Biology Study Set: Q4 Week 5 Micro Terms & Definitions
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What are some options to control infections?
- Antimicrobial drugs
- Induction of the immune response
- Improvement in Public health
What are antibiotic drugs used for?
Bacterial infections
What are antibiotics?
Substances produced natrually by microorganisms that kill other organisms
What are naturally occurring antibiotics?
Antibiotics produced by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi
What are semisynthetic antibiotics?
Chemically altered antibiotics that are more effective, longer lasting, or easier to administer than natrually occurring antibiotics
What are synthetic antibiotics?
Antibiotics made in a lab
What is selectively toxic antimicrobial drugs?
This means that antimicrobial drugs selectively inhibit microorganisms but not human cells aka they damage only the cells we want them to not our own cells
What are three ways antibiotics target bacteria?
- Bacterial cell envelope
- Biosynthetic processes within bacteria
- Bacterial metabolism
T or F
Selective toxicity is achieved by targeting the structural and/or biochemical properties unique to bacteria.
True
What drugs target the inhibition of cell wall synthesis?
- B lactam antibiotics
- Vancomycin
- Bacitracin
What are some examples of B lactam antibiotics?
- Penicillins
- Cephalosporins
- Carbapenems
- Monobactams
What is the core of B lactam antibiotics?
B-lactam ring
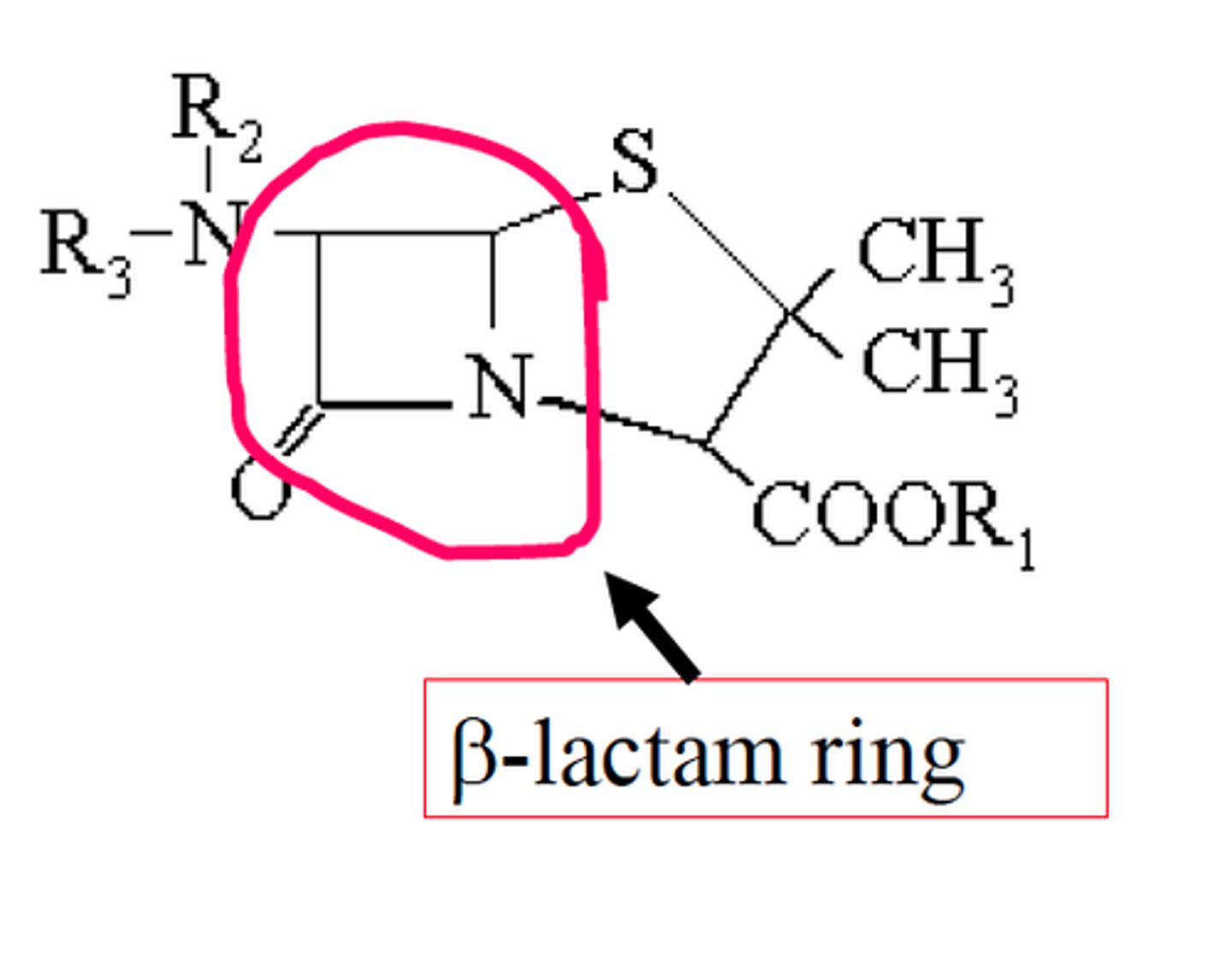
What is responsible for antimicrobial activity in B lactam antibiotics?
B lactam ring
What mechanism do B lactams use to kill bacteria?
They impair the last stage of cell wall synthesis by interfereing with PBP (penicillin binding protein)
How do B lactam subclasses differ from one another?
They are different in their side chains and presence of other ring structures
How does Vancomycin work?
It binds to PBP binding site
What is the difference between B lactams and Vanomycin?
B lactams bind to PBP directly
Vanomycin binds to PBP binding site
What antibiotic classes inhibit the 30S ribosomal subunit?
- Aminoglycosides
- Tetracyclines
What antibiotic classes inhibit the 50S ribosomal subunit?
- Macrolines
- Chloramphenicol
- Lincosamides
- Oxazolidinones
What is folic acid essential for?
Synthesis of nucleotides and many amino acids
How do bacteria make folic acid?
They use PABA and other substrates to make folic acid
How do sulfonamides work?
They bind to the enzyme in bacteria that make Folic acid which inhibits the production of nucleic acids and kills the bacteria
What antibiotics inhibit nucleic acid synthesis?
- Quinolones
- Matronidazole
- Rifampin
How does quinolone inhibit nucleic acid synthesis?
Inhibits topoisomerases that regulate DNA coiling
How does metronidazole inhibit nucleic acid synthesis?
Disrupts energy metabolism in anaerobes by hindering the replication, transcription, and repair process of DNA
How does Rifampin work?
Inhibits bacterial RNA synthesis
What is an antibiotic spectrum?
The range of bacteria that an antibiotic agent inhibits or kills
How can antibiotics be described in terms of spectrum?
Narrow spectrum drugs - effective against few
Broad spectrum drugs - effective against many organisms
What is a disadvantage of broad spectrum antibiotics?
Can cause damage against host and secondary infections by transient pathogens
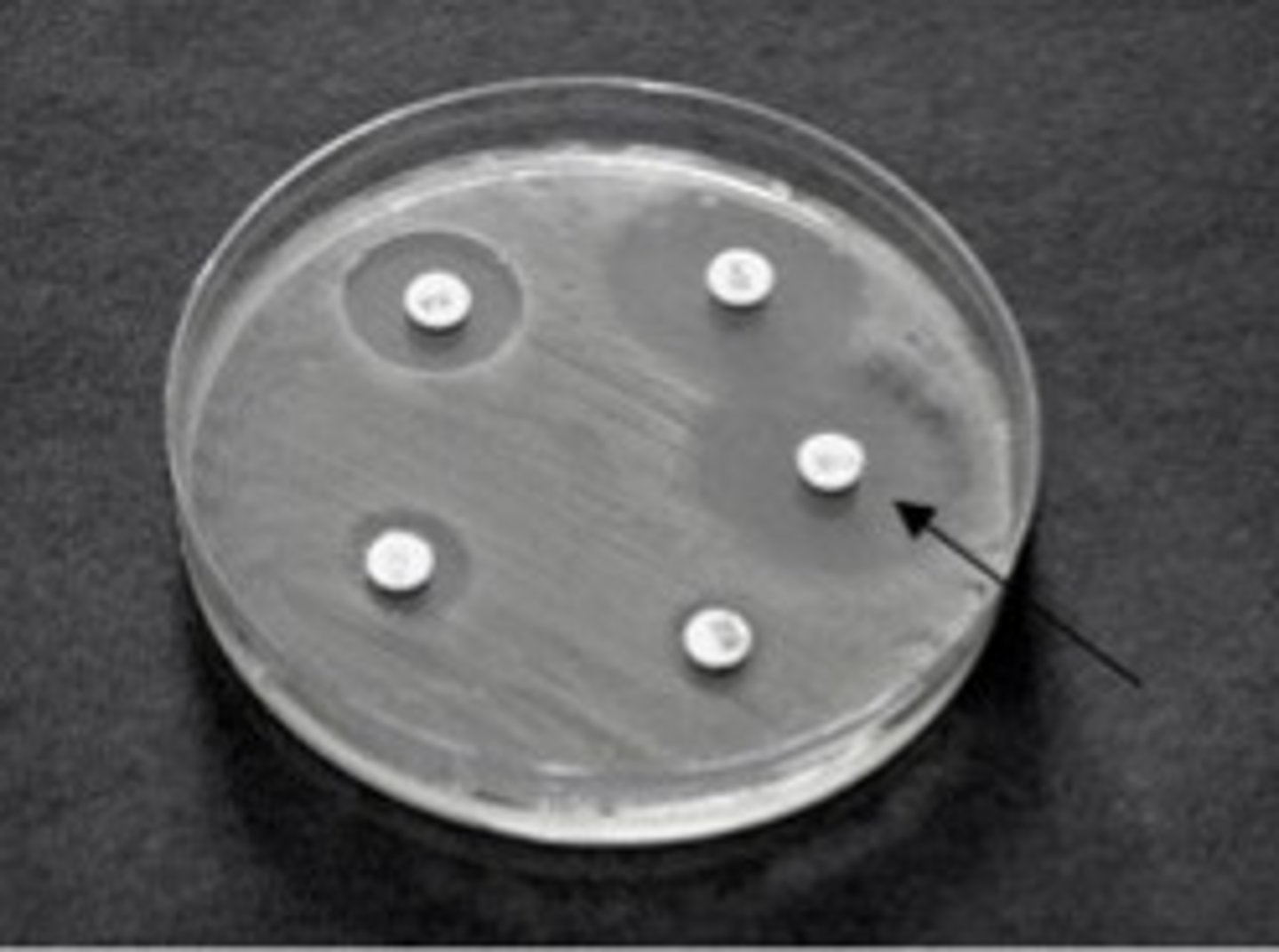
What does the diffusion susceptibility test test for?
This evaluates the antimicrobial efficancy of a drug and reveals which drug is most effective against a particular pathogen
What does the zone of inhibition tell us on a diffusion susceptibility test?
This tells us how effective a drug is.
Larger zone of inhibition, the more effective that drug is
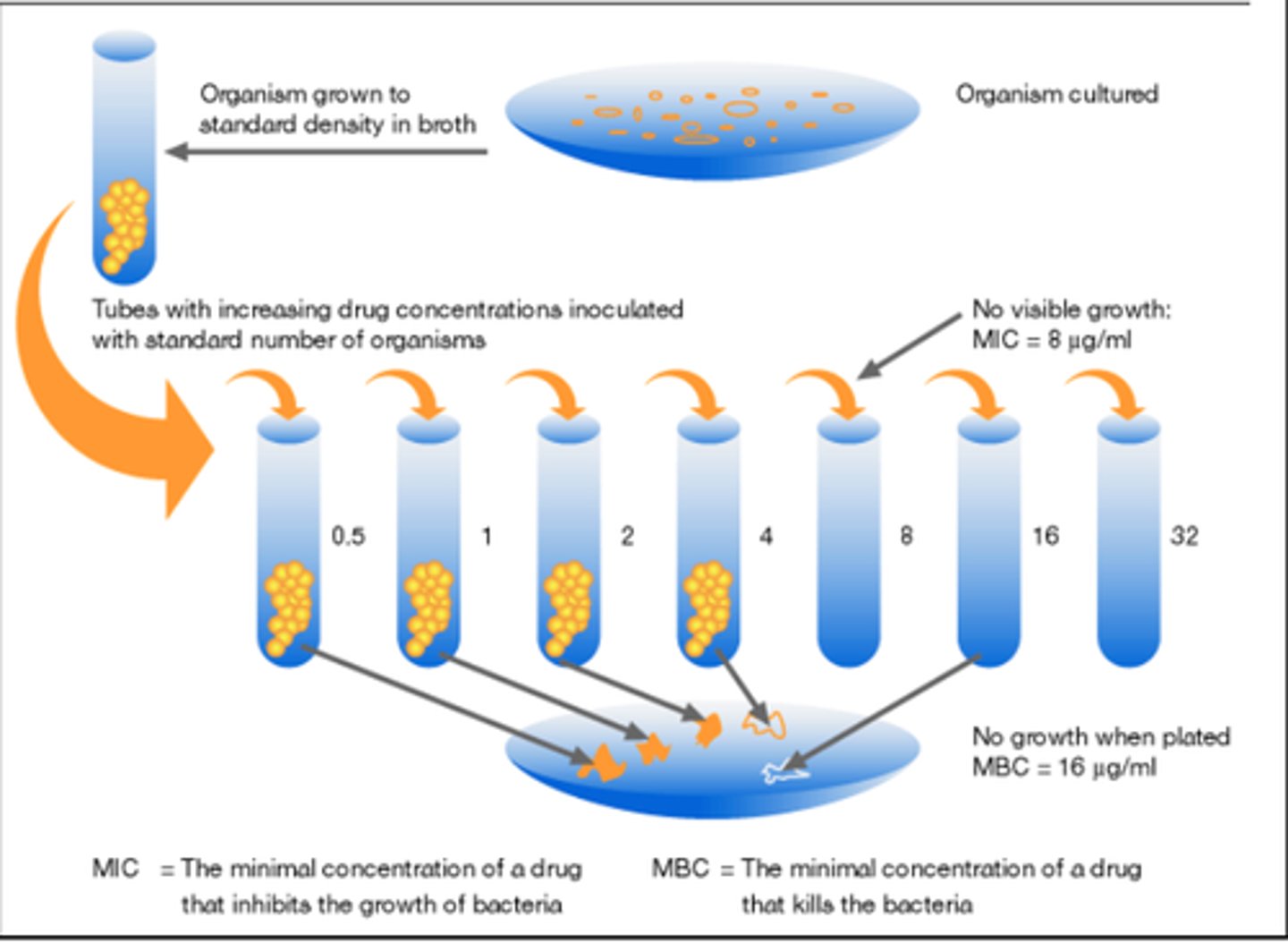
What does MIC test determine?
The minimum concentration of antibiotic that will be able to suppress growth of a bacteria
What does MBC test determine?
The minimum concentration of antibiotic that will kill the bacteria
What determines if an antibiotic is bactericidal or bacteriostatic?
The ratio of MBC to MIC
ratio of ability to kill to the ability to arrest growth
Antibiotics that kill bacteria are called ______
bacteriocidal
Antibiotics that arrest growth in bacteria are called _______
bacteriostatic
What do bacteriostatic antibiotics rely on?
The host immunity to eradicate the non-multiplying bacteria
How do you perform a test to get MIC and MBC?
Antibiotic dilution test and agar growth test
What drug causes black hairy tongue?
Metronidazole
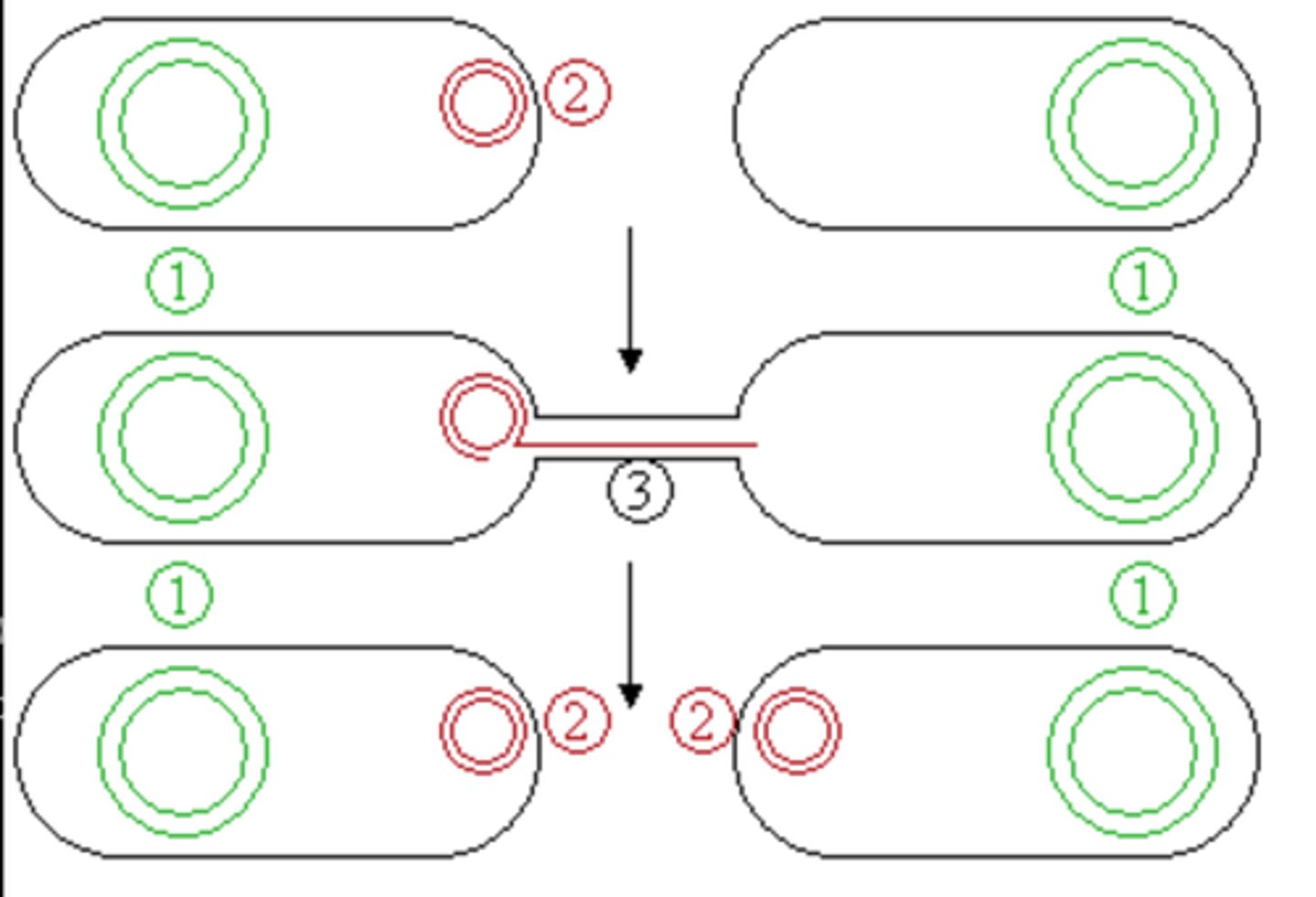
What are two ways that bacteria acquire resistiance?
- Mutation within the species
- Acquisition of a R plasmid via horizontal gene transfer
What are mechanisms that bacteria have to resist antibiotic drugs?
- Inactivation of the drug
- Altered uptake by efflux pump (pump out the drug)
-Modification of structural target of drug
What is an example of antibiotic resistance to B lactam drugs?
B lactamase enzyme that breaks down and deactivates B lactam drugs
What are 3 prescription uses for antimicrobial drugs?
- Prophylaxis
- Specific/definitive therapy
- Empirical/presumptive therapy