lots of energy has been used,
What is ADP its basic structure?
stands for Adenosine diphosphate, a adenosine, a ribose and contains 2 phosphate, happens during cellular respiration
What is ATP its basic structure?
stands for Adenosine Triphosphate, main short term energy supply for cells. Energy is released when phosphate bonds of ATP are broken, the supply of ATP is limited and must be replenished, made up of a adenosine, a ribose and contains 3 phosphate