Infrared radiation and black bodies: Waves: Physics: GCSE (9:1)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Infrared radiation
Radiation that all bodies (objects) emit and absorb, no matter what temperature they are

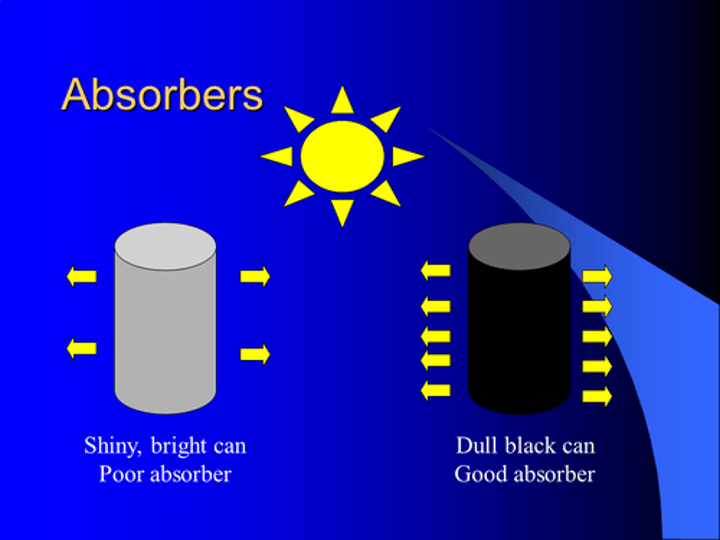
Good absorbers and emitters of infrared radiation
Black and dull surfaces are the best absorbers and emitters, as they absorb all visible light wavelengths
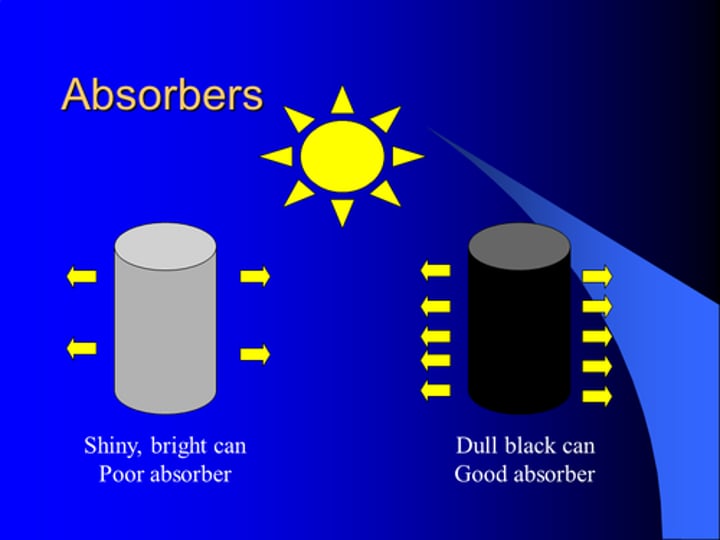
Poor absorbers and emitters of infrared radiation
White and shiny silvery surfaces are the worst absorbers and emitters, as they reflect all visible light wavelengths
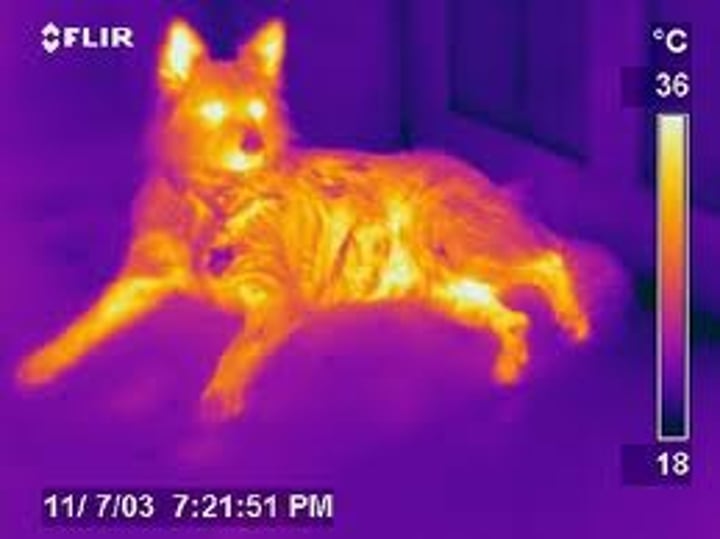
Effect of temperature on infrared radiation emissions
The hotter a body, the more infrared radiation it radiates in a given time and the greater proportion is emitted as visible light
Black body
A theoretical object that absorbs all of the radiation incident on it
Properties of a black body
It would absorb all the radiation that falls on it, would not reflect or transmit any radiation and would be the best possible emitter of radiation
Why stars are considered to be black bodies
They emit and absorb most wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum
Other examples of black bodies
Planets, black holes
(higher-tier only)
Rate of absorption and emission of infrared radiation
Determines whether the temperature of a body is increasing, decreasing or constant
(higher-tier only)
When an object's temperature is increasing
The rate of absorption of infrared is greater than the rate of emission
(higher-tier only)
When an object's temperature is decreasing
The rate of absorption of infrared is less than the rate of emission
(higher-tier only)
When an object's temperature is constant
The rate of absorption of infrared is equal to the rate of emission
(higher-tier only)
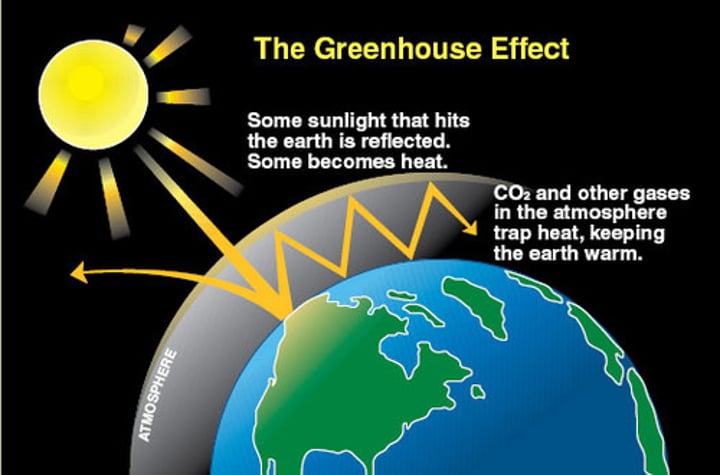
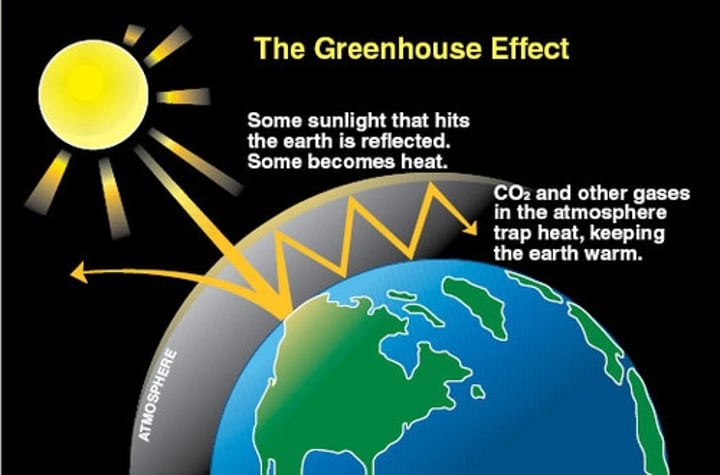
Factors affecting the Earth's temperature
The rates of absorption and emission of radiation, reflection of radiation into space, concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
(higher-tier only)
The greenhouse effect
Caused by naturally occurring greenhouse gases and stabilises the surface temperature of Earth