Probabilistic Reasoning
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Probability fundamentals in addition to Bayes' networks
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
In the context of a supposed lottery ticket worth winning £1 if a proposition p was to hold, and £0 if not, what would be an agent’s degree of belief?
The price considered fair for buying the ticket
What is a “Dutch book” scenario?
A sequence of bets, each of which the agent is disposed to accept, yet taken together, will cause the agent to lose money no matter what happens.
When is an agent vulnerable to Dutch book scenario?
When its degrees of belief do not satisfy a probability function.
What is a prior in conditional probability?
A single probability of a single event i.e. P(e) = 0.5.
Formalise causal inference as P(cause | effect) ?
P(effect | cause)P(cause) / P(effect) - using Bayes’ theorem
Assuming independence, generalise the above formalisation to cases where there is more one effect ?
P(cause, effect1, effect2…, effectn) = P(cause) Prod[P(effecti | cause)]
When are propositions p1,…,pn mutually exclusive?
When at most one is true.
When are propositions p1,…,pn jointly exhaustive?
When at least one is true.
When do propositions p1,…,pn form a partition and how might that be applied to a conditional statement P(x|y) using the law of total probability?
When at most one is true. In that case, we will have:
P(x|y) = P(x|p1,y)P(p1|y) + … + P(x|pn,y)P(pn|y)
Given x,y, when are they conditionally independent?
When P(x|y) = P(x)
Given x,y when are they positively relevant?
When P(x|y) > P(x)
Given x,y when are they negatively relevant?
When P(x|y) < P(y)
To store a probability distribution over a language with n propositions, how many numbers do we need to store in memory?
2n-1
Define a Bayes’ network, assuming independence.

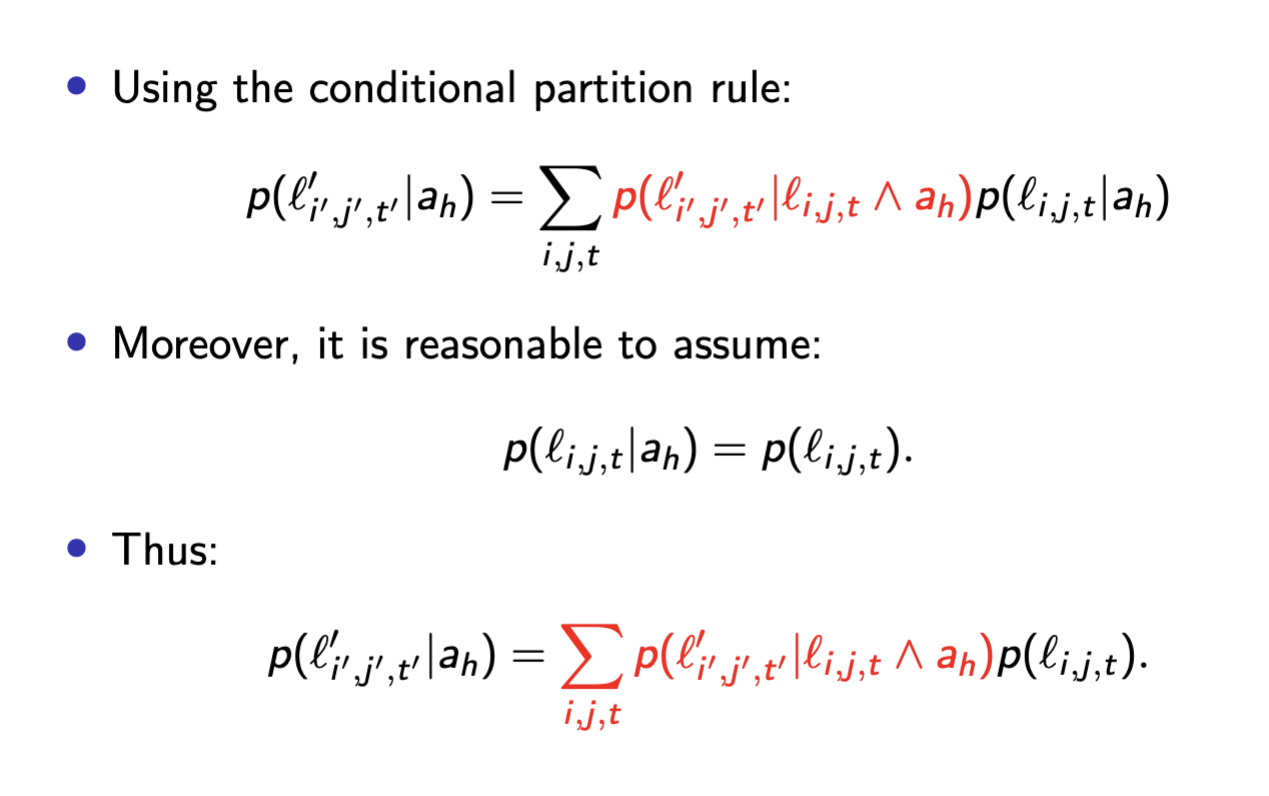
Briefly recall and explain the probability sensor model for robot navigation.
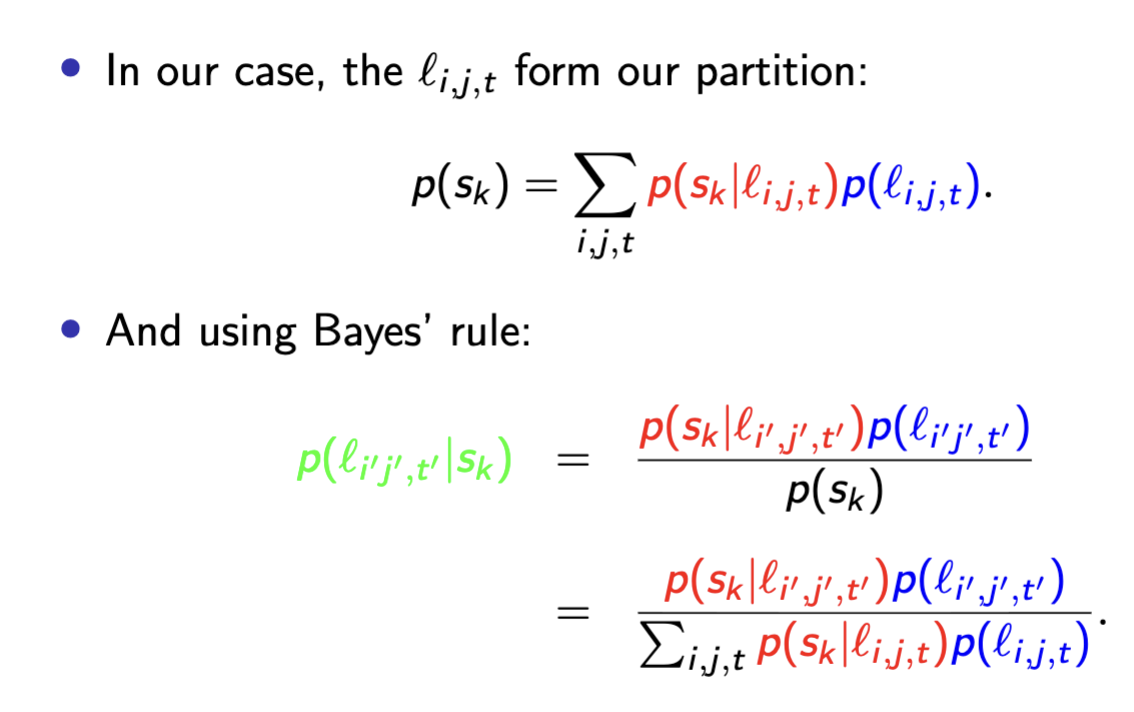
Briefly recall and outline the probability actuator model for robot navigation.